|
1
|
Dogru M and Tsubota K: Pharmacotherapy of
dry eye. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 12:325–334. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin PY, Tsai SY, Cheng CY, Liu JH, Chou P
and Hsu WM: Prevalence of dry eye among an elderly chinese
population in Taiwan: The Shihpai eye study. Ophthalmology.
110:1096–1101. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Klotz SA, Penn CC, Negvesky GJ and Butrus
SI: Fungal and parasitic infections of the eye. Clin Microbiol Rev.
13:662–685. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bo R, Ma X, Feng Y, Zhu Q, Huang Y, Liu Z,
Liu C, Gao Z, Hu Y and Wang D: Optimization on conditions of
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides liposome by RSM and its
effects on the peritoneal macrophages function. Carbohyd Polym.
117:215–222. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cheng J, Zhou ZW, Sheng HP, He LJ, Fan XW,
He ZX, Sun T, Zhang X, Zhao RJ, Gu L, et al: An evidence-based
update on the pharmacological activities and possible molecular
targets of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides. Drug Des Devel
Ther. 9:33–78. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Qian D, Zhao Y, Yang G and Huang L:
Systematic review of chemical constituents in the genus
Lycium (Solanaceae). Molecules. 22:pii: E911. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xing X, Liu F, Xiao J and So KF:
Neuro-protective mechanisms of Lycium barbarum.
Neuromolecular Med. 18:253–263. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Amagase H, Sun BX and Borek C: Lycium
barbarum (goji) juice improves in vivo antioxidant biomarkers
in serum of healthy adults. Nutr Res. 29:19–25. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li SY, Yang D, Yeung CM, Yu WY, Chang RC,
So KF, Wong D and Lo AC: Lycium barbarum polysaccharides
reduce neuronal damage, blood-retinal barrier disruption and
oxidative stress in retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One.
6:e163802011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gan L, Zhang SH, Liu Q and Xu HB: A
polysaccharide-protein complex from Lycium barbarum
upregulates cytokine expression in human peripheral blood
mononuclear cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 471:217–222. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li XM, Ma YL and Liu XJ: Effect of the
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on age-related oxidative
stress in aged mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 111:504–511. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yu MS, Lai CS, Ho YS, Zee SY, So KF, Yuen
WH and Chang RC: Characterization of the effects of anti-aging
medicine Fructus lycii on beta-amyloid peptide neurotoxicity. Int J
Mol Med. 20:261–268. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ha KT, Yoon SJ, Choi DY, Kim DW, Kim JK
and Kim CH: Protective effect of Lycium chinense fruit on
carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity. J Ethnopharmacol.
96:529–535. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Luo Q, Cai Y, Yan J, Sun M and Corke H:
Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects and antioxidant activity of
fruit extracts from Lycium barbarum. Life Sci. 76:137–149.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gong H, Shen P, Jin L, Xing C and Tang F:
Therapeutic effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide (LBP)
on irradiation or chemotherapy-induced myelosuppressive mice.
Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 20:155–162. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He M, Pan H, Chang RC, So KF, Brecha NC
and Pu M: Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway
contributes to the protective effects of Lycium barbarum
polysaccharides in the rodent retina after
ischemia-reperfusion-induced damage. PLoS One. 9:e848002014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mi XS, Feng Q, Lo AC, Chang RC, Lin B,
Chung SK and So KF: Protection of retinal ganglion cells and
retinal vasculature by Lycium barbarum polysaccharides in a
mouse model of acute ocular hypertension. PLoS One. 7:e454692012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bucheli P, Vidal K, Shen L, Gu Z, Zhang C,
Miller LE and Wang J: Goji berry effects on macular characteristics
and plasma antioxidant levels. Optom Vis Sci. 88:257–262. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chan HC, Chang RC, Koon-Ching Ip A, Chiu
K, Yuen WH, Zee SY and So KF: Neuroprotective effects of Lycium
barbarum Lynn on protecting retinal ganglion cells in an ocular
hypertension model of glaucoma. Exp Neurol. 203:269–273. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qi B, Ji Q, Wen Y, Liu L, Guo X, Hou G,
Wang G and Zhong J: Lycium barbarum polysaccharides protect
human lens epithelial cells against oxidative stress-induced
apoptosis and senescence. PLoS One. 9:e1102752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Horng CT, Huang JK, Wang HY, Huang CC and
Chen FA: Antioxidant and antifatigue activities of polygonatum
alte-lobatum hayata rhizomes in rats. Nutrients. 6:5327–5337. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers P
and Smith F: Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and
related substances. Anal Chem. 28:350–356. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lee HW, Kim YH, Kim YH, Lee GH and Lee MY:
Discrimination of Lycium chinense and Lycium barbarum
by taste pattern and betaine analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med.
7:2053–2059. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bron AJ, Evans VE and Smith JA: Grading of
corneal and conjunctival staining in the context of other dry eye
tests. Cornea. 22:640–650. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma YS, Weng SW, Lin MW, Lu CC, Chiang JH,
Yang JS, Lai KC, Lin JP, Tang NY, Lin JG and Chung JG: Antitumor
effects of emodin on LS1034 human colon cancer cells in vitro and
in vivo: Roles of apoptotic cell death and LS1034 tumor xenografts
model. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:1271–1278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kashkouli MB, Pakdel F, Amani A, Asefi M,
Aghai GH and Falavarjani KG: A modified Schirmer test in dry eye
and normal subjects: Open versus closed eye and 1-minute versus
5-minute tests. Cornea. 29:384–387. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lemp MA: Advances in understanding and
managing dry eye disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 146:350–356. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liao CL, Lai KC, Huang AC, Yang JS, Lin
JJ, Wu SH, Wood Gibson W, Lin JG and Chung JG: Gallic acid inhibits
migration and invasion in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells through
suppressing the matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9, protein kinase B
(PKB) and PKC signaling pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:1734–1740.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Altinors DD, Bozbeyoglu S, Karabay G and
Akova YA: Evaluation of ocular surface changes in a rabbit dry eye
model using a modified impression cytology technique. Curr Eye Res.
32:301–307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
McCarty CA, Bansal AK, Livingston PM,
Stanislavsky YL and Taylor HR: The epidemiology of dry eye in
Melbourne, Australia. Ophthalmology. 105:1114–1119. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lai KC, Huang AC, Hsu SC, Kuo CL, Yang JS,
Wu SH and Chung JG: Benzyl isothiocyanate (BITC) inhibits migration
and invasion of human colon cancer HT29 cells by inhibiting matrix
metalloproteinase-2/-9 and urokinase plasminogen (uPA) through PKC
and MAPK signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 58:2935–2942. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Uchino M and Schaumberg DA: Dry eye
disease: Impact on quality of life and vision. Curr Ophthalmol Rep.
1:51–57. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bhavsar AS, Bhavsar SG and Jain SM: A
review on recent advances in dry eye: Pathogenesis and management.
Oman J Ophthalmol. 4:50–56. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gayton JL: Etiology, prevalence, and
treatment of dry eye disease. Clin Ophthalmol. 3:405–412. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Johnson EJ, Chung HY, Caldarella SM and
Snodderly DM: The influence of supplemental lutein and
docosahexaenoic acid on serum, lipoproteins, and macular
pigmentation. Am J Clin Nutr. 87:1521–1529. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Messmer EM: The pathophysiology,
diagnosis, and treatment of dry eye disease. Dtsch Arztebl Int.
112:71–81. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Stevenson W, Chauhan SK and Dana R: Dry
eye disease: An immune-mediated ocular surface disorder. Arch
Ophthalmol. 130:90–100. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zheng Q, Ren Y, Reinach PS, She Y, Xiao B,
Hua S, Qu J and Chen W: Reactive oxygen species activated NLRP3
inflammasomes prime environment-induced murine dry eye. Exp Eye
Res. 125:1–8. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu H, Begley C, Chen M, Bradley A,
Bonanno J, McNamara NA, Nelson JD and Simpson T: A link between
tear instability and hyperosmolarity in dry eye. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 50:3671–3679. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Deng R, Hua X, Li J, Chi W, Zhang Z, Lu F,
Zhang L, Pflugfelder SC and Li DQ: Oxidative stress markers induced
by hyperosmolarity in primary human corneal epithelial cells. PLoS
One. 10:e01265612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xiao B, Wang Y, Reinach PS, Ren Y, Li J,
Hua S, Lu H and Chen W: Dynamic ocular surface and lacrimal gland
changes induced in experimental murine dry eye. PLoS One.
10:e01153332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Karn PR, Kim HD, Kang H, Sun BK, Jin SE
and Hwang SJ: Supercritical fluid-mediated liposomes containing
cyclosporin A for the treatment of dry eye syndrome in a rabbit
model: Comparative study with the conventional cyclosporin A
emulsion. Int J Nanomedicine. 9:3791–3800. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Donnenfeld E and Pflugfelder SC: Topical
ophthalmic cyclosporine: Pharmacology and clinical uses. Surv
Ophthalmol. 54:321–338. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ciarcia R, Damiano S, Florio A, Spagnuolo
M, Zacchia E, Squillacioti C, Mirabella N, Florio S, Pagnini U,
Garofano T, et al: The protective effect of apocynin on
cyclosporine a-induced hypertension and nephrotoxicity in rats. J
Cell Biochem. 116:1848–1856. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
De Paiva CS, Corrales RM, Villarreal AL,
Farley WJ, Li DQ, Stern ME and Pflugfelder SC: Corticosteroid and
doxycycline suppress MMP-9 and inflammatory cytokine expression,
MAPK activation in the corneal epithelium in experimental dry eye.
Exp Eye Res. 83:526–535. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mocan A, Vlase L, Vodnar DC, Bischin C,
Hanganu D, Gheldiu AM, Oprean R, Silaghi-Dumitrescu R and Crișan G:
Polyphenolic content, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of
Lycium barbarum L. and Lycium chinense Mill. leaves.
Molecules. 19:10056–10073. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Uchino Y, Kawakita T, Miyazawa M, Ishii T,
Onouchi H, Yasuda K, Ogawa Y, Shimmura S, Ishii N and Tsubota K:
Oxidative stress induced inflammation initiates functional decline
of tear production. PLoS One. 7:e458052012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Drouault-Holowacz S, Bieuvelet S, Burckel
A, Rigal D, Dubray C, Lichon JL, Bringer P, Pilon F and
Chiambaretta FR: Antioxidants intake and dry eye syndrome: A
crossover, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Eur J Ophthalmol.
19:337–342. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Blades KJ, Patel S and Aidoo KE: Oral
antioxidant therapy for marginal dry eye. Eur J Clin Nutr.
55:589–597. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Higuchi A, Inoue H, Kawakita T, Ogishima T
and Tsubota K: Selenium compound protects corneal epithelium
against oxidative stress. PLoS One. 7:e456122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang JH, Wang HZ, Zhang M and Zhang SH:
Effect of anti-aging Lycium barbarum polysaccharide. Acta
Nutrimenta Sinica. 24:189–191. 2002.(In Chinese).
|
|
52
|
Petrov A, Perekhvatova N, Skulachev M,
Stein L and Ousler G: SkQ1 ophthalmic solution for dry eye
treatment: Results of a phase 2 safety and efficacy clinical study
in the environment and during challenge in the controlled adverse
environment model. Adv Ther. 33:96–115. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kim YG, Lim HH, Lee SH, Shin MS, Kim CJ
and Yang HJ: Betaine inhibits vascularization via suppression of
Akt in the retinas of streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemic rats.
Mol Med Rep. 12:1639–1644. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li JM, Ge CX, Xu MX, Wang W, Yu R, Fan CY
and Kong LD: Betaine recovers hypothalamic neural injury by
inhibiting astrogliosis and inflammation in fructose-fed rats. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 59:189–202. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hua X, Su Z, Deng R, Lin J, Li DQ and
Pflugfelder SC: Effects of L-carnitine, erythritol and betaine on
pro-inflammatory markers in primary human corneal epithelial cells
exposed to hyperosmotic stress. Curr Eye Res. 40:657–667. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Schwab U, Törrönen A, Toppinen L, Alfthan
G, Saarinen M, Aro A and Uusitupa M: Betaine supplementation
decreases plasma homocysteine concentrations but does not affect
body weight, body composition, or resting energy expenditure in
human subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 76:961–967. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Garrett Q, Khandekar N, Shih S, Flanagan
JL, Simmons P, Vehige J and Willcox MD: Betaine stabilizes cell
volume and protects against apoptosis in human corneal epithelial
cells under hyperosmotic stress. Exp Eye Res. 108:33–41. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
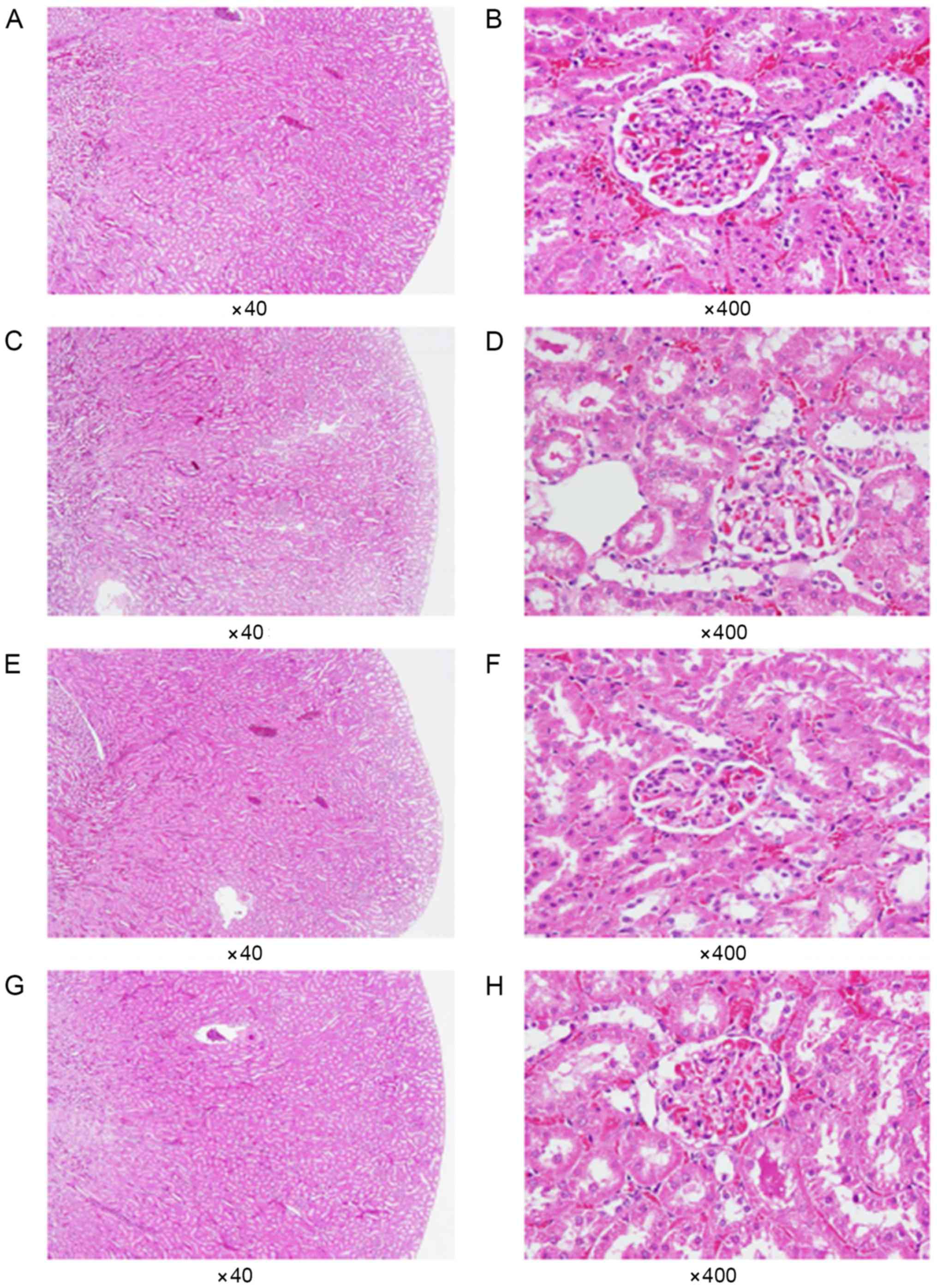
Amagase H: General toxicity and
histological analysis from acute toxicological study of a
standardized Lycium barbarum (Goji) juice (GoChiTM) in
rodents. Faseb J. 22:S7222008.
|