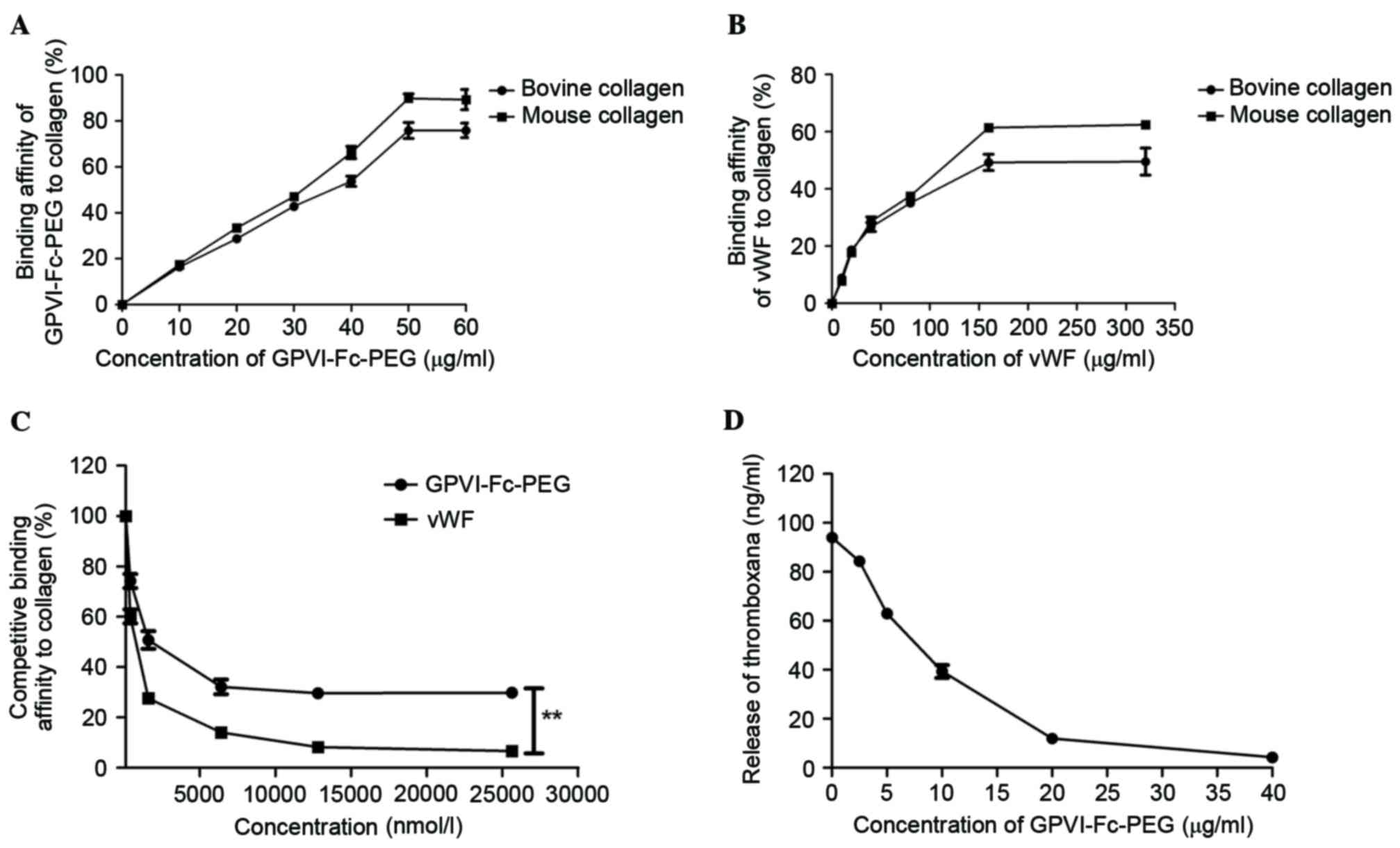
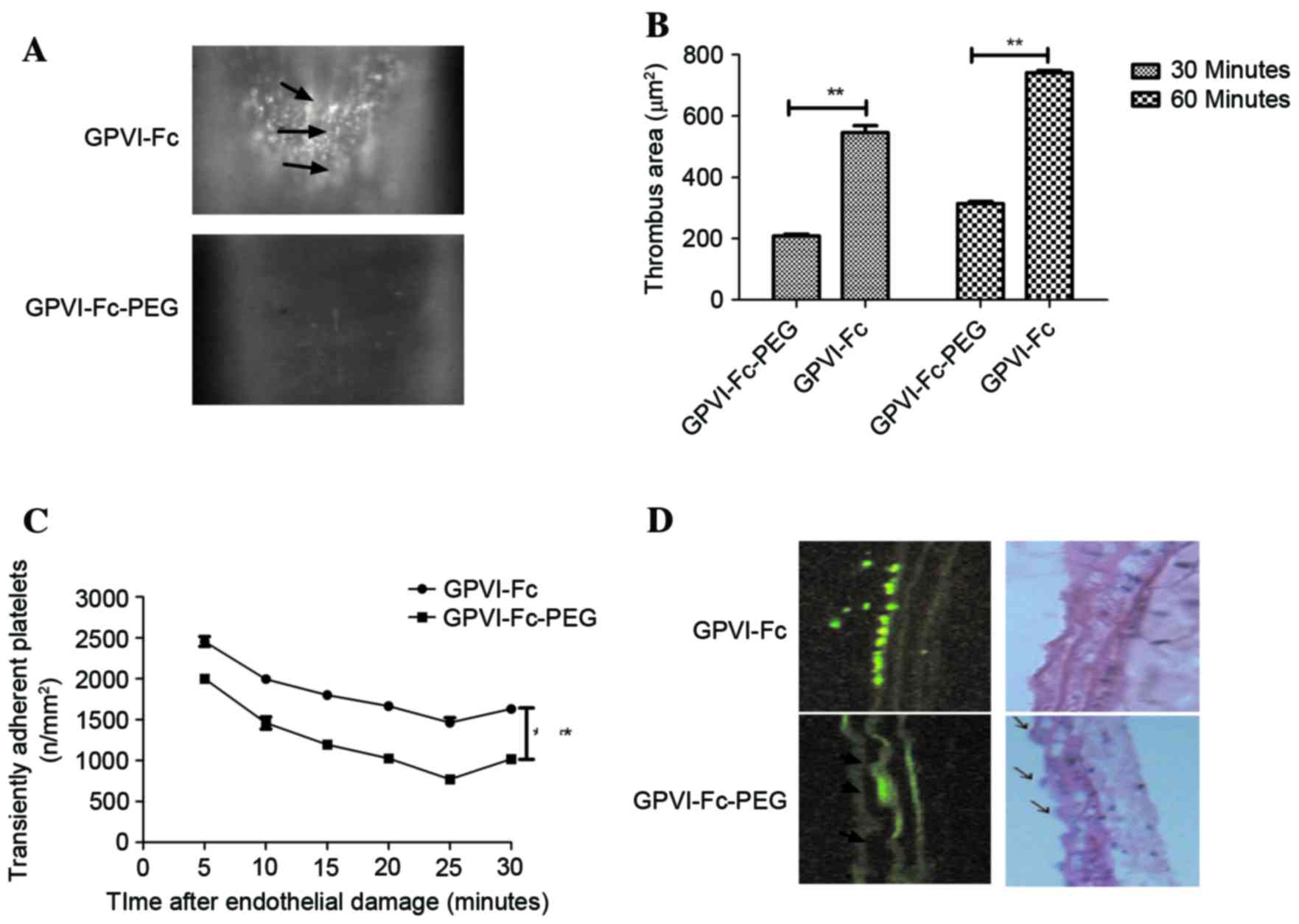
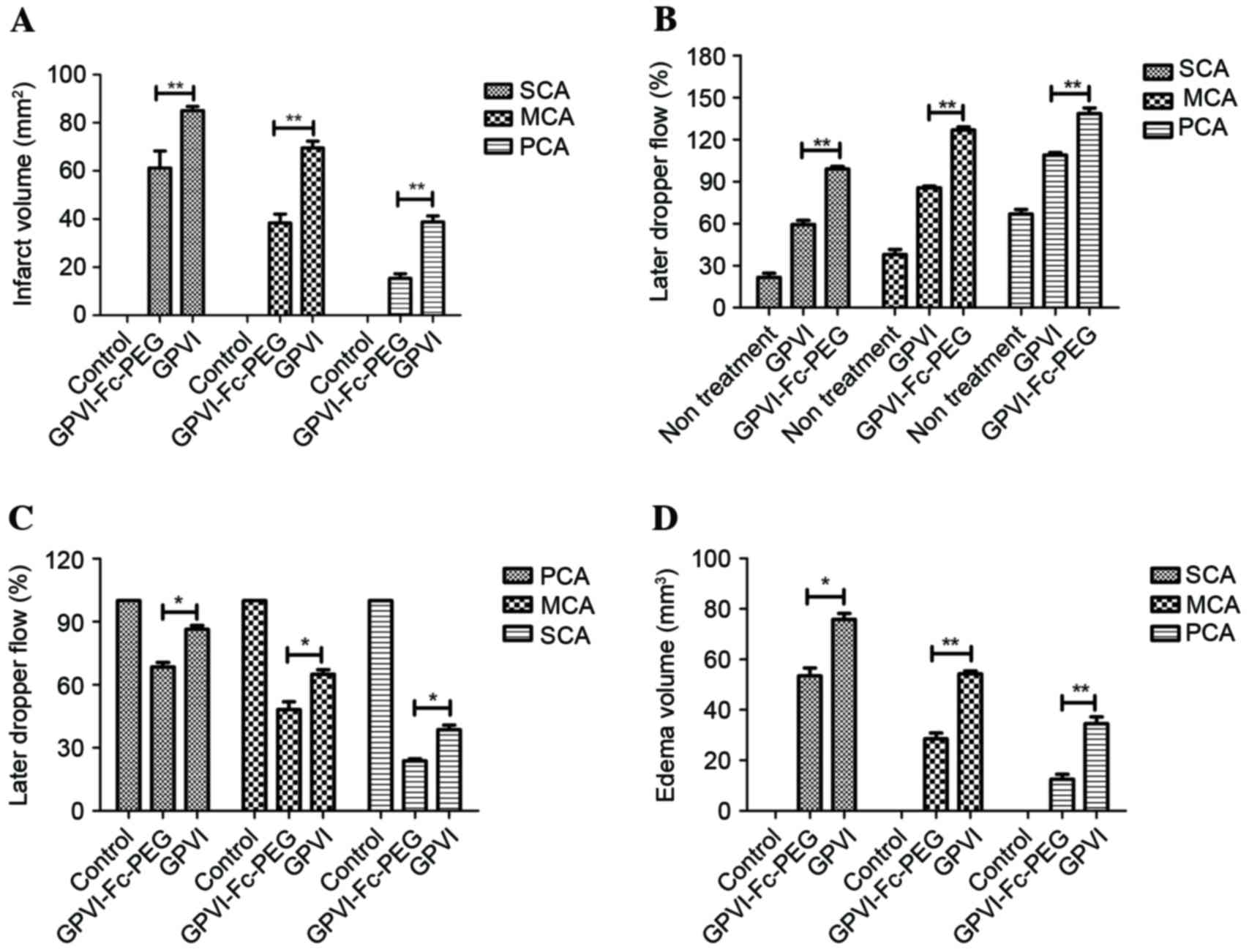
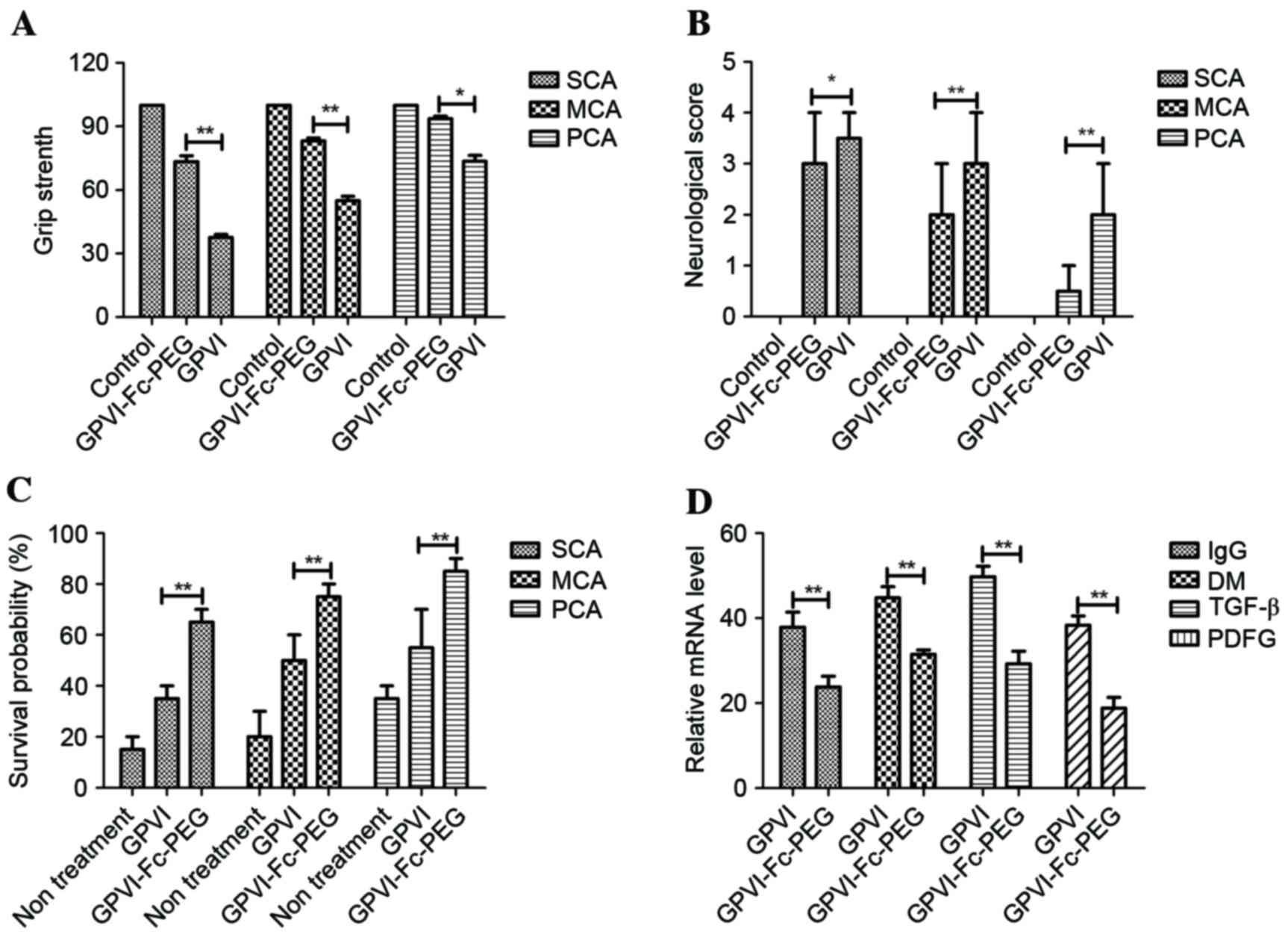
|
1
|
Kanamaru K, Suzuki H and Taki W: Cerebral
infarction after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir
Suppl. 121:167–172. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee DH, Na DG, Ihn YK, Kim DJ, Kim EY, Kim
YS, Lim SM, Roh HG and Sohn CH: Stroke Study Group: Review of the
current status of intra-arterial thrombolysis for treating acute
cerebral infarction: A retrospective analysis of the data from
multiple centers in Korea. Korean J Radiol. 8:87–93. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nakagomi T, Nakano-Doi A, Narita A and
Matsuyama T: Concise review: Are stimulated somatic cells truly
reprogrammed into an ES/iPS-like pluripotent state? Better
understanding by ischemia-induced multipotent stem cells in a mouse
model of cerebral infarction. Stem Cells Int. 2015:6306932015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang W, Zhao D, Wu G, Liu J, Liu S, Qin L
and Wu Z: Trend analyses in the incidence of acute intracerebral
hemorrhage events and acute cerebral infarction events in urban
areas in Beijing. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 23:352–355.
2002.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chang CC and Chen CJ: Secular trend of
mortality from cerebral infarction and cerebral hemorrhage in
Taiwan, 1974–1988. Stroke. 24:212–218. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
WHO publishes definitive atlas on global
heart disease and stroke epidemic. Indian J Med Sci. 58:405–406.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yamamoto K, Koh H, Shimada H, Takeuchi J,
Yamakawa Y, Kawamura M and Miki T: Cerebral infarction in the left
hemisphere compared with the right hemisphere increases the risk of
aspiration pneumonia. Osaka City Med J. 60:81–86. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Quinn CT: Breakthrough: New guidance for
silent cerebral ischemia and infarction in sickle cell disease.
Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2014:438–443.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Repossini A, Tononi L, Martinil G, Di
Bacco L, Girolettiz L, Rosati F and Muneretto C: Platelet
activation after sorin freedom solo valve implantation: A
comparative study with Carpentier-Edwards Perimount Magna. J Heart
Valve Dis. 23:777–782. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kinsella JA, Tobin WO, Hamilton G and
McCabe DJ: Platelet activation, function, and reactivity in
atherosclerotic carotid artery stenosis: A systematic review of the
literature. Int J Stroke. 8:451–464. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pei HY and Han Y: Platelet activation
through signal transduction-review. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za
Zhi. 12:704–707. 2004.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chang MC, Lee AY, Chang WF and Chen TJ:
Embolic cerebral infarction and gastrointestinal hemorrhage
following thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction.
Echocardiography. 19:139–141. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
McConnell ED, Wei HS, Reitz KM, Kang H,
Takano T, Vates GE and Nedergaard M: Cerebral microcirculatory
failure after subarachnoid hemorrhage is reversed by hyaluronidase.
J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 36:1537–1552. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Alshehri OM, Montague S, Watson S, Carter
P, Sarker N, Manne BK, Miller JL, Herr AB, Pollitt AY, O'Callaghan
CA, et al: Activation of glycoprotein VI (GPVI) and C-type
lectin-like receptor-2 (CLEC-2) underlies platelet activation by
diesel exhaust particles and other charged/hydrophobic ligands.
Biochem J. 468:459–473. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bigalke B, Haap M, Stellos K, Geisler T,
Seizer P, Kremmer E, Overkamp D and Gawaz M: Platelet glycoprotein
VI (GPVI) for early identification of acute coronary syndrome in
patients with chest pain. Thromb Res. 125:e184–e189. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jung SM, Tsuji K and Moroi M: Glycoprotein
(GP) VI dimer as a major collagen-binding site of native platelets:
Direct evidence obtained with dimeric GPVI-specific Fabs. J Thromb
Haemost. 7:1347–1355. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bigalke B, Stellos K, Stakos D, Joos T,
Pötz O, Geisler T, Bischofs C, Kremmer E, Krämer BF, Seizer P, et
al: Influence of platelet count on the expression of platelet
collagen receptor glycoprotein VI (GPVI) in patients with acute
coronary syndrome. Thromb Haemost. 101:911–915. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Goebel S, Li Z, Vogelmann J, Holthoff HP,
Degen H, Hermann DM, Gawaz M, Ungerer M and Münch G: The GPVI-Fc
fusion protein Revacept improves cerebral infarct volume and
functional outcome in stroke. PLoS One. 8:e669602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Furie B and Furie BC: Mechanisms of
thrombus formation. N Engl J Med. 359:938–949. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stoll G, Kleinschnitz C and Nieswandt B:
Molecular mechanisms of thrombus formation in ischemic stroke:
Novel insights and targets for treatment. Blood. 112:3555–3562.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rigg RA, Aslan JE, Healy LD, Wallisch M,
Thierheimer ML, Loren CP, Pang J, Hinds MT, Gruber A and McCarty
OJ: Oral administration of Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitors
impairs GPVI-mediated platelet function. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
310:C373–C380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rietscher R, Czaplewska JA, Majdanski TC,
Gottschaldt M, Schubert US, Schneider M and Lehr CM: Impact of PEG
and PEG-b-PAGE modified PLGA on nanoparticle formation, protein
loading and release. Int J Pharm. 500:187–195. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shi J, Chen Z, Wang L, Wang B, Xu L, Hou L
and Zhang Z: A tumor-specific cleavable nanosystem of PEG-modified
C60@Au hybrid aggregates for radio frequency-controlled release,
hyperthermia, photodynamic therapy and X-ray imaging. Acta
Biomater. 29:282–297. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu L, Wu M, Zeng Y, Zhang D, Zheng A, Liu
X and Liu J: Multifunctional PEG modified DOX loaded mesoporous
silica nanoparticle@CuS nanohybrids as photo-thermal agent and
thermal-triggered drug release vehicle for hepatocellular carcinoma
treatment. Nanotechnology. 26:0251022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hashimoto K, Tagami T, Yamakage H,
Muranaka K, Tanaka M, Odori S, Kono S, Shimatsu A, Ogawa Y and
Satoh-Asahara N: Serum free thyroxine levels is associated with the
efficacy of weight reduction therapy in obese female patients.
Endocr J. 63:221–229. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ledzewicz U, Schättler H, Gahrooi MR and
Dehkordi SM: On the MTD paradigm and optimal control for multi-drug
cancer chemotherapy. Math Biosci Eng. 10:803–819. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Akbar H, Shang X, Perveen R, Berryman M,
Funk K, Johnson JF, Tandon NN and Zheng Y: Gene targeting
implicates Cdc42 GTPase in GPVI and non-GPVI mediated platelet
filopodia formation, secretion and aggregation. PLoS One.
6:e221172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu H, Zhu L, Huang Z, Ji Q, Chatterjee M,
Zhang W and Li N: Platelets enhance lymphocyte adhesion and
infiltration into arterial thrombus. Thromb Haemost. 104:1184–1192.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Joglekar MV, Ware J, Xu J, Fitzgerald ME
and Gartner TK: Platelets, glycoprotein Ib-IX, and von Willebrand
factor are required for FeCl(3)-induced occlusive thrombus
formation in the inferior vena cava of mice. Platelets. 24:205–212.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bae ON, Lim KM, Noh JY, Chung SM, Kim SH
and Chung JH: Trivalent methylated arsenical-induced
phosphatidylserine exposure and apoptosis in platelets may lead to
increased thrombus formation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 239:144–153.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Whyte CS, Swieringa F, Mastenbroek TG,
Lionikiene AS, Lancé MD, Van Der Meijden PE, Heemskerk JW and Mutch
NJ: Plasminogen associates with phosphatidylserine-exposing
platelets and contributes to thrombus lysis under flow. Blood.
125:2568–2578. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fuly AL, Soares AM, Marcussi S, Giglio JR
and Guimarães JA: Signal transduction pathways involved in the
platelet aggregation induced by a D-49 phospholipase A2 isolated
from Bothrops jararacussu snake venom. Biochimie. 86:731–739. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Newman PJ and Newman DK: Signal
transduction pathways mediated by PECAM-1: New roles for an old
molecule in platelet and vascular cell biology. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 23:953–964. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cardoso LE, Little PJ, Ballinger ML, Chan
CK, Braun KR, Potter-Perigo S, Bornfeldt KE, Kinsella MG and Wight
TN: Platelet-derived growth factor differentially regulates the
expression and post-translational modification of versican by
arterial smooth muscle cells through distinct protein kinase C and
extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. J Biol Chem.
285:6987–6995. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mendoza E, Malong CL, Tanchee-Ngo MJ and
Mercado-Asis L: Acromegaly with cardiomyopathy, cardiac thrombus
and hemorrhagic cerebral infarct: A case report of therapeutic
dilemma with review of literature. Int J Endocrinol Metab.
13:e188412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Walsh TG, Berndt MC, Carrim N, Cowman J,
Kenny D and Metharom P: The role of Nox1 and Nox2 in GPVI-dependent
platelet activation and thrombus formation. Redox Biol. 2:178–186.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ungerer M, Li Z, Baumgartner C, Goebel S,
Vogelmann J, Holthoff HP, Gawaz M and Münch G: The GPVI-Fc fusion
protein Revacept reduces thrombus formation and improves vascular
dysfunction in atherosclerosis without any impact on bleeding
times. PLoS One. 8:e711932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|