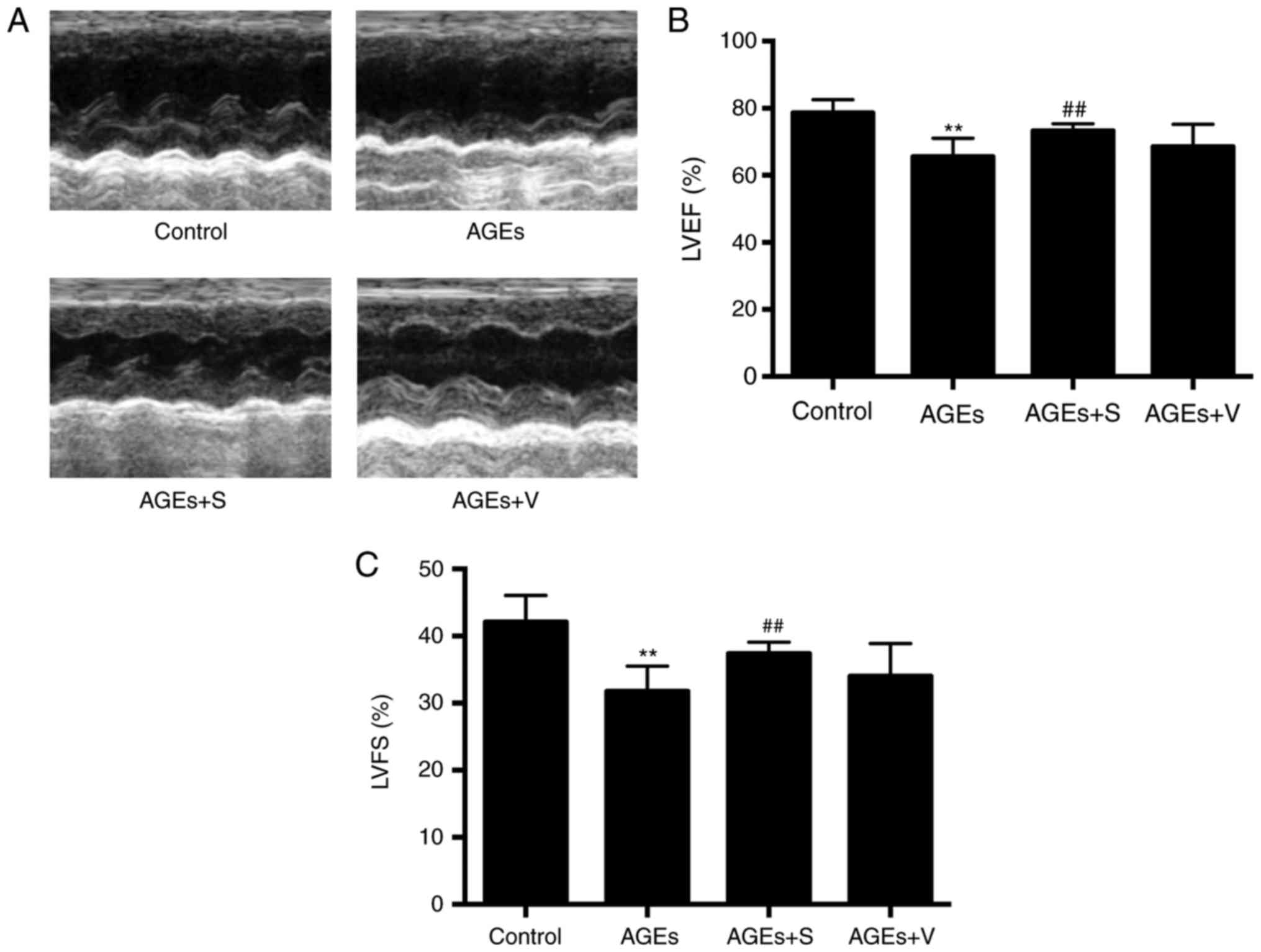
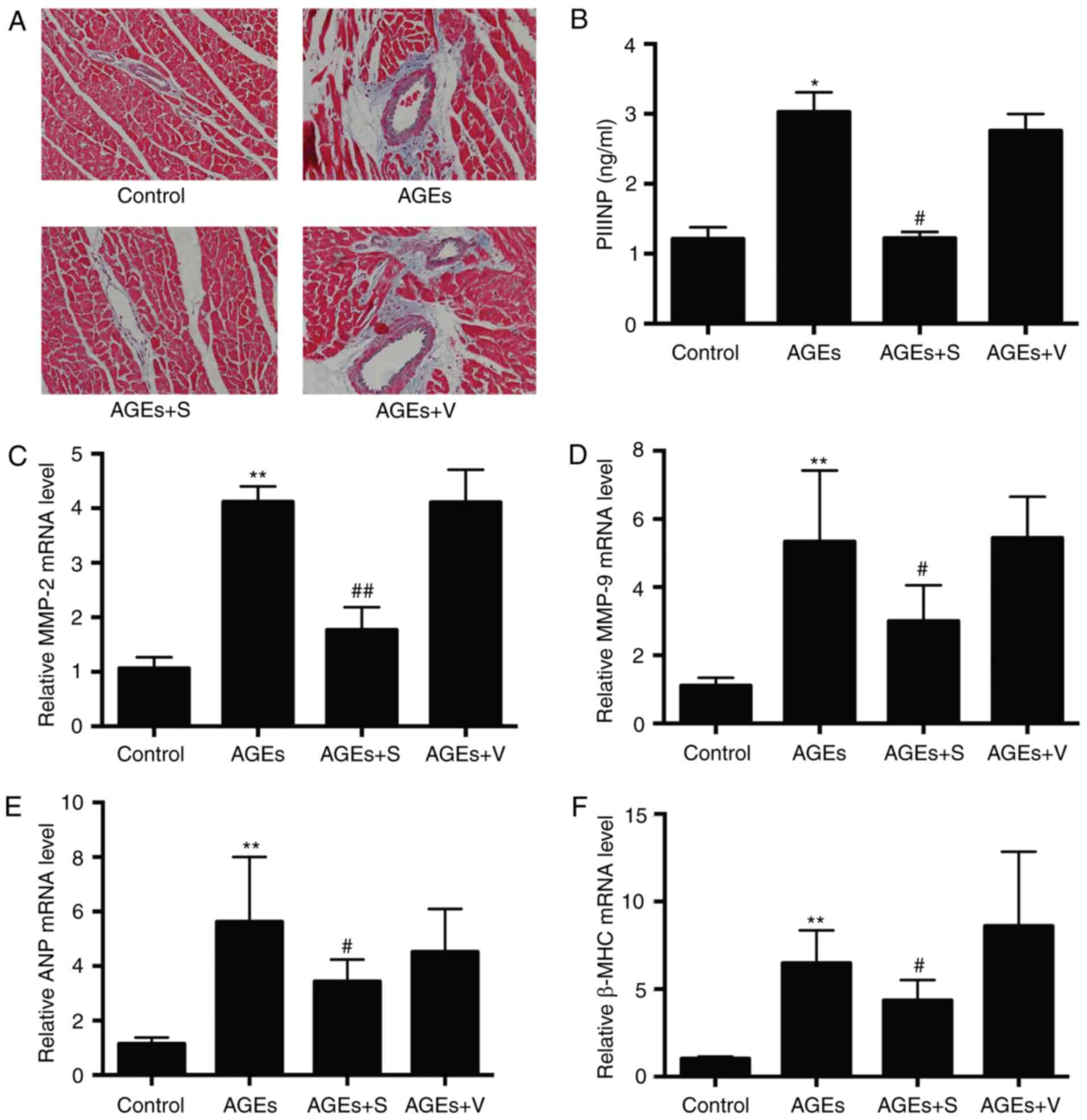
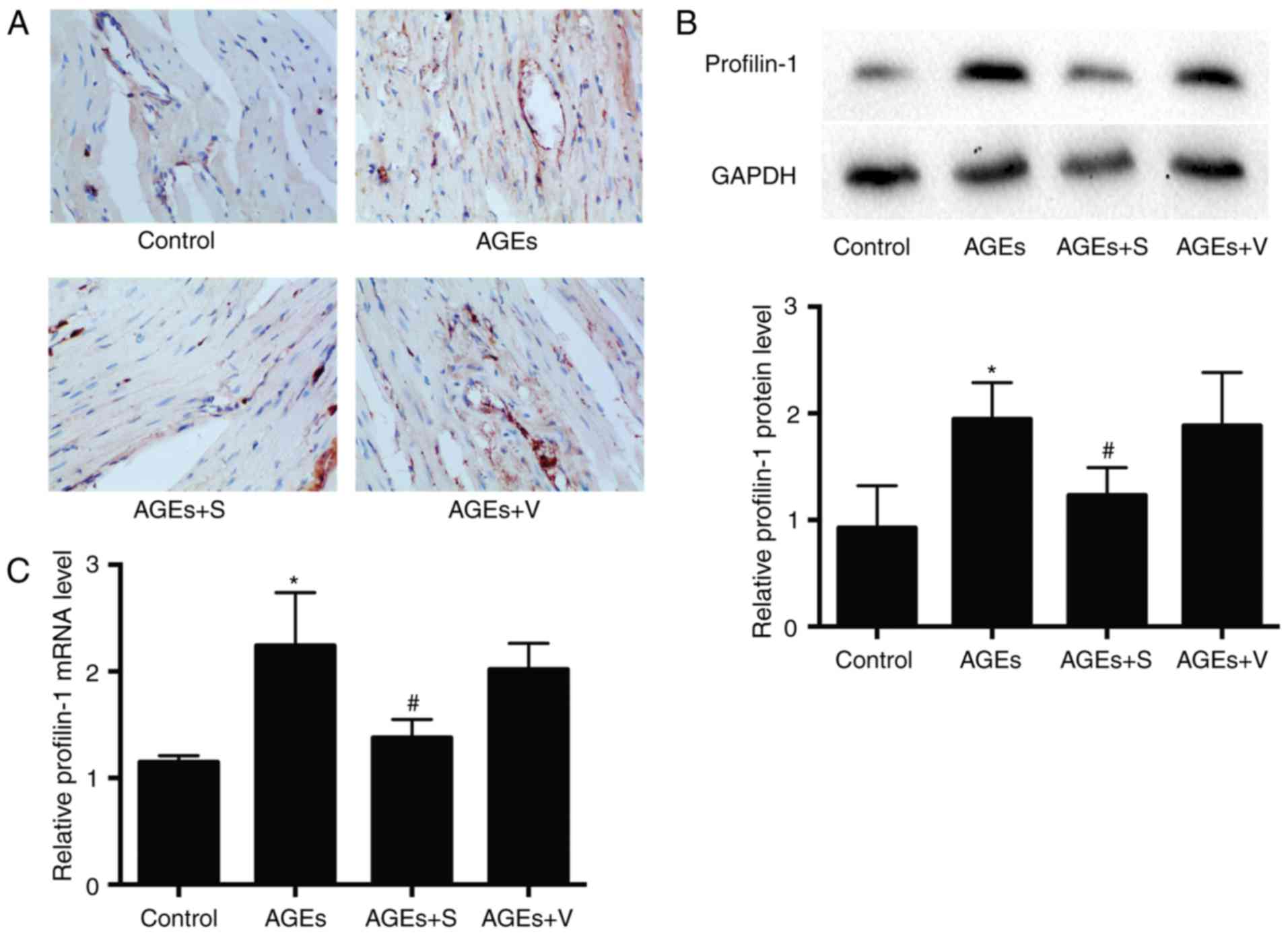
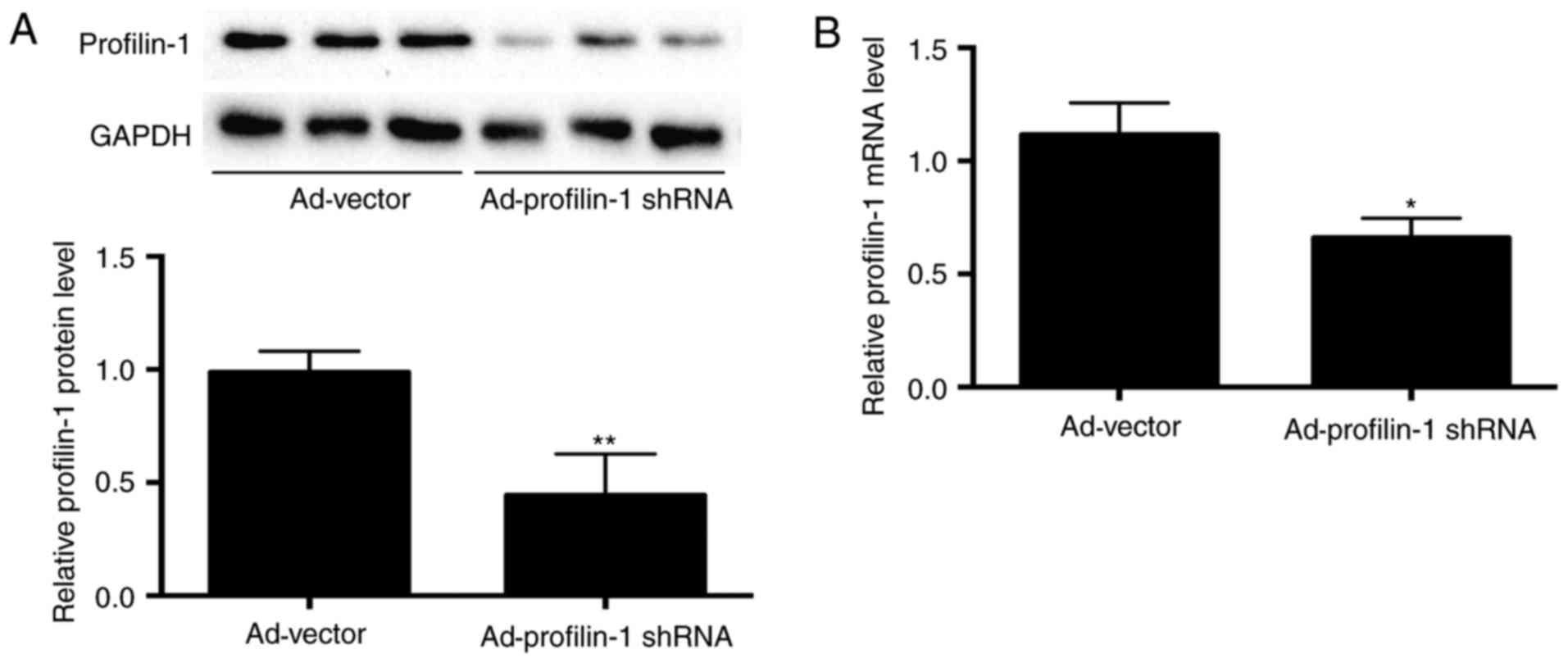
|
1
|
Miki T, Yuda S, Kouzu H and Miura T:
Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Pathophysiology and clinical features.
Heart Fail Rev. 18:149–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bodiga VL, Eda SR and Bodiga S: Advanced
glycation end products: Role in pathology of diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Heart Fail Rev. 19:49–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sveen KA, Nerdrum T, Hanssen KF, Brekke M,
Torjesen PA, Strauch CM, Sell DR, Monnier VM, Dahl-Jørgensen K and
Steine K: Impaired left ventricular function and myocardial blood
flow reserve in patients with long-term type 1 diabetes and no
significant coronary artery disease: Associations with protein
glycation. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 11:84–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cooper ME: Importance of advanced
glycation end products in diabetes-associated cardiovascular and
renal disease. Am J Hypertens. 17:31S–38S. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ko SY, Lin IH, Shieh TM, Ko HA, Chen HI,
Chi TC, Chang SS and Hsu YC: Cell hypertrophy and MEK/ERK
phosphorylation are regulated by glyceraldehyde-derived AGEs in
cardiomyocyte H9c2 cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. 66:537–544. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li SY, Sigmon VK, Babcock SA and Ren J:
Advanced glycation endproduct induces ROS accumulation, apoptosis,
MAP kinase activation and nuclear O-GlcNAcylation in human cardiac
myocytes. Life Sci. 80:1051–1056. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guo R, Liu W, Liu B, Zhang B, Li W and Xu
Y: SIRT1 suppresses cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic
cardiomyopathy: An insight into endoplasmic reticulum stress
response mechanism. Int J Cardiol. 191:36–45. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brouwers O, de Vos-Houben JM, Niessen PM,
Miyata T, van Nieuwenhoven F, Janssen BJ, Hageman G, Stehouwer CD
and Schalkwijk CG: Mild oxidative damage in the diabetic rat heart
is attenuated by glyoxalase-1 overexpression. Int J Mol Sci.
14:15724–15739. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pernier J, Shekhar S, Jegou A, Guichard B
and Carlier MF: Profilin interaction with actin filament barbed end
controls dynamic instability, capping, branching, and motility. Dev
Cell. 36:201–214. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Witke W: The role of profilin complexes in
cell motility and other cellular processes. Trends Cell Biol.
14:461–469. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jockusch BM, Murk K and Rothkegel M: The
profile of profilins. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 159:131–149.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Z, Zhong Q, Yang T, Xie X and Chen M:
The role of profilin-1 in endothelial cell injury induced by
advanced glycation end products (AGEs). Cardiovasc Diabetol.
12:1412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Romeo G, Frangioni JV and Kazlauskas A:
Profilin acts downstream of LDL to mediate diabetic endothelial
cell dysfunction. FASEB J. 18:725–727. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cheng JF, Ni GH, Chen MF, Li YJ, Wang YJ,
Wang CL, Yuan Q, Shi RZ, Hu CP and Yang TL: Involvement of
profilin-1 in angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation. Vascul Pharmacol. 55:34–41. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin HY, Song B, Oudit GY, Davidge ST, Yu
HM, Jiang YY, Gao PJ, Zhu DL, Ning G, Kassiri Z, et al: ACE2
deficiency enhances angiotensin II-mediated aortic profilin-1
expression, inflammation and peroxynitrite production. PLoS One.
7:e385022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Caglayan E, Romeo GR, Kappert K, Odenthal
M, Südkamp M, Body SC, Shernan SK, Hackbusch D, Vantler M,
Kazlauskas A and Rosenkranz S: Profilin-1 is expressed in human
atherosclerotic plaques and induces atherogenic effects on vascular
smooth muscle cells. PLoS One. 5:e136082010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kooij V, Viswanathan MC, Lee DI, Rainer
PP, Schmidt W, Kronert WA, Harding SE, Kass DA, Bernstein SI, Van
Eyk JE and Cammarato A: Profilin modulates sarcomeric organization
and mediates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res.
110:238–248. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao SH, Qiu J, Wang Y, Ji X, Liu XJ, You
BA, Sheng YP, Li X and Gao HQ: Profilin-1 promotes the development
of hypertension-induced cardiac hypertrophy. J Hypertens.
31:576–586. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Elnakish MT, Hassanain HH and Janssen PM:
Vascular remodeling-associated hypertension leads to left
ventricular hypertrophy and contractile dysfunction in profilin-1
transgenic mice. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 60:544–552. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hein S, Kostin S, Heling A, Maeno Y and
Schaper J: The role of the cytoskeleton in heart failure.
Cardiovasc Res. 45:273–278. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao SH, Gao HQ, Ji X, Wang Y, Liu XJ, You
BA, Cui XP and Qiu J: Effect of ouabain on myocardial
ultrastructure and cytoskeleton during the development of
ventricular hypertrophy. Heart Vessels. 28:101–113. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu S, Song T, Zhou S, Liu Y, Chen G, Huang
N and Liu L: Involvement of Na+/H+ exchanger
1 in advanced glycation end products-induced proliferation of
vascular smooth muscle cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
375:384–389. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
National Institutes of Health Guide for
the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press.
85-23 revised. Washington, DC: 1996, https://grants.nih.gov/grants/olaw/guide-for-the-care-and-use-of-laboratory-animals.pdf
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nielsen JM, Kristiansen SB, Nørregaard R,
Andersen CL, Denner L, Nielsen TT, Flyvbjerg A and Bøtker HE:
Blockage of receptor for advanced glycation end products prevents
development of cardiac dysfunction in db/db type 2 diabetic mice.
Eur J Heart Fail. 11:638–647. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma H, Li SY, Xu P, Babcock SA, Dolence EK,
Brownlee M, Li J and Ren J: Advanced glycation endproduct (AGE)
accumulation and AGE receptor (RAGE) up-regulation contribute to
the onset of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Cell Mol Med. 13:1751–1764.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Russo I and Frangogiannis NG:
Diabetes-associated cardiac fibrosis: Cellular effectors, molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
90:84–93. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bando YK and Murohara T: Diabetes-related
heart failure. Circ J. 78:576–583. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Soro-Paavonen A, Zhang WZ, Venardos K,
Coughlan MT, Harris E, Tong DC, Brasacchio D, Paavonen K,
Chin-Dusting J, Cooper ME, et al: Advanced glycation end-products
induce vascular dysfunction via resistance to nitric oxide and
suppression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J Hypertens.
28:780–788. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vlassara H, Fuh H, Makita Z, Krungkrai S,
Cerami A and Bucala R: Exogenous advanced glycosylation end
products induce complex vascular dysfunction in normal animals: A
model for diabetic and aging complications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
89:12043–12047. 1992; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Soliman H, Gador A, Lu YH, Lin G, Bankar G
and MacLeod KM: Diabetes-induced increased oxidative stress in
cardiomyocytes is sustained by a positive feedback loop involving
Rho kinase and PKCβ2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
303:H989–H1000. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lin G, Craig GP, Zhang L, Yuen VG, Allard
M, McNeill JH and MacLeod KM: Acute inhibition of Rho-kinase
improves cardiac contractile function in streptozotocin-diabetic
rats. Cardiovasc Res. 75:51–58. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou H, Li YJ, Wang M, Zhang LH, Guo BY,
Zhao ZS, Meng FL, Deng YG and Wang RY: Involvement of RhoA/ROCK in
myocardial fibrosis in a rat model of type 2 diabetes. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 32:999–1008. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lorenzo O, Picatoste B, Ares-Carrasco S,
Ramírez E, Egido J and Tuñón J: Potential role of nuclear factor κB
in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Mediators Inflamm. 2011:6520972011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Thomas CM, Yong QC, Rosa RM, Seqqat R,
Gopal S, Casarini DE, Jones WK, Gupta S, Baker KM and Kumar R:
Cardiac-specific suppression of NF-κB signaling prevents diabetic
cardiomyopathy via inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 307:H1036–H1045. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|