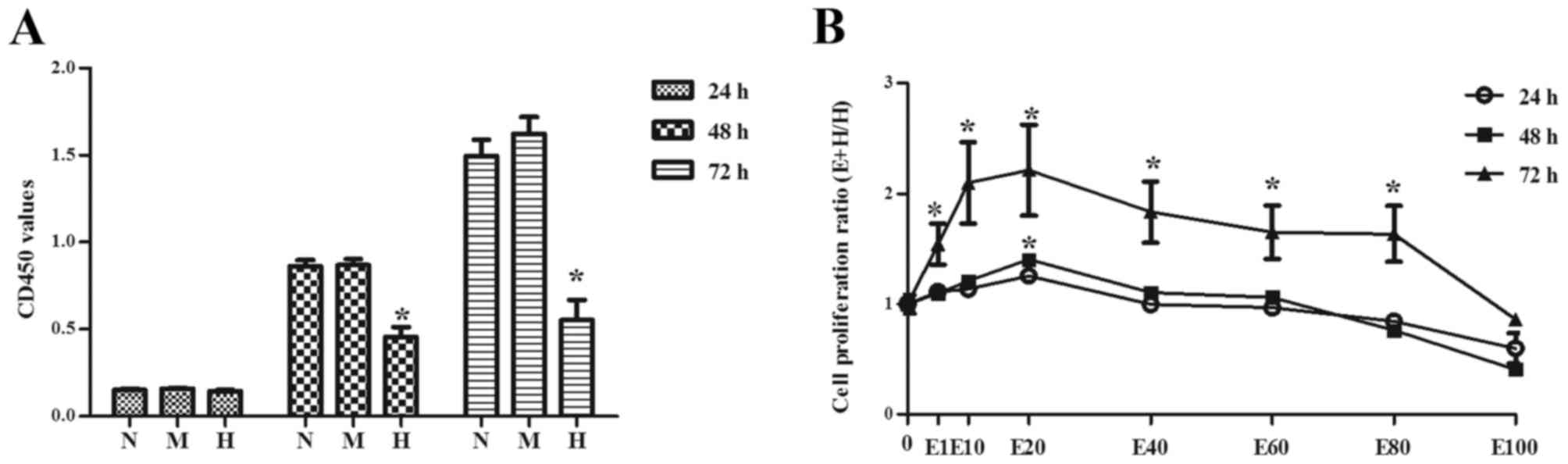
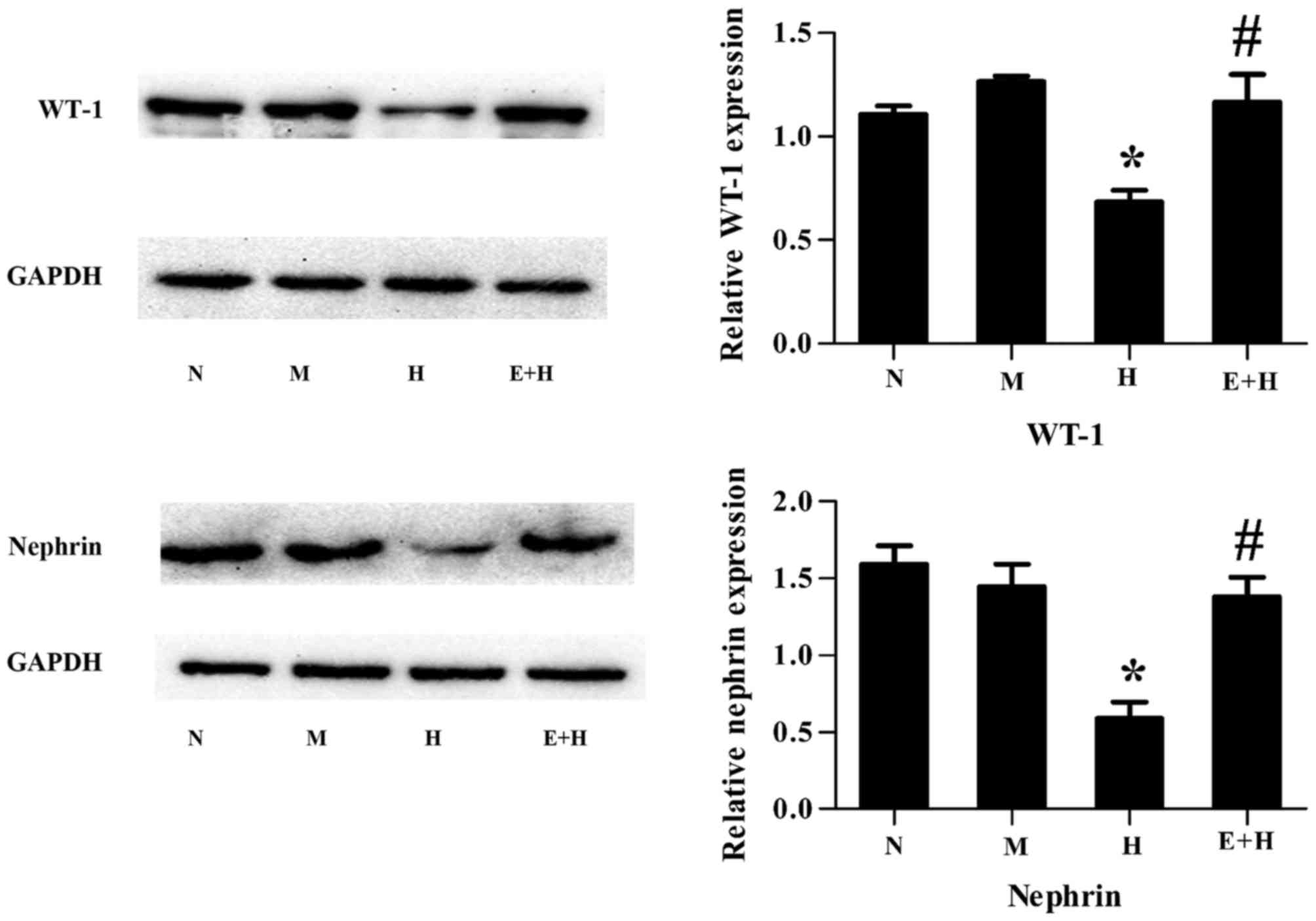
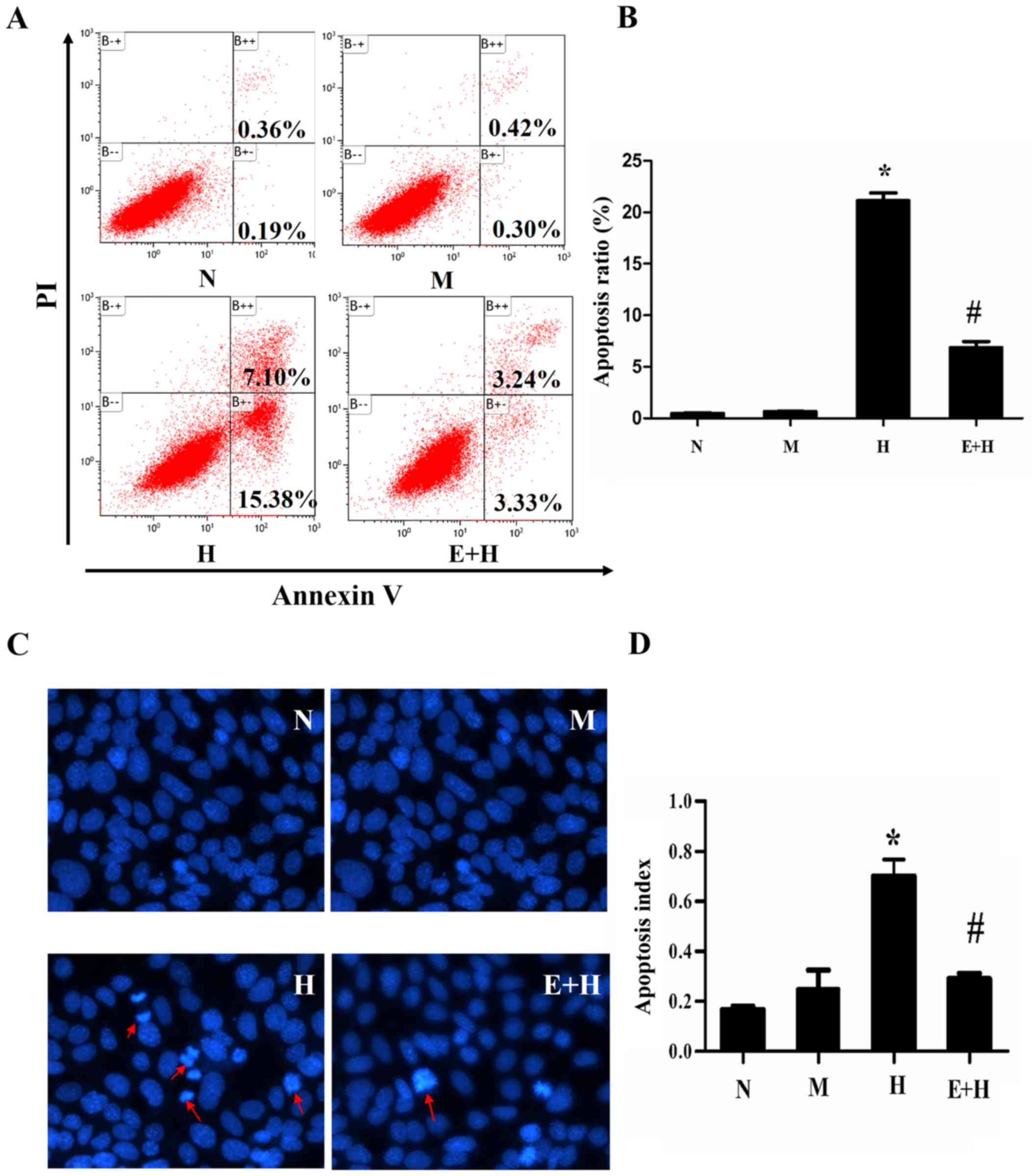
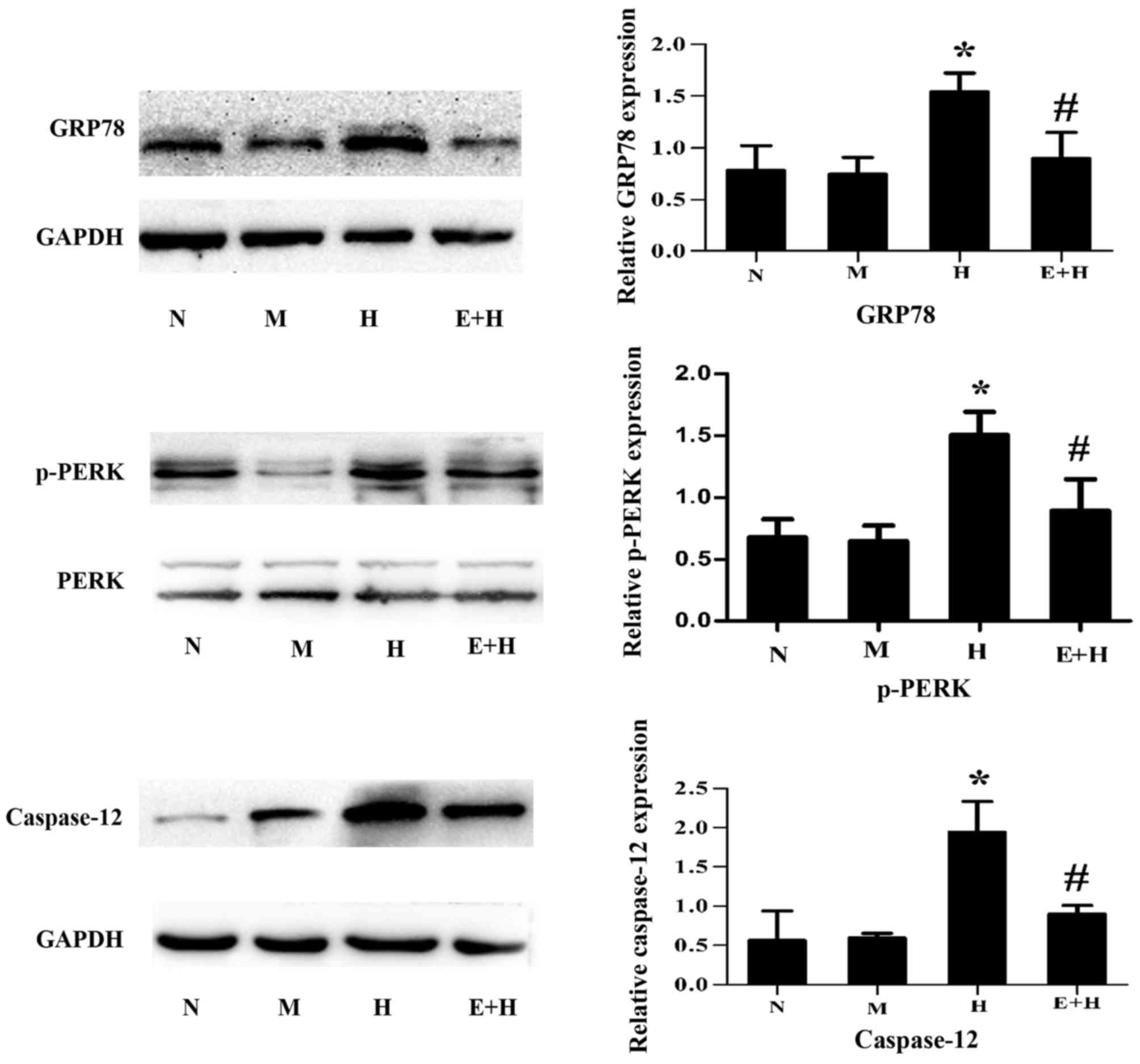
|
1
|
Ilatovskaya DV, Levchenko V, Lowing A,
Shuyskiy LS, Palygin O and Staruschenko A: Podocyte injury in
diabetic nephropathy: Implications of angiotensin II-dependent
activation of TRPC channels. Sci Rep. 5:176372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khazim K, Gorin Y, Cavaglieri RC, Abboud
HE and Fanti P: The antioxidant silybin prevents high
glucose-induced oxidative stress and podocyte injury in vitro and
in vivo. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 305:F691–F700. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ma J, Wu H, Zhao CY, Panchapakesan U,
Pollock C and Chadban SJ: Requirement for TLR2 in the development
of albuminuria, inflammation and fibrosis in experimental diabetic
nephropathy. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:481–495. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu BC, Song X, Lu XY, Li DT, Eaton DC,
Shen BZ, Li XQ and Ma HP: High glucose induces podocyte apoptosis
by stimulating TRPC6 via elevation of reactive oxygen species.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:1434–1442. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brunskill EW, Georgas K, Rumballe B,
Little MH and Potter SS: Defining the molecular character of the
developing and adult kidney podocyte. PLoS one. 6:e246402011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cao AL, Wang L, Chen X, Wang YM, Guo HJ,
Chu S, Liu C, Zhang XM and Peng W: Ursodeoxycholic acid and
4-phenylbutyrate prevent endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced
podocyte apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy. Lab Invest. 96:610–622.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Madhusudhan T, Wang H, Dong W, Ghosh S,
Bock F, Thangapandi VR, Ranjan S, Wolter J, Kohli S, Shahzad K, et
al: Defective podocyte insulin signalling through p85-XBP1 promotes
ATF6-dependent maladaptive ER-stress response in diabetic
nephropathy. Nat Commun. 6:64962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brown MK and Naidoo N: The endoplasmic
reticulum stress response in aging and age-related diseases. Front
Physiol. 3:2632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ron D and Walter P: Signal integration in
the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:519–529. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Luo B and Lee AS: The critical roles of
endoplasmic reticulum chaperones and unfolded protein response in
tumorigenesis and anticancer therapies. Oncogene. 32:805–818. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Okada T, Yoshida H, Akazawa R, Negishi M
and Mori K: Distinct roles of activating transcription factor 6
(ATF6) and double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase-like
endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) in transcription during the
mammalian unfolded protein response. Biochem J. 366:585–594. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Koumenis C, Naczki C, Koritzinsky M,
Rastani S, Diehl A, Sonenberg N, Koromilas A and Wouters BG:
Regulation of protein synthesis by hypoxia via activation of the
endoplasmic reticulum kinase PERK and phosphorylation of the
translation initiation factor eIF2alpha. Mol Cell Biol.
22:7405–7416. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Harding HP, Calfon M, Urano F, Novoa I and
Ron D: Transcriptional and translational control in the Mammalian
unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 18:575–599.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu
J, Yankner BA and Yuan J: Caspase-12 mediates
endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by
amyloid-beta. Nature. 403:98–103. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nowakowska A and Tarasiuk J: Comparative
effects of selected plant polyphenols, gallic acid and
epigallocatechin gallate, on matrix metalloproteinases activity in
multidrug resistant MCF7/DOX breast cancer cells. Acta Biochim Pol.
63:571–577. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Granja A, Pinheiro M and Reis S:
Epigallocatechin gallate nanodelivery systems for cancer therapy.
Nutrients. 8(pii): E3072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ortiz-López L, Márquez-Valadez B,
Gómez-Sánchez A, Silva-Lucero MD, Torres-Pérez M,
Téllez-Ballesteros RI, Ichwan M, Meraz-Ríos MA, Kempermann G and
Ramírez-Rodríguez GB: Green tea compound
epigallo-catechin-3-gallate (EGCG) increases neuronal survival in
adult hippocampal neurogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Neuroscience.
322:208–220. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang SM, Chang YH, Chao YC, Lin JA, Wu
CH, Lai CY, Chan KC, Tseng ST and Yen GC: EGCG-rich green tea
extract stimulates sRAGE secretion to inhibit S100A12-RAGE axis
through ADAM10-mediated ectodomain shedding of extracellular RAGE
in type 2 diabetes. Mol Nutr Food Res. 57:2264–2268. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim SJ, Li M, Jeong CW, Bae HB, Kwak SH,
Lee SH, Lee HJ, Heo BH, Yook KB and Yoo KY:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a green tea catechin, protects the
heart against regional ischemia-reperfusion injuries through
activation of RISK survival pathways in rats. Arch Pharm Res.
37:1079–1085. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang EJ, Lee J, Lee SY, Kim EK, Moon YM,
Jung YO, Park SH and Cho ML: EGCG attenuates autoimmune arthritis
by inhibition of STAT3 and HIF-1alpha with Th17/Treg control. PLoS
One. 9:e860622014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Leu JG, Lin CY, Jian JH, Shih CY and Liang
YJ: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate combined with alpha lipoic acid
attenuates high glucose-induced receptor for advanced glycation end
products (RAGE) expression in human embryonic kidney cells. An Acad
Bras Cienc. 85:745–752. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mundel P and Shankland SJ: Podocyte
biology and response to injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:3005–3015.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Butt A and Riaz S: Study of protein
profiling of human urine in diabetic hypertensive nephropathy
versus normal healthy controls. Diabetes Technol Ther. 12:379–386.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lv J, Feng M, Zhang L, Wan X, Zeng YC,
Liang PF and Xu AP: Protective effect of epigallocatechin gallate,
a major constituent of green tea, against renal
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Int Urol Nephrol.
47:1429–1435. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen B, Liu G, Zou P, Li X, Hao Q, Jiang
B, Yang X and Hu Z: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate protects against
cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibiting endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
240:1513–1519. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zou P, Song J, Jiang B, Pei F, Chen B,
Yang X, Liu G and Hu Z: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate protects against
cisplatin nephrotoxicity by inhibiting the apoptosis in mouse. Int
J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:4607–4616. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ozcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi
NN, Ozdelen E, Tuncman G, Görgün C, Glimcher LH and Hotamisligil
GS: Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action and
type 2 diabetes. Science. 306:457–461. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cao Y, Hao Y, Li H, Liu Q, Gao F, Liu W
and Duan H: Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in apoptosis of
differentiated mouse podocytes induced by high glucose. Int J Mol
Med. 33:809–816. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun XY, Qin HJ, Zhang Z, Xu Y, Yang XC,
Zhao DM, Li XN and Sun LK: Valproate attenuates diabetic
nephropathy through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum
stressinduced apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 13:661–668. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Groenendyk J, Sreenivasaiah PK, Kim DH,
Agellon LB and Michalak M: Biology of endoplasmic reticulum stress
in the heart. Circ Res. 107:1185–1197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B and Reed JC:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Cell life and death decisions. J Clin
Invest. 115:2656–2664. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schroder M and Kaufman RJ: ER stress and
the unfolded protein response. Mutat Res. 569:29–63. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|