Introduction
Escherichia coli (E. coli) O157:H7 is
a type of pathogenic bacterium that infects humans and livestock
primarily through contaminated food. It can cause abdominal pain,
hemorrhagic fever or bloody stools, and can induce secondary
haemolytic uraemic syndrome in infants, preschool children or weak,
elderly individuals. In addition, due to its strong drug
resistance, it is very hard to eliminate O157:H7 from contaminated
food sources. O157:H7 contamination has now become an international
food security concern (1). The
American Centers for Disease Control has revealed that E.
coli O157:H7 is one of the major pathogenic bacteria causing
food-borne diseases; thus, poses a serious threat to public health.
Furthermore, this strain has been detected in pork, beef and mutton
in China (2).
There are several detection methods currently used
for pathogenic bacteria, including culture-based, enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and polymerase chain reaction
(PCR)-based methods (3–5). However, these methods are usually
time-consuming, expensive and insensitive, which makes them
unsuitable for the detection of this pathogen. Therefore, it is
necessary to develop more efficient detection apparatus.
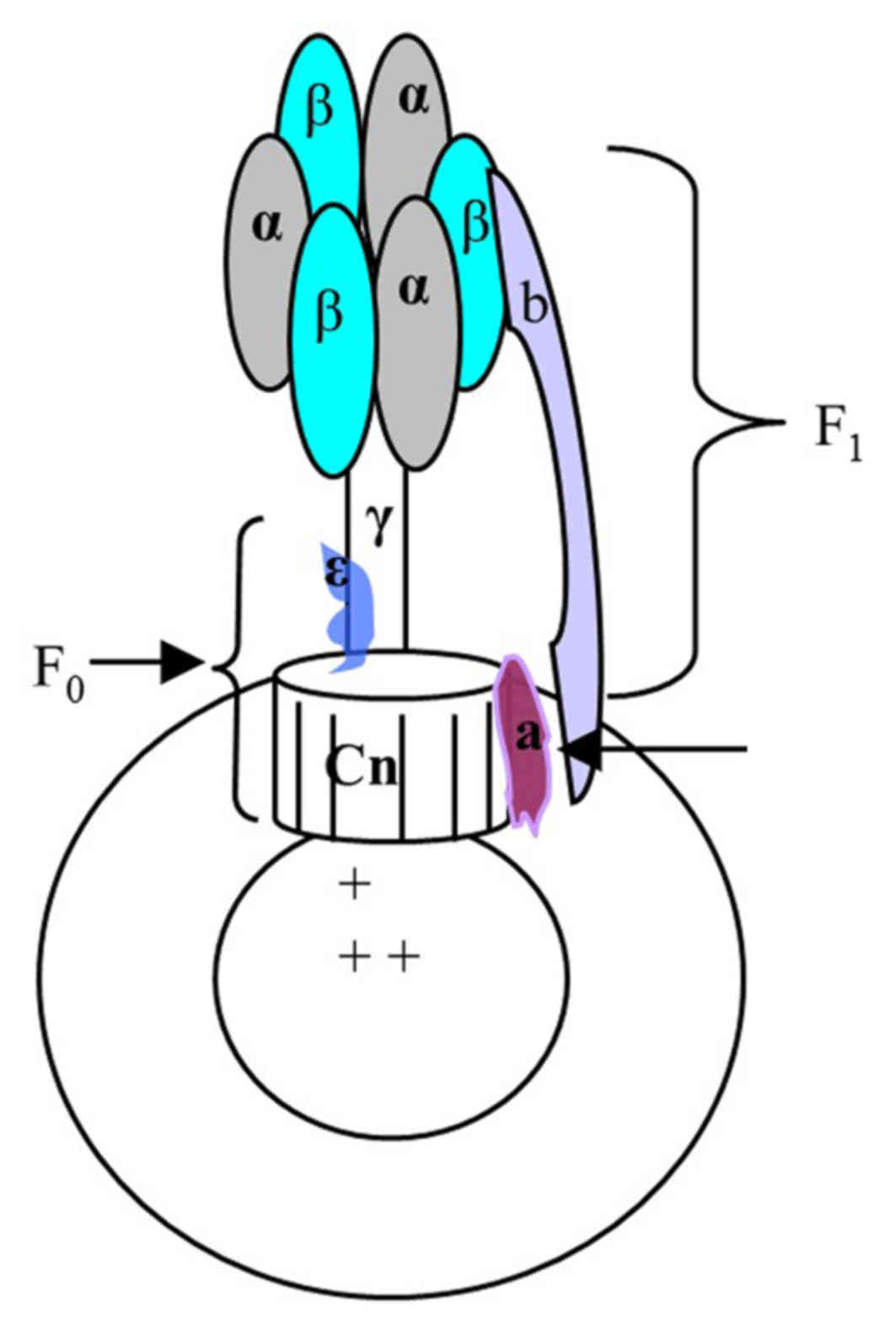
F0F1-ATPase, located in the mitochondria and/or the
chloroplast thylakoid of eukaryotic organisms and the bacterial
plasma membrane, catalyzes the synthesis of ATP using the
transmembrane proton gradient. In E. coli, the soluble F1
and transmembrane F0 parts are comprised of the α3β3γδε and ab2cn
subunits, respectively. These two parts are connected by the stalks
of γε in the centre and b2 δ on the outside. When the downhill
proton passes through F0, the c and γε subunits are rotated leading
to conformational changes in F1, which promotes the formation of
ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate, and vice versa. As a result,
F0F1-ATPase forms a molecule size motor, which can transform the
electric chemical potential energy into chemical energy. If this
process is disturbed by other factors, the rate of ATP synthesis
and proton flux maybe altered; this phenomenon maybe reflected by
pH sensitive substances (6–7).
F1300 is a pH sensitive fluorescent probe that can be used as an
indicator of changes in the pH of F0F1-ATPase. During ATP
synthesis, protons are pumped out of the chromatophore and this
transfer of protons is detected by F1300 (4–5,8).
This concept was used to construct the immuno-rotary biosensor
(IRB) for detecting specific targets, which achieved great success
(4–5,9–10).
Although this type of biosensor has been used to detect a virus
(3,6–7),
detection of much larger antigen such as a single bacterium has not
been reported. The aim of the present study was to investigate the
potential use of this method for the detection of E. coli
O157:H7.
Materials and methods
Bacterial strains
E. coli O157:H7 (strain no. ATCC35150) was
obtained from the Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center
(Guangzhou, China) and was incubated in nutrient broth medium at
37°C for 24 h. The bacterial suspension was then diluted to
10−4, 10−5 and 10−6 in
bacteria-free PBS. A total of 100 µl was transferred to a panel for
further cultivation and each dilution gradient sample was tripled.
The bacterial clone in the incubated sample was counted 24 h later.
Surplus bacteria were in activated by heating to 80°C for 1 h, then
10 ml was centrifuged for 30 min at 4,000 × g and 4°C. The
supernatant was discarded and the precipitate was resuspended with
sterile normal saline (NS) to the original volume. This process was
repeated twice to remove medium complex components and the
precipitate was resuspended with sterile NS to the original volume
following the third centrifugation.
Salmonella (strain no. ATCC14028; American
Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA, USA) and Escherichia
coli (E. coli; strain no. CMCC-44101; China Medical
Culture Collection, Beijing, China) were also subjected to the same
procedure as O157:H7; they were tested with the same methodology to
estimate the specificity of O157:H7.
Preparation of ‘signal into
components’
‘Signal into components’ is a chromatophore with the
pH sensitive fluorescent probe, F1300.
Preparation of chromatophores
Thermomicrobium-roseumwa0073 (ATCC27502) were
purchased from the American Type Culture Collection and incubated
at 60°C for 24 h. The cells were harvested by centrifugation at
4,000 × g for 30 min at 4°C and resuspended in buffer (20 mM
Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, 0.1 mM PMSF and 2 mM
MgCl2, pH 8.0) followed by ultrasonication for 10 min in
an ice bath. The suspension was centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 30
min at 4°C to remove unbroken cells and cell fractions. The
cell-free supernatant was centrifuged at 40,000 × g for 1 h at 4°C
to collect membrane vesicles, termed chromatophores. The
chromatophores were stored in 50% glycerol at −80°C. The
chromatophore structure is presented in Fig. 1.
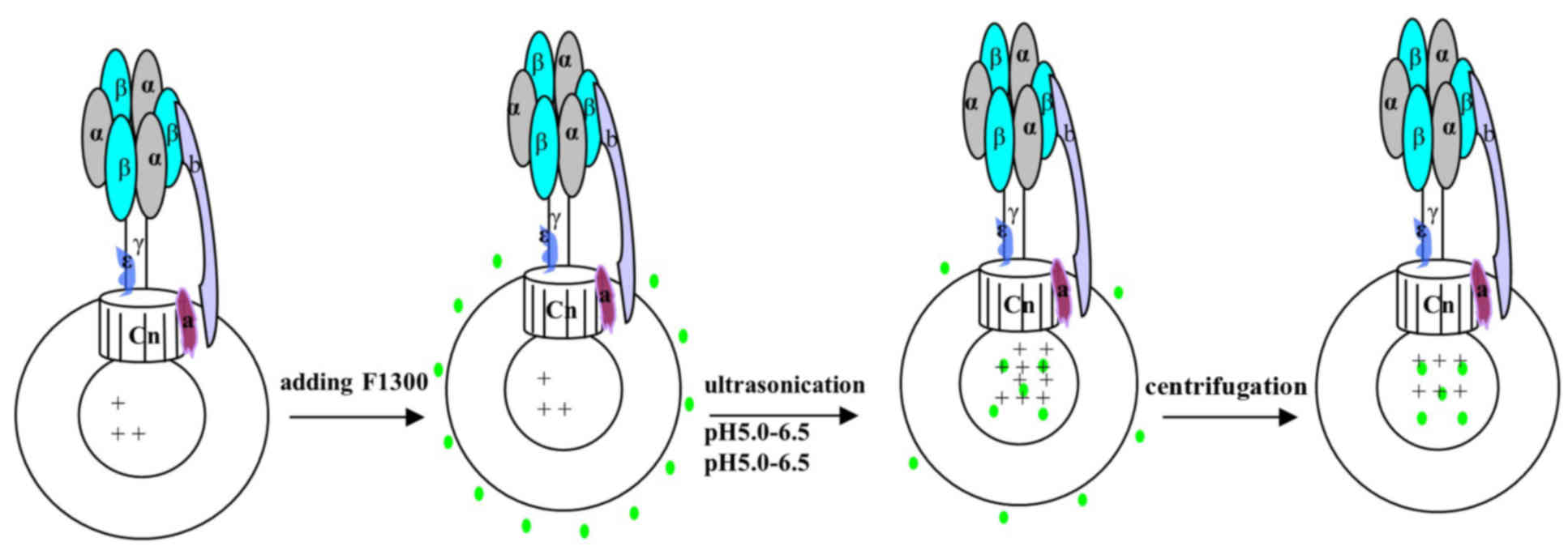
Labeling of chromatophores with
F1300
The chromatophores were centrifuged at 12,000 × g at
4°C for 30 min to remove glycerol, then they were resuspended with
buffer (pH 6.0, 0.1 mM tricine, 5 mM MgCl2 and 5 mM
KCl). A total of 1–2 µl F1300 (1 mg/ml) was added to 600 µl
chromatophores prior to ultrasonication for 3 min in an ice bath,
to incorporate the probe into the inner part of the chromatophores.
The free F1300 fraction was purified by centrifugation at 12,000 ×
g for 30 min at 4°C. The purification process was repeated three
times to remove free F1300, and aliquots of the supernatant were
collected to assess the level of purification. The precipitate was
resuspended in tricine-NaOH buffer (0.1 mM tricine, 5 mM
MgCl2 and 5 mM KCl, pH 6.5) and then the relative
fluorescence signal was detected using the Varioskan Flash spectral
scanning multimode reader (excitation, 485 nm; emission, 538 nm;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). When the
relative fluorescence signal did not decrease further, the free
F1300 was removed completely. The ATP hydrolysis activity of the
labeled chromatophores was assayed using the enzyme coupling method
with pyruvate kinase and lactate dehydrogenase, as described
previously (4). The unit of enzyme
activity was defined by hydrolyzing 1 µmol ATP per minute with 1 mg
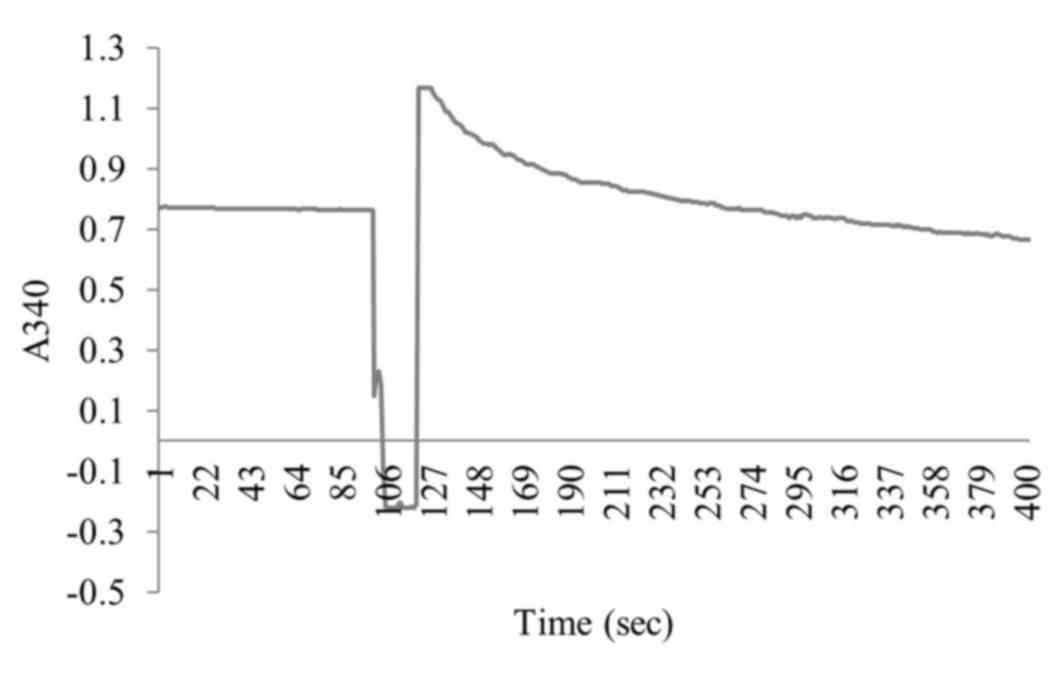
chromatophores (Fig. 2).
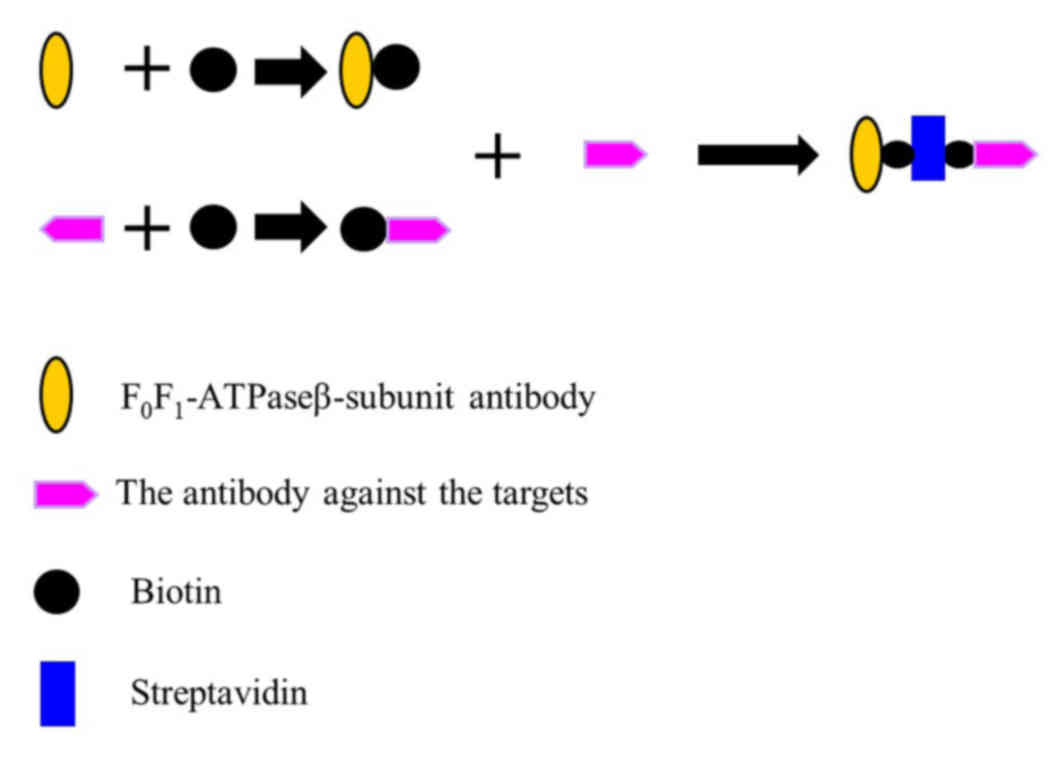
Constructing the O157:H7 detector
A ATPase β-subunit antibody [Homemade, as previously
described (10)], biotin
(Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) and an antibody
targeted against O157:H7 (cat. no. AB81131; Abcam, Cambridge, UK)
were used for the following: 2 µl of 10 mM biotin was added to 500
µl of 3 mg/ml β-subunit antibody for 15–30 min at room temperature,
then free biotin was removed via dialysis to produce the β-subunit
antibody-biotin complex. In addition, 2 µl of 10 mM biotin was
added to 500 µl of 3 mg/ml O157:H7 antibody for 15–30 min at room
temperature, then free biotin was removed via dialysis to produce
the O157:H7 antibody-biotin complex. To create the capture system
complex, a reaction was set up that contained equal amounts
ofβ-subunit antibody-biotin complex (200 µl, 50 mM) and O157:H7
antibody-biotin complex (200 µl, 50 mM). Subsequently, 200 µl 55 mM
streptavidin (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) was added and incubated
for 15–30 min at room temperature. This produced the capture system
complex: the β-subunit antibody-biotin-Streptavidin-biotin-O157:H7
antibody (Fig. 3). The capture
system complexes and chromatophores labeled with F1300 (F1300-ch)
were then mixed to a 4:1 dilution, and were incubated at 37°C for 1
h. This produced the biosensor used in the present study (Fig. 4). Three different reactions were
set up, Group A, Group Band Group C, to demonstrate that the
construction of the immuno-biosensor was successful, based on the
fluorescence of F1300-ch with different loads: Group A, F1300-ch
control; Group B, F1300-ch-β-subunit antibody-biotin-Streptavidin
complex; Group C, F1300-ch-β-subunit
antibody-biotin-Streptavidin-biotin-O157:H7 antibody complex.
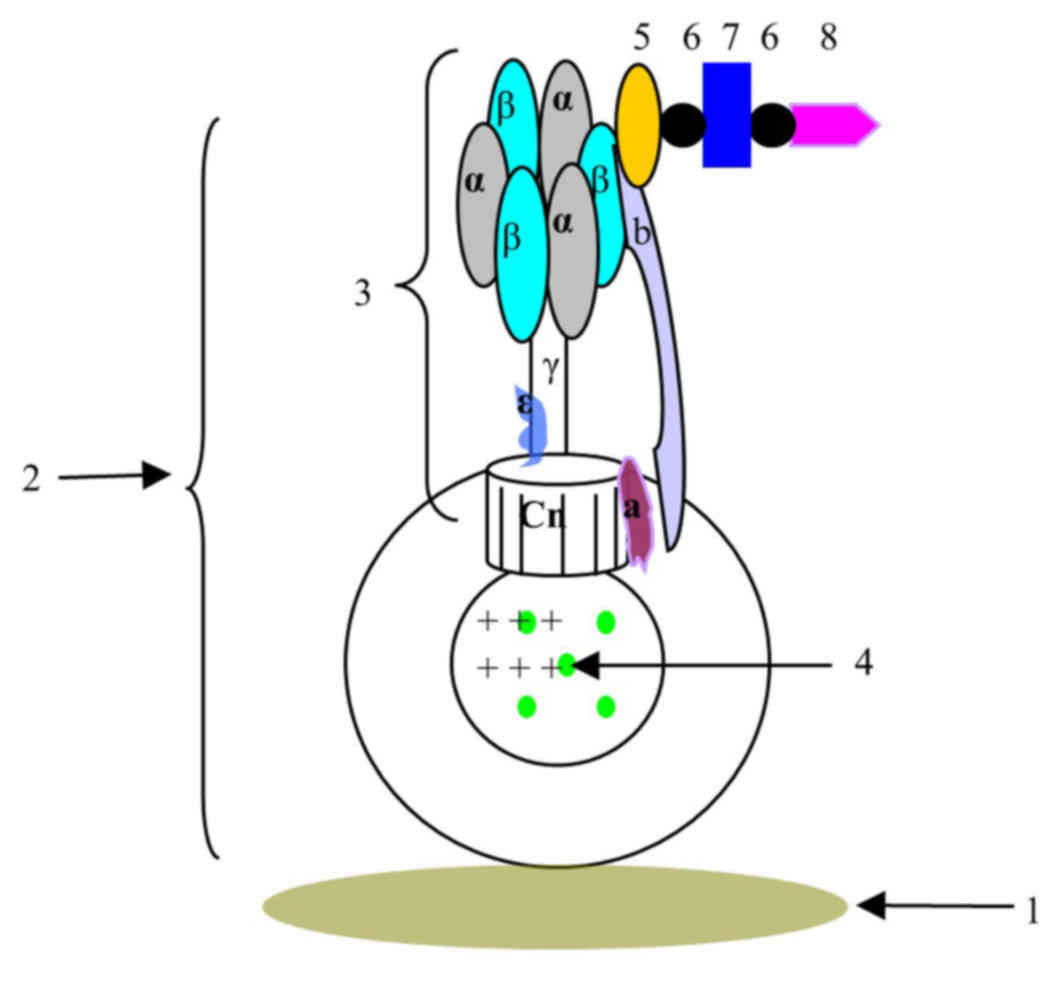 | Figure 4.Schematic view of the biosensor
constructed based on F0F1-ATPase. 1, detection carrier; 2,
chromatophore complex; 3, ATPase; F1300-ch; 5, β-subunit antibody;
6, biotin; 7, streptavidin; 8, O157:H7 antibody; Cn, subunit c; a,
subunit a; b, subunit b. |
Fluorescence assay
The concentration of the bacterial suspension was
adjusted to 5×103, 5×104 and 5×105
cfu/ml. In order to generate 102, 103 and
104 cfu bacteria/well, respectively, four groups were
set up: Group 1, control (sterile NS); Group 2, 102 cfu
bacteria/well; Group 3, 103 cfu bacteria/well; Group 4,
104 cfu bacteria/well. To each well, 50 µl biosensor and
20 µl of the bacterial suspension were added. Following incubation
for 30 min at 37°C, 70 µl ATP synthesis buffer (50 mmol/l tricine,
10% glycerol, 2 mmol/ADP, 5 mmol/l NaH2PO4
and 5 mmol/l MgCl2, pH 8.0) was added to each well for
further incubation at 45°C for 15 min. The relative fluorescence
signal was detected using the Varioskan Flash spectral scanning
multimode reader (excitation, 485 nm; emission, 538 nm; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.).
Specificity
ATCC14028 Salmonella and CMCC44101 E.
coli were subjected to the same protocols in order to determine
the specificity to O157:H7. The bacterial concentration for each
group and pathogenic bacteria are presented in Table I.
 | Table I.Bacterial concentration in assay
wells to estimate the specificity of the O157:H7 biosensor. |
Table I.
Bacterial concentration in assay
wells to estimate the specificity of the O157:H7 biosensor.
|
| Bacterial
concentration (cfu/well) |
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
| Strain of
pathogenic bacteria | Control | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 5 |
|---|
| E. coli
O157:H7 | 0 | 27 | 133 | 265 | 1,325 |
| E. coli
CMCC44101 | 0 | 35 | 175 | 350 | 1,750 |
| Salmonella
ATCC14028 | 0 | 26 | 128 | 255 | 1,275 |
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 10 software (SPSS,
Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The correlation was assessed by linear
regression and a Dunnett's T3 post hoc test was used for multiple
comparisons. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically
significant difference.
Results
Construction of the
immuno-biosensor
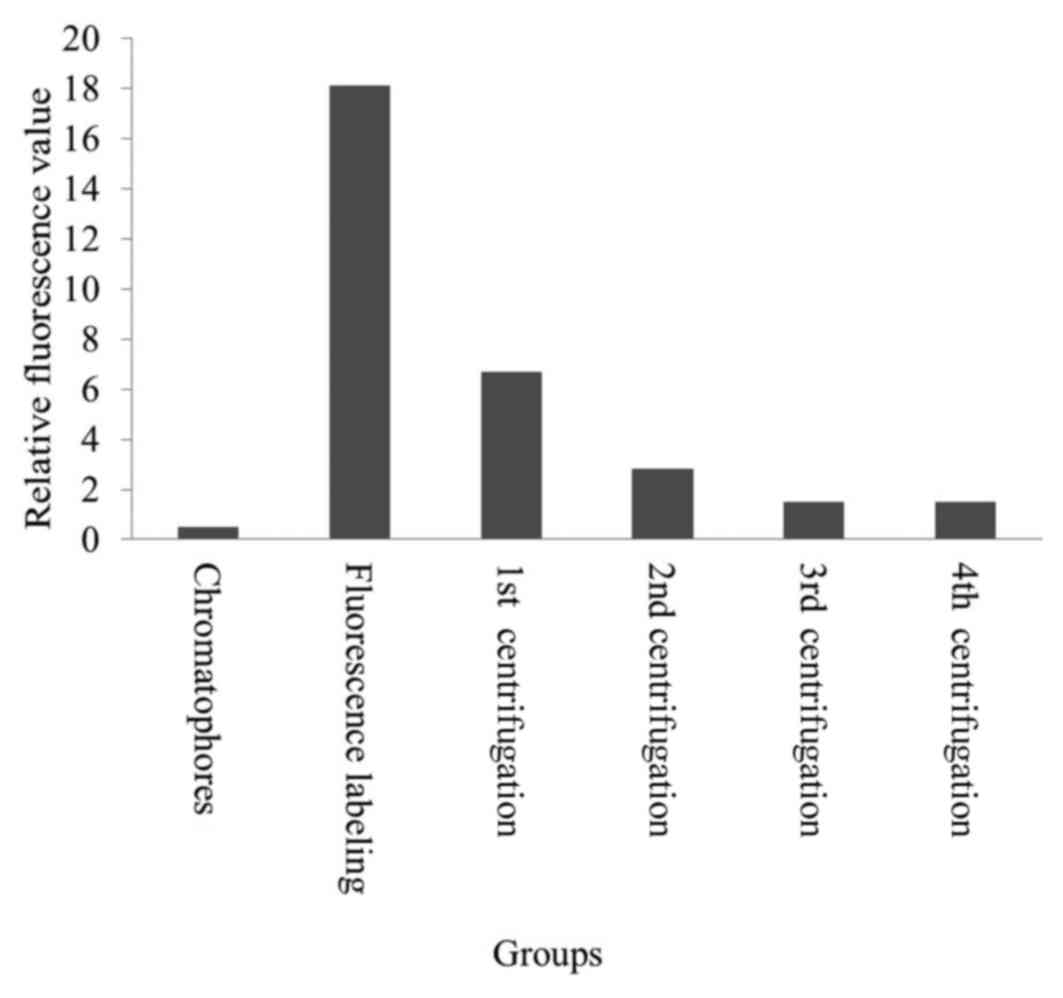
The inner chromatophores were successfully labeled
with the fluorescent pH indicator F1300 as a unidirectional label
(Fig. 5; Table II). The fluorescence intensity of
the control chromatophores was the lowest. The fluorescence
intensity of the mixture of chromatophores and F1300 was much
higher than the control; however, it decreased with ultrasonication
and the four subsequent centrifugation steps. Initially, a part of
F1300 entered the chromatophore with ultrasonication; however, the
remaining free F1300 stayed out of the chromatophore, producing
high fluorescence intensity. Following three centrifugation
procedures, the fluorescence intensity decreased to 1.49. This
indicated that the free F1300 were removed by centrifugation. The
fluorescence intensity did not change following the fourth round of
centrifugation; it was 2.8 times higher than that of the control.
The results revealed that free F1300 was completely removed, while
the fluorescent probe F1300 labeled the inner chromatophores. The
synthetic activity of F1300-chisshown in Fig. 6; the enzyme activity was 106.4
µmol/mg/min.
 | Table II.Results of F1300 labelling in the
inner chromatophores. |
Table II.
Results of F1300 labelling in the
inner chromatophores.
| Group | Relative
fluorescence value |
|---|
| Chromatophores |
0.519 |
| Fluorescence
labeling | 18.12 |
| 1st
centrifugation |
6.69 |
| 2nd
centrifugation |
2.82 |
| 3rd
centrifugation |
1.49 |
| 4th
centrifugation |
1.48 |
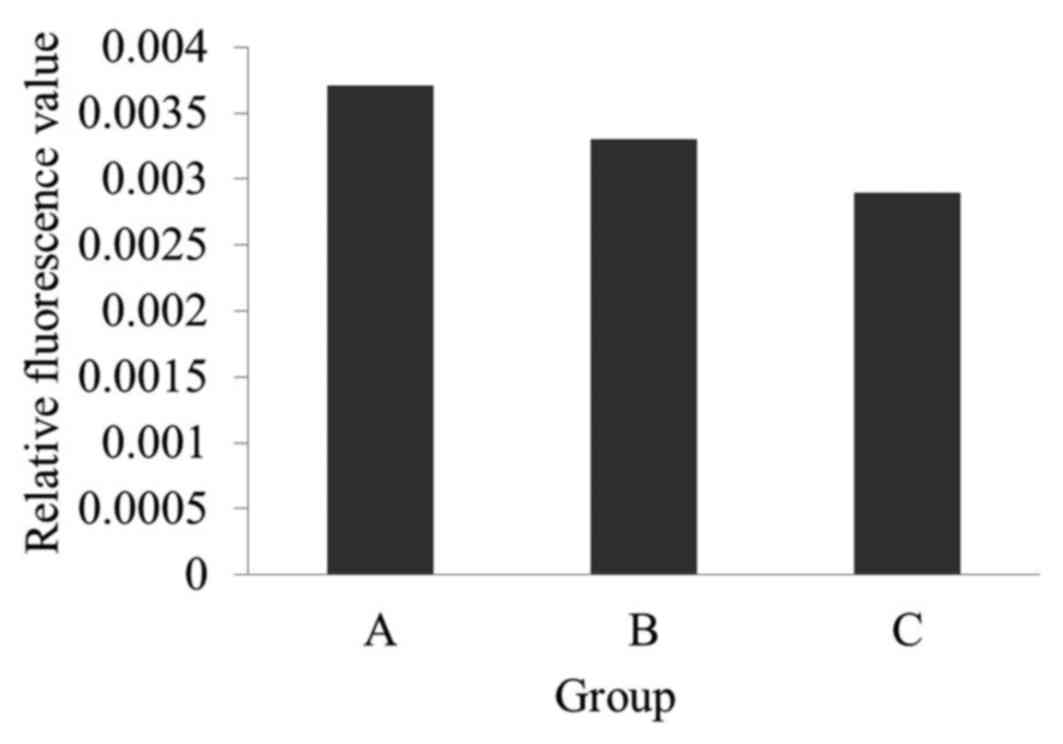
As presented in Fig.
7, the fluorescence intensity of group A was the highest, while
group C was the lowest. This indicated that the capture system
complex (β-subunit antibody-biotin-Streptavidin-biotin-substrate
antibody) was successfully established. In addition, it revealed
that the greater the load on F0F1-ATPase, the lower the enzyme
activity and thus, the lower the relative fluorescence. Therefore,
the F1300-labeled chromatophores were used in the present
study.
Sensitivity for O157:H7
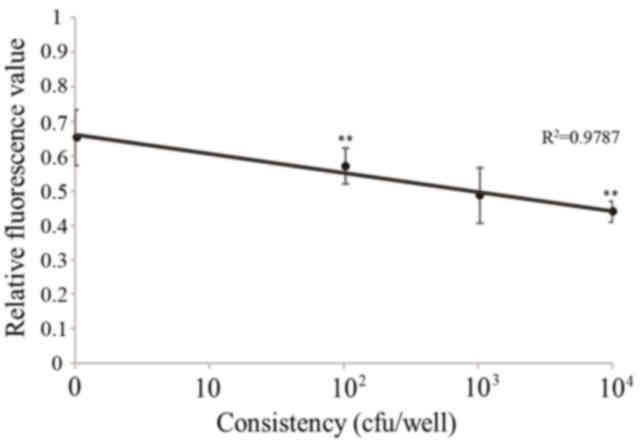
The fluorescence value gradually decreased with the
increasing concentration of O157:H7 (Fig. 8; Table III). Following statistical
analysis, the results revealed that there were significant
differences between the control and 104 cfu group
(P<0.01), and between the 102 and 104 cfu
groups (P<0.01). The results of O157:H7 detection using this
method identified a strong positive gradient between
102−104 cfu (R2=0.9818).
 | Table III.Results of the comparison between the
concentration groups. |
Table III.
Results of the comparison between the
concentration groups.
| Concentration group
(cfu/well) | P-value |
|---|
| 0 | 102 | 0.19239 |
| 0 | 103 | −0.06347 |
| 0 | 104 |
0.00327a |
| 102 | 103 | 0.63584 |
| 102 | 104 |
0.00015b |
| 103 | 104 | 0.60539 |
Specificity for O157:H7
The curve of 101−103 cfu
identified a good separation, which is consistent with the positive
threshold value for O157:H7, 0.063–0.075. The relative fluorescence
value of the CMCC44101 E. coli groups was 0.035–0.043 and
0.035–0.052 for Salmonella. These results demonstrated that
this biosensor has specificity for O157:H7 (Fig. 9; Table IV).
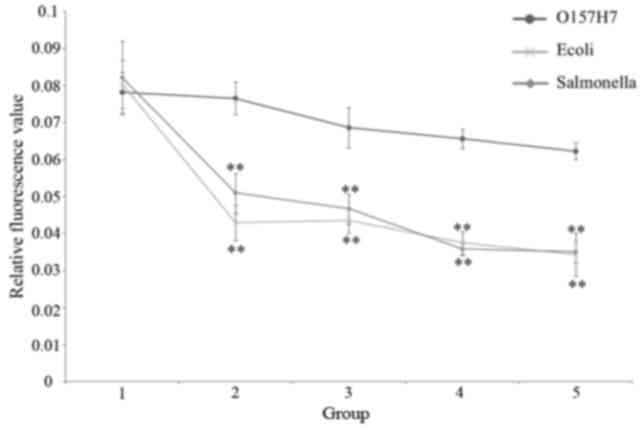 | Figure 9.Specificity for O157:H7 in Groups 1
to 5, comparing O157:H7, Salmonella and E. coli. **P<0.01
vs. O157:H7. E. coli, Escherichia coli; Group 1, control
(sterile normal saline); Group 2, 27, 35 and 26 cfu/well for
O157:H7, E. coli and Salmonella, respectively; Group
3,133, 175 and 128 cfu/well for O157:H7, E. coli and
Salmonella, respectively; Group 4, 265, 350 and 255 cfu/well
for O157:H7, E. coli and Salmonella, respectively;
Group 5, 1,325, 1,750 and 1,275 cfu/well for O157:H7, E.
coli and Salmonella, respectively. |
 | Table IV.Results of the comparison between the
O157:H7, E. coli and salmonella groups. |
Table IV.
Results of the comparison between the
O157:H7, E. coli and salmonella groups.
| Group
comparison | P-value |
|---|
| O157:H7 vs. E.
coli |
|
Group1 | 0.69 |
| Group
2 |
2.81×10−5a |
| Group
3 |
1.03×10−4a |
| Group
4 |
1.89×10−7a |
| Group
5 |
9.82×10−7a |
| O157:H7 vs.
Salmonella |
| Group
1 | 0.36 |
| Group
2 |
2.15×10−5b |
| Group
3 |
2.00×10−4b |
| Group
4 |
1.16×10−6b |
| Group
5 |
4.92×10−5b |
Time of detection
This method is short and includes only four steps:
bacterium solution treatment, preparation of biosensors, loading
and testing. The time required for each step was 2, 1.75, 0.5 and
0.25 h, respectively, thus 4.5 h in total. Though this method
requires separation and enrichment of target bacteria when testing
samples, the limit of detection was 100 cfu. In addition, by
combining it with the immune magnetic separation technique, the
time required for sample pretreatment was 8.5 h and the total time
for testing samples was <16 h.
Discussion
F0F1-ATPase has the following two characteristics:
i) it can use the H+ gradient between the inside and
outside of chromatophores to produce ATP and it can also hydrolyze
ATP by reverse transporting H+. During ATP synthesis,
protons are pumped to the outside from the inside of
chromatophores, which leads to a change in proton concentration
inside the chromatophores; ii) F0F1-ATPase rotation speed and the
loads on its subunits are positively correlated. Based on its two
enzymology characteristics, the F0F1-ATPase nano-biosensor is
labeled by pH sensitive F1300, a fluorospectrophotometric probe, to
produce the functional unit, F1300-ch. The F1300-ch combined with
the capture system achieves the molecular motor nano-biosensor,
which can be used as a fast detection technique (7,11–13).
Liu et al (8) directly
observed the mechanically driven proton influx or efflux in F0
coupled with rotation of F1 at a single molecular level; the
specific underlying mechanism will be studied further in the
future.
F0F1-ATPase activity is regulated by external links
on b subunits with different molecular weights. It is inhibited
when anti-b subunit antibodies, streptavidin and H9 antibodies link
on to the β subunits successively (7). The holoenzyme activity was inhibited
as it linked to more external substances, including
Chloramphenicol, Listeria monocytogenes, H9 virus, Clenbuterol and
Deoxynivalenol (4–5,7,9,10).
When the O157:H7 loads into the chromatophore, the chromatophore
cannot move completely and there are no alterations in protons
between the internal and external chromatophore, therefore the
alteration in relative fluorescence intensity should be generated
by those non-O157:H7-loaded chromatophores in each detection well.
In another way, this is similar to the competition method in ELISA;
the stronger the concentration, the lower the changing biosensors
and so the smaller the change value (14,15).
The application of F0F1-ATPase immuno-biosensors for
the detection of O157:H7 has not been reported previously. The
present study used biosensors to detect O157:H7, demonstrating that
this method is rapid, sensitive, simple and has a low cost.
When compared with other novel detection methods,
this method is faster, more sensitive and easier to operate. In
addition, the present study investigated its specificity, as well
as the feasibility of this method using standard strains. The
results demonstrated that it has a good specificity to E.
coli. Table V presents a
comparison of the results between the current different methods. At
present, the sophisticated testing methods of pathogenic
microorganisms include the microbial method, PCR and ELISA. The
microbial method is time-consuming and involves complicated
processes. PCR is the most mature method in the national testing
methods of pathogenic microorganisms, however, its reagents are
expensive and the procedure is complex. In addition, as this method
is extremely sensitive, the experimental conditions, the exogenous
DNA, improper controls, primer design and the target selection of
sequence will all affect the results. The ELISA method is
relatively time-efficient; however, it requires skilled operation
and a detection limit of 106 cfu/l. Surface plasmon
resonance, biosensors, capillary zone electrophoresis and other
technologies are also being studied by the researchers, as they are
quicker than the microbial method and simpler than PCR; however,
they require expensive instruments and the low detection limit is
105−106 cfu/ml (16–23).
 | Table V.A comparison of the current methods
used for detection. |
Table V.
A comparison of the current methods
used for detection.
| Method | Time | Detection
limit | Specificity | Cost |
|---|
| F0F1-ATPase
immuno-biosensor | 13 h | 1–5 cfu/25 g | 95% | Very low |
| Microbial
method | 5–7 d | 1 cfu/25 g | 100% | Low |
| PCR | >48 h |
102−7×103
cfu/ml | 99% (DNA easily
polluted) | High |
| ELISA | 36–48 h | 106
cfu/ml | 95% | Low |
| Reverse
transcription PCR | 48 h | 1–5 cfu/25 g | 99% (DNA easily
polluted) | High |
| SPR biosensor | >24 h | 2×106
cfu/ml | 95% | High |
| CEZ | >24 h |
105−106 cfu/ml | 95% | Low |
The present study performed preliminary research on
the feasibility of applying F0F1-ATPase immuno-biosensors for
O157:H7 detection. The detection techniques based on F0F1-ATPase
can rapidly detect the disease markers in patient serum or feces,
which will aid rapid clinical diagnosis. To promote its
application, novel fluorescent material could be chosen as
fluorescent probe to improve the sensitivity and accuracy of this
method (21–25). In addition, high specificity immune
magnetic beads could be used to enrich the target bacterial, which
can minimize the interference of other bacterial (26–28).
Due to the complexity of the sample and the variety of bacteria in
different samples, the application of a biosensor for the detection
of pathogens is rarely reported. Furthermore, the application of
biosensors in pathogenic bacteria detection is rarely reported;
therefore, sample pretreatment, and increasing bacteria and
bacteria solution treatment, will require extensive research in
practical sample testing.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Professor Jia-Chang
Yue (Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing,
China) for his technical assistance, as well as Professor Yan-Qun
Li (South of China Normal University, Guangdong, China) for the
revisions and modifications made to this paper. The present study
was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the
People's Republic of China (grant no. 2008IM021600), the Beijing
Academy of Science and Technology of China (grant no. IG200905N),
the Beijing Municipal Party Organization of China (grant no.
2010D002022000009) and the National Key Foundation for Exploring
Scientific Instrument (grant no. 2013YQ140405).
References
|
1
|
Naugle AL, Holt KG, Levine P and Eckel R:
Food safety and inspection service regulatory testing program for
Escherichia coli O157:H7 in raw ground beef. J Food Prot.
68:462–468. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang HH and Wu RM: Survey on contamination
status of food-borne pathogens in chilled broilers. Shiyong Yufang
Yixue. 17:1314–1315. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
3
|
Liu X, Zhang Y, Yue J, Jiang P and Zhang
Z: F0F1-ATPase as biosensor to detect single virus. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 342:1319–1322. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu HJWL and Liu QJ: Application of nano
biosensortechnology in chloramphenicol detection. Food Sci.
31:167–170. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Wu HJ, Wei L, Lun YZ, Kang ZJ and Zhao L:
The preliminary study of a rapid detecting technology for
Listeria monocytogenes based on immunobiosensor. Zhongguo
Weishengtai Xue Zazhi. 22:743–745. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Deng Z, Zhang Y, Yue J, Tang F and Wei Q:
Green and orange CdTe quantum dots as effective pH-sensitive
fluorescent probes for dual simultaneous and independent detection
of viruses. J Phys Chem B. 111:12024–12031. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yun Z, Zhengtao D, Jiachang Y, Fangqiong T
and Qun W: Using cadmium telluride quantum dots as a proton flux
sensor and applying to detect H9 avian influenza virus. Anal
Biochem. 364:122–127. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu XL, Zhang XA, Cui YB, Yue JC, Luo ZY
and Jiang PD: Mechanically driven proton conduction in single
delta-free F0F1-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 347:752–757.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao Y, Wang P, Wang F, Zhou H, Li W, Yue
J and Ha Y: A novel biosensor regulated by the rotator of
F0F1-ATPase to detect deoxynivalenolrapidly.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 423:195–199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lu HT, Zhang Y, Yue JC, et al: Application
of immuno-rotary biosensor based on FoF1-ATPase in Chromatophores
for detecting clenbuterol. Food Science. 28:446–450. 2007.(In
Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Capaldi RA and Aggeler R: Mechanism of the
F(1)F(0)-type ATP syn-thase, a biological rotary motor. Trends
Biochem Sci. 27:154–160. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Karplus M and Gao YQ: Biomolecular motors:
The F1-ATPase para-digm. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 14:250–259. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Clark LC Jr and Lyons C: Electrode systems
for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 102:29–45. 1962. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wei L, Wu HJ, Li BM, et al: The pollution
and detection research progress of four pathogenic bacterias. Food
Sci. 32:302–306. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Wei L, Wu HJ, Lun YZ, Li BM, Gao LJ, Zhang
XL and Kang ZJ: An immunobiosensor for rapid detection of
Staphylococcus aureusenes. Zhongguo Shipin Weisheng Zazhi.
22:498–501. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Mousavi SL, Rasooli I, Nazarian S and
Amani J: Simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7,
toxigenic Vibrio cholerae and Salmonella typhimurium
by multiplex PCR. Iranian Journal of Clinical Infectious Diseases.
4:97–103. 2009.
|
|
17
|
Zordan MD, Grafton MM, Acharya G, Reece
LM, Cooper CL, Aronson AI, Park K and Leary JF: Detection of
pathogenic E. coli O157:H7 by a hybrid microfluidic SPR and
molecular imaging cytometry device. Cytometry A. 75:155–162. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bahşi ZB, Buyukaksoy A, Aslan MH and Oral
AY: DNA biosensors for E. coli O157:H7 detection in drinking water
resources using sol-gel derived waveguides. South Biomed Eng Conf.
24:203–206. 2009.
|
|
19
|
Oda M, Morita M, Unno H and Tanji Y: Rapid
detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 by using green
fluorescent protein-labeled PP01 bacteriophage. Appl Environ
Microbiol. 70:527–534. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li F, Zhao C, Zhang W, Cui S, Meng J, Wu J
and Zhang DY: Use of ramification amplification assay for detection
of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and other E. J Clin Microbiol.
43:6086–6090. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang Z, Kotov NA and Giersig M:
Spontaneous organization of single CdTe nanoparticles into
luminescent nanowires. Science. 297:237–240. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nanduri V, Bhunia AK, Tu SI, Paoli GC and
Brewster JD: SPR biosensor for the detection of L.
monocytogenes using phage-displayed antibody. Biosens
Bioelectron. 23:248–252. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao P, Xu G, Shi X, Yuan K and Tian J:
Rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus by a combination of
monoclonal antibody-coated latex and capillary electrophoresis.
Electrophoresis. 27:1784–1789. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu X, Liu H, Liu J, Haley KN, Treadway JA,
Larson JP, Ge N, Peale F and Bruchez MP: Immunofluorescent labeling
of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor
quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol. 21:41–46. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chan WC and Nie S: Quantum dot
bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science.
281:2016–2018. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nou X, Arthur TM, Bosilevac JM,
Brichta-Harhay DM, Guerini MN, Kalchayanand N and Koohmaraie M:
Improvement of immunomagnetic separation for Escherichia
coli O157:H7 detection by the PickPen magnetic particle
separation device. J Food Prot. 69:2870–2874. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fu Z, Rogelj S and Kieft TL: Rapid
detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by immunomagnetic
separation and real-time PCR. Int J Food Microbiol. 99:47–57. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chapman PA, Malo AT, Siddons CA and Harkin
M: Use of commercial enzyme immunoassays and immunomagnetic
separation systems for detecting Escherichia coli O157 in
bovine fecal samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 63:2549–2553.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|