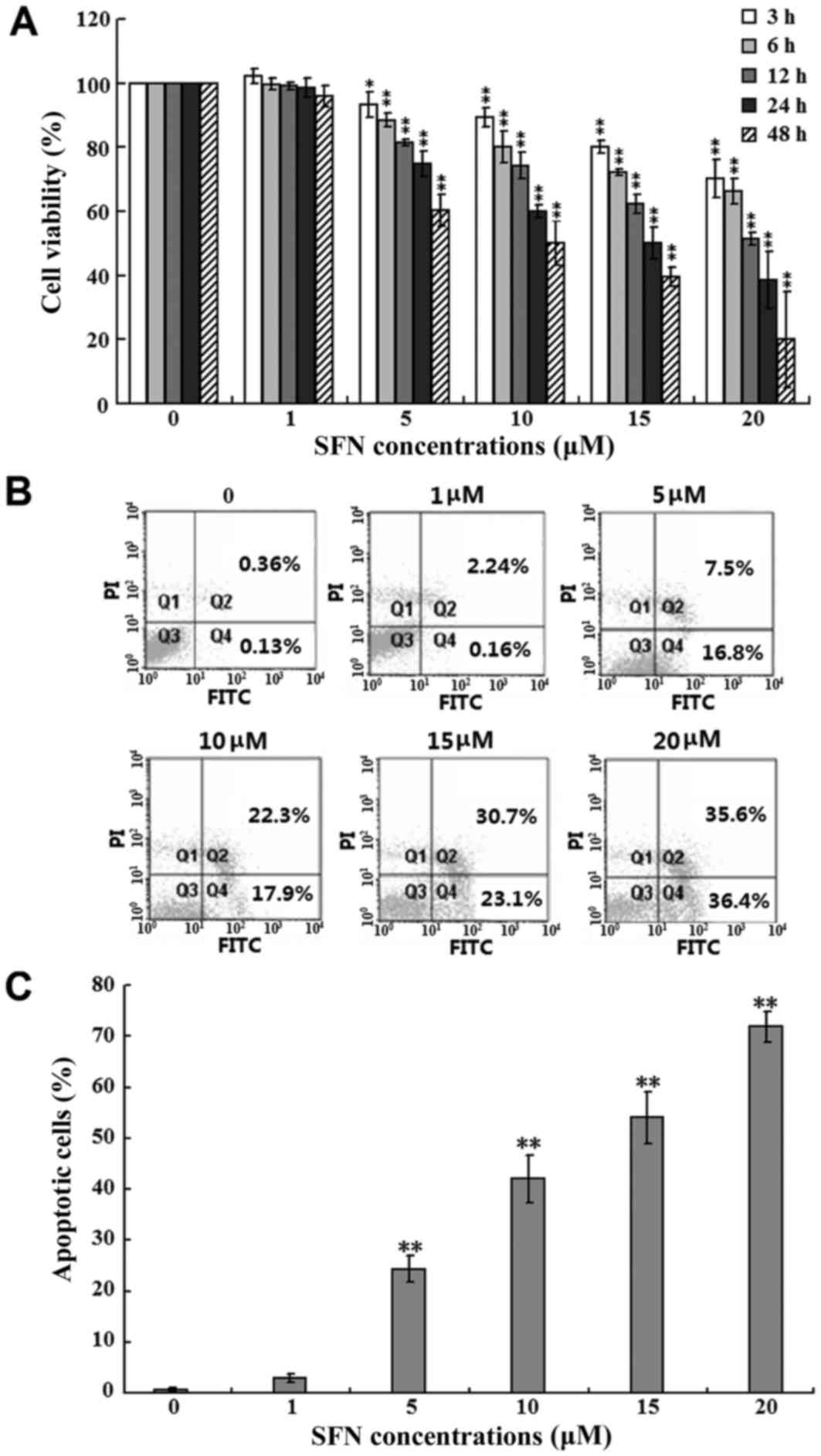
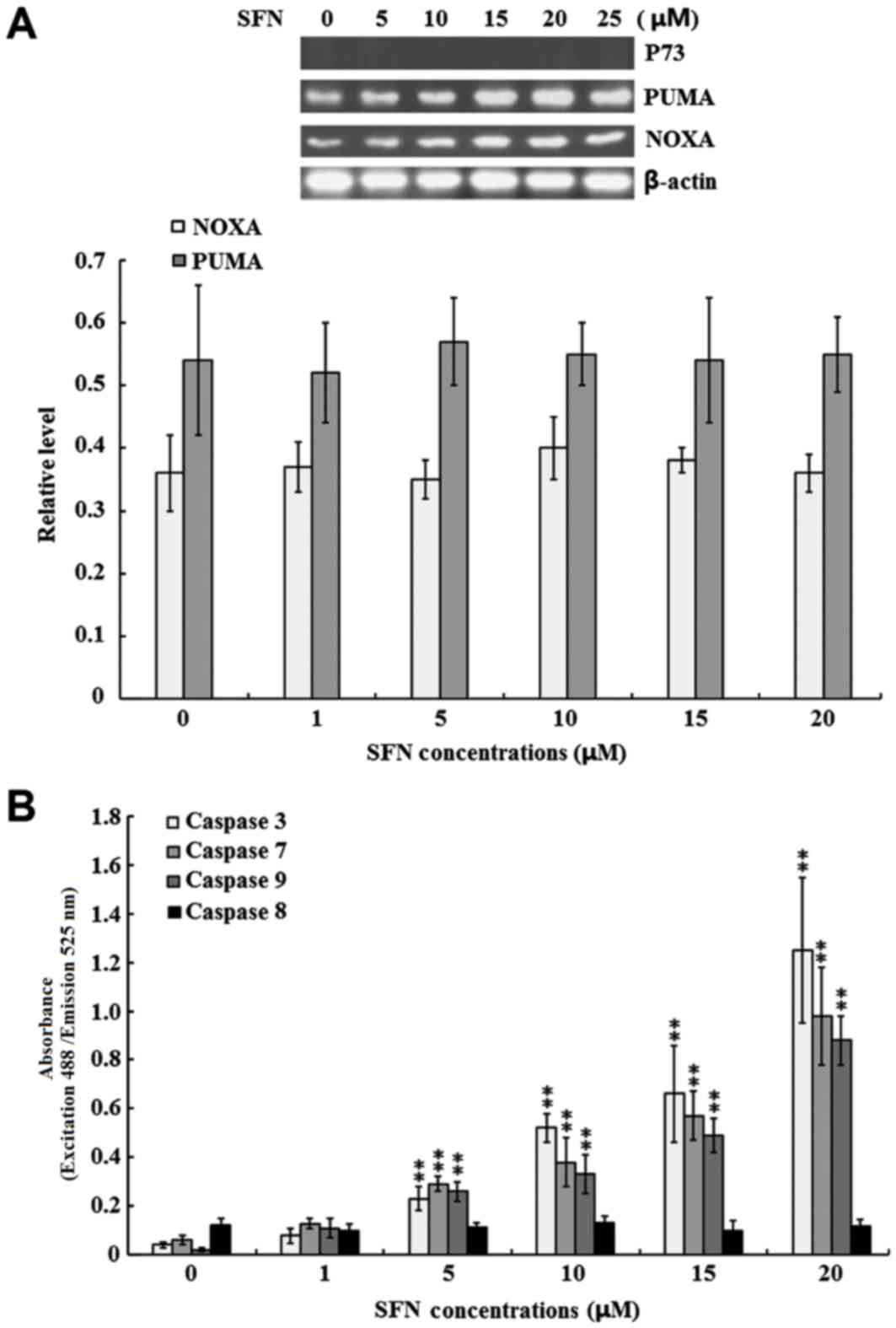
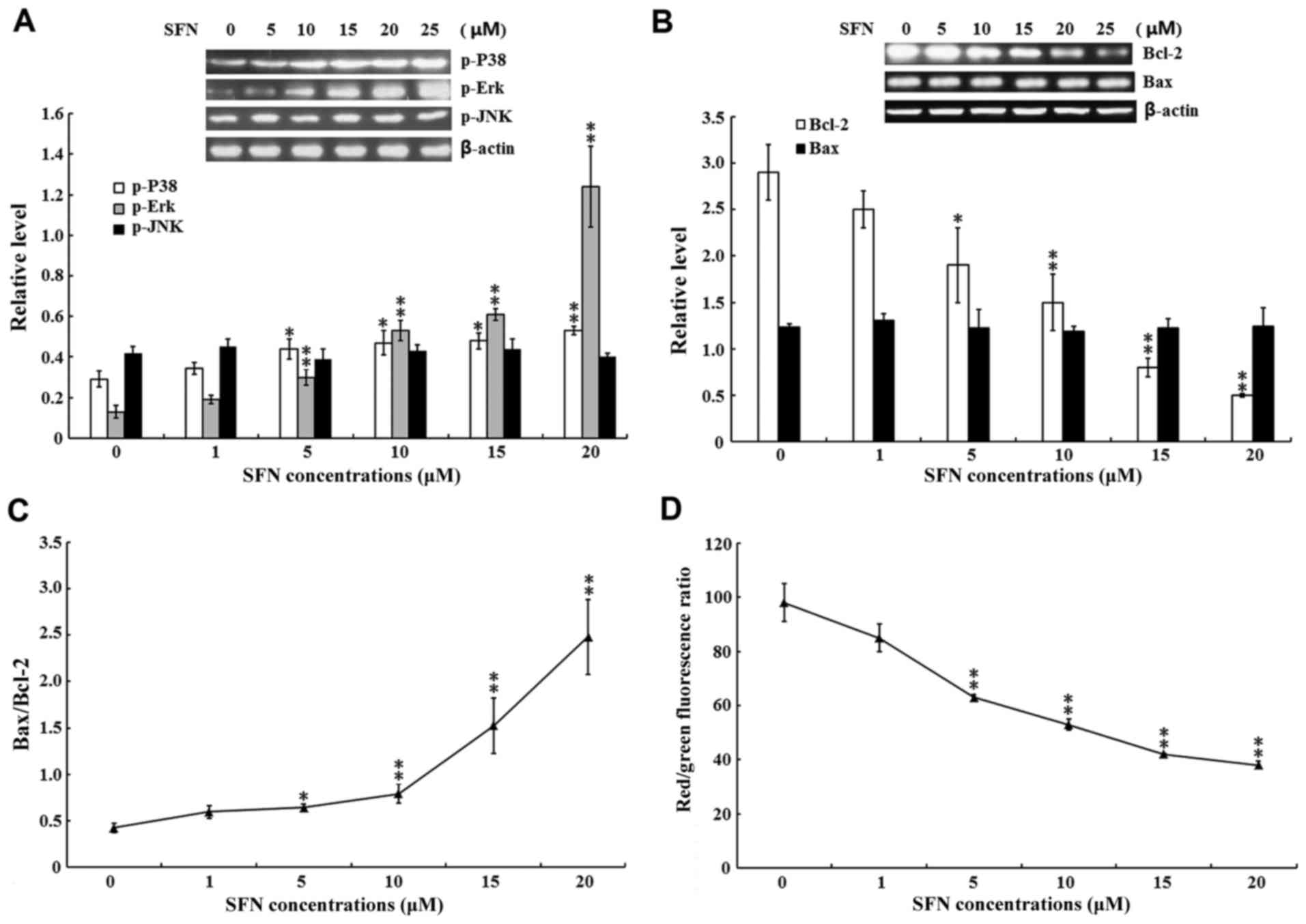
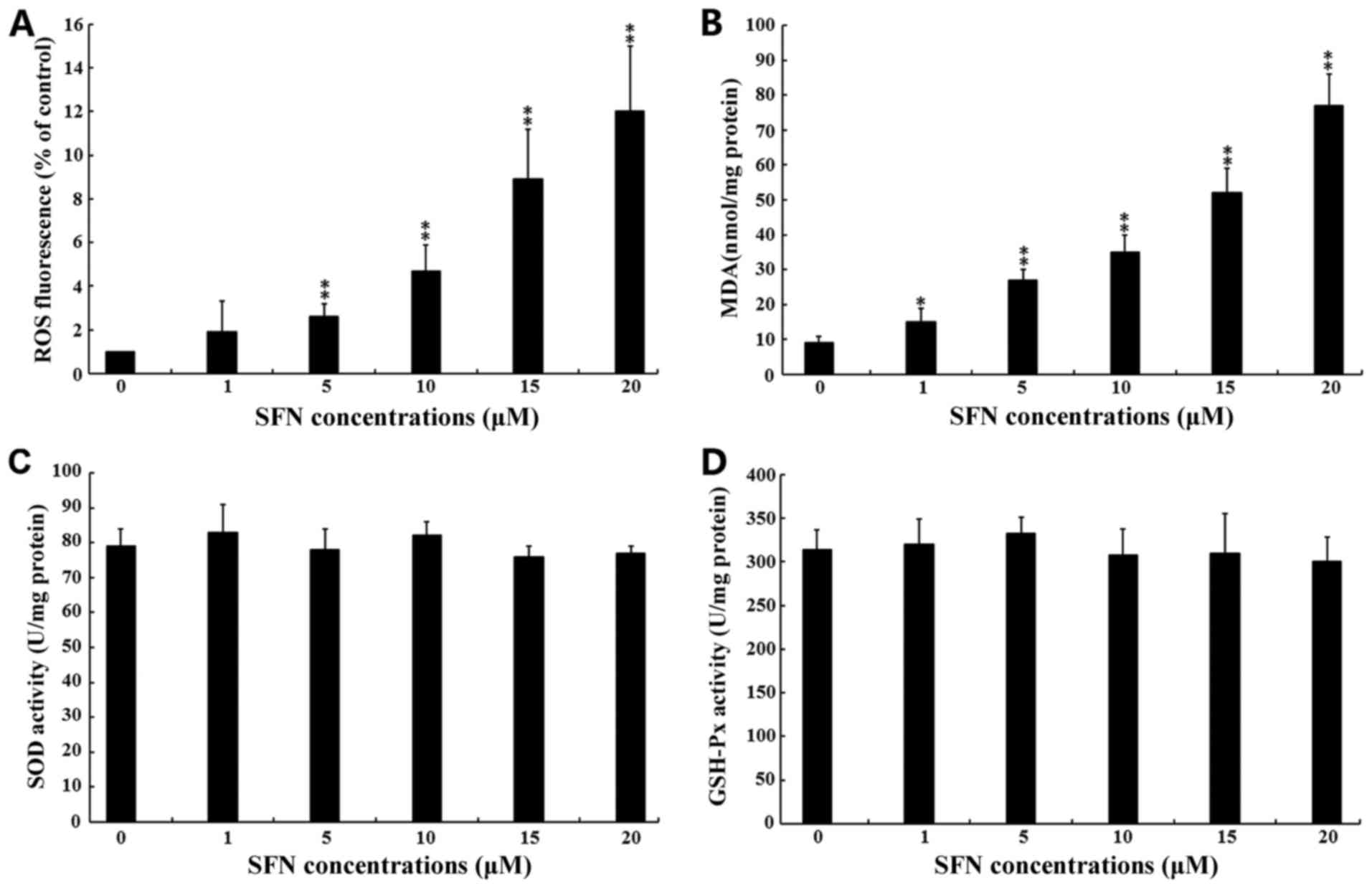
|
1
|
Bauman JE, Zang Y, Sen M, Li C, Wang L,
Egner PA, Fahey JW, Normolle DP, Grandis JR, Kensler TW and Johnson
DE: Prevention of carcinogen-induced oral cancer by sulforaphane.
Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 9:547–557. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Amjad AI, Parikh RA, Appleman LJ, Hahm ER,
Singh K and Singh SV: Broccoli-derived sulforaphane and
chemoprevention of prostate cancer: From bench to bedside. Curr
Pharmacol Rep. 1:382–390. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Traka MH, Melchini A and Mithen RF:
Sulforaphane and prostate cancer interception. Drug Discov Today.
19:1488–1492. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Folkard DL, Marlow G, Mithen RF and
Ferguson LR: Effect of Sulforaphane on NOD2 via NF-κB: Implications
for Crohn's disease. J Inflamm (Lond). 12:62015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun CC, Li SJ, Yang CL, Xue RL, Xi YY,
Wang L, Zhao QL and Li DJ: Sulforaphane attenuates muscle
inflammation in dystrophin-deficient mdx mice via NF-E2-related
factor 2 (Nrf2)-mediated Inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway. J
Biol Chem. 290:17784–17795. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jang M and Cho IH: Sulforaphane
ameliorates 3-nitropropionic acid-induced striatal toxicity by
activating the keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway and Inhibiting the MAPKs and
NF-κB pathways. Mol Neurobiol. 53:2619–2635. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tammali R, Reddy AB, Saxena A, Rychahou
PG, Evers BM, Qiu S, Awasthi S, Ramana KV and Srivastava SK:
Inhibition of aldose reductase prevents colon cancer metastasis.
Carcinogenesis. 32:1259–1267. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Coriat R, Marut W, Leconte M, Ba LB,
Vienne A, Chéreau C, Alexandre J, Weill B, Doering M, Jacob C, et
al: The organotelluride catalyst LAB027 prevents colon cancer
growth in the mice. Cell Death Dis. 2:e1912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu T, Wang L, Zhang L, Lu L, Shen J, Chan
RL, Li M, Wu WK, To KK and Cho CH: Sensitivity of
apoptosis-resistant colon cancer cells to tanshinones is mediated
by autophagic cell death and p53-independent cytotoxicity.
Phytomedicine. 22:536–544. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Acedo P and Zawacka-Pankau J: p53 family
members-important messengers in cell death signaling in
photodynamic therapy of cancer? Photochem Photobiol Sci.
14:1390–1396. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Basu S and Murphy ME: p53 family members
regulate cancer stem cells. Cell Cycle. 15:1403–1404. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pflaum J, Schlosser S and Müller M: p53
family and cellular stress responses in cancer. Front Oncol.
4:2852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tu HC, Ren D, Wang GX, Chen DY, Westergard
TD, Kim H, Sasagawa S, Hsieh JJ and Cheng EH: The p53-cathepsin
axis cooperates with ROS to activate programmed necrotic death upon
DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:1093–1098. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wiseman A: p53 protein or BID protein
select the route to either apoptosis (programmed cell death) or to
cell cycle arrest opposing carcinogenesis after DNA damage by ROS.
Med Hypotheses. 67:296–299. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang Y, Jiang L, She Y, Chen M, Li Q, Yang
G, Geng C, Tang L, Zhong L, Jiang L and Liu X: Olaquindox induces
DNA damage via the lysosomal and mitochondrial pathway involving
ROS production and p53 activation in HEK293 cells. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 40:792–799. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dueñas M, Santos M, Aranda JF, Bielza C,
Martínez-Cruz AB, Lorz C, Taron M, Ciruelos EM, Rodríguez-Peralto
JL, Martín M, et al: Mouse p53-deficient cancer models as platforms
for obtaining genomic predictors of human cancer clinical outcomes.
PLoS One. 7:e424942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou S, Kachhap S and Singh KK:
Mitochondrial impairment in p53-deficient human cancer cells.
Mutagenesis. 18:287–292. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Robles AI and Harris CC: Clinical outcomes
and correlates of TP53 mutations and cancer. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 2:a0010162010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Oren M, Tal P and Rotter V: Targeting
mutant p53 for cancer therapy. Aging (Albany NY). 8:1159–1160.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Q, Zeng SX and Lu H: Targeting
p53-MDM2-MDMX loop for cancer therapy. Subcell Biochem. 85:281–319.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiang JF, Wang WQ, Liu L, Xu HX, Wu CT,
Yang JX, Qi ZH, Wang YQ, Xu J, Liu C, et al: Mutant p53 determines
pancreatic cancer poor prognosis to pancreatectomy through
upregulation of cavin-1 in patients with preoperative serum CA19-9
≥1,000 U/ml. Sci Rep. 6:192222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shi Y, Nikulenkov F, Zawacka-Pankau J, Li
H, Gabdoulline R, Xu J, Eriksson S, Hedström E, Issaeva N, Kel A,
et al: ROS-dependent activation of JNK converts p53 into an
efficient inhibitor of oncogenes leading to robust apoptosis. Cell
Death Differ. 21:612–623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu B, Yuan B, Zhang L, Mu W and Wang C:
ROS/p38/p53/Puma signaling pathway is involved in emodin-induced
apoptosis of human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:15413–15422. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Panieri E and Santoro MM: ROS homeostasis
and metabolism: A dangerous liason in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis.
7:e22532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Prasad S, Gupta SC and Tyagi AK: Reactive
oxygen species (ROS) and cancer: Role of antioxidative
nutraceuticals. Cancer Lett. 387:95–105. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Walton EL: The dual role of ROS,
antioxidants and autophagy in cancer. Biomed J. 39:89–92. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nogueira V and Hay N: Molecular pathways:
Reactive oxygen species homeostasis in cancer cells and
implications for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 19:4309–4314.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Santabárbara-Ruiz P, López-Santillán M,
Martínez-Rodríguez I, Binagui-Casas A, Pérez L, Milán M, Corominas
M and Serras F: ROS-Induced JNK and p38 signaling is required for
unpaired cytokine activation during Drosophila regeneration. PLoS
Genet. 11:e10055952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Amin PJ and Shankar BS: Sulforaphane
induces ROS mediated induction of NKG2D ligands in human cancer
cell lines and enhances susceptibility to NK cell mediated lysis.
Life Sci. 126:19–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhai JW, Gao C, Ma WD, Wang W, Yao LP, Xia
XX, Luo M, Zu YG and Fu YJ: Geraniin induces apoptosis of human
breast cancer cells MCF-7 via ROS-mediated stimulation of p38 MAPK.
Toxicol Mech Methods. 26:311–318. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Youn GS, Lee KW, Choi SY and Park J:
Overexpression of HDAC6 induces pro-inflammatory responses by
regulating ROS-MAPK-NF-κB/AP-1 signaling pathways in macrophages.
Free Radic Biol Med. 97:14–23. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang H, Li D, Hu Z, Zhao S, Zheng Z and Li
W: Protective effects of green tea polyphenol against renal injury
through ROS-Mediated JNK-MAPK pathway in lead exposed rats. Mol
Cells. 39:508–513. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang S, Xu R, Luo X, Jiang Z and Shu H:
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of MAPK and
MAPKK gene family in Malus domestica. Gene. 531:377–387. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rhim JH, Luo X, Gao D, Xu X, Zhou T, Li F,
Wang P, Wong ST and Xia X: Cell type-dependent Erk-Akt pathway
crosstalk regulates the proliferation of fetal neural progenitor
cells. Sci Rep. 6:265472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu E, Li J, Shi S, Wang X, Liang T, Wu B
and Li Q: Sustained ERK activation-mediated proliferation
inhibition of farrerol on human gastric carcinoma cell line by
G0/G1-phase cell-cycle arrest. Eur J Cancer Prev. 25:490–499. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hsu YC, Chang SJ, Wang MY, Chen YL and
Huang TY: Growth inhibition and apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells
through ROS-independent MEK/ERK activation by sulforaphane. Cell
Biochem Biophys. 66:765–774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen YJ, Liu WH, Kao PH, Wang JJ and Chang
LS: Involvement of p38 MAPK- and JNK-modulated expression of Bcl-2
and Bax in Naja nigricollis CMS-9-induced apoptosis of human
leukemia K562 cells. Toxicon. 55:1306–1316. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Smaili SS, Hsu YT, Sanders KM, Russell JT
and Youle RJ: Bax translocation to mitochondria subsequent to a
rapid loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. Cell Death Differ.
8:909–920. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Benadiba M, Dos Santos RR, Dde O Silva and
Colquhoun A: Inhibition of C6 rat glioma proliferation by
[Ru2Cl(Ibp)4] depends on changes in p21, p27, Bax/Bcl2 ratio and
mitochondrial membrane potential. J Inorg Biochem. 104:928–935.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ray G, Batra S, Shukla NK, Deo S, Raina V,
Ashok S and Husain SA: Lipid peroxidation, free radical production
and antioxidant status in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
59:163–170. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rebillard A, Lagadic-Gossmann D and
Dimanche-Boitrel MT: Cisplatin cytotoxicity: DNA and plasma
membrane targets. Curr Med Chem. 5:2656–2663. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Redon CE, Dickey JS, Bonner WM and
Sedelnikova OA: γ-H2AX as a biomarker of DNA damage induced by
ionizing radiation in human peripheral blood lymphocytes and
artificial skin. Adv Space Res. 43:1171–1178. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Buenz EJ: Aloin induces apoptosis in
Jurkat cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 22:422–429. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tabolacci C, Rossi S, Lentini A,
Provenzano B, Turcano L, Facchiano F and Beninati S: Aloin enhances
cisplatin antineoplastic activity in B16-F10 melanoma cells by
transglutaminase-induced differentiation. Amino Acids. 44:293–300.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jing S, Jiang WH and Sun W: Effects of
smoking on serum SOD and GSH-PX activities and MDA contents in rats
with gastric ulcer. Appl Mech Mater 675–677. 1–129. 2014.
|
|
46
|
Bragado P, Armesilla A, Silva A and Porras
A: Apoptosis by cisplatin requires p53 mediated p38alpha MAPK
activation through ROS generation. Apoptosis. 12:1733–1742. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hao W, Wang S and Zhou Z: Tubeimoside-1
(TBMS1) inhibits lung cancer cell growth and induces cells
apoptosis through activation of MAPK-JNK pathway. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:12075–12083. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bao FK: The bcl-2 gene family, an
important regulator of apoptosis. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan.
27:67–69. 1996.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wu Y and Tang L: Bcl-2 family proteins
regulate apoptosis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition by
calcium signals. Curr Pharm Des. 22:4700–4704. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Carpio MA, Michaud M, Zhou W, Fisher JK,
Walensky LD and Katz SG: BCL-2 family member BOK promotes apoptosis
in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 112:7201–7206. 2015; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gallenne T, Gautier F, Oliver L, Hervouet
E, Noël B, Hickman JA, Geneste O, Cartron PF, Vallette FM, Manon S
and Juin P: Bax activation by the BH3-only protein Puma promotes
cell dependence on antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members. J Cell Biol.
185:279–290. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cory S, Huang DC and Adams JM: The Bcl-2
family: Roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene.
22:8590–8607. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Melino G, Bernassola F, Ranalli M, Yee K,
Zong WX, Corazzari M, Knight RA, Green DR, Thompson C and Vousden
KH: p73 Induces apoptosis via PUMA transactivation and Bax
mitochondrial translocation. J Biol Chem. 279:8076–8083. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Haddad JJ: The role of Bax/Bcl-2 and
pro-caspase peptides in hypoxia/reperfusion-dependent regulation of
MAPK(ERK): Discordant proteomic effect of MAPK(p38). Protein Pept
Lett. 14:361–371. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Pan MH, Chiou YS, Cheng AC, Bai N, Lo CY,
Tan D and Ho CT: Involvement of MAPK, Bcl-2 family, cytochrome c,
and caspases in induction of apoptosis by
1,6-O,O-diacetylbritannilactone in human leukemia cells. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 51:229–238. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
He G, He G, Zhou R, Pi Z, Zhu T, Jiang L
and Xie Y: Enhancement of cisplatin-induced colon cancer cells
apoptosis by shikonin, a natural inducer of ROS in vitro and in
vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 469:1075–1082. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|