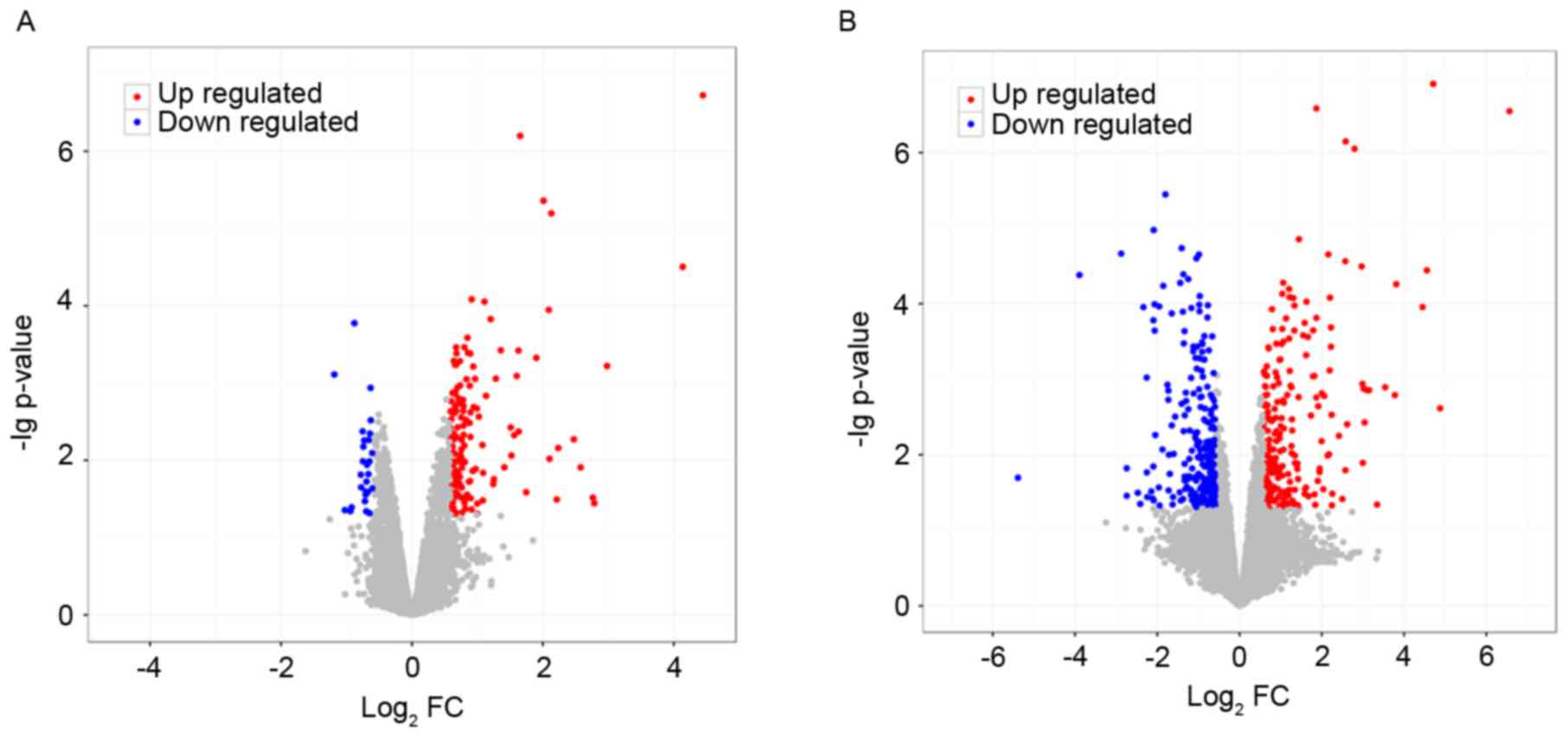
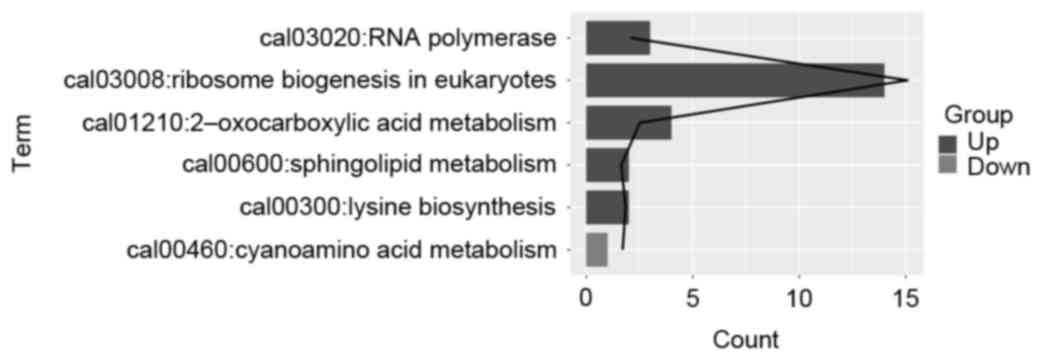
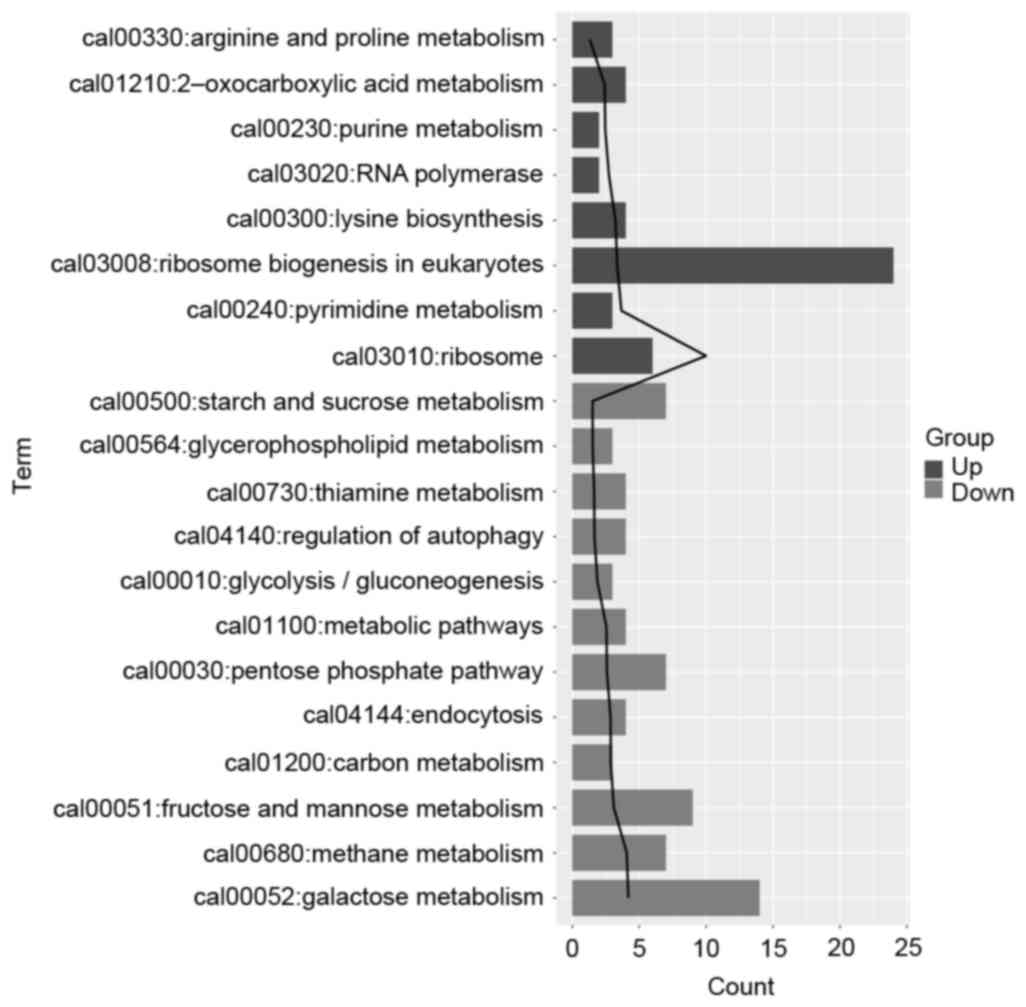
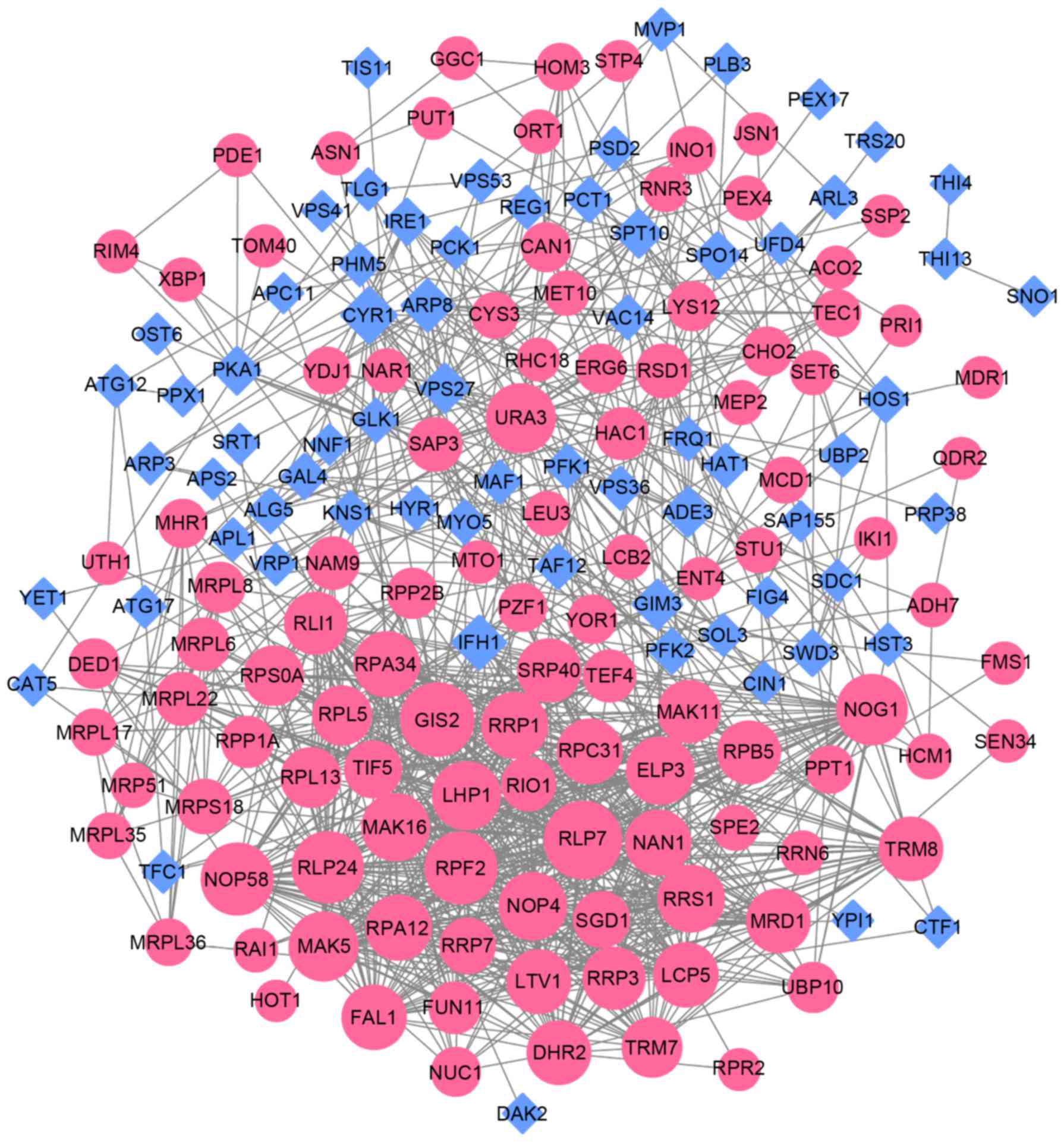
|
1
|
Lara HH, Romero-Urbina DG, Pierce C,
Lopez-Ribot JL, Arellano-Jiménez MJ and Jose-Yacaman M: Effect of
silver nanoparticles on Candida albicans biofilms: An
ultrastructural study. J Nanobiotechnology. 13:912015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yapar N: Epidemiology and risk factors for
invasive candidiasis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 10:95–105. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kullberg BJ and Arendrup MC: Invasive
candidiasis. N Engl J Med. 373:1445–1456. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Odds FC, Brown AJ and Gow NA: Antifungal
agents: Mechanisms of action. Trends Microbiol. 11:272–279. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sharma M, Biswas D, Kotwal A, Thakuria B,
Kakati B, Chauhan BS and Patras A: Ibuprofen-mediated reversal of
fluconazole resistance in clinical isolates of Candida. J Clin
Diagn Res. 9:DC20–DC22. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Magnuson JG: Potential role of RTA3 and
GNP3 transport genes in the quorum sensing response of Candida
albicans. 2015.
|
|
7
|
Raska M, Běláková J, Krupka M and Weigl E:
Candidiasis-Do we need to fight or to tolerate the Candida fungus?
Folia Microbiol (Praha). 52:297–312. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Soll DR: The role of phenotypic switching
in the basic biology and pathogenesis of Candida albicans. J Oral
Microbiol. 6:2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vandeputte P, Ischer F, Sanglard D and
Coste AT: In vivo systematic analysis of Candida albicans Zn2-Cys6
transcription factors mutants for mice organ colonization. PLoS
One. 6:e269622011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sanglard D, Coste A and Ferrari S:
Antifungal drug resistance mechanisms in fungal pathogens from the
perspective of transcriptional gene regulation. FEMS Yeast Res.
9:1029–1050. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M and
Speed TP: A comparison of normalization methods for high density
oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias.
Bioinformatics. 19:185–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Smyth GK: LIMMA: Linear models for
microarray dataBioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions
Using R and Bioconductor. Gentleman R, Carey V, Huber W, Irizarry R
and Dudoit S: Springer-Verlag New York; New York, NY: pp. 397–420.
2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID gene functional classification tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, Schmidt
S, Bork P and Snel B: STRING: A database of predicted functional
associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:258–261. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tang Y, Li M, Wang J, Pan Y and Wu FX:
CytoNCA: A cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation
of protein interaction networks. Biosystems. 127:67–72. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
He X and Zhang J: Why do hubs tend to be
essential in protein networks? PLoS Genet. 2:e882006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu G, Dawson E, Duong A, Haw R and Stein
L: ReactomeFIViz: A Cytoscape app for pathway and network-based
data analysis. Version 2. F1000Res. 3:1462014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Genschik P, Billy E, Swianiewicz M and
Filipowicz W: The human RNA 3′-terminal phosphate cyclase is a
member of a new family of proteins conserved in Eucarya, Bacteria
and Archaea. EMBO J. 16:2955–2967. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Horn DM, Mason SL and Karbstein K: Rcl1
protein, a novel nuclease for 18 S ribosomal RNA production. J Biol
Chem. 286:34082–34087. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Delprato A, Al Kadri Y, Pérébaskine N,
Monfoulet C, Henry Y, Henras AK and Fribourg S: Crucial role of the
Rcl1p-Bms1p interaction for yeast pre-ribosomal RNA processing.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42:10161–10172. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Enjalbert B, Smith DA, Cornell MJ, Alam I,
Nicholls S, Brown AJ and Quinn J: Role of the Hog1 stress-activated
protein kinase in the global transcriptional response to stress in
the fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Mol Biol Cell. 17:1018–1032.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huh WK, Falvo JV, Gerke LC, Carroll AS,
Howson RW, Weissman JS and O'Shea EK: Global analysis of protein
localization in budding yeast. Nature. 425:686–691. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rodríguez-Mateos M, Abia D, García-Gómez
JJ, Morreale A, de la Cruz J, Santos C, Remacha M and Ballesta JP:
The amino terminal domain from Mrt4 protein can functionally
replace the RNA binding domain of the ribosomal P0 protein. Nucleic
Acids Res. 37:3514–3521. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rodríguez-Mateos M, García-Gómez JJ,
Francisco-Velilla R, Remacha M, de la Cruz J and Ballesta JP: Role
and dynamics of the ribosomal protein P0 and its related
trans-acting factor Mrt4 during ribosome assembly in Saccharomyces
cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:7519–7532. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kressler D, Hurt E, Bergler H and Bassler
J: The power of AAA-ATPases on the road of pre-60S ribosome
maturation-molecular machines that strip pre-ribosomal particles.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1823:92–100. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jang Y, Lee H, Lee SW, Choi YS, Ahn BJ,
Kim GH and Kim JJ: Cu(II)-induced molecular and physiological
responses in the brown-rot basidiomycete Polyporales sp. KUC9061. J
Appl Microbiol. 113:790–797. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sammons MA, Samir P and Link AJ:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Gis2 interacts with the translation
machinery and is orthogonal to myotonic dystrophy type 2 protein
ZNF9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 406:13–19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Matia-González AM and Gerber AP:
Approaches for dissecting RNA-binding protein networks. Fungal RNA
Biology. 347–370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Scherrer T, Femmer C, Schiess R, Aebersold
R and Gerber AP: Defining potentially conserved RNA regulons of
homologous zinc-finger RNA-binding proteins. Genome Biol.
12:R32011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Anderson I, Göker M, Nolan M, Lucas S,
Hammon N, Deshpande S, Cheng JF, Tapia R, Han C, Goodwin L, et al:
Complete genome sequence of the hyperthermophilic
chemolithoautotroph Pyrolobus fumarii type strain (1A). Stand
Genomic Sci. 4:381–392. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mircus G, Albert N, Ben-Yaakov D,
Chikvashvili D, Shadkchan Y, Kontoyiannis DP and Osherov N:
Identification and characterization of a novel family of selective
antifungal compounds (CANBEFs) that interfere with fungal protein
synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 59:5631–5640. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun C and Woolford JL Jr: The yeast NOP4
gene product is an essential nucleolar protein required for
pre-rRNA processing and accumulation of 60S ribosomal subunits.
EMBO J. 13:3127–3135. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun C and Woolford JL Jr: The yeast
nucleolar protein Nop4p contains four RNA recognition motifs
necessary for ribosome biogenesis. J Biol Chem. 272:25345–25352.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Harnpicharnchai P, Jakovljevic J, Horsey
E, Miles T, Roman J, Rout M, Meagher D, Imai B, Guo Y, Brame CJ, et
al: Composition and functional characterization of yeast 66S
ribosome assembly intermediates. Mol Cell. 8:505–515. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|