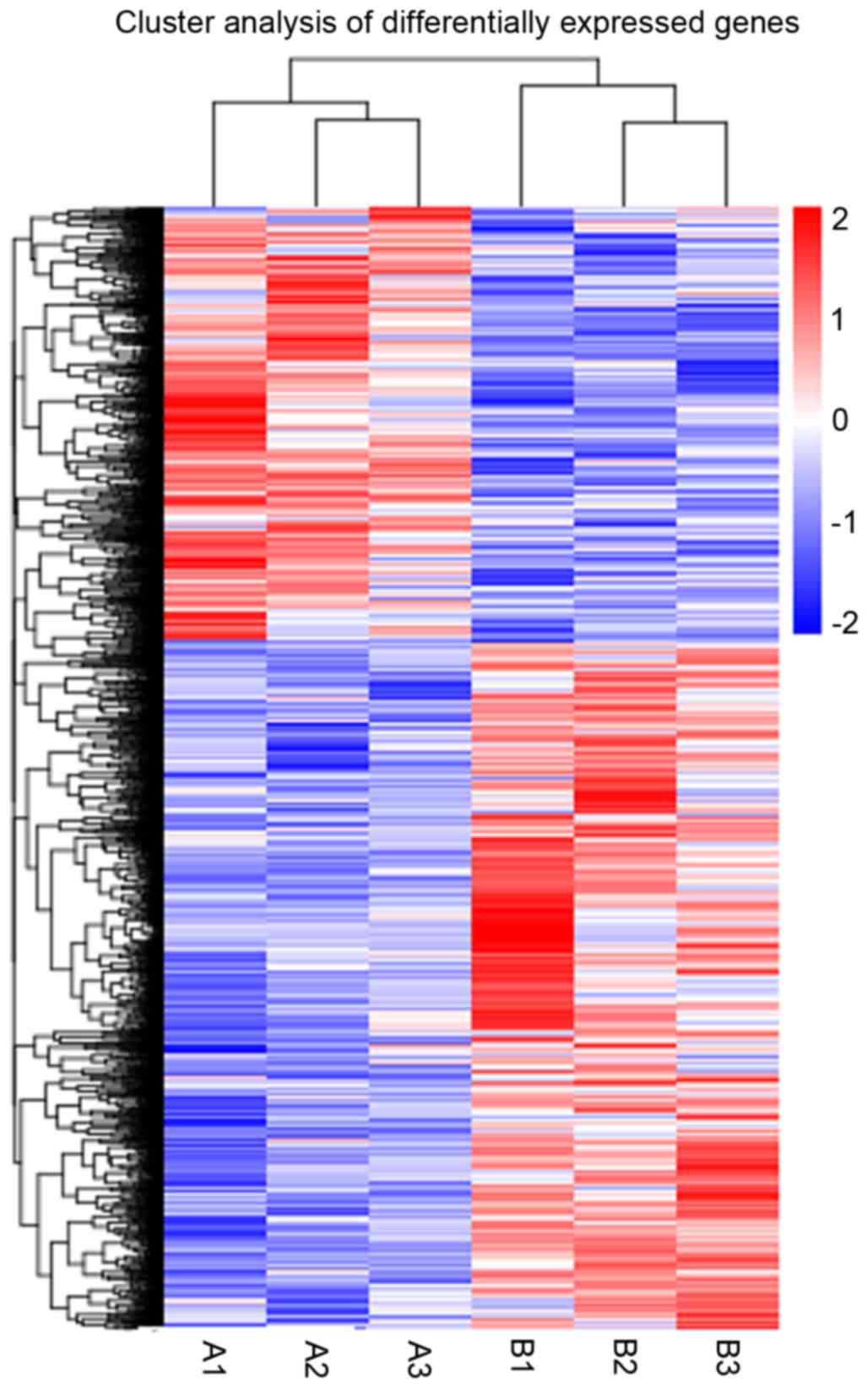
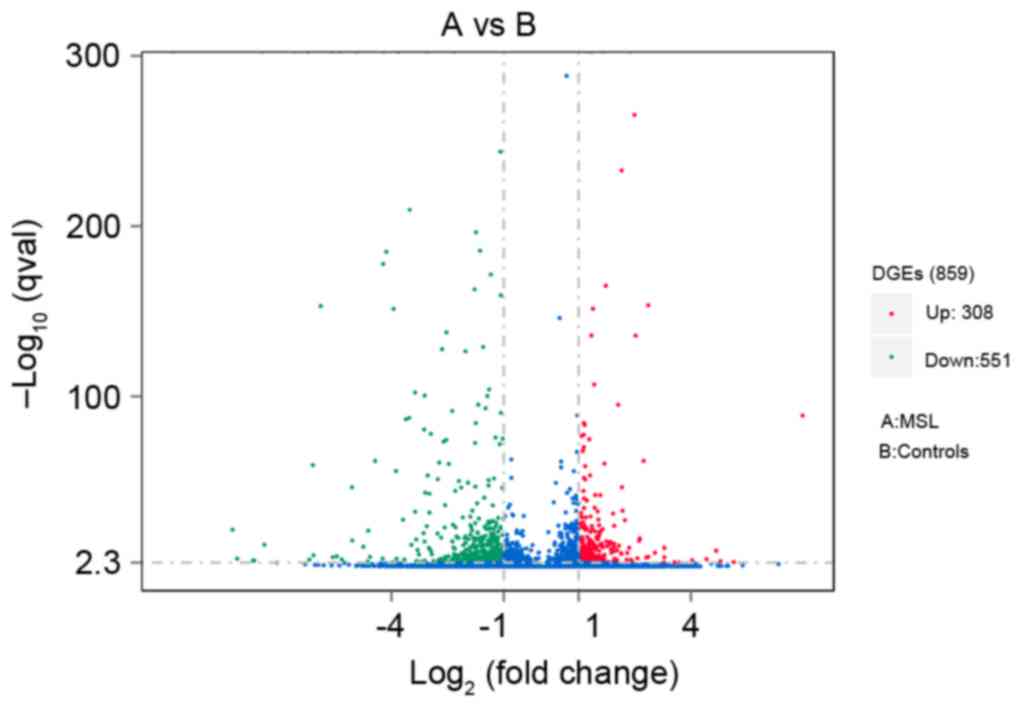
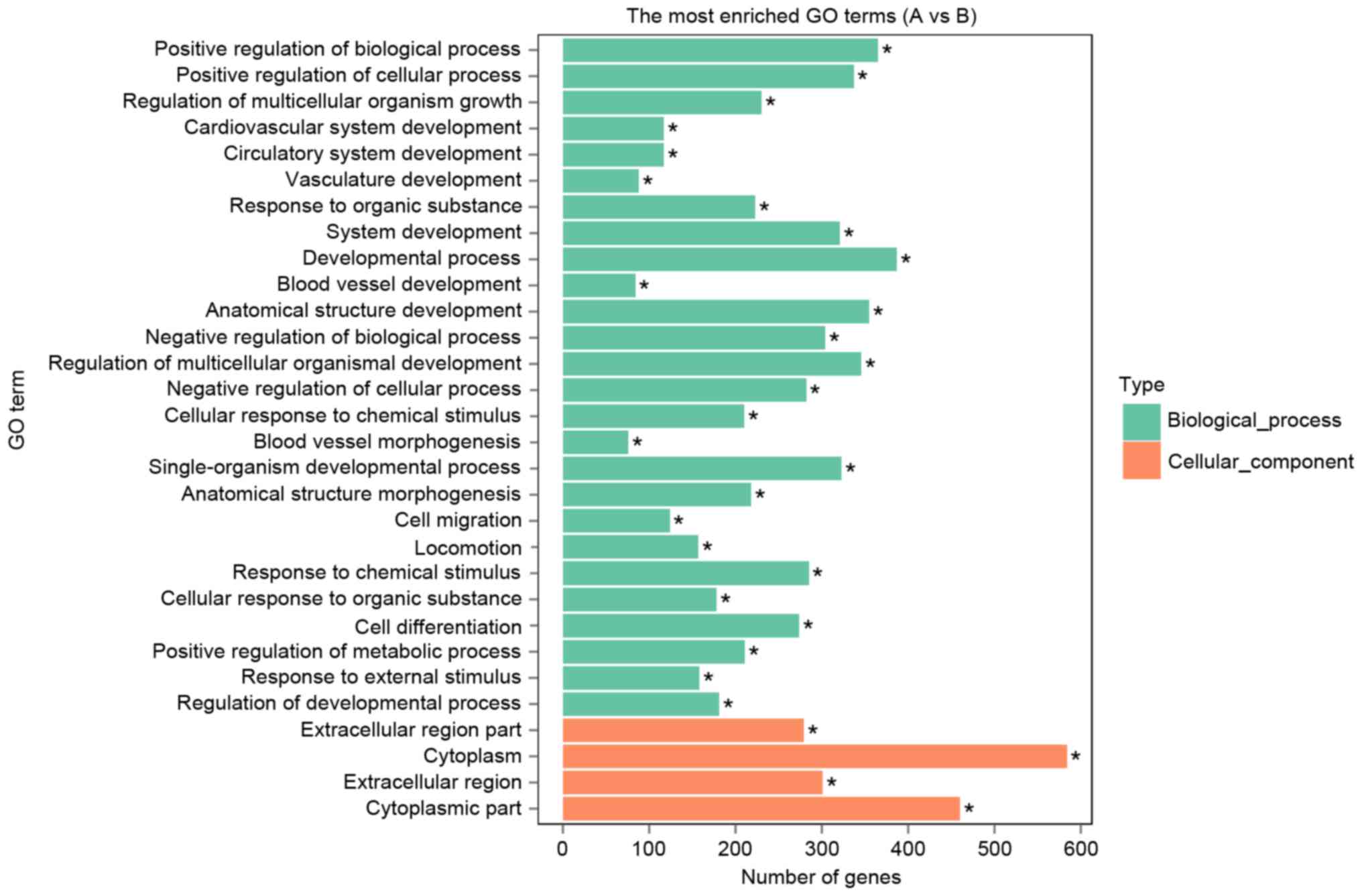
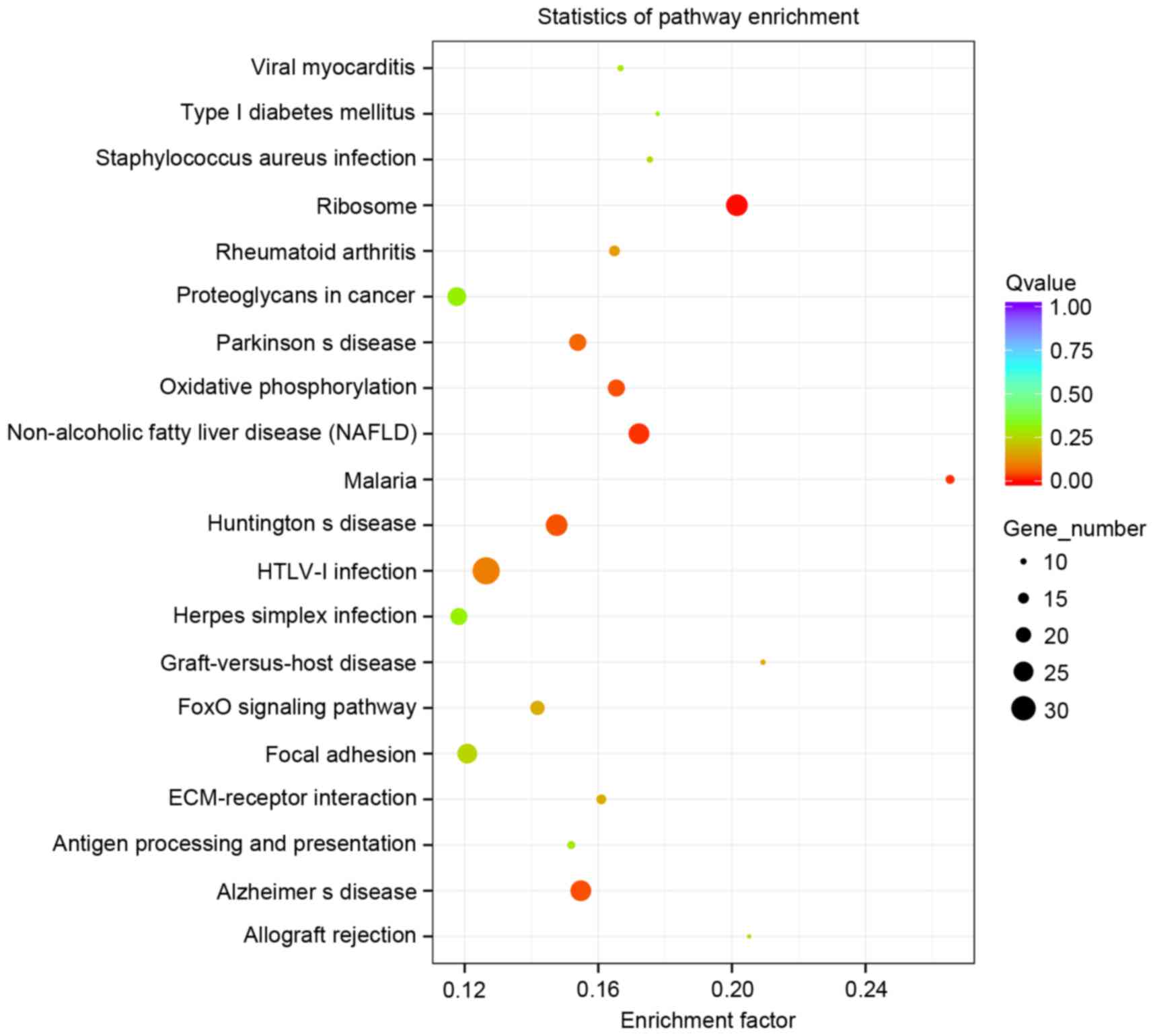
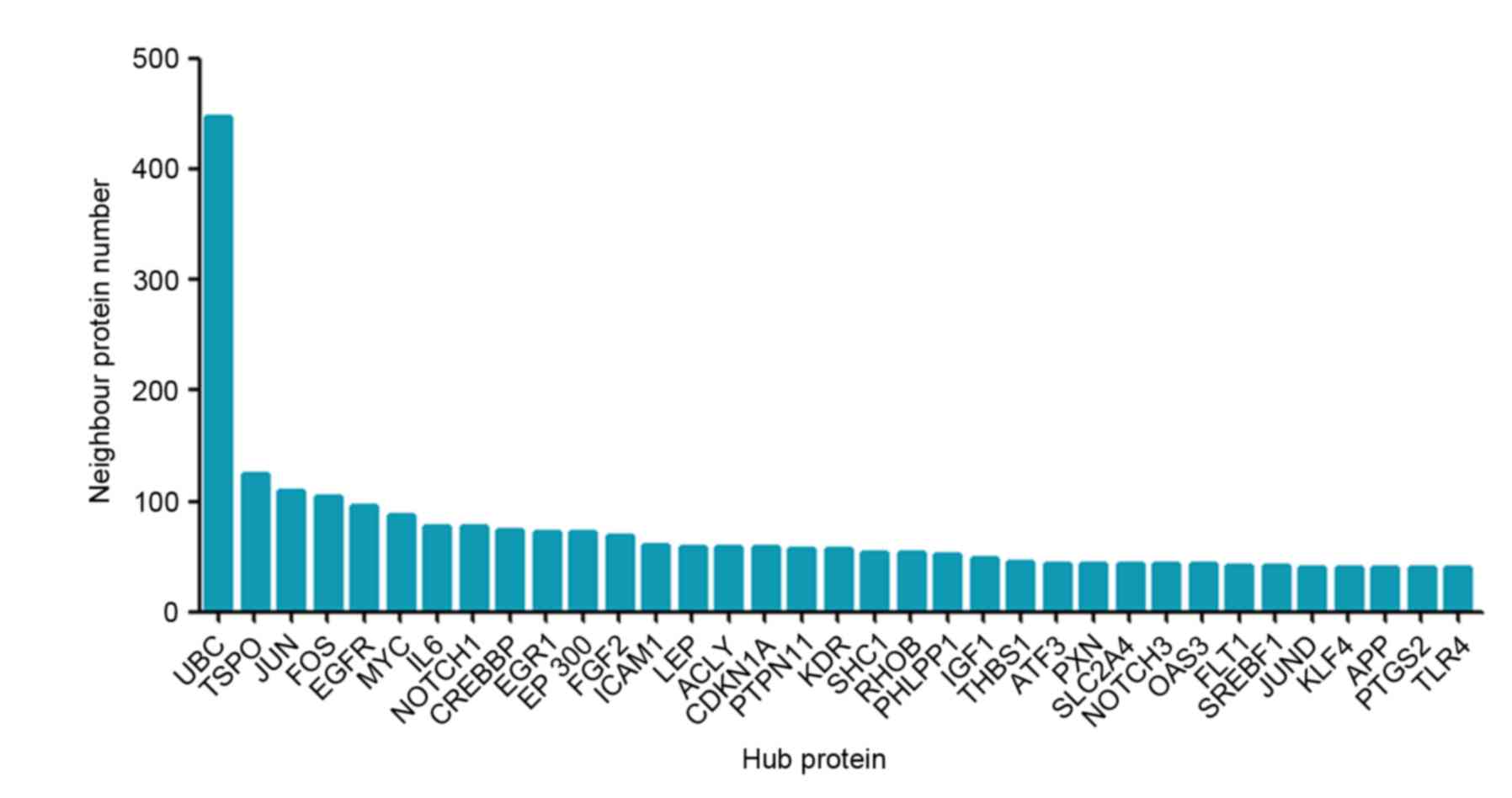
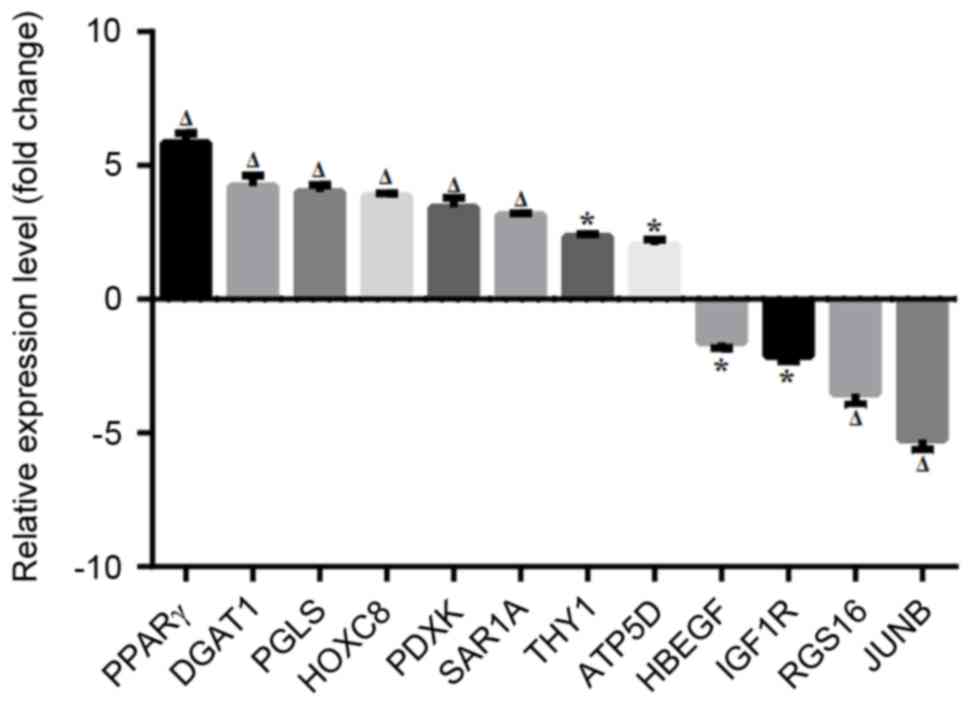
|
1
|
Brodie BC: Lecture XIV: On Fatty or
Adipose TumorsLectures Illustrative of Various Subjects In
Pathology and Surgery. Longman, Brown, Green and Longmans; London:
pp. 275–282. 1846
|
|
2
|
Nisi G and Sisti A: Images in clinical
medicine. Madelung's disease. N Engl J Med. 374:5722016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rendina D, De Filippo G, Nazzaro A and
Strazzullo P: Impaired gonadal function in a woman with multiple
symmetric lipomatosis. Minerva Endocrinol. 38:211–215.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Palacios E, Neitzschman HR and Nguyen J:
Madelung disease: Multiple symmetric lipomatosis. Ear Nose Throat
J. 93:94–96. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Esteban J, úlvez L, Perelló Aragonés S and
Bargalló X Aguilar: Sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome and multiple
symmetrical lipomatosis. Arch Bronconeumol. 49:86–87. 2013.(In
English, Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ardeleanu V, Chicos S, Georgescu C and
Tutunaru D: Multiple benign symmetric lipomatosis-a differential
diagnosis of obesity. Chirurgia (Bucur). 108:580–583.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yeh NC, Yang CY, Chou CW, Yen FC, Lee SY
and Tien KJ: Madelung's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
97:3012–3013. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tadisina KK, Mlynek KS, Hwang LK, Riazi H,
Papay FA and Zins JE: Syndromic lipomatosis of the head and neck: A
review of the literature. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 39:440–448. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haap M, Siewecke C, Thamer C, Machann J,
Schick F, Häring HU, Szeimies RM and Stumvoll M: Multiple symmetric
lipomatosis: A paradigm of metabolically innocent obesity? Diabetes
Care. 27:794–795. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen K, Xie Y, Hu P, Zhao S and Mo Z:
Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis: Substantial subcutaneous adipose
tissue accumulation did not induce glucose and lipid metabolism
dysfunction. Ann Nutr Metab. 57:68–73. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cojocaru DC, Cozma CD and Postolache P:
Markers of insulin resistance in a case of Launois-Bensaude
syndrome. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 117:404–408.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brea-García B, Cameselle-Teijeiro J,
Couto-González I, Taboada-Suárez A and González-Álvarez E:
Madelung's disease: Comorbidities, fatty mass distribution and
response to treatment of 22 patients. Aesthetic Plast Surg.
37:409–416. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Heike Z, Gudrun UM, Frank RD, Vetter H and
Walger P: Multiple benign symmetric lipomatosis-a differential
diagnosis of obesity: Is there a rationale for fibrate treatment?
Obes Surg. 18:240–242. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Verhelle NA, Nizet JL, van den Hof B,
Guelinckx P and Heymans O: Liposuction in benign symmetric
lipomatosis: Sense or senseless? Aesthetic Plast Surg. 27:319–321.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Enzi G, Busetto L, Sergi G, Coin A,
Inelmen EM, Vindigni V, Bassetto F and Cinti S: Multiple symmetric
lipomatosis: A rare disease and its possible links to brown adipose
tissue. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 25:347–353. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ballester S, ánchez R, Mira MÁ Navarro,
Marco C Pujol and Estrada R Botella: Symmetric benign lipomatosis:
Madelung syndrome. Med Clin (Barc). 141:366–367. 2013.(In Spanish).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kobayashi J, Nagao M, Miyamoto K and
Matsubara S: MERRF syndrome presenting with multiple symmetric
lipomatosis in a Japanese patient. Intern Med. 49:479–482. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schoffer K and Grant I: Multiple lipomas,
alcoholism, and neuropathy: Madelung's disease or MERRF? Muscle
Nerve. 33:142–146. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nisoli E, Regianini L, Briscini L,
Bulbarelli A, Busetto L, Coin A, Enzi G and Carruba MO: Multiple
symmetric lipomatosis may be the consequence of defective
noradrenergic modulation of proliferation and differentiation of
brown fat cells. J Pathol. 198:378–387. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Plummer C, Spring PJ, Marotta R, Chin J,
Taylor G, Sharpe D, Athanasou NA, Thyagarajan D and Berkovic SF:
Multiple symmetrical lipomatosis-a mitochondrial disorder of brown
fat. Mitochondrion. 13:269–276. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Prantl L, Schreml J, Gehmert S, Klein S,
Bai X, Zeitler K, Schreml S, Alt E, Gehmert S and Felthaus O:
Transcription profile in sporadic multiple symmetric lipomatosis
reveals differential expression at the level of adipose
tissue-derived stem cells. Plast Reconstr Surg. 137:1181–1190.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen K, He H, Xie Y, Zhao L, Zhao S, Wan
X, Yang W and Mo Z: miR-125a-3p and miR-483-5p promote adipogenesis
via suppressing the RhoA/ROCK1/ERK1/2 pathway in multiple symmetric
lipomatosis. Sci Rep. 5:119092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang L, Feng Z, Wang X, Wang X and Zhang
X: DEGseq: An Rpackage for identifying differentially expressed
genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics. 26:136–138. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multipletesting. J R Statist Soc. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
25
|
Mao X, Cai T, Olyarchuk JG and Wei L:
Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the
KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics.
21:3787–3793. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M,
Hirakawa M, Itoh M, Katayama T, Kawashima S, Okuda S, Tokimatsu T
and Yamanishi Y: KEGG for linking genomes to life and the
environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 36(Database Issue): D480–D484.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Harsch IA, Bergmann T, Koebnick C,
Wiedmann R, Ruderich F, Hahn EG and Konturek PC: Adiponectin,
resistin and subclinical inflammation-the metabolic burden in
Launois Bensaude Syndrome, a rare form of obesity. J Physiol
Pharmacol. 58 Suppl 1:S65–S76. 2007.
|
|
29
|
Ouchi N: Adipocytokines in cardiovascular
and metabolic diseases. J Atheroscler Thromb. 23:645–654. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matsuzawa Y: Therapy insight:
Adipocytokines in metabolic syndrome and related cardiovascular
disease. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 3:35–42. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ryu KY, Maehr R, Gilchrist CA, Long MA,
Bouley DM, Mueller B, Ploegh HL and Kopito RR: The mouse
polyubiquitin gene UbC is essential for fetal liver development,
cell-cycle progression and stress tolerance. EMBO J. 26:2693–2706.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dikic I, Wakatsuki S and Walters KJ:
Ubiquitin-binding domains-from structures to functions. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 10:659–671. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ciechanover A: Intracellular protein
degradation: From a vague idea through the lysosome and the
ubiquitin-proteasome system and onto human diseases and drug
targeting. Neurodegener Dis. 10:7–22. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wójcik C, Lohe K, Kuang C, Xiao Y, Jouni Z
and Poels E: Modulation of adipocyte differentiation by omega-3
polyunsaturated fatty acids involves the ubiquitin-proteasome
system. J Cell Mol Med. 18:590–599. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Santoro A, Raso G Mattace, Taliani S, Da
Pozzo E, Simorini F, Costa B, Martini C, Laneri S, Sacchi A,
Cosimelli B, et al: TSPO-ligands prevent oxidative damage and
inflammatory response in C6 glioma cells by neurosteroid synthesis.
Eur J Pharm Sci. 88:124–131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wyatt SK, Manning HC, Bai M, Ehtesham M,
Mapara KY, Thompson RC and Bornhop DJ: Preclinical molecular
imaging of the translocator protein (TSPO) in a metastases model
based on breast cancer xenografts propagated in the murine brain.
Curr Mol Med. 12:458–466. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Repalli J: Translocator protein (TSPO)
role in aging and Alzheimer's disease. Curr Aging Sci. 7:168–175.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cumming P and Borghammer P: Molecular
imaging and the neuropathologies of Parkinson's disease. Curr Top
Behav Neurosci. 11:117–148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Qi X, Xu J, Wang F and Xiao J:
Translocator protein (18 kDa): A promising therapeutic target and
diagnostic tool for cardiovascular diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2012:1629342012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li F, Liu J, Liu N, Kuhn LA, Garavito RM
and Ferguson-Miller S: Protein 18 kDa (TSPO): An Old protein with
new functions? Biochemistry. 55:2821–2831. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dimitrova-Shumkovska J, Veenman L,
Ristoski T, Leschiner S and Gavish M: Chronic high fat, high
cholesterol supplementation decreases 18 kDa translocator protein
binding capacity in association with increased oxidative stress in
rat liver and aorta. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:910–921. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lecanu L, Yao ZX, McCourty A, Sidahmed
el-K, Orellana ME, Burnier MN and Papadopoulos V: Control of
hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis using the cholesterol
recognition/interaction amino acid sequence of the translocator
protein TSPO. Steroids. 78:137–146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wagner EF and Eferl R: Fos/AP-1 proteins
in bone and the immune system. Immunol Rev. 208:126–140. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kveiborg M, Sabatakos G, Chiusaroli R, Wu
M, Philbrick WM, Horne WC and Baron R: DeltaFosB induces
osteosclerosis and decreases adipogenesis by two independent
cell-autonomous mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 24:2820–2830. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Luther J, Driessler F, Megges M, Hess A,
Herbort B, Mandic V, Zaiss MM, Reichardt A, Zech C, Tuckermann JP,
et al: Elevated Fra-1 expression causes severe lipodystrophy. J
Cell Sci. 124:1465–1476. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|