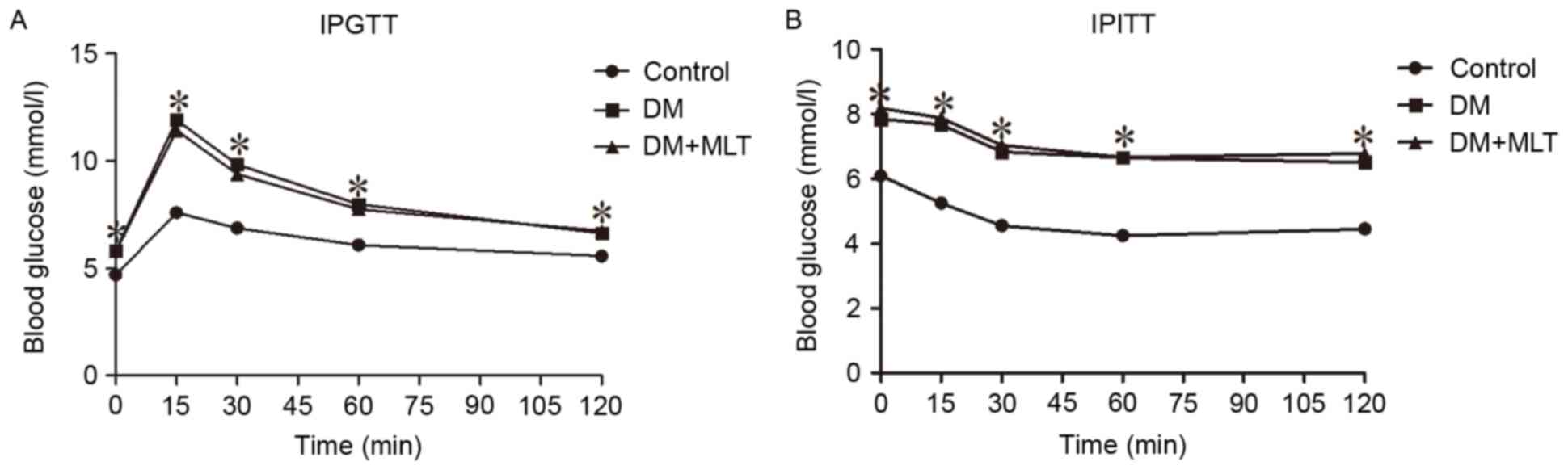
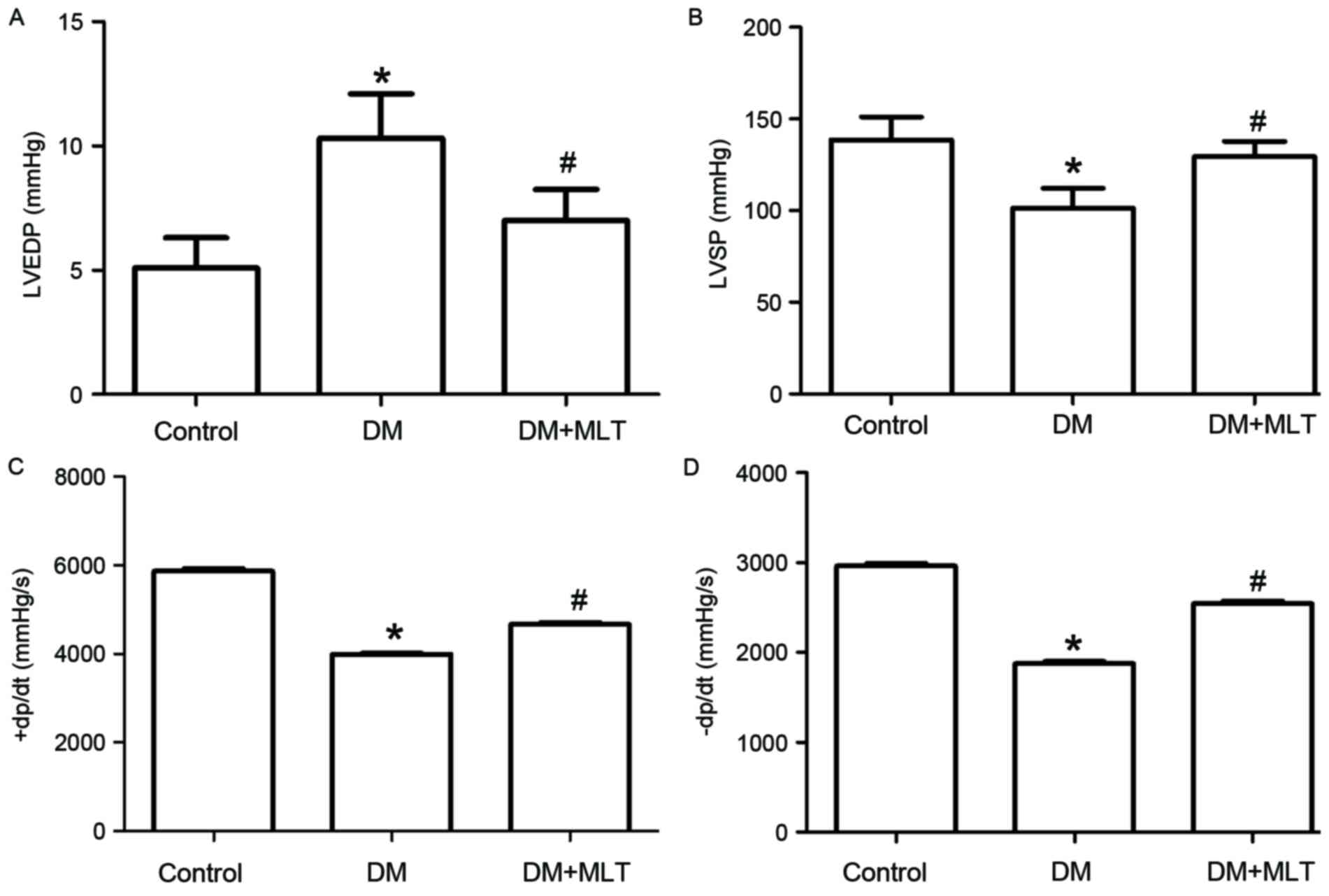
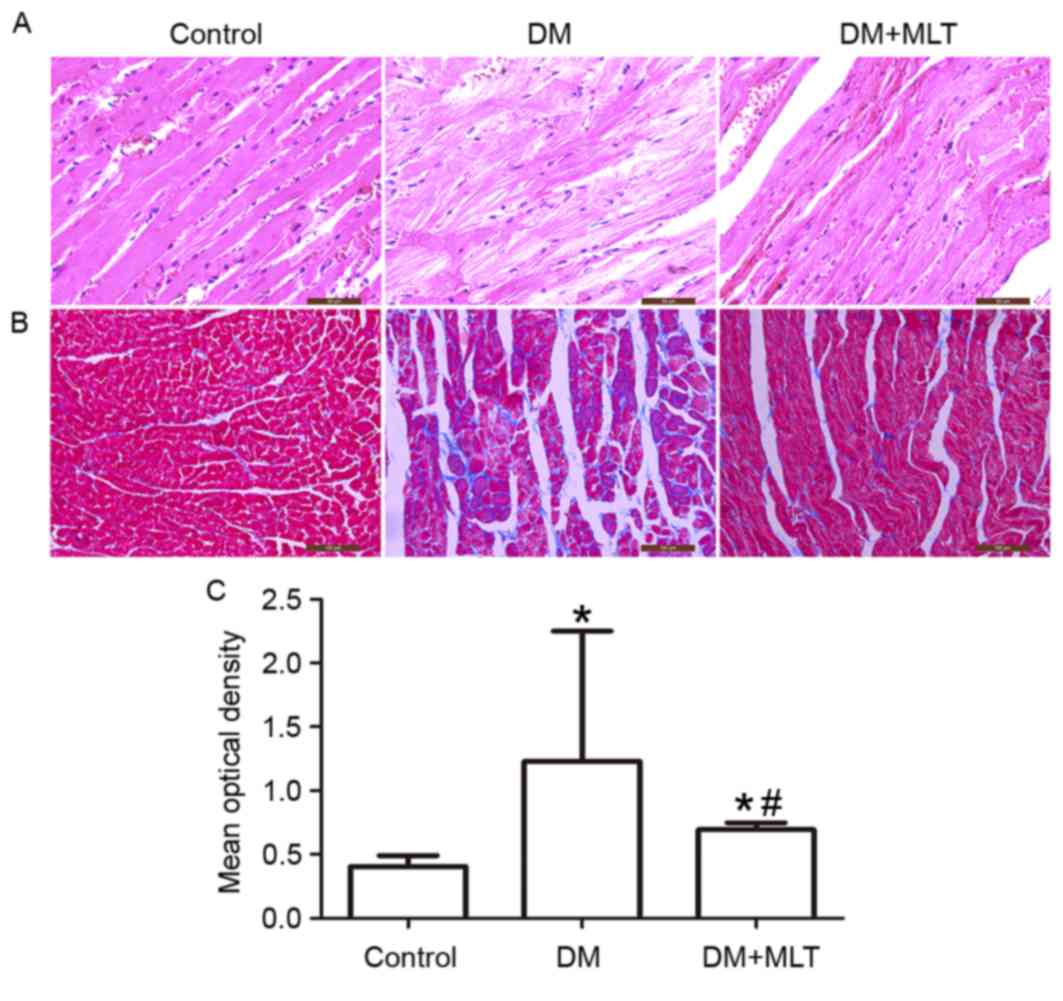
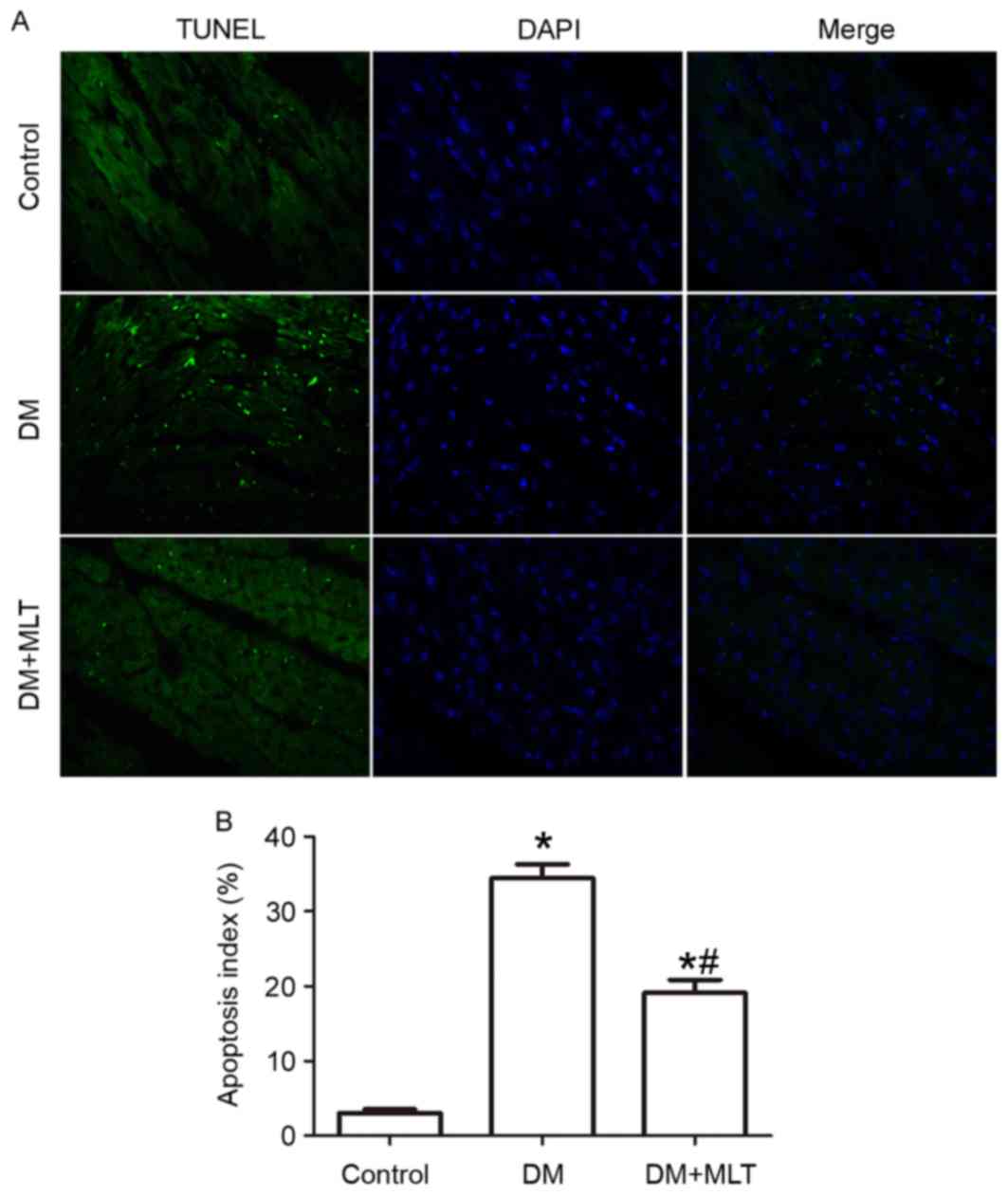
|
1
|
Gregg EW, Li Y, Wang J, Burrows NR, Ali
MK, Rolka D, Williams DE and Geiss L: Changes in diabetes-related
complications in the United States, 1990–2010. N Engl J Med.
370:1514–1523. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Duckworth WC: Hyperglycemia and
cardiovascular disease. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 3:383–391. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cicek FA, Toy A, Tuncay E, Can B and Turan
B: Beta-blocker timolol alleviates hyperglycemia-induced cardiac
damage via inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Bioenerg
Biomembr. 46:377–387. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang X, Ma X, Zhao M, Zhang B, Chi J, Liu
W, Chen W, Fu Y, Liu Y and Yin X: H2 and H3 relaxin inhibit high
glucose-induced apoptosis in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes.
Biochimie. 108:59–67. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Z, Zhang T, Dai H, Liu G, Wang H, Sun
Y, Zhang Y and Ge Z: Endoplasmic reticulum stress is involved in
myocardial apoptosis of streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. J
Endocrinol. 196:565–572. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sari FR, Watanabe K, Widyantoro B,
Thandavarayan RA, Harima M, Zhang S, Muslin AJ, Kodama M and Aizawa
Y: Partial inactivation of cardiac 14-3-3 protein in vivo elicits
endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) and activates ERS-initiated
apoptosis in ERS-induced mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 26:167–178.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lakshmanan AP, Harima M, Suzuki K,
Soetikno V, Nagata M, Nakamura T, Takahashi T, Sone H, Kawachi H
and Watanabe K: The hyperglycemia stimulated myocardial endoplasmic
reticulum (ER) stress contributes to diabetic cardiomyopathy in the
transgenic non-obese type 2 diabetic rats: A differential role of
unfolded protein response (UPR) signaling proteins. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 45:438–447. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cai L and Kang YJ: Cell death and diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 3:219–228. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gao Q, Wang XM, Ye HW, Yu Y, Kang PF, Wang
HJ, Guan SD and Li ZH: Changes in the expression of cardiac
mitofusin-2 in different stages of diabetes in rats. Mol Med Rep.
6:811–814. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Groenendyk J, Agellon LB and Michalak M:
Coping with endoplasmic reticulum stress in the cardiovascular
system. Annu Rev Physiol. 75:49–67. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Prins D and Michalak M: Endoplasmic
reticulum proteins in cardiac development and dysfunction. Can J
Physiol Pharmacol. 87:419–425. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou H and Liu R: ER stress and hepatic
lipid metabolism. Front Genet. 9:1122014.
|
|
13
|
Senft D and Ronai ZA: UPR, autophagy, and
mitochondria crosstalk underlies the ER stress response. Trends
Biochem Sci. 40:141–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang L, Lai E, Teodoro T and Volchuk A:
GRP78, but not protein-disulfide isomerase, partially reverses
hyperglycemia induced inhibition of insulin synthesis and secretion
in pancreatic {beta}-cells. J Biol Chem. 284:5289–5298. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kepp O, Semeraro M, Pedro Bravo-San JM,
Bloy N, Buqué A, Huang X, Zhou H, Senovilla L, Kroemer G and
Galluzzi L: eIF2α phosphorylation as a biomarker of immunogenic
cell death. Semin Cancer Biol. 33:86–92. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Scull CM and Tabas I: Mechanisms of ER
stress-induced apoptosis in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 31:2792–2797. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sano R and Reed JC: ER stress-induced cell
death mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:3460–3470. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Boyce M and Yuan J: Cellular response to
endoplasmic reticulum stress: A matter of life or death. Cell Death
Differ. 13:363–373. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu L, Cai B, Zheng S, Liu X, Cai H and Li
H: Effect of emodin on endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with
severe acute pancreatitis. Inflammation. 36:1020–1029. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Araki E, Oyadomari S and Mori M:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and diabetes mellitus. Intern Med.
42:7–14. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Oyadomari S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu
J, Yankner BA and Yuan J: Caspase-12 mediates
endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by
amyloid-beta. Nature. 403:98–103. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hill SM, Frasch T, Xiang S, Yuan L,
Duplessis T and Mao L: Molecular mechanisms of melatonin anticancer
effects. Integr Cancer Ther. 8:337–346. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mauriz JL, Collado PS, Veneroso C, Reiter
RJ and González-Gallego J: A review of the molecular aspects of
melatonins anti-inflammatory actions: Recent insights and new
perspectives. J Pineal Res. 54:1–14. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Galano A, Tan DX and Reiter RJ: Melatonin
as a naturally against oxidative stress: A physiochemical
examination. J Pineal Res. 51:1–16. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu L, Liang H, Dong X, Zhao G, Jin Z, Zhai
M, Yang Y, Chen W, Liu J, Yi W, et al: Reduced silent information
regulator 1 signaling exacerbates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury in type 2 diabetic rats and the protective effect of
melatonin. J Pineal Res. 59:376–390. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang Y, Duan W, Jin Z, Yi W, Yan J, Zhang
S, Wang N, Liang Z, Li Y, Chen W, et al: JAK2/STAT3 activation by
melatonin attenuates the mitochondrial oxidative damage induced by
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Pineal Res. 55:275–286.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Amin AH, El-Missiry MA and Othman AL:
Melatonin ameliorates metabolic risk factors, modulates apoptotic
proteins, and protects the rat heart against diabetes-induced
apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 747:166–173. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dominguez-Rodriguez A, Abreu-Gonzalez P
and Reiter RJ: The potential usefulness of serum melatonin level to
predict heart failure in patients with hypertensive cardiomyopathy.
Int J Cardiol. 174:415–417. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hadj Ayed Tka K, Mahfoudh Boussaid A,
Zaouali MA, Kammoun R, Bejaoui M, Mazgar Ghoul S, Catafau Rosello J
and Ben Abdennebi H: Melatonin modulates endoplasmic reticulum
stress and Akt/GSK3-beta signaling pathway in a rat model of renal
warm ischemia reperfusion. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst).
2015:6351722015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fernández A, Ordóñez R, Reiter RJ,
González-Gallego J and Mauriz JL: Melatonin and endoplasmic
reticulum stress: Relation to autophagy and apoptosis. J Pineal
Res. 59:292–307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Layland J, Cave AC, Warren C, Grieve DJ,
Sparks E, Kentish JC, Solaro RJ and Shah AM: Protection against
endotoxemia-induced contractile dysfunction in mice with
cardiac-specific expression of slow skeletal troponin I. FASEB J.
19:1137–1139. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ouyang C, You J and Xie Z: The interplay
between autophagy and apoptosis in the diabetic heart. J Mol Cell
Cardio. 71:71–80. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Liu Q, Wang S and Cai L: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy and its mechanisms: Role of oxidative stress and
damage. J Diabetes Investig. 5:623–634. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Roos WP and Kaina B: DNA damage-induced
cell death by apoptosis. Trends Mol Med. 12:440–450. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang JY: DNA damage and apoptosis. Cell
Death Differ. 8:1047–1048. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tsujimoto Y: Role of Bcl-2 family proteins
in apoptosis: Apoptosomes or mitochondria? Genes Cells. 3:697–707.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Acikel M, Buyukokuroglu ME, Aksoy H,
Erdogan F and Erol MK: Protective effects of melatonin against
myocardial injury induced by isoproterenol in rats. J Pineal Res.
35:75–79. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sheu JJ, Chang LT, Chiang CH, Sun CK,
Chang NK, Youssef AA, Wu CJ, Lee FY and Yip HK: Impact of diabetes
on cardiomyocyte apoptosis and connexin43 gap junction integrity:
Role of pharmacological modulation. Int Heart J. 48:233–245. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ghosh S, Pulinilkunnil T, Yuen G,
Kewalramani G, An D, Qi D, Abrahani A and Rodrigues B:
Cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by short-term diabetes requires
mitochondrial GSH depletion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
289:H768–H776. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li Z, Zhang T, Dai H, Liu G, Wang H, Sun
Y, Zhang Y and Ge Z: Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress in
myocardial apoptosis of streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. J Clin
Biochem Nutr. 41:58–67. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sovolyova N, Healy S, Samali A and Logue
SE: Stressed to death-mechanisms of ER stress-induced cell death.
Biol Chem. 395:1–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Di Sano F, Ferraro E, Tufi R, Achsel T,
Piacentini M and Cecconi F: Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces
apoptosis by an apoptosome-dependent but Caspase 12-independent
mechanism. J Biol Chem. 281:2693–2700. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM and Samali
A: Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.
EMBO Rep. 7:880–885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xu MF, Ho S, Qian ZM and Tang PL:
Melatonin protects against cardiac toxicity of doxorubicin in rat.
J Pineal Res. 31:301–307. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Erşahin M, Sehirli O, Toklu HZ,
Süleymanoglu S, Emekli-Alturfan E, Yarat A, Tatlidede E, Yeğen BC
and Sener G: Melatonin improves cardiovascular function and
ameliorates renal, cardiac and cerebral damage in rats with
renovascular hypertension. J Pineal Res. 47:97–106. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|