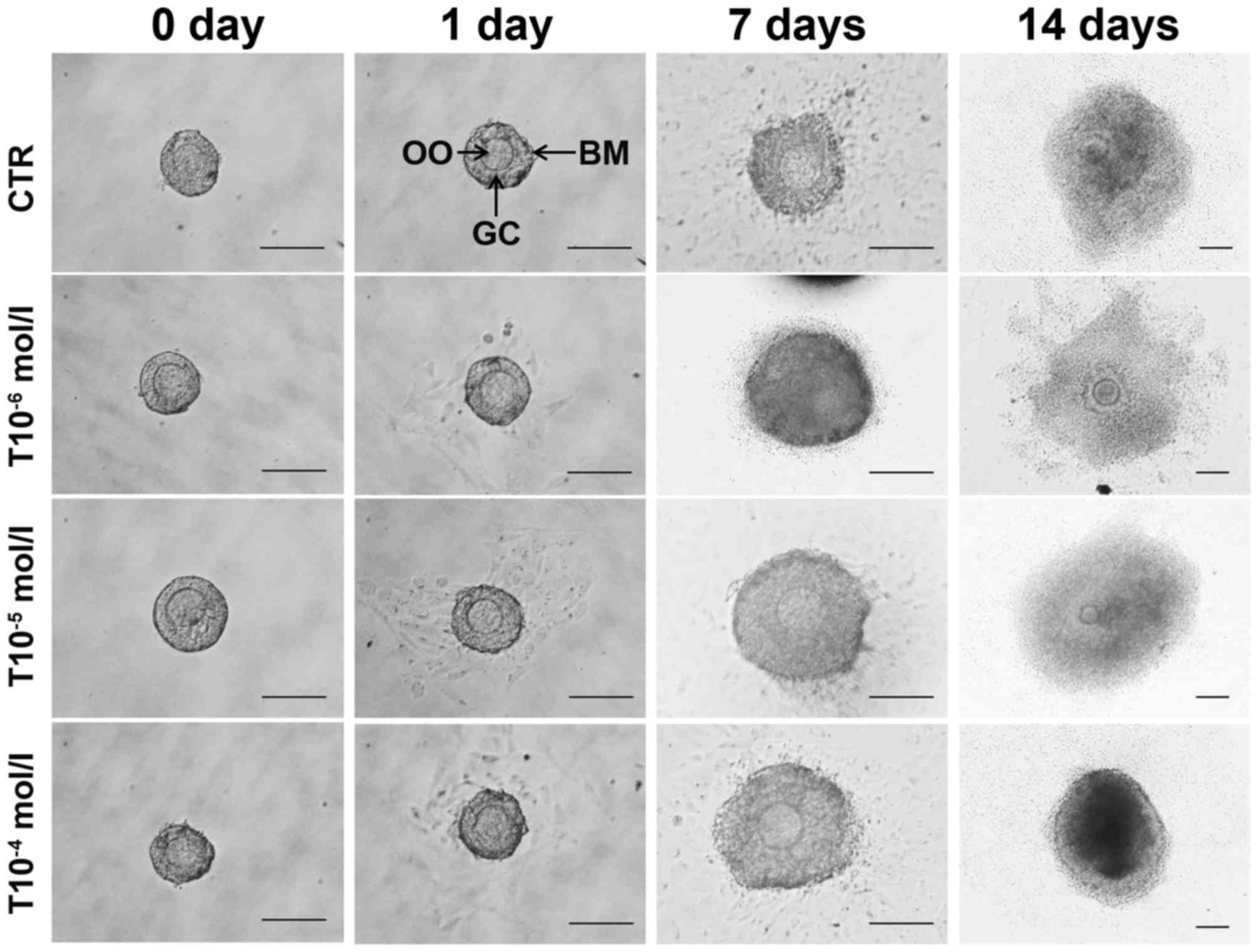
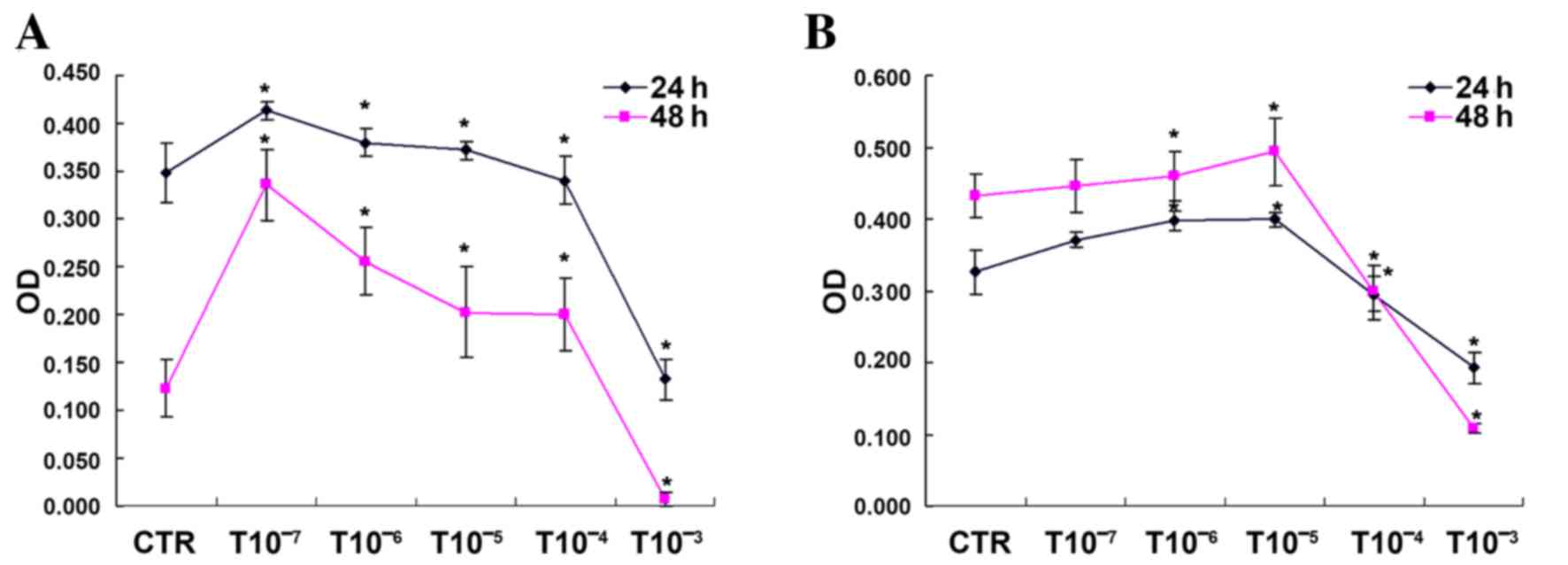
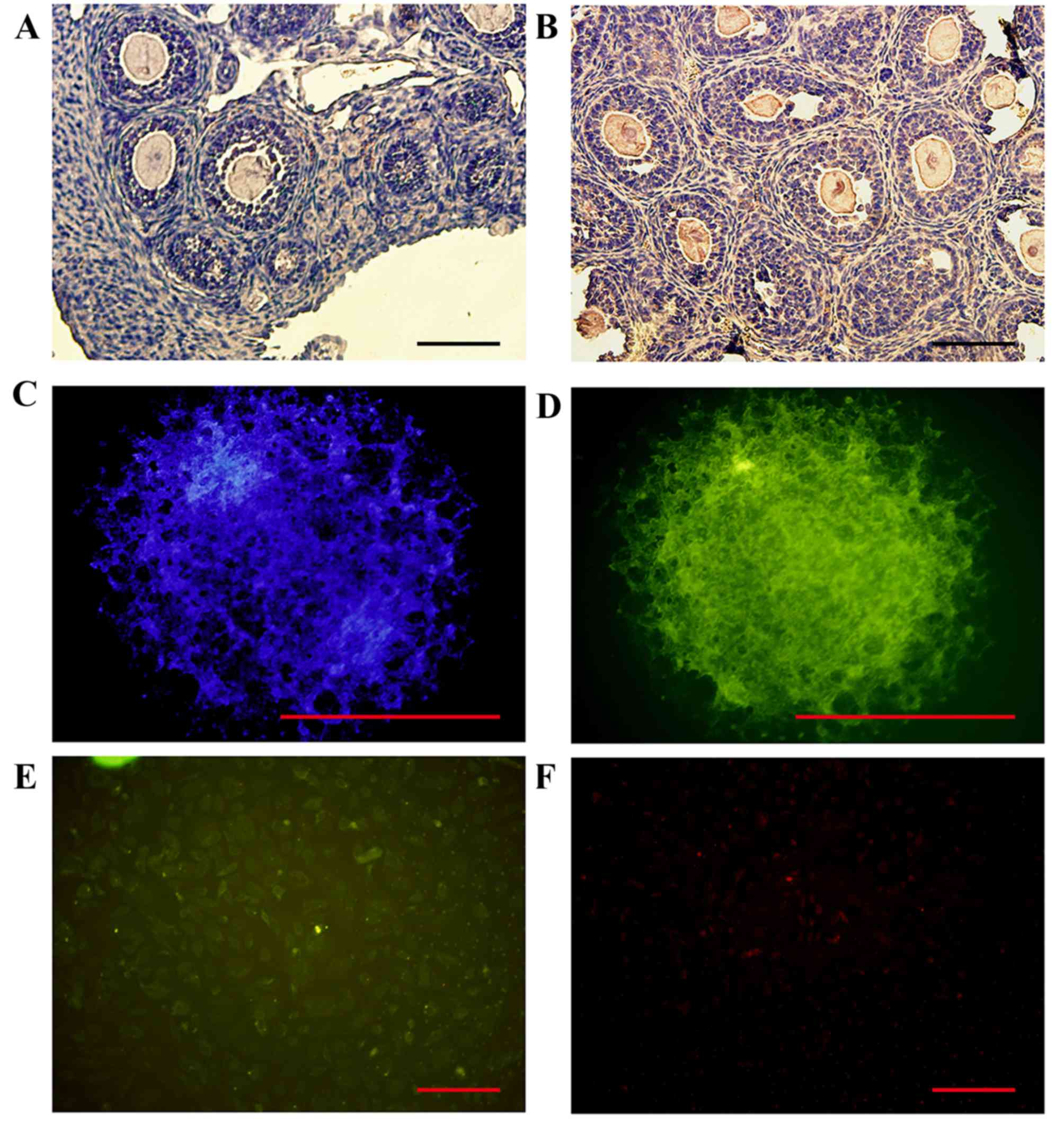
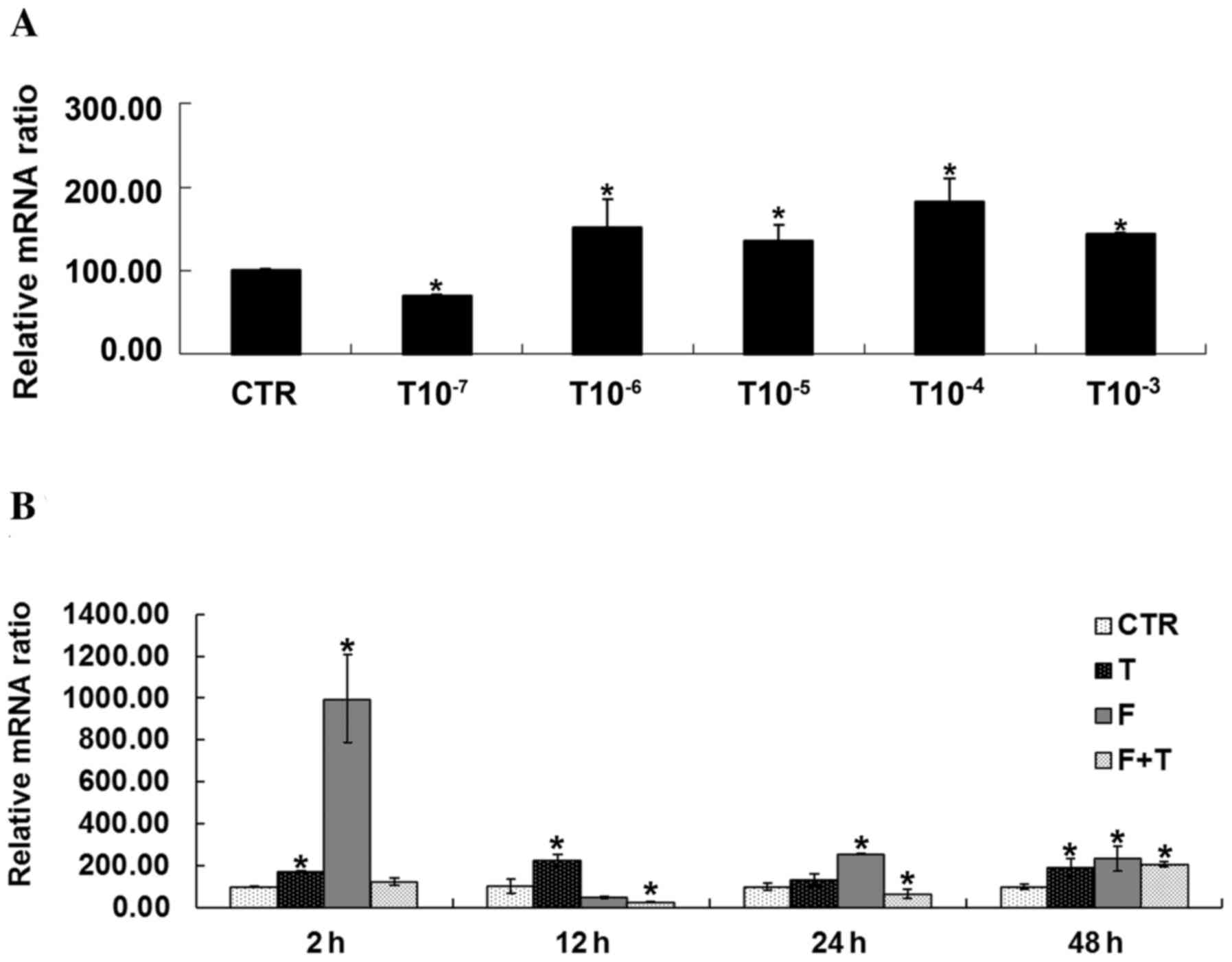
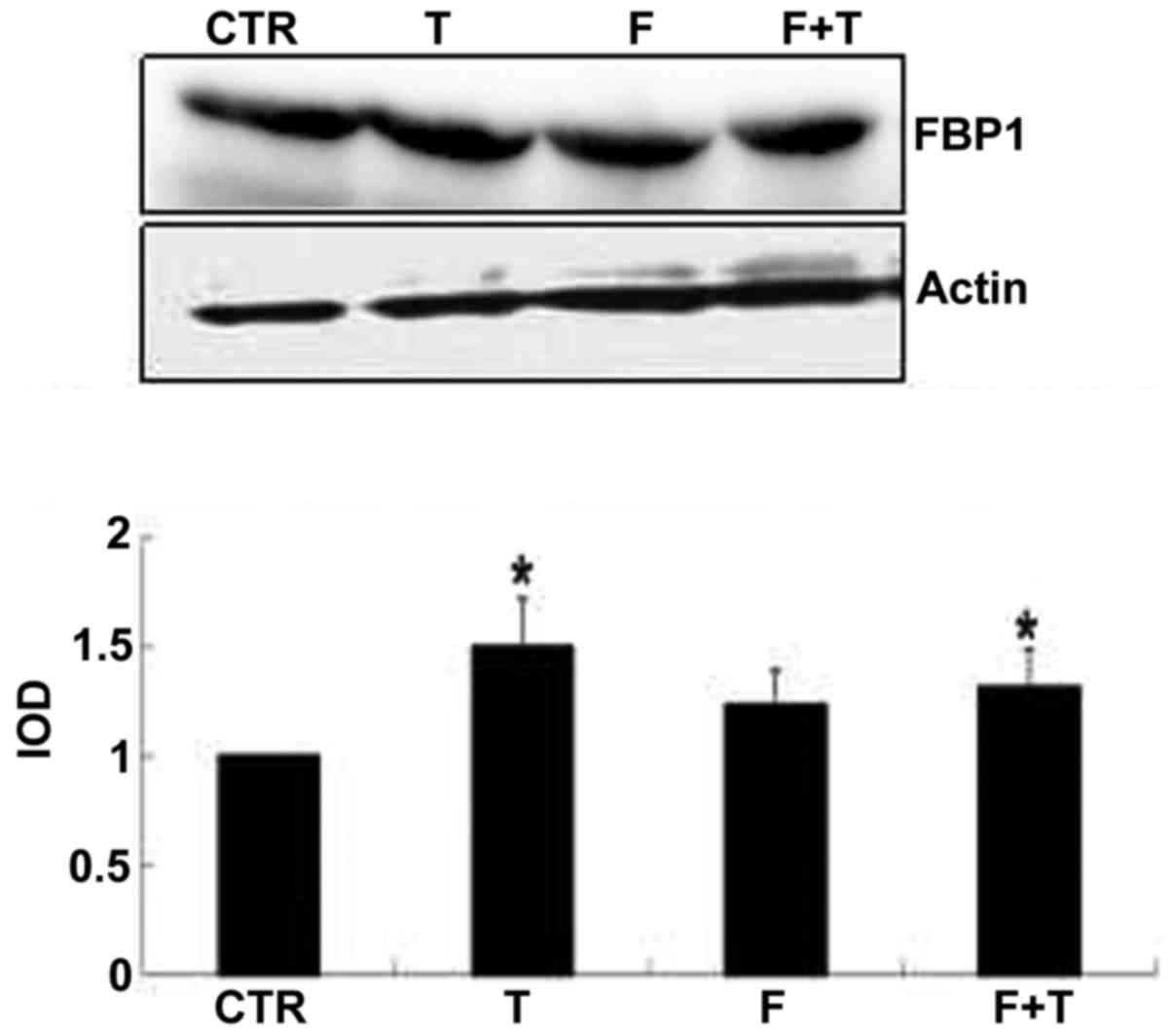
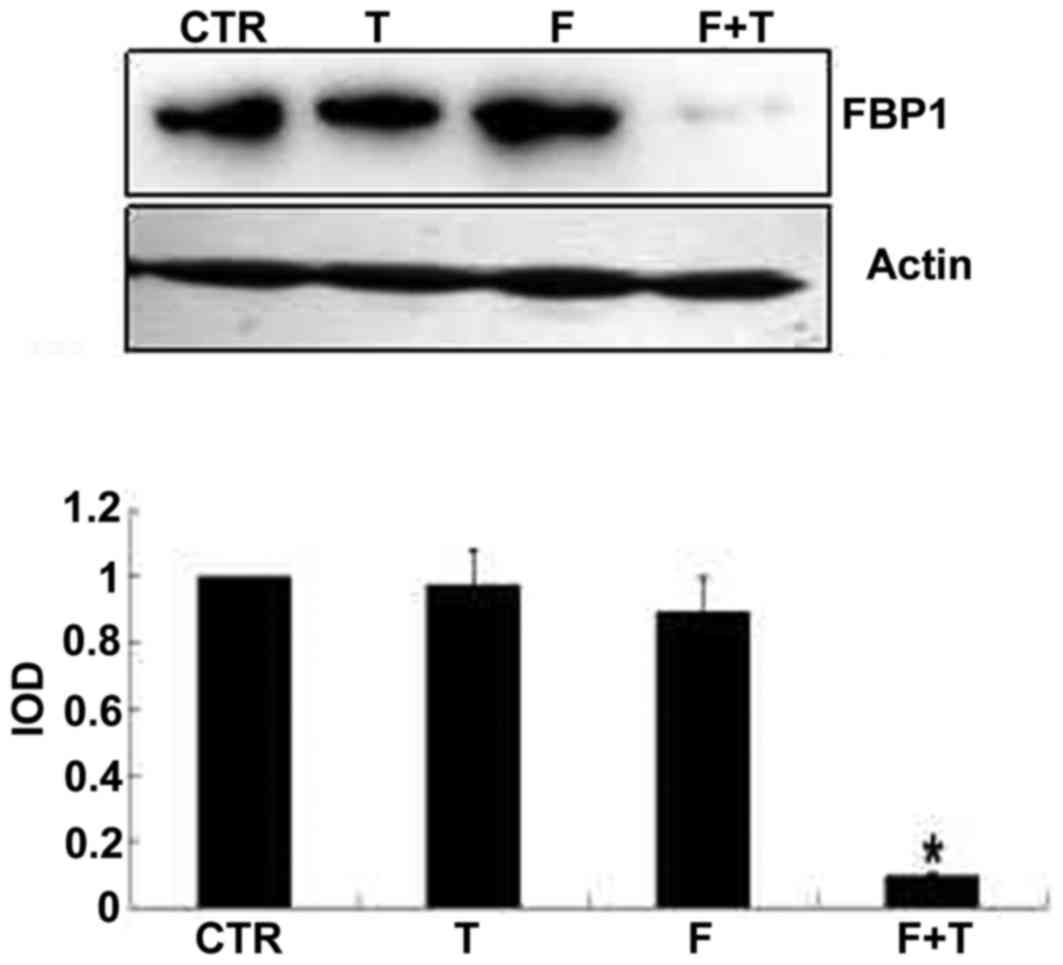
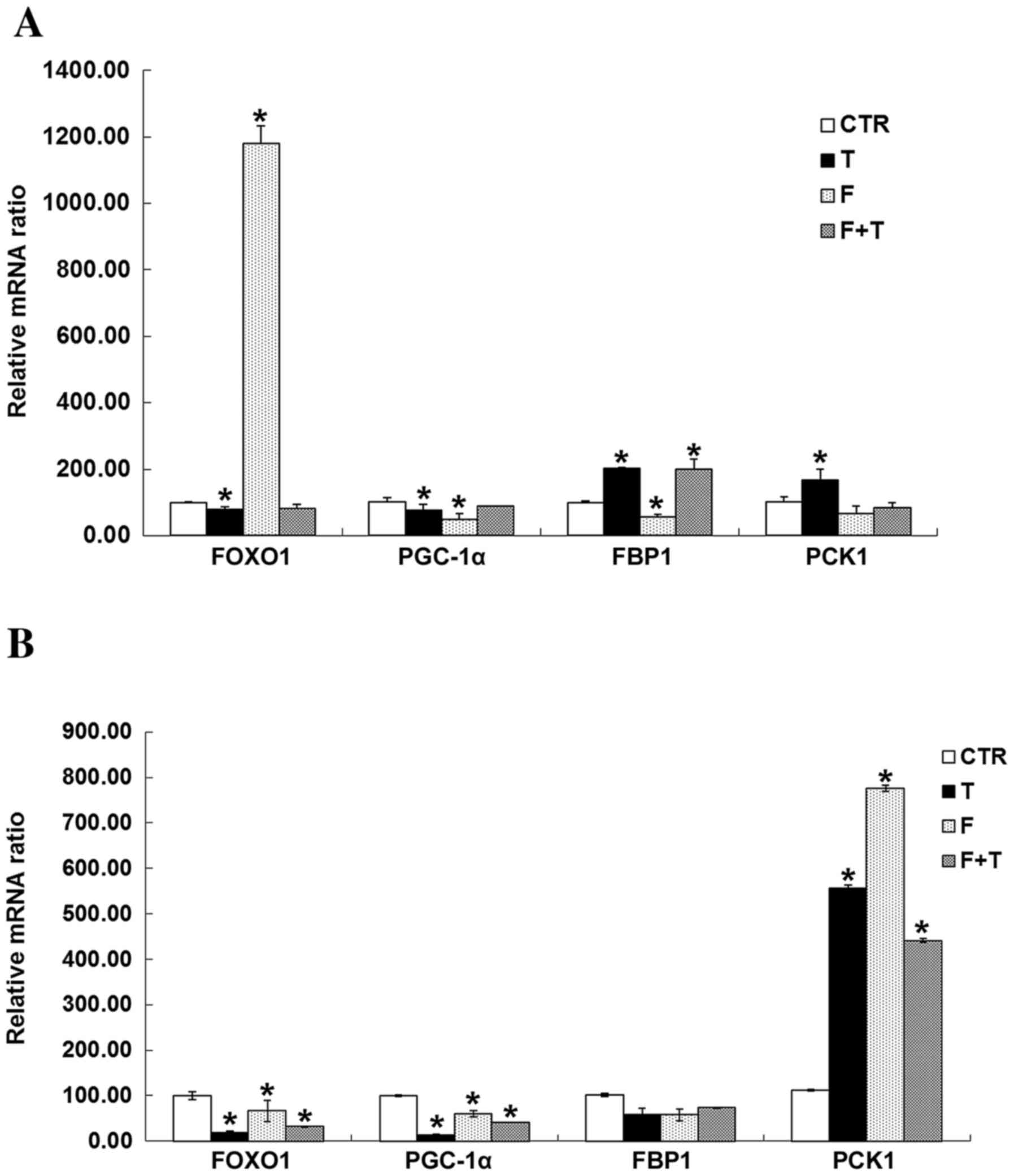
|
1
|
Chang C, Lee SO, Wang RS, Yeh S and Chang
TM: Androgen receptor (AR) physiological roles in male and female
reproductive systems: Lessons learned from AR-knockout mice lacking
AR in selective cells. Biol Reprod. 89:212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shea LD, Woodruff TK and Shikanov A:
Bioengineering the ovarian follicle microenvironment. Annu Rev
Biomed Eng. 16:29–52. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim JY, Xue K, Cao M, Wang Q, Liu JY,
Leader A, Han JY and Tsang BK: Chemerin suppresses ovarian
follicular development and its potential involvement in follicular
arrest in rats treated chronically with dihydrotestosterone.
Endocrinology. 154:2912–2923. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dumesic DA, Oberfield SE, Stener-Victorin
E, Marshall JC, Laven JS and Legro RS: Scientific statement on the
diagnostic criteria, epidemiology, pathophysiology, and molecular
genetics of polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocr Rev. 36:487–525.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McGee WK, Bishop CV, Bahar A, Pohl CR,
Chang RJ, Marshall JC, Pau FK, Stouffer RL and Cameron JL: Elevated
androgens during puberty in female rhesus monkeys lead to increased
neuronal drive to the reproductive axis: A possible component of
polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod. 27:531–540. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Usadi RS and Legro RS: Reproductive impact
of polycystic ovary syndrome. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes.
19:505–511. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shi Y, Zhao H, Shi Y, Cao Y, Yang D, Li Z,
Zhang B, Liang X, Li T, Chen J, et al: Genome-wide association
study identifies eight new risk loci for polycystic ovary syndrome.
Nat Genet. 44:1020–1025. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Makieva S, Saunders PT and Norman JE:
Androgens in pregnancy: Roles in parturition. Hum Reprod Update.
20:542–559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lebbe M and Woodruff TK: Involvement of
androgens in ovarian health and disease. Mol Hum Reprod.
19:828–837. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Connolly F, Rae MT, Späth K, Boswell L,
McNeilly AS and Duncan WC: In an ovine model of polycystic ovary
syndrome (PCOS) prenatal androgens suppress female fetal renal
gluconeogenesis. PLoS One. 10:e01321132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nicol LE, O'Brien TD, Dumesic DA, Grogan
T, Tarantal AF and Abbott DH: Abnormal infant islet morphology
precedes insulin resistance in PCOS-like monkeys. PLoS One.
9:e1065272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takagi D, Ben-Ari J, Nemet D, Zeharia A
and Eliakim A: Recurrent infantile hypoglycemia due to combined
fructose-1,6-diphosphatase deficiency and growth hormone
deficiency. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 26:761–763. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Drabovich AP, Pavlou MP, Dimitromanolakis
A and Diamandis EP: Quantitative analysis of energy metabolic
pathways in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by selected reaction
monitoring assay. Mol Cell Proteomics. 11:422–434. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thorn SR, Sekar SM, Lavezzi JR, O'Meara
MC, Brown LD, Hay WW Jr and Rozance PJ: A physiological increase in
insulin suppresses gluconeogenic gene activation in fetal sheep
with sustained hypoglycemia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp
Physiol. 303:R861–R869. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Romero S and Smitz J: Exposing cultured
mouse ovarian follicles under increased gonadotropin tonus to
aromatizable androgens influences the steroid balance and reduces
oocyte meiotic capacity. Endocrine. 38:243–253. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Roland AV, Nunemaker CS, Keller SR and
Moenter SM: Prenatal androgen exposure programs metabolic
dysfunction in female mice. J Endocrinol. 207:213–223. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang CP, Yang JL, Zhang J, Li L, Huang L,
Ji SY, Hu ZY, Gao F and Liu YX: Notch signaling is involved in
ovarian follicle development by regulating granulosa cell
proliferation. Endocrinology. 152:2437–2447. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Itami S, Yasuda K, Yoshida Y, Matsui C,
Hashiura S, Sakai A and Tamotsu S: Co-culturing of follicles with
interstitial cells in collagen gel reproduce follicular development
accompanied with theca cell layer formation. Reprod Biol
Endocrinol. 9:1592011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang JL, Zhang CP, Li L, Huang L, Ji SY,
Lu CL, Fan CH, Cai H, Ren Y, Hu ZY, et al: Testosterone induces
redistribution of forkhead box-3a and down-regulation of growth and
differentiation factor 9 messenger ribonucleic acid expression at
early stage of mouse folliculogenesis. Endocrinology. 151:774–782.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Forsgren KL and Young G: Stage-specific
effects of androgens and estradiol-17beta on the development of
late primary and early secondary ovarian follicles of coho salmon
(Oncorhynchus kisutch) in vitro. Biol Reprod. 87:642012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lenie S and Smitz J: Functional AR
signaling is evident in an in vitro mouse follicle culture bioassay
that encompasses most stages of folliculogenesis. Biol Reprod.
80:685–695. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expresison data using real-time quantitiative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang P, Tu B, Wang H, Cao Z, Tang M,
Zhang C, Gu B, Li Z, Wang L, Yang Y, et al: Tumor suppressor p53
cooperates with SIRT6 to regulate gluconeogenesis by promoting
FoxO1 nuclear exclusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:10684–10689.
2014; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Puigserver P, Rhee J, Donovan J, Walkey
CJ, Yoon JC, Oriente F, Kitamura Y, Altomonte J, Dong H, Accili D
and Spiegelman BM: Insulin-regulated hepatic gluconeogenesis
through FOXO1-PGC-1alpha interaction. Nature. 423:550–555. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Walters KA, Allan CM and Handelsman DJ:
Rodent models for human polycystic ovary syndrome. Biol Reprod.
86:1492012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li T, Wu K, You L, Xing X, Wang P, Cui L,
Liu H, Cui Y, Bian Y, Ning Y, et al: Common variant rs9939609 in
gene FTO confers risk to polycystic ovary syndrome. PLoS One.
8:e662502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen ZJ, Zhao H, He L, Shi Y, Qin Y, Shi
Y, Li Z, You L, Zhao J, Liu J, et al: Genome-wide association study
identifies susceptibility loci for polycystic ovary syndrome on
chromosome 2p16.3, 2p21 and 9q33.3. Nat Genet. 43:55–59. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang HY, Guo CX, Zhu FF, Qu PP, Lin WJ
and Xiong J: Clinical characteristics, metabolic features, and
phenotype of Chinese women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A
large-scale case-control study. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 287:525–531.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Z: Polycystic ovary syndrome etiology
and clinical research. J Reprod Med. 16:2322007.
|
|
30
|
Kahsar-Miller MD, Nixon C, Boots LR, Go RC
and Azziz R: Prevalence of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in
first-degree relatives of patients with PCOS. Fertil Steril.
75:53–58. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Connolly F, Rae MT, Späth K, Boswell L,
McNeilly AS and Duncan WC: In an ovine model of polycystic ovary
syndrome (PCOS) prenatal androgens suppress female fetal renal
gluconeogenesis. PLoS One. 10:e01321132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dupont J and Scaramuzzi RJ: Insulin
signalling and glucose transport in the ovary and ovarian function
during theovarian cycle. Biochem J. 473:1483–1501. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|