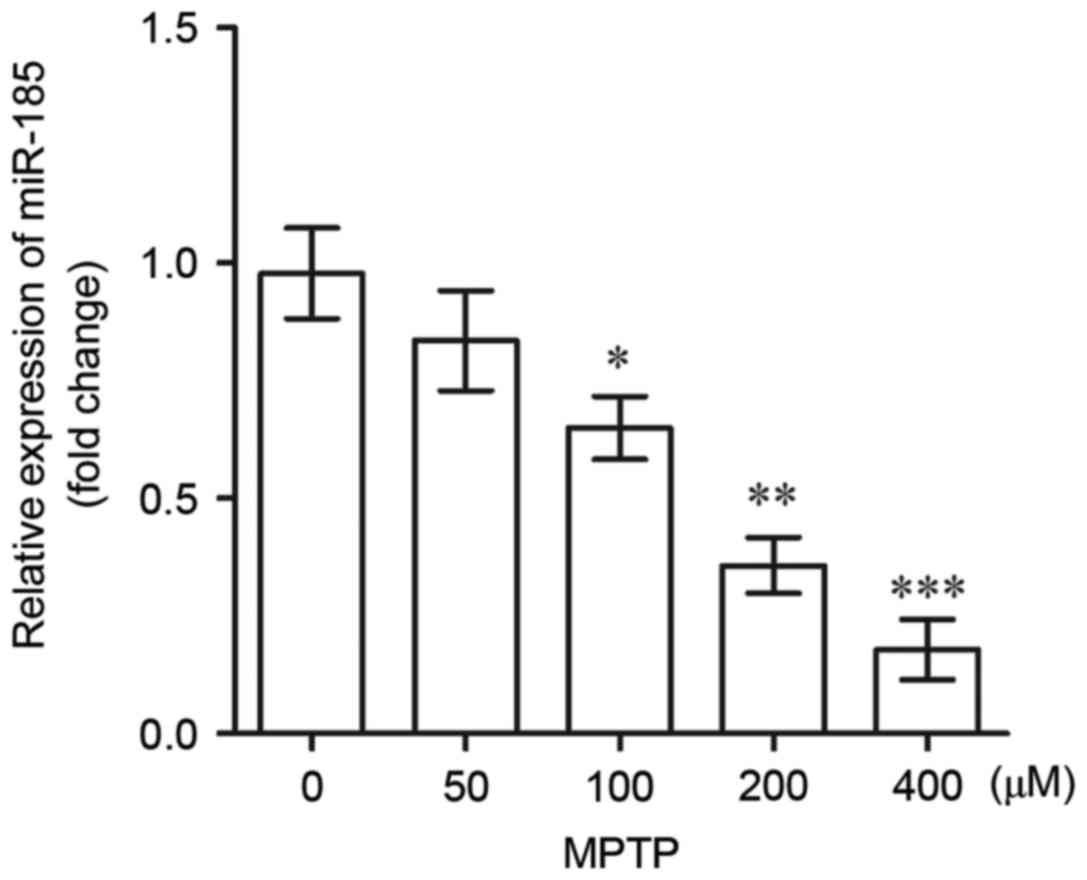
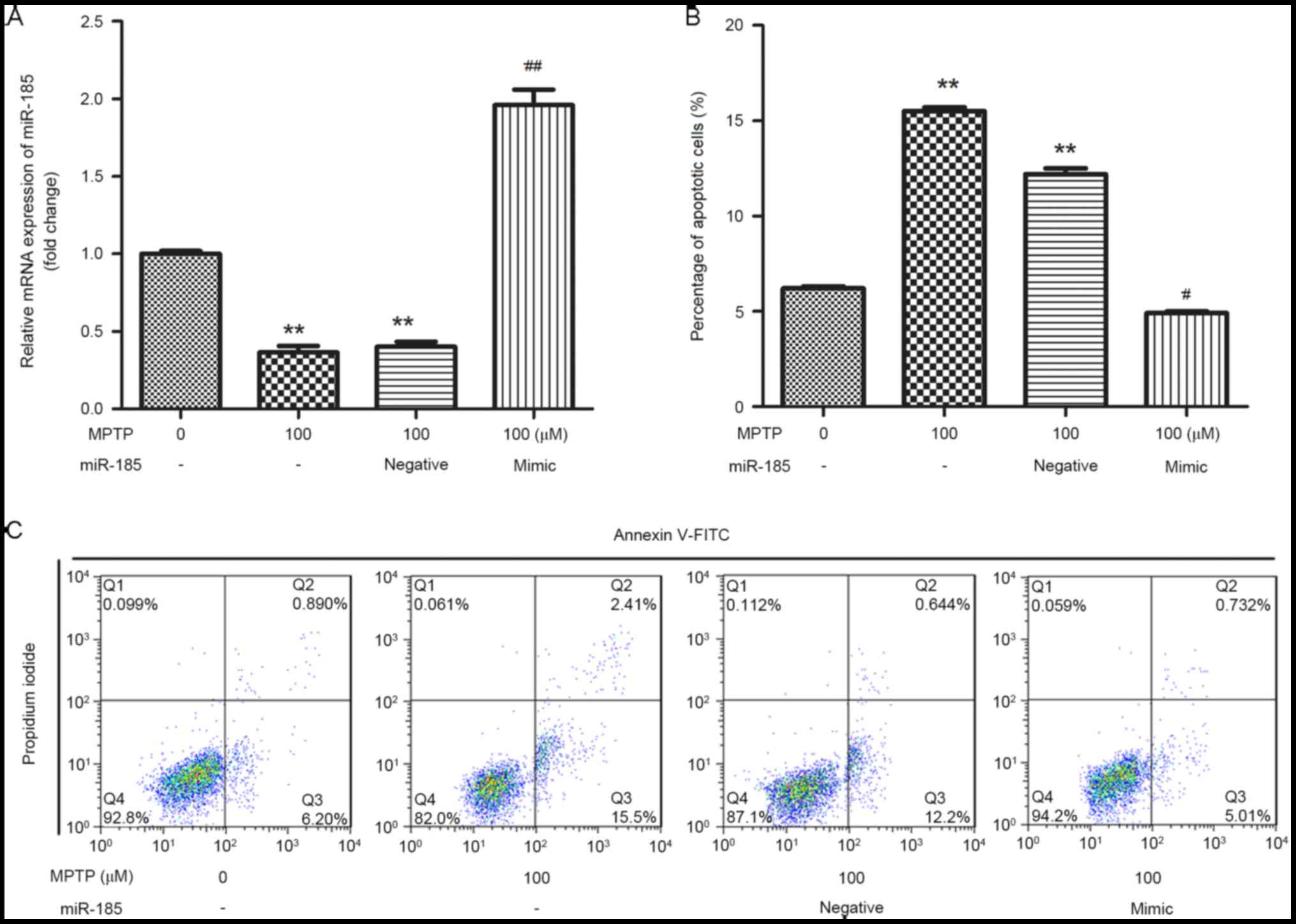
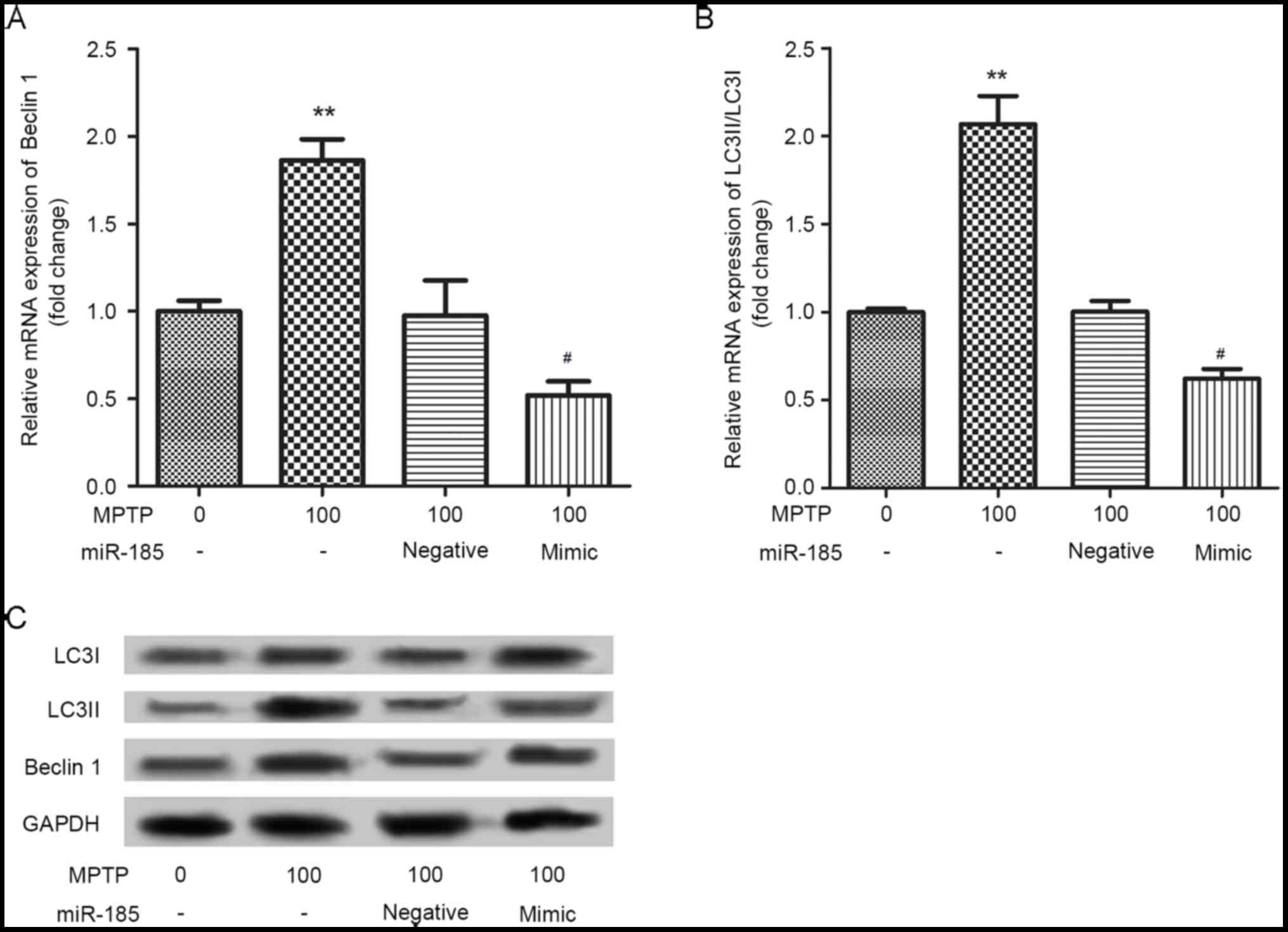
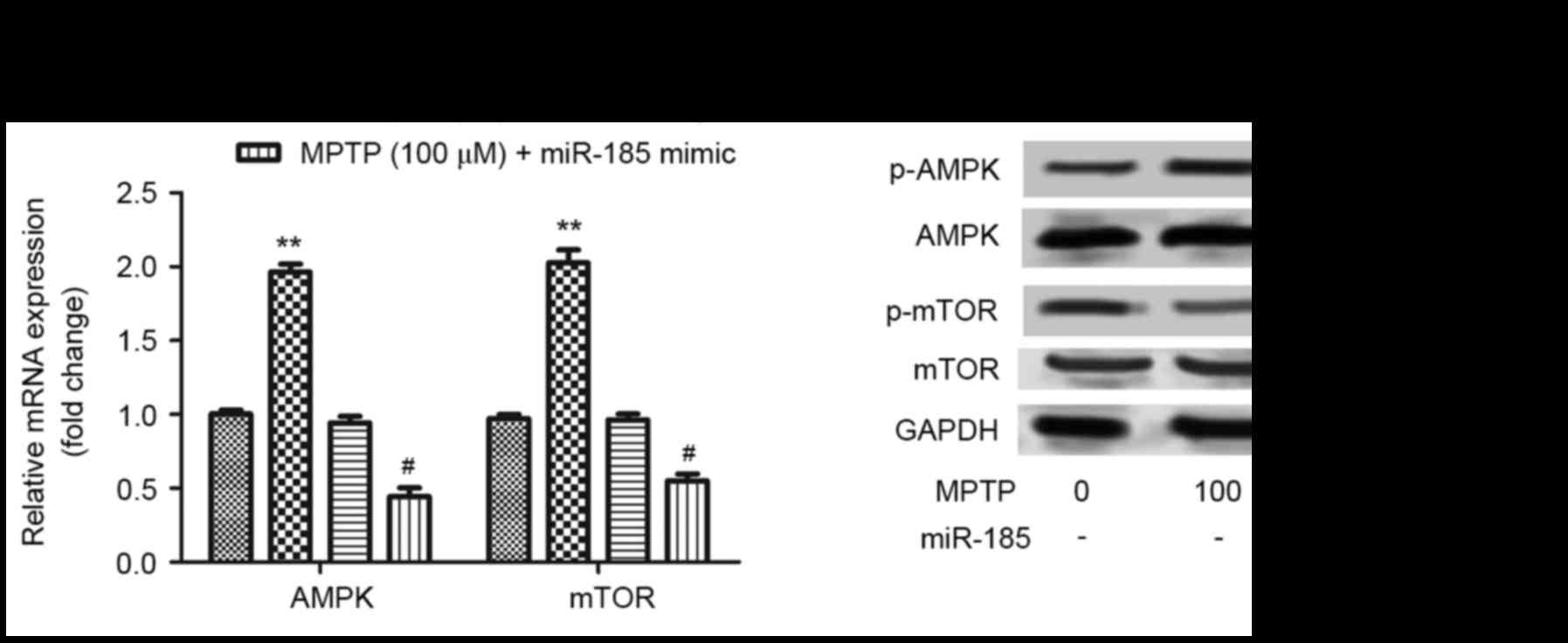
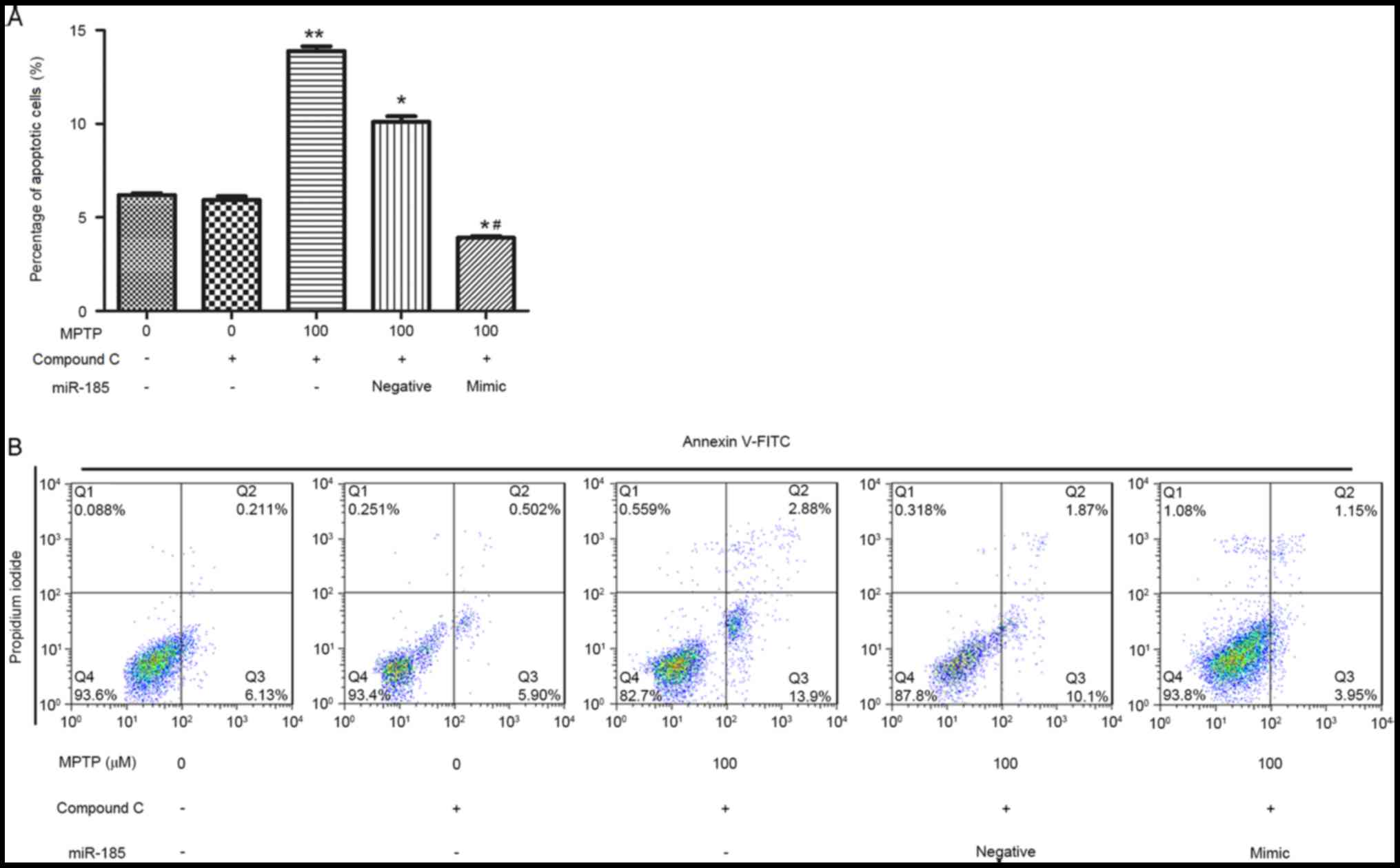
|
1
|
Moore DJ, West AB, Dawson VL and Dawson
TM: Molecular pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease. Annu Rev
Neurosci. 28:57–87. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Valente EM, Abou-Sleiman PM, Caputo V,
Muqit MM, Harvey K, Gispert S, Ali Z, Del Turco D, Bentivoglio AR,
Healy DG, et al: Hereditary early-onset Parkinson's disease caused
by mutations in PINK1. Science. 304:1158–1160. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dexter DT and Jenner P: Parkinson disease:
From pathology to molecular disease mechanisms. Free Radic Biol
Med. 62:132–144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Olanow CW and Tatton WG: Etiology and
pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 22:123–144.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jankovic J: Parkinson's disease: Clinical
features and diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 79:368–376.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bonifati V: Genetics of Parkinson's
disease-state of the art, 2013. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 20 Suppl
1:S23–S28. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Campdelacreu J: Parkinson disease and
Alzheimer disease: Environmental risk factors. Neurologia.
29:541–549. 2014.(In English, Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Collier TJ, Kanaan NM and Kordower JH:
Ageing as a primary risk factor for Parkinson's disease: Evidence
from studies of non-human primates. Nat Rev Neurosci. 12:359–366.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hwang O: Role of oxidative stress in
Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurobiol. 22:11–17. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Noyce AJ, Bestwick JP, Silveira-Moriyama
L, Hawkes CH, Giovannoni G, Lees AJ and Schrag A: Meta-analysis of
early nonmotor features and risk factors for Parkinson disease. Ann
Neurol. 72:893–901. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mouradian MM: MicroRNAs in Parkinson's
disease. Neurobiol Dis. 46:279–284. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Petillo D, Orey S, Tan AC, Forsgren L and
Khoo SK: Parkinson's disease-related circulating microRNA
biomarkers-a validation study. AIMS Med Sci. 2:7–14. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Khoo SK, Petillo D, Kang UJ, Resau JH,
Berryhill B, Linder J, Forsgren L, Neuman LA and Tan AC:
Plasma-based circulating microRNA biomarkers for Parkinson's
disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2:321–331. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hao B, Chen X, Dai D, Zou C, Wu X and Chen
J: Bioinformatic analysis of microRNA expression in Parkinson's
disease. Mol Med Rep. 11:1079–1084. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang H, Ye Y, Zhu Z, Mo L, Lin C, Wang Q,
Wang H, Gong X, He X, Lu G, et al: MiR-124 regulates apoptosis and
autophagy process in MPTP model of Parkinson's disease by targeting
to bim. Brain Pathol. 26:167–176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li S, Lv X, Zhai K, Xu R, Zhang Y, Zhao S,
Qin X, Yin L and Lou J: MicroRNA-7 inhibits neuronal apoptosis in a
cellular Parkinson's disease model by targeting Bax and Sirt2. Am J
Transl Res. 8:993–1004. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou Y, Lu M, Du RH, Qiao C, Jiang CY,
Zhang KZ, Ding JH and Hu G: MicroRNA-7 targets Nod-like receptor
protein 3 inflammasome to modulate neuroinflammation in the
pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Mol Neurodegener. 11:282016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ding H, Huang Z, Chen M, Wang C, Chen X,
Chen J and Zhang J: Identification of a panel of five serum miRNAs
as a biomarker for Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord.
22:68–73. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Langston JW and Irwin I: MPTP: Current
concepts and controversies. Clin Neuropharmacol. 9:485–507. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Itano Y and Nomura Y:
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-pyridinium ion (MPP+) causes DNA fragmentation
and increases the Bcl-2 expression in human neuroblastoma, SH-SY5Y
cells, through different mechanisms. Brain Res. 704:240–245. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ghavami S, Shojaei S, Yeganeh B, Ande SR,
Jangamreddy JR, Mehrpour M, Christoffersson J, Chaabane W, Moghadam
AR, Kashani HH, et al: Autophagy and apoptosis dysfunction in
neurodegenerative disorders. Prog Neurobiol. 112:24–49. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xiong N, Xiong J, Jia M, Liu L, Zhang X,
Chen Z, Huang J, Zhang Z, Hou L, Luo Z, et al: The role of
autophagy in Parkinson's disease: Rotenone-based modeling. Behav
Brain Funct. 9:132013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Perier C, Bové J and Vila M: Mitochondria
and programmed cell death in Parkinson's disease: Apoptosis and
beyond. Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:883–895. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tatton WG, Chalmers-Redman R, Brown D and
Tatton N: Apoptosis in Parkinson's disease: Signals for neuronal
degradation. Ann Neurol. 53 Suppl 3:S61–S72. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lynch-Day MA, Mao K, Wang K, Zhao M and
Klionsky DJ: The role of autophagy in Parkinson's disease. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2:a0093572012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pickford F, Masliah E, Britschgi M, Lucin
K, Narasimhan R, Jaeger PA, Small S, Spencer B, Rockenstein E,
Levine B and Wyss-Coray T: The autophagy-related protein beclin 1
shows reduced expression in early Alzheimer disease and regulates
amyloid beta accumulation in mice. J Clin Invest. 118:2190–2199.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang D, Lee H, Cao Y, Dela Cruz CS and
Jin Y: MiR-185 mediates lung epithelial cell death after oxidative
stress. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 310:L700–L710. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu J, Ai Q, Cao H and Liu Q: MiR-185-3p
and miR-324-3p predict radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
and modulate cancer cell growth and apoptosis by targeting SMAD7.
Med Sci Monit. 21:2828–2836. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mizushima N, Yamamoto A, Matsui M,
Yoshimori T and Ohsumi Y: In vivo analysis of autophagy in response
to nutrient starvation using transgenic mice expressing a
fluorescent autophagosome marker. Mol Biol Cell. 15:1101–1111.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schmelzle T and Hall MN: TOR, a central
controller of cell growth. Cell. 103:253–262. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hay N and Sonenberg N: Upstream and
downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 18:1926–1945. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Maiese K: mTOR: Driving apoptosis and
autophagy for neurocardiac complications of diabetes mellitus.
World J Diabetes. 6:217–224. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nakatsu Y, Kotake Y, Takai N and Ohta S:
Involvement of autophagy via mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)
inhibition in tributyltin-induced neuronal cell death. J Toxicol
Sci. 35:245–251. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen L, Xu B, Liu L, Luo Y, Yin J, Zhou H,
Chen W, Shen T, Han X and Huang S: Hydrogen peroxide inhibits mTOR
signaling by activation of AMPKalpha leading to apoptosis of
neuronal cells. Lab Invest. 90:762–773. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Arsikin K, Kravic-Stevovic T, Jovanovic M,
Ristic B, Tovilovic G, Zogovic N, Bumbasirevic V, Trajkovic V and
Harhaji-Trajkovic L: Autophagy-dependent and-independent
involvement of AMP-activated protein kinase in 6-hydroxydopamine
toxicity to SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1822:1826–1836. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|