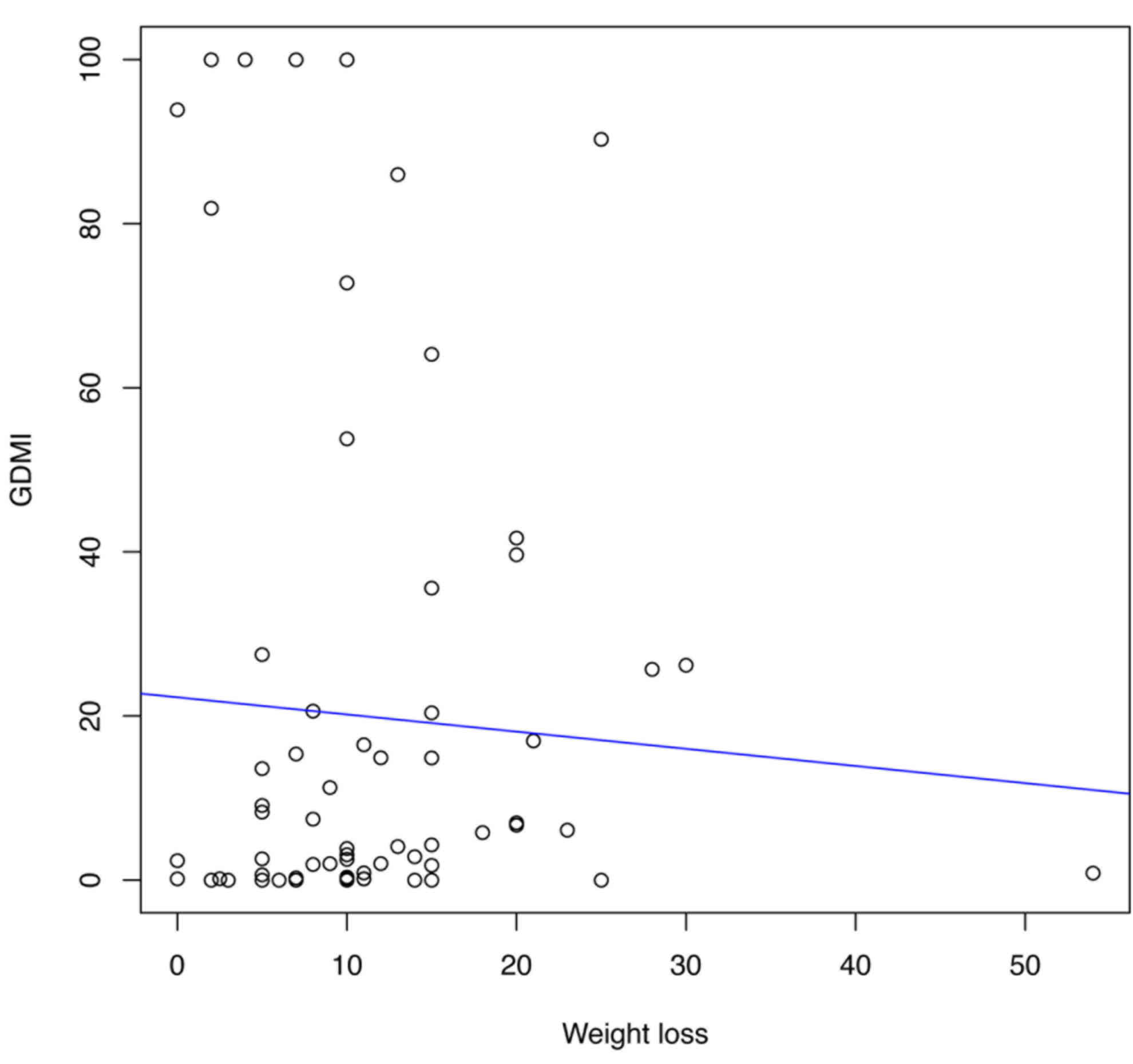
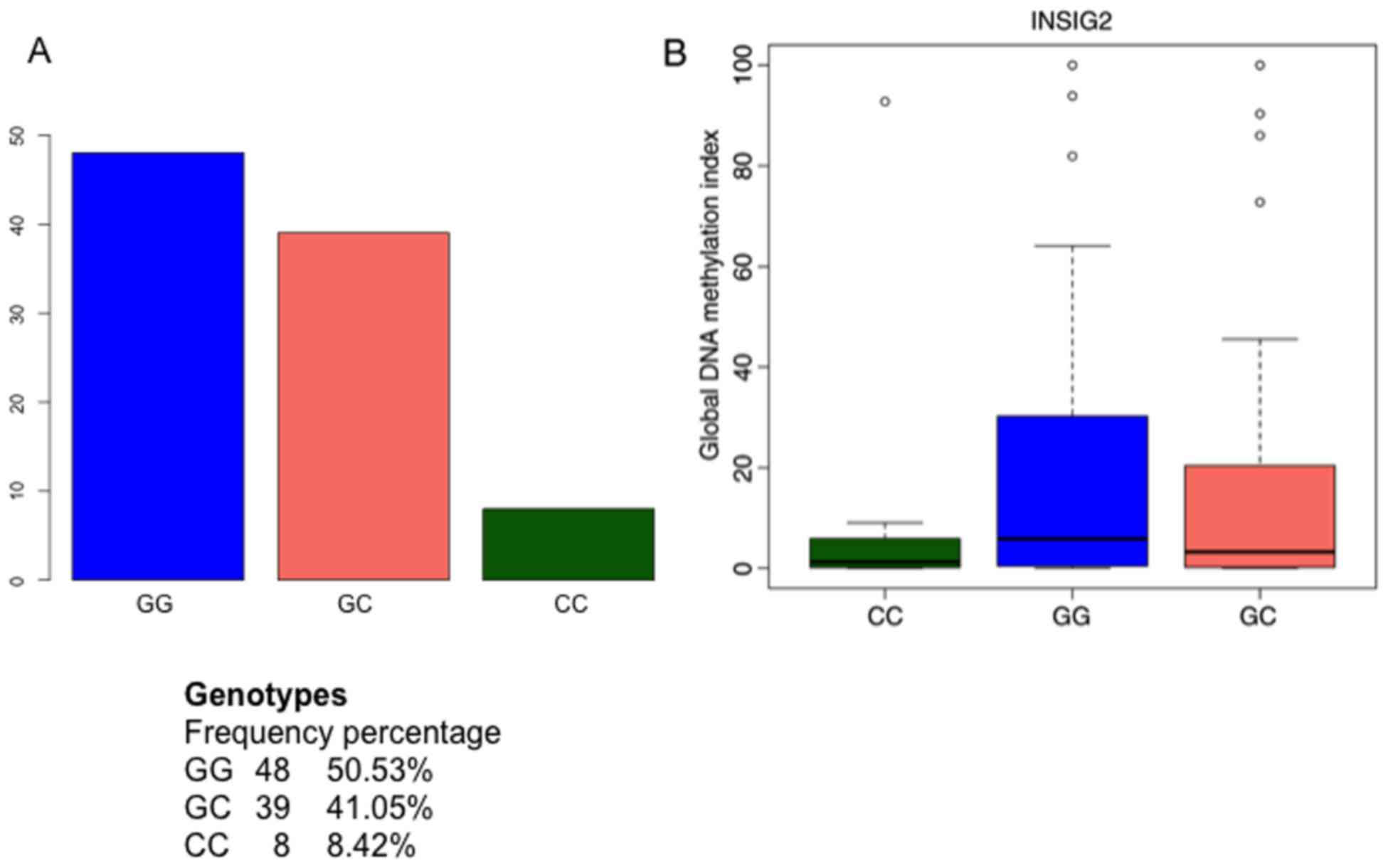
|
1
|
Jiang Y, Chen Y, Manuel D, Morrison H and
Mao Y: Obesity Working Group: Quantifying the impact of obesity
category on major chronic diseases in Canada.
ScientificWorldJournal. 7:1211–1221. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Huxley R, James WP, Barzi F, Patel JV,
Lear SA, Suriyawongpaisal P, Janus E, Caterson I, Zimmet P,
Prabhakaran D, et al: Ethnic comparisons of the cross-sectional
relationships between measures of body size with diabetes and
hypertension. Obes Rev. 9 Suppl 1:S53–S61. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Obesity in Asia Collaboration: Is central
obesity a better discriminator of the risk of hypertension than
body mass index in ethnically diverse populations? J Hypertens.
26:169–177. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Goni L, Milagro FI, Cuervo M and Martínez
JA: Single-nucleotide polymorphisms and DNA methylation markers
associated with central obesity and regulation of body weight. Nutr
Rev. 72:673–690. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lau DC, Douketis JD, Morrison KM, Hramiak
IM, Sharma AM and Ur E: Obesity Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines
Expert Panel: 2006 Canadian clinical practice guidelines on the
management and prevention of obesity in adults and children
(summary). CMAJ. 176:S1–S13. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Stroh C, Köckerling F, Weiner R, Horbach
T, Ludwig K, Dressler M, Lange V, Loermann P, Wolff S, Schmidt U,
et al: Are there gender-specific aspects of sleeve gastrectomy-data
analysis from the quality assurance study of surgical treatment of
obesity in Germany. Obes Surg. 22:1214–1219. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Moleres A, Campión J, Milagro FI, Marcos
A, Campoy C, Garagorri JM, Gómez-Martínez S, Martínez JA,
Azcona-Sanjulián MC and Martí A: EVASYON Study Group: Differential
DNA methylation patterns between high and low responders to a
weight loss intervention in overweight or obese adolescents: The
EVASYON study. FASEB J. 27:2504–2512. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bouchard L, Rabasa-Lhoret R, Faraj M,
Lavoie ME, Mill J, Pérusse L and Vohl MC: Differential epigenomic
and transcriptomic responses in subcutaneous adipose tissue between
low and high responders to caloric restriction. Am J Clin Nutr.
91:309–320. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mansego ML, Milagro FI, Zulet MA and
Martinez JA: SH2B1 CpG-SNP is associated with body weight reduction
in obese subjects following a dietary restriction program. Ann Nutr
Metab. 66:1–9. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
van Dijk SJ, Tellam RL, Morrison JL,
Muhlhausler BS and Molloy PL: Recent developments on the role of
epigenetics in obesity and metabolic disease. Clin Epigenetics.
7:662015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Campión J, Milagro FI, Goyenechea E and
Martínez JA: TNF-alpha promoter methylation as a predictive
biomarker for weight-loss response. Obesity (Silver Spring).
17:1293–1297. 2009.
|
|
12
|
Wang K, Li WD, Zhang CK, Wang Z, Glessner
JT, Grant SF, Zhao H, Hakonarson H and Price RA: A genome-wide
association study on obesity and obesity-related traits. PLoS One.
6:e189392011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Mansego ML, Garcia-Lacarte M, Milagro FI,
Marti A and Martinez JA: GENOI members: DNA methylation of miRNA
coding sequences putatively associated with childhood obesity.
Pediatr Obes. 12:19–27. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
van Dijk SJ, Molloy PL, Varinli H,
Morrison JL and Muhlhausler BS: Members of EpiSCOPE: Epigenetics
and human obesity. Int J Obes (Lond). 39:85–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Youngson NA and Morris MJ: What obesity
research tells us about epigenetic mechanisms. Philos Trans R Soc
Lond B Biol Sci. 368:201103372013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Na YK, Hong HS, Lee DH, Lee WK and Kim DS:
Effect of body mass index on global DNA methylation in healthy
Korean women. Mol Cells. 37:467–672. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Nomura Y, Lambertini L, Rialdi A, Lee M,
Mystal EY, Grabie M, Manaster I, Huynh N, Finik J, Davey M, et al:
Global methylation in the placenta and umbilical cord blood from
pregnancies with maternal gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and
obesity. Reprod Sci. 21:131–137. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
BLUEPRINT consortium: Quantitative
comparison of DNA methylation assays for biomarker development and
clinical applications. Nat Biotechnol. 34:726–737. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Crary-Dooley FK, Tam ME, Dunaway KW,
Hertz-Picciotto I, Schmidt RJ and LaSalle JM: A comparison of
existing global DNA methylation assays to low-coverage whole-genome
bisulfite sequencing for epidemiological studies. Epigenetics.
12:206–214. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Perng W, Mora-Plazas M, Marín C, Rozek LS,
Baylin A and Villamor E: A prospective study of LINE-1DNA
methylation and development of adiposity in school-age children.
PLoS One. 8:e625872013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Pearce MS, McConnell JC, Potter C, Barrett
LM, Parker L, Mathers JC and Relton CL: Global LINE-1 DNA
methylation is associated with blood glycaemic and lipid profiles.
Int J Epidemiol. 41:210–217. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Duggan C, Xiao L, Terry MB and McTiernan
A: No effect of weight loss on LINE-1 methylation levels in
peripheral blood leukocytes from postmenopausal overweight women.
Obesity (Silver Spring). 22:2091–2096. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Demerath EW, Guan W, Grove ML, Aslibekyan
S, Mendelson M, Zhou YH, Hedman ÅK, Sandling JK, Li LA, Irvin MR,
et al: Epigenome-wide association study (EWAS) of BMI, BMI change
and waist circumference in African American adults identifies
multiple replicated loci. Hum Mol Genet. 24:4464–4479. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Aslibekyan S, Demerath EW, Mendelson M,
Zhi D, Guan W, Liang L, Sha J, Pankow JS, Liu C, Irvin MR, et al:
Epigenome-wide study identifies novel methylation loci associated
with body mass index and waist circumference. Obesity (Silver
Spring). 23:1493–1501. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Dick KJ, Nelson CP, Tsaprouni L, Sandling
JK, Aïssi D, Wahl S, Meduri E, Morange PE, Gagnon F, Grallert H, et
al: DNA methylation and body-mass index: A genome-wide analysis.
Lancet. 383:1990–1998. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kaz AM, Wong CJ, Varadan V, Willis JE,
Chak A and Grady WM: Global DNA methylation patterns in Barrett's
esophagus, dysplastic Barrett's and esophageal adenocarcinoma are
associated with BMI, gender, and tobacco use. Clin Epigenetics.
8:1112016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Lillycrop K, Murray R, Cheong C, Teh AL,
Clarke-Harris R, Barton S, Costello P, Garratt E, Cook E, Titcombe
P, et al: ANRIL promoter DNA methylation: A perinatal marker for
later adiposity. EBioMedicine. 19:60–72. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Lumey LH, Terry MB, Delgado-Cruzata L,
Liao Y, Wang Q, Susser E, McKeague I and Santella RM: Adult global
DNA methylation in relation to pre-natal nutrition. Int J
Epidemiol. 41:116–123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tobi EW, Slieker RC, Stein AD, Suchiman
HE, Slagboom PE, van Zwet EW, Heijmans BT and Lumey LH: Early
gestation as the critical time-window for changes in the prenatal
environment to affect the adult human blood methylome. Int J
Epidemiol. 44:1211–1223. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Tobi EW, Goeman JJ, Monajemi R, Gu H,
Putter H, Zhang Y, Slieker RC, Stok AP, Thijssen PE and Müller F:
DNA methylation signatures link prenatal famine exposure to growth
and metabolism. Nat Commun. 5:55922014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Agha G, Hajj H, Rifas-Shiman SL, Just AC,
Hivert MF, Burris HH, Lin X, Litonjua AA, Oken E, DeMeo DL, et al:
Birth weight-for-gestational age is associated with DNA methylation
at birth and in childhood. Clin Epigenetics. 8:1182016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Kupers LK, Xu X, Jankipersadsing SA, Vaez
A, la Bastide-van Gemert S, Scholtens S, Nolte IM, Richmond RC,
Relton CL, Felix JF, et al: DNA methylation mediates the effect of
maternal smoking during pregnancy on birthweight of the offspring.
Int J Epidemiol. 44:1224–1237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Kresovich JK, Zheng Y, Cardenas A, Joyce
BT, Rifas-Shiman SL, Oken E, Gillman MW, Hivert MF, Baccarelli AA
and Hou L: Cord blood DNA methylation and adiposity measures in
early and mid-childhood. Clin Epigenetics. 9:862017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Godfrey KM, Sheppard A, Gluckman PD,
Lillycrop KA, Burdge GC, McLean C, Rodford J, Slater-Jefferies JL,
Garratt E, Crozier SR, et al: Epigenetic gene promoter methylation
at birth is associated with child's later adiposity. Diabetes.
60:1528–34. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Richmond SA, Rothman L, Buliung R,
Schwartz N, Larsen K and Howard A: Exploring the impact of a
dedicated streetcar right-of-way on pedestrian motor vehicle
collisions: A quasi experimental design. Accid Anal Prev.
71:222–227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Stel J and Legler J: The role of
epigenetics in the latent effects of early life exposure to
obesogenic endocrine disrupting chemicals. Endocrinology.
156:3466–3472. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Do C, Shearer A, Suzuki M, Terry MB,
Gelernter J, Greally JM and Tycko B: Genetic-epigenetic
interactions in cis: A major focus in the post-GWAS era. Genome
Biol. 18:1202017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Do C, Lang CF, Lin J, Darbary H, Krupska
I, Gaba A, Petukhova L, Vonsattel JP, Gallagher MP, Goland RS, et
al: Mechanisms and disease associations of haplotype-dependent
allele-specific DNA methylation. Am J Hum Genet. 98:934–955. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Cole SA: Epigenetic studies of perinatal
determinants of later obesity link important, but previously
unrelated, genetic and epidemiological findings. EBioMedicine.
20:15–16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Day SE, Coletta RL, Kim JY, Garcia LA,
Campbell LE, Benjamin TR, Roust LR, De Filippis EA, Mandarino LJ
and Coletta DK: Potential epigenetic biomarkers of obesity-related
insulin resistance in human whole-blood. Epigenetics. 12:254–263.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Aronica L, Levine AJ, Brennan K, Mi J,
Gardner C, Haile RW and Hitchins MP: A systematic review of studies
of DNA methylation in the context of a weight loss intervention.
Epigenomics. 9:769–787. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
den Dunnen JT, Dalgleish R, Maglott DR,
Hart RK, Greenblatt MS, McGowan-Jordan J, Roux AF, Smith T,
Antonarakis SE and Taschner PE: HGVS recommendations for the
description of sequence variants: 2016 update. Hum Mutat.
37:564–569. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Le Hellard S, Theisen FM, Haberhausen M,
Raeder MB, Fernø J, Gebhardt S, Hinney A, Remschmidt H, Krieg JC,
Mehler-Wex C, et al: Association between the insulin-induced gene 2
(INSIG2) and weight gain in a German sample of
antipsychotic-treated schizophrenic patients: Perturbation of
SREBP-controlled lipogenesis in drug-related metabolic adverse
effects? Mol Psychiatry. 14:308–317. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Prakash J, Mittal B, Apurva S, Shally A,
Pranjal S and Neena S: Common genetic variant of insig2 gene
rs7566605 polymorphism is associated with severe obesity in north
India. Iran Biomed J. 21:261–269. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Apalasamy YD, Moy FM, Rampal S, Bulgiba A
and Mohamed Z: Genetic associations of the INSIG2 rs7566605
polymorphism with obesity-related metabolic traits in malaysian
malays. Genet Mol Res. 13:4904–10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kaulfers AM, Deka R, Dolan L and Martin
LJ: Association of INSIG2 polymorphism with overweight and LDL in
children. PLoS One. 10:e01163402015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Chambers JC, Elliott P, Zabaneh D, Zhang
W, Li Y, Froguel P, Balding D, Scott J and Kooner JS: Common
genetic variation near MC4R is associated with waist circumference
and insulin resistance. Nat Genet. 40:716–718. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Loos RJ, Lindgren CM, Li S, Wheeler E,
Zhao JH, Prokopenko I, Inouye M, Freathy RM, Attwood AP, Beckmann
JS, et al: Common variants near MC4R are associated with fat mass,
weight and risk of obesity. Nat Genet. 40:768–775. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Xi B, Chandak GR, Shen Y, Wang Q and Zhou
D: Association between common polymorphism near the MC4R gene and
obesity risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One.
7:e45731 View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Paolini B, Maltese PE, Del Ciondolo I,
Tavian D, Missaglia S, Ciuoli C, Zuntini M, Cecchin S, Bertelli M
and Pompucci G: Prevalence of mutations in LEP, LEPR and MC4R genes
in individuals with severe obesity. Genet Mol Res. 15:2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Takenaka A, Nakamura S, Mitsunaga F,
Inoue-Murayama M, Udono T and Suryobroto B: Human-specific SNP in
obesity genes, adrenergic receptor beta2 (ADRB2), Beta3 (ADRB3) and
PPAR γ2 (PPARG), during primate evolution. PLoS One. 7:e434612012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Ruiz JR, Larrarte E, Margareto J, Ares R
and Labayen I: Role of β2-adrenergic receptor
polymorphisms on body weight and body composition response to
energy restriction in obese women: Preliminary results. Obesity
(Silver Spring). 19:212–215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Ruiz JR, Larrarte E, Margareto J, Ares R,
Alkorta P and Labayen I: Preliminary findings on the role of PLIN1
polymorphisms on body composition and energy metabolism response to
energy restriction in obese women. Br J Nutr. 106:486–90. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Large V, Hellström L, Reynisdottir S,
Lönnqvist F, Eriksson P, Lannfelt L and Arner P: Human beta-2
adrenoceptor gene polymorphisms are highly frequent in obesity and
associate with altered adipocyte beta-2 adrenoceptor function. J
Clin Invest. 100:3005–3013. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
55
|
Ishiyama-Shigemoto S, Yamada K, Yuan X,
Ichikawa F and Nonaka K: Association of polymorphisms in the
beta2-adrenergic receptor gene with obesity, hypertriglyceridaemia,
and diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 42:98–101. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Martin S, Nicaud V, Humphries SE and
Talmud PJ: EARS group: Contribution of APOA5 gene variants to
plasma triglyceride determination and to the response to both fat
and glucose tolerance challenges. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1637:217–225. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Kisfali P, Mohás M, Maasz A, Hadarits F,
Markó L, Horvatovich K, Oroszlán T, Bagosi Z, Bujtor Z, Gasztonyi
B, et al: Apolipoprotein A5 IVS3+476A allelic variant associates
with increased trigliceride levels and confers risk for development
of metabolic syndrome in Hungarians. Circ J. 72:40–43. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Elosua R, Ordovas JM, Cupples LA, Lai CQ,
Demissie S, Fox CS, Polak JF, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB Sr and
O'Donnell CJ: Variants at the APOA5 locus, association with carotid
atherosclerosis and modification by obesity: The Framingham Study.
J Lipid Res. 47:990–996. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Sánchez-Moreno C, Ordovás JM, Smith CE,
Baraza JC, Lee YC and Garaulet M: APOA5 gene variation interacts
with dietary fat intake to modulate obesity and circulating
triglycerides in a Mediterranean population. J Nutr. 141:380–385.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
60
|
Garelnabi M, Lor K, Jin J, Chai F and
Santanam N: The paradox of ApoA5 modulation of triglycerides:
Evidence from clinical and basic research. Clin Biochem. 46:12–19.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Aberle J, Evans D, Beil FU and Seedorf U:
A polymorphism in the apolipoprotein A5 gene is associated with
weight loss after short-term diet. Clin Genet. 68:152–154. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Hauner H, Meier M, Jöckel KH, Frey UH and
Siffert W: Prediction of successful weight reduction under
sibutramine therapy through genotyping of the G-protein beta3
subunit gene (GNB3) C825T polymorphism. Pharmacogenetics.
13:453–459. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Hsiao TJ, Hwang Y, Liu CH, Chang HM and
Lin E: Association of the C825T polymorphism in the GNB3 gene with
obesity and metabolic phenotypes in a Taiwanese population. Genes
Nutr. 8:137–144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Maniotis C, Chantziara K, Kokkoris P,
Papadogiannis D, Andreou C, Tsioufis C, Vaiopoulos G and Stefanadis
C: The AGT and the GNB3 polymorphisms and insulin resistance in
prehypertension. Hormones (Athens). 13:79–86. 2014.
|
|
65
|
Michalsen A, Knoblauch NT, Lehmann N,
Grossman P, Kerkhoff G, Wilhelm FH, Moebus S, Konstantinides S,
Binder L and Heusch G: Effects of lifestyle modification on the
progression of coronary atherosclerosis, autonomic function and
angina-the role of GNB3 C825T polymorphism. Am Heart J.
151:870–877. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Hoque MO, Lee CC, Cairns P, Schoenberg M
and Sidransky D: Genome-wide genetic characterization of bladder
cancer: A comparison of high-density single-nucleotide polymorphism
arrays and PCR-based microsatellite analysis. Cancer Res.
63:2216–2222. 2003.
|
|
67
|
Smith AJ, Cooper JA, Li LK and Humphries
SE: INSIG2 gene polymorphism is not associated with obesity in
Caucasian, Afro-Caribbean and Indian subjects. Int J Obes (Lond).
31:1753–1755. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Granell S, Serra-Juhé C, Martos-Moreno GÁ,
Díaz F, Pérez-Jurado LA, Baldini G and Argente J: A novel
melanocortin-4 receptor mutation MC4R-P272L associated with severe
obesity has increased propensity to be ubiquitinated in the ER in
the face of correct folding. PLoS One. 7:e508942012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
69
|
Corella D, Ortega-Azorín C, Sorlí JV,
Covas MI, Carrasco P, Salas-Salvadó J, Martínez-González MÁ, Arós
F, Lapetra J, Serra-Majem L, et al: Statistical and biological
gene-lifestyle interactions of MC4R and FTO with diet and physical
activity on obesity: New effects on alcohol consumption. PLoS One.
7:e523442012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
70
|
Feigelson HS, Teras LR, Diver WR, Tang W,
Patel AV, Stevens VL, Calle EE, Thun MJ and Bouzyk M: Genetic
variation in candidate obesity genes ADRB2, ADRB3, GHRL, HSD11B1,
IRS1, IRS2 and SHC1 and risk for breast cancer in the cancer
prevention study II. Breast Cancer Res. 10:R572008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
71
|
Brøgger J, Steen VM, Eiken HG, Gulsvik A
and Bakke P: Genetic association between COPD and polymorphisms in
TNF, ADRB2 and EPHX1. Eur Respir J. 27:682–688. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Park HW, Yang MS, Park CS, Kim TB, Moon
HB, Min KU, Kim YY and Cho SH: Additive role of tiotropium in
severe asthmatics and Arg16Gly in ADRB2 as a potential marker to
predict response. Allergy. 64:778–783. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Sánchez González JL, Proenza AM, Martínez
Larrad MT, Ramis JM, Pérez Fernández C, Palou A and Ríos Serrano M:
The glutamine 27 glutamic acid polymorphism of the
beta2-adrenoceptor gene is associated with abdominal obesity and
greater risk of impaired glucose tolerance in men but not in women:
A population-based study in Spain. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf).
59:476–481. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Kawaguchi H, Masuo K, Katsuya T, Sugimoto
K, Rakugi H, Ogihara T and Tuck ML: Beta2- and beta3-Adrenoceptor
polymorphisms relate to subsequent weight gain and blood pressure
elevation in obese normotensive individuals. Hypertens Res.
29:951–959. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Masuo K, Katsuya T, Kawaguchi H, Fu Y,
Rakugi H, Ogihara T and Tuck ML: Beta2-adrenoceptor polymorphisms
relate to obesity through blunted leptin-mediated sympathetic
activation. Am J Hypertens. 19:1084–1091. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Maasz A, Kisfali P, Jaromi L, Horvatovich
K, Szolnoki Z, Csongei V, Safrany E, Sipeky C, Hadarits F and
Melegh B: Apolipoprotein A5 gene IVS3+G476A allelic variant confers
susceptibility for development of ischemic stroke. Circ J.
72:1065–1070. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Maász A, Kisfali P, Szolnoki Z, Hadarits F
and Melegh B: Apolipoprotein A5 gene C56G variant confers risk for
the development of large-vessel associated ischemic stroke. J
Neurol. 255:649–654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Elosua R, Cupples LA, Fox CS, Polak JF,
D'Agostino RA Sr, Wolf PA, O'Donnell CJ and Ordovas JM: Association
between well-characterized lipoprotein-related genetic variants and
carotid intimal medial thickness and stenosis: The framingham heart
study. Atherosclerosis. 189:222–228. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Casiglia E, Tikhonoff V, Boschetti G,
Bascelli A, Saugo M, Guglielmi G, Caffi S, Rigoni G, Giordano N,
Grasselli C, et al: The C825T GNB3 polymorphism, independent of
blood pressure, predicts cerebrovascular risk at a population
level. Am J Hypertens. 25:451–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Frey UH, Moebus S, Möhlenkamp S, Kälsch H,
Bauer M, Lehmann N, Nöthen M, Mühleisen TW, Stang A, Erbel R, et
al: GNB3 gene 825 TT variant predicts hard coronary events in the
population-based HEINZ NIXDORF RECALL study. Atherosclerosis.
237:437–442. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Nishimura R, Tanabe N, Sekine A, Kasai H,
Suda R, Kato F, Jujo T, Sugiura T, Shigeta A, Sakao S and Tatsumi
K: Synergistic effects of ACE Insertion/deletion and GNB3 C825T
polymorphisms on the efficacy of PDE-5 inhibitor in patients with
pulmonary hypertension. Respiration. 91:132–140. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Sperling H, Eisenhardt A, Virchow S, Hauck
E, Lenk S, Porst H, Stief C, Wetterauer U, Rubben H, Muller N and
Siffert W: Sildenafil response is influenced by the G protein beta
3 subunit GNB3 C825T polymorphism: A pilot study. J Urol.
169:1048–1051. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Bell CG, Xia Y, Yuan W, Gao F, Ward K,
Roos L, Mangino M, Hysi PG, Bell J, Wang J and Spector TD: Novel
regional age-associated DNA methylation changes within human common
disease-associated loci. Genome Biol. 17:1932016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
84
|
Murray R, Bryant J, Titcombe P, Barton SJ,
Inskip H, Harvey NC, Cooper C, Lillycrop K, Hanson M and Godfrey
KM: DNA methylation at birth within the promoter of ANRIL predicts
markers of cardiovascular risk at 9 years. Clin Epigenetics.
8:902016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
85
|
Pal S and Tyler JK: Epigenetics and aging.
Sci Adv. 2:e16005842016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
86
|
Wu X, Cao N, Fenech M and Wang X: Role of
sirtuins in maintenance of genomic stability: Relevance to cancer
and healthy aging. DNA Cell Biol. 35:542–575. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Perng W, Villamor E, Shroff MR, Nettleton
JA, Pilsner JR, Liu Y and Diez-Roux AV: Dietary intake, plasma
homocysteine and repetitive element DNA methylation in the
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Nutr Metab Cardiovasc
Dis. 24:614–622. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Needham BL, Smith JA, Zhao W, Wang X,
Mukherjee B, Kardia SL, Shively CA, Seeman TE, Liu Y and Diez Roux
AV: Life course socioeconomic status and DNA methylation in genes
related to stress reactivity and inflammation: The multi-ethnic
study of atherosclerosis. Epigenetics. 10:958–969. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
89
|
Guerrero-Preston R, Goldman LR,
Brebi-Mieville P, Ili-Gangas C, Lebron C, Witter FR, Apelberg BJ,
Hernández-Roystacher M, Jaffe A, Halden RU and Sidransky D: Global
DNA hypomethylation is associated with in utero exposure to
cotinine and perfluorinated alkyl compounds. Epigenetics.
5:539–546. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
90
|
Chater-Diehl EJ, Laufer BI, Castellani CA,
Alberry BL and Singh SM: Alteration of gene expression, DNA
methylation and histone methylation in free radical scavenging
networks in adult mouse hippocampus following fetal alcohol
exposure. PLoS One. 11:e01548362016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
91
|
Garcia-Lacarte M, Milagro FI, Zulet MA,
Martinez JA and Mansego ML: LINE-1 methylation levels, a biomarker
of weight loss in obese subjects, are influenced by dietary
antioxidant capacity. Redox Rep. 21:67–74. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Marques-Rocha JL, Milagro FI, Mansego ML,
Mourão DM, Martínez JA and Bressan J: LINE-1 methylation is
positively associated with healthier lifestyle but inversely
related to body fat mass in healthy young individuals. Epigenetics.
11:49–60. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
93
|
Carraro JC, Mansego ML, Milagro FI, Chaves
LO, Vidigal FC, Bressan J and Martínez JA: LINE-1 and inflammatory
gene methylation levels are early biomarkers of metabolic changes:
Association with adiposity. Biomarkers. 21:625–632. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Nicoletti CF, Nonino CB, de Oliveira BA,
Pinhel MA, Mansego ML, Milagro FI, Zulet MA and Martinez JA: DNA
methylation and hydroxymethylation levels in relation to two weight
loss strategies: Energy-restricted diet or bariatric surgery. Obes
Surg. 26:603–611. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Weiner R, El-Sayes I, Manger T, Weiner S,
Lippert H and Stroh C: Obesity Surgery Working Group, Competence
Network Obesity: Antidiabetic efficacy of obesity surgery in
Germany: A quality assurance nationwide survey. Surg Obes Relat
Dis. 10:322–327. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Stroh C, Weiner R, Wolff S, Knoll C and
Manger T: Obesity Surgery Working Group; Competence Network
Obesity: Influences of gender on complication rate and outcome
after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: Data analysis of more than 10,000
operations from the german bariatric surgery registry. Obes Surg.
24:1625–1633. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|