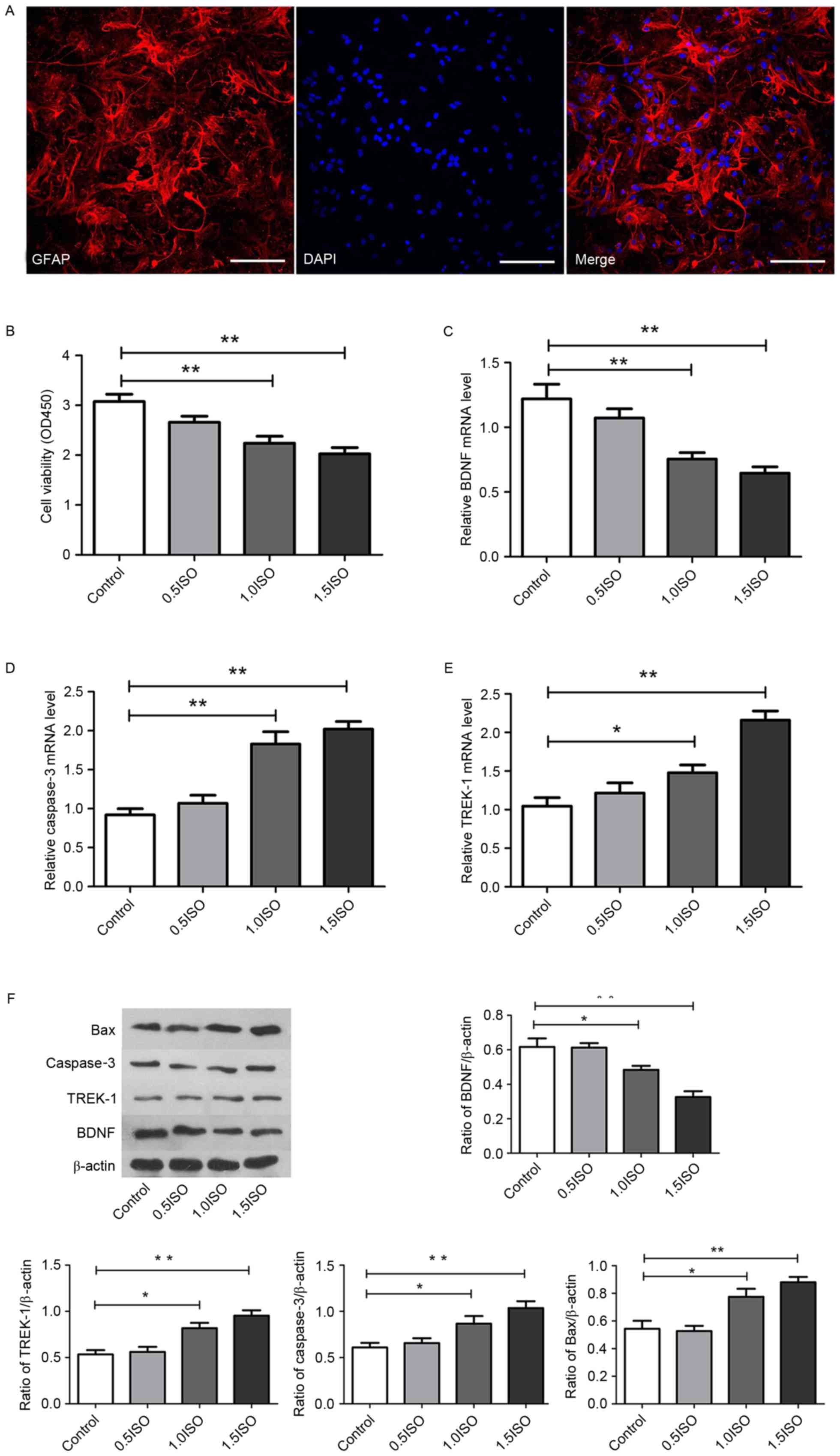
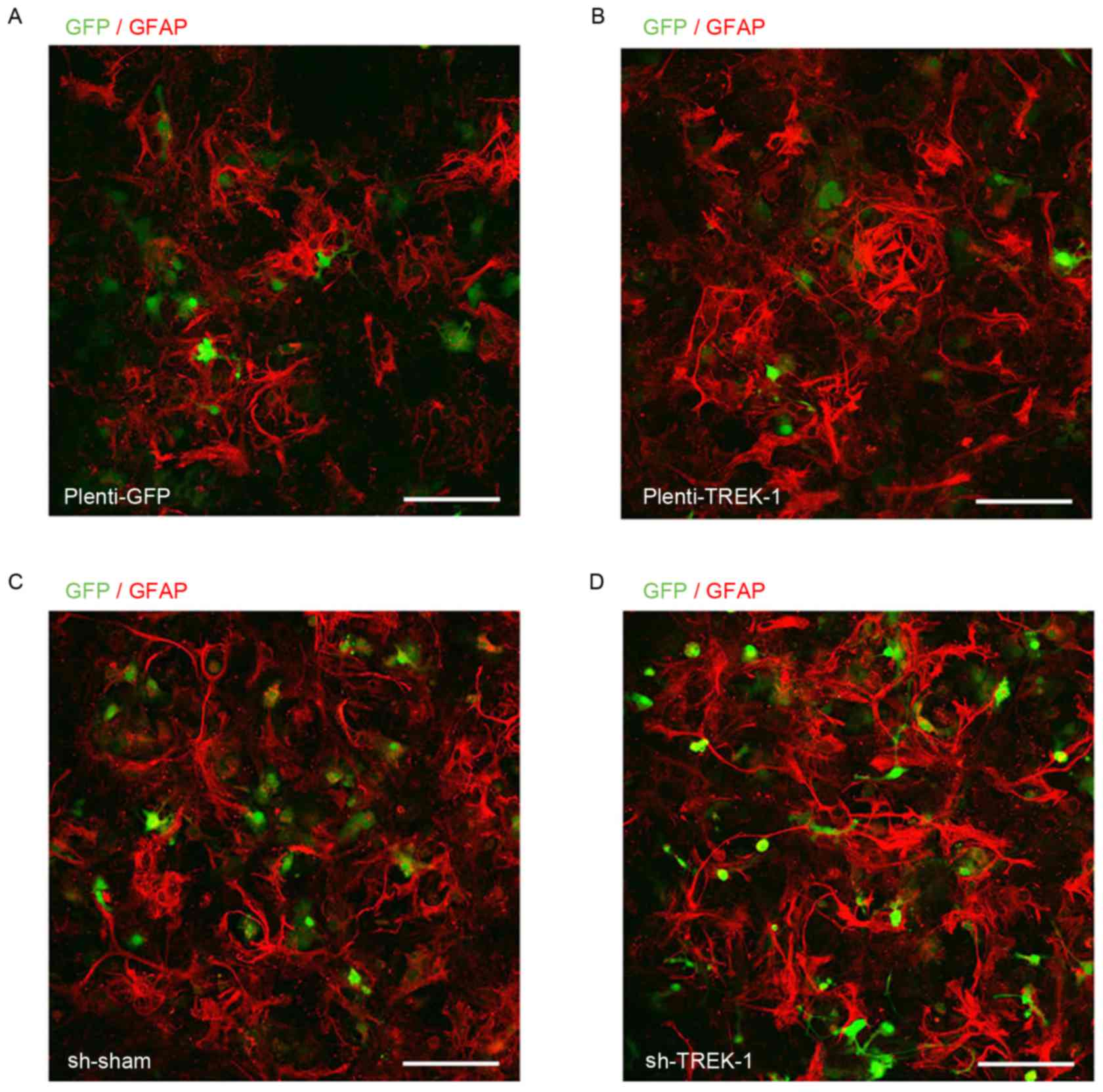
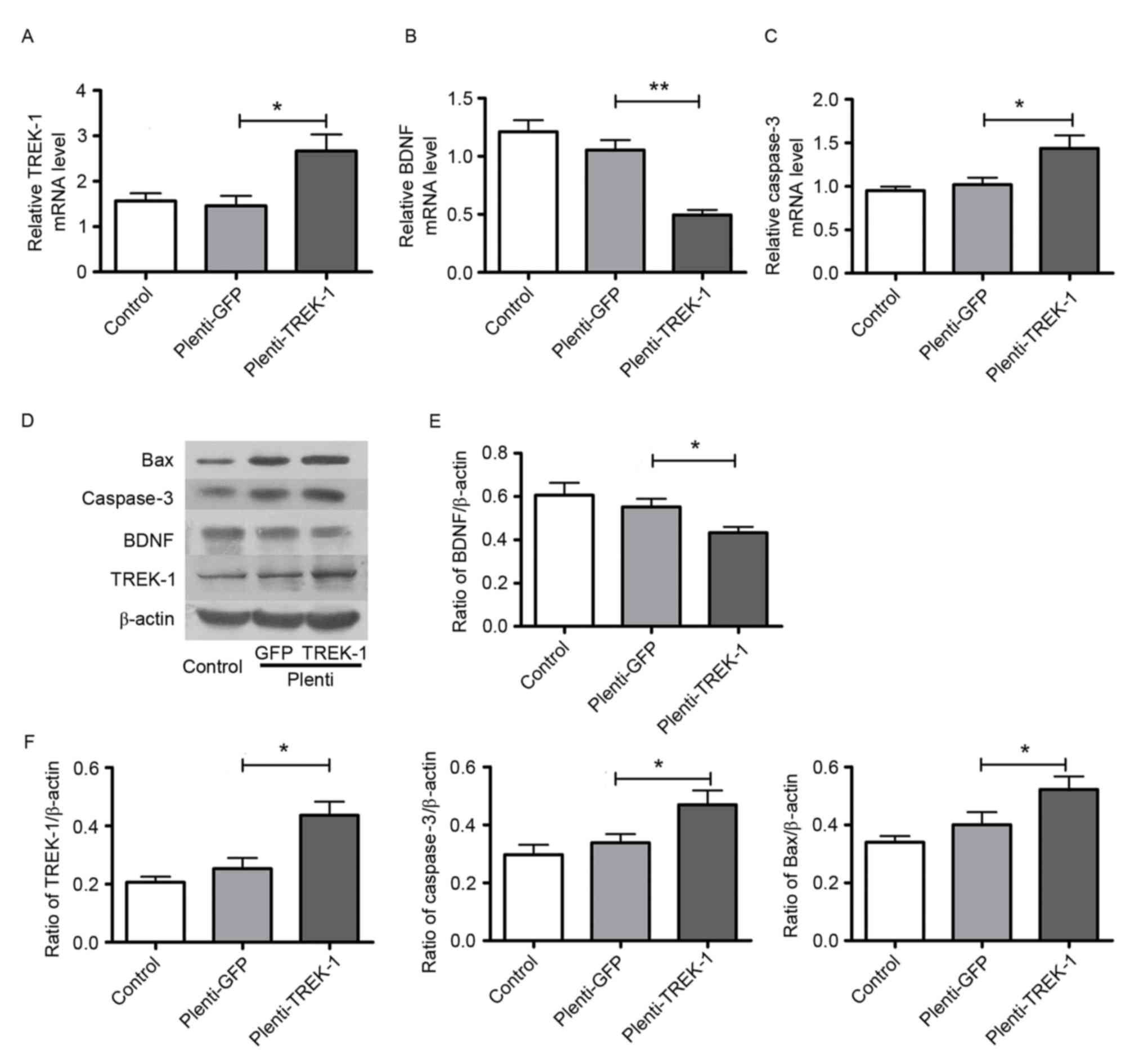
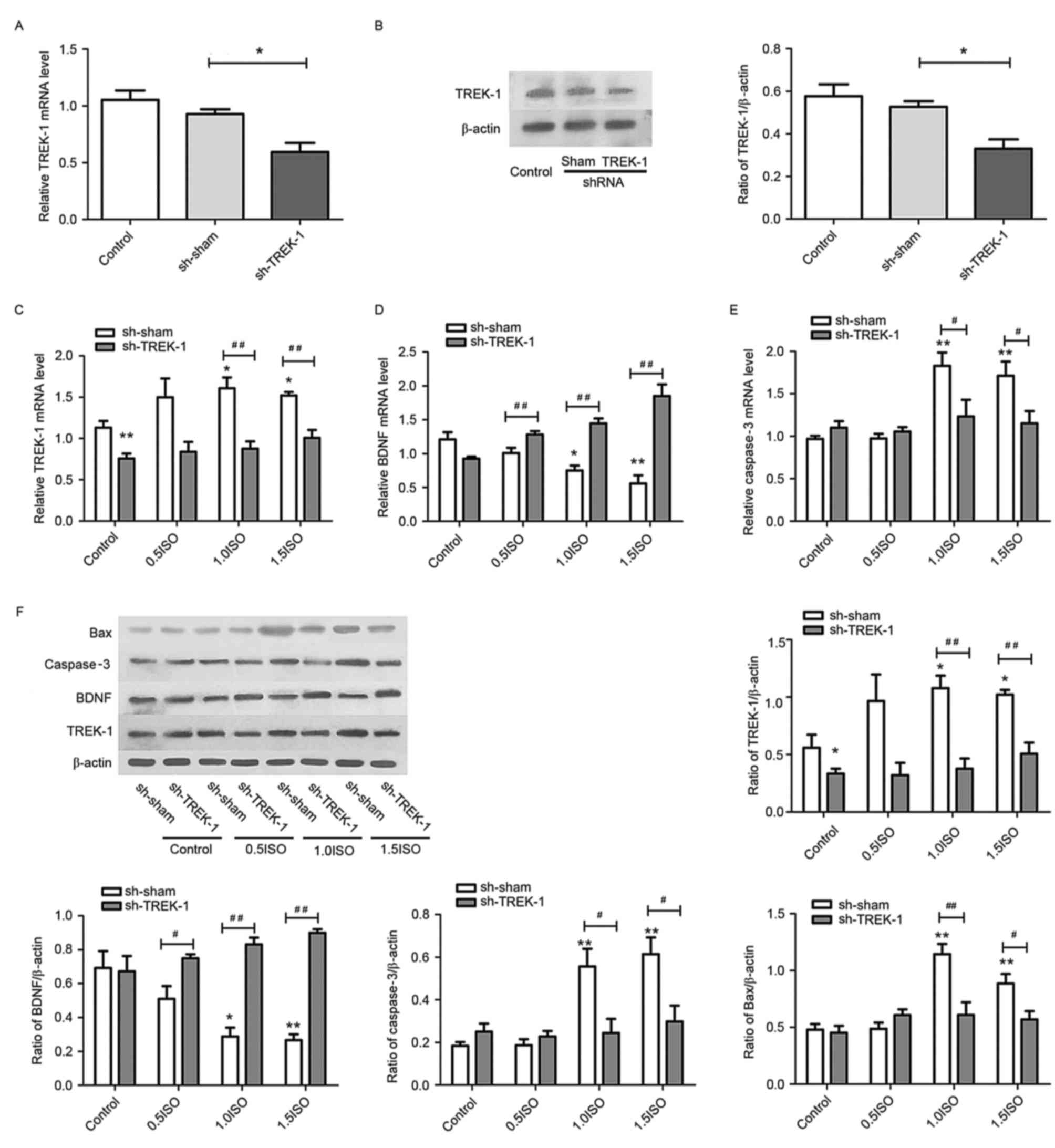
|
1
|
Sall JW, Stratmann G, Leong J, McKleroy W,
Mason D, Shenoy S, Pleasure SJ and Bickler PE: Isoflurane inhibits
growth but does not cause cell death in hippocampal neural
precursor cells grown in culture. Anesthesiology. 110:826–833.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ballesteros KA, Sikorski A, Orfila JE and
Martinez JL Jr: Effects of inhaled anesthetic isoflurane on
long-term potentiation of CA3 pyramidal cell afferents in vivo. Int
J Gen Med. 5:935–942. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang B, Tian M, Zhen Y, Yue Y, Sherman J,
Zheng H, Li S, Tanzi RE, Marcantonio ER and Xie Z: The effects of
isoflurane and desflurane on cognitive function in humans. Anesth
Analg. 114:410–415. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang F, Zhu ZQ, Liu DX, Zhang C, Gong QH
and Zhu YH: Emulsified isoflurane anesthesia decreases
brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression and induces cognitive
dysfunction in adult rats. Exp Ther Med. 8:471–477. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu C, Gao J, Karlsson N, Li Q, Zhang Y,
Huang Z, Li H, Kuhn HG and Blomgren K: Isoflurane anesthesia
induced persistent, progressive memory impairment, caused a loss of
neural stem cells, and reduced neurogenesis in young, but not
adult, rodents. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 30:1017–1030. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mellon RD, Simone AF and Rappaport BA: Use
of anesthetic agents in neonates and young children. Anesth Analg.
104:509–520. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shetty AK: Hippocampal injury-induced
cognitive and mood dysfunction, altered neurogenesis and epilepsy:
Can early neural stem cell grafting intervention provide
protection. Epilepsy Behav. 38:117–124. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao N, Zhong C, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Gong N,
Zhou G, Xu T and Hong Z: Impaired hippocampal neurogenesis is
involved in cognitive dysfunction induced by thiamine deficiency at
early pre-pathological lesion stage. Neurobiol Dis. 29:176–185.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kuhn HG, Dickinson-Anson H and Gage FH:
Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: Age-related
decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. J Neurosci.
16:2027–2033. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Donovan MH, Yazdani U, Norris RD, Games D,
German DC and Eisch AJ: Decreased adult hippocampal neurogenesis in
the PDAPP mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Comp Neurol.
495:70–83. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rubino T, Realini N, Braida D, Guidi S,
Capurro V, Viganò D, Guidali C, Pinter M, Sala M, Bartesaghi R and
Parolaro D: Changes in hippocampal morphology and neuroplasticity
induced by adolescent THC treatment are associated with cognitive
impairment in adulthood. Hippocampus. 19:763–772. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim TW, Choi HH and Chung YR: Treadmill
exercise alleviates impairment of cognitive function by enhancing
hippocampal neuroplasticity in the high-fat diet-induced obese
mice. J Exerc Rehabil. 12:156–162. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Secchiero P, Melloni E, di Iasio MG,
Tiribelli M, Rimondi E, Corallini F, Gattei V and Zauli G: Nutlin-3
up-regulates the expression of Notch1 in both myeloid and lymphoid
leukemic cells, as part of a negative feedback anti-apoptotic
mechanism. Blood. 113:4300–4308. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schitine C, Nogaroli L, Costa MR and
Hedin-Pereira C: Astrocyte heterogeneity in the brain: From
development to disease. Front Cell Neurosci. 9:762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Barker AJ and Ullian EM: Astrocytes and
synaptic plasticity. Neuroscientist. 16:40–50. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jones OD: Astrocyte-mediated
metaplasticity in the hippocampus: Help or hindrance. Neuroscience.
309:113–124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pabst M, Braganza O, Dannenberg H, Hu W,
Pothmann L, Rosen J, Mody I, van Loo K, Deisseroth K, Becker AJ, et
al: Astrocyte intermediaries of septal cholinergic modulation in
the hippocampus. Neuron. 90:853–865. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin D and Zuo Z: Isoflurane induces
hippocampal cell injury and cognitive impairments in adult rats.
Neuropharmacology. 61:1354–1359. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nie H, Peng Z, Lao N, Dong H and Xiong L:
Effects of sevoflurane on self-renewal capacity and differentiation
of cultured neural stem cells. Neurochem Res. 38:1758–1767. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheung SW, Nagarajan SS, Bedenbaugh PH,
Schreiner CE, Wang X and Wong A: Auditory cortical neuron response
differences under isoflurane versus pentobarbital anesthesia. Hear
Res. 156:115–127. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Noel J, Sandoz G and Lesage F: Molecular
regulations governing TREK and TRAAK channel functions. Channels.
5:402–409. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ehling P, Cerina M, Budde T, Meuth SG and
Bittner S: The CNS under pathophysiologic attack-examining the role
of K2p channels. Pflugers Arch. 467:959–972. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu L, Wang W, Peng Y, Li J, Wang L and
Wang X: Electrophysiology and pharmacology of tandem domain
potassium channel TREK-1 related BDNF synthesis in rat astrocytes.
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 387:303–312. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Patel AJ, Honoré E, Lesage F, Fink M,
Romey G and Lazdunski M: Inhalational anesthetics activate
two-pore-domain background K+ channels. Nat Neurosci. 2:422–426.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang K and Kong X: Isoflurane
preconditioning induces neuroprotection by up-regulation of TREK1
in a rat model of spinal cord ischemic injury. Biomol Ther (Seoul).
24:495–500. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yin X, Su B, Zhang H, Song W, Wu H, Chen
X, Zhang X, Dong H and Xiong L: TREK1 activation mediates spinal
cord ischemic tolerance induced by isoflurane preconditioning in
rats. Neurosci Lett. 515:115–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ye D, Li Y, Zhang X, Guo F, Geng L, Zhang
Q and Zhang Z: TREK1 channel blockade induces an
antidepressant-like response synergizing with 5-HT1A receptor
signaling. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 25:2426–2436. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Olsen ML, Khakh BS, Skatchkov SN, Zhou M,
Lee CJ and Rouach N: New insights on astrocyte ion channels:
Critical for homeostasis and neuron-glia signaling. J Neurosci.
35:13827–13835. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
O'Callaghan EL, Bassi JK, Porrello ER,
Delbridge LM, Thomas WG and Allen AM: Regulation of angiotensinogen
by angiotensin II in mouse primary astrocyte cultures. J Neurochem.
119:18–26. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Panickar KS, Jayakumar AR, Rao KV Rama and
Norenberg MD: Downregulation of the 18-kDa trans-locator protein:
Effects on the ammonia-induced mitochondrial permeability
transition and cell swelling in cultured astrocytes. Glia.
55:1720–1727. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee J, Kim MS, Park C, Jung EB, Choi DH,
Kim TY, Moon SK and Park R: Morphine prevents glutamate-induced
death of primary rat neonatal astrocytes through modulation of
intracellular redox. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 26:17–28. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang H, Xu Z, Feng C, Wang Y, Jia X, Wu A
and Yue Y: Changes of learning and memory in aged rats after
isoflurane inhalational anaesthesia correlated with hippocampal
acetylcholine level. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 31:e61–e66. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu J, Wang P, Zhang X, Zhang W and Gu G:
Effects of different concentration and duration time of isoflurane
on acute and long-term neurocognitive function of young adult
C57BL/6 mouse. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:5828–5836. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Uhrig L, Dehaene S and Jarraya B: Cerebral
mechanisms of general anesthesia. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 33:72–82.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vlisides P and Xie Z: Neurotoxicity of
general anesthetics: An update. Curr Pharm Des. 18:6232–6240. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
DiMaggio C, Sun LS, Ing C and Li G:
Pediatric anesthesia and neurodevelopmental impairments: A Bayesian
meta-analysis. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 24:376–381. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Hartman RE, Izumi Y,
Benshoff ND, Dikranian K, Zorumski CF, Olney JW and Wozniak DF:
Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread
neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent
learning deficits. J Neurosci. 23:876–882. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Brambrink AM, Evers AS, Avidan MS, Farber
NB, Smith DJ, Zhang X, Dissen GA, Creeley CE and Olney JW:
Isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis in the neonatal rhesus macaque
brain. Anesthesiology. 112:834–841. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zou X, Liu F, Zhang X, Patterson TA,
Callicott R, Liu S, Hanig JP, Paule MG, Slikker W Jr and Wang C:
Inhalation anesthetic-induced neuronal damage in the developing
rhesus monkey. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 33:592–597. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang SQ, Fang F, Xue ZG, Cang J and Zhang
XG: Neonatal sevoflurane anesthesia induces long-term memory
impairment and decreases hippocampal PSD-95 expression without
neuronal loss. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 17:941–950.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mintz CD, Barrett KM, Smith SC, Benson DL
and Harrison NL: Anesthetics interfere with axon guidance in
developing mouse neocortical neurons in vitro via a γ-aminobutyric
acid type A receptor mechanism. Anesthesiology. 118:825–833. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mintz CD, Smith SC, Barrett KM and Benson
DL: Anesthetics interfere with the polarization of developing
cortical neurons. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 24:368–375. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Culley DJ, Boyd JD, Palanisamy A, Xie Z,
Kojima K, Vacanti CA, Tanzi RE and Crosby G: Isoflurane decreases
self-renewal capacity of rat cultured neural stem cells.
Anesthesiology. 115:754–763. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Allen NJ, Bennett ML, Foo LC, Wang GX,
Chakraborty C, Smith SJ and Barres BA: Astrocyte glypicans 4 and 6
promote formation of excitatory synapses via GluA1 AMPA receptors.
Nature. 486:410–414. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kucukdereli H, Allen NJ, Lee AT, Feng A,
Ozlu MI, Conatser LM, Chakraborty C, Workman G, Weaver M, Sage EH,
et al: Control of excitatory CNS synaptogenesis by
astrocyte-secreted proteins Hevin and SPARC. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 108:E440–E449. 2011; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Clarke LE and Barres BA: Emerging roles of
astrocytes in neural circuit development. Nat Rev Neurosci.
14:311–321. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hong S, Xin Y, HaiQin W, GuiLian Z, Ru Z,
ShuQin Z, HuQing W, Li Y and Yun D: The PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone
prevents cognitive impairment by inhibiting astrocyte activation
and oxidative stress following pilocarpine-induced status
epilepticus. Neurol Sci. 33:559–566. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Thrane AS, Thrane V Rangroo, Zeppenfeld D,
Lou N, Xu Q, Nagelhus EA and Nedergaard M: General anesthesia
selectively disrupts astrocyte calcium signaling in the awake mouse
cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:18974–18979. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Creed MS, Sun XY and Rona GG: Astrocytes
protect against isoflurane neurotoxicity by buffering
pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Anesthesiology. 123:810–819.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ryu YK, Khan S, Smith SC and Mintz CD:
Isoflurane impairs the capacity of astrocytes to support neuronal
development in a mouse dissociated co-culture model. J Neurosurg
Anesthesiol. 26:363–368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yu W, Zhu H, Wang Y, Li G, Wang L and Li
H: Reactive Transformation and Increased BDNF Signaling by
Hippocampal Astrocytes in Response to MK-801. PLoS One.
10:01456512015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Rocha SM, Cristovão AC, Campos FL, Fonseca
CP and Baltazar G: Astrocyte-derived GDNF is a potent inhibitor of
microglial activation. Neurobiol Dis. 47:407–415. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hong Y, Zhao T, Li XJ and Li S: Mutant
Huntingtin impairs BDNF release from astrocytes by disrupting
conversion of Rab3a-GTP into Rab3a-GDP. J Neurosci. 36:8790–8801.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhang XY, Chen DC, Xiu MH, Haile CN, Luo
X, Xu K, Zhang HP, Zuo L, Zhang Z, Zhang X, et al: Cognitive and
serum BDNF correlates of BDNF Val66Met gene polymorphism in
patients with schizophrenia and normal controls. Hum Genet.
131:1187–1195. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kuczewski N, Porcher C and Gaiarsa JL:
Activity-dependent dendritic secretion of brain-derived
neurotrophic factor modulates synaptic plasticity. Eur J Neurosci.
32:1239–1244. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Siuda J, Patalong-Ogiewa M, Żmuda W,
Targosz-Gajniak M, Niewiadomska E, Matuszek I,
Jędrzejowska-Szypułka H and Rudzińska-Bar M: Cognitive impairment
and BDNF serum levels. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 51:24–32.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dixon KJ and Sherrard RM: Brain-derived
neurotrophic factor induces post lesion trans-commissural growth of
olivary axons that develop normal climbing fibers on mature
Purkinje cells. Exp Neurol. 202:44–56. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Willson ML, McElnea C, Mariani J, Lohof AM
and Sherrard RM: BDNF increases homotypic olivocerebellar
reinnervation and associated fine motor and cognitive skill. Brain.
131:1099–1112. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sun H, Zhang J, Zhang L, Liu H, Zhu H and
Yang Y: Environmental enrichment influences BDNF and NR1 levels in
the hippocampus and restores cognitive impairment in chronic
cerebral hypo-perfused rats. Curr Neurovasc Res. 7:268–280. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wu J, Zhang M, Li H, Sun X, Hao S, Ji M,
Yang J and Li K: BDNF pathway is involved in the protective effects
of SS-31 on isoflurane-induced cognitive deficits in aging mice.
Behav Brain Res. 305:115–121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lu LX, Yon JH, Carter LB and
Jevtovic-Todorovic V: General anesthesia activates BDNF-dependent
neuro-apoptosis in the developing rat brain. Apoptosis.
11:1603–1615. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Xu H, Gao HL, Zheng W, Xin N, Chi ZH, Bai
SL and Wang ZY: Lactational zinc deficiency-induced hippocampal
neuronal apoptosis by a BDNF-independent TrkB signaling pathway.
Hippocampus. 21:495–501. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ji M, Dong L, Jia M, Liu W, Zhang M, Ju L
and Yang J, Xie Z and Yang J: Epigenetic enhancement of
brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling pathway improves
cognitive impairments induced by isoflurane exposure in aged rats.
Mol Neurobiol. 50:937–944. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wang WY, Luo Y, Jia LJ, Hu SF, Lou XK,
Shen SL, Lu H, Zhang HH, Yang R, Wang H, et al: Inhibition of
aberrant cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity attenuates isoflurane
neurotoxicity in the developing brain. Neuropharmacology. 77:90–99.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Campos FL, Cristovão AC, Rocha SM, Fonseca
CP and Baltazar G: GDNF contributes to oestrogen-mediated
protection of midbrain dopaminergic neurones. J Neuroendocrinol.
24:1386–1397. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cho HJ, Sung YH, Lee SH, Chung JY, Kang JM
and Yi JW: Isoflurane induces transient anterograde amnesia through
suppression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampus. J
Korean Neurosurg Soc. 53:139–144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Tyler WJ, Alonso M, Bramham CR and
Pozzo-Miller LD: From acquisition to consolidation: On the role of
brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in
hippocampal-dependent learning. Learn Mem. 9:224–237. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lesage F, Terrenoire C, Romey G and
Lazdunski M: Human TREK2, a 2P domain mechano-sensitive K+ channel
with multiple regulations by polyunsaturated fatty acids,
lysophospholipids and Gs, Gi, and Gq protein-coupled receptors. J
Biol Chem. 275:28398–28405. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Heurteaux C, Guy N, Laigle C, Blondeau N,
Duprat F, Mazzuca M, Lang-Lazdunski L, Widmann C, Zanzouri M, Romey
G and Lazdunski M: TREK-1, a K+ channel involved in neuroprotection
and general anesthesia. EMBO J. 23:2684–2695. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Moha Ou Maati H, Veyssiere J, Labbal F,
Coppola T, Gandin C, Widmann C, Mazella J, Heurteaux C and Borsotto
M: Spadin as a new antidepressant: Absence of TREK-1-related side
effects. Neuropharmacology. 62:278–288. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Borsotto M, Veyssiere J, Moha Ou Maati H,
Devader C, Mazella J and Heurteaux C: Targeting two-pore domain
K(+) channels TREK-1 and TASK-3 for the treatment of depression: A
new therapeutic concept. Br J Pharmacol. 172:771–784. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Mazella J, Pétrault O, Lucas G, Deval E,
Béraud-Dufour S, Gandin C, El-Yacoubi M, Widmann C, Guyon A, Chevet
E, et al: Spadin, a sortilin-derived peptide, targeting rodent
TREK-1 channels: A new concept in the antidepressant drug design.
PLoS Biol. 8:10003552010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Zhang HP, Sun YY, Chen XM, Yuan LB, Su BX,
Ma R, Zhao RN, Dong HL and Xiong L: The neuroprotective effects of
isoflurane preconditioning in a murine transient global cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion model: The role of the Notch signaling
pathway. Neuromolecular Med. 16:191–204. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yin J, Li H, Feng C and Zuo Z: Inhibition
of brain ischemia-caused notch activation in microglia may
contribute to isoflurane post-conditioning-induced neuroprotection
in male rats. CNS & neurological disorders drug targets.
13:718–732. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|