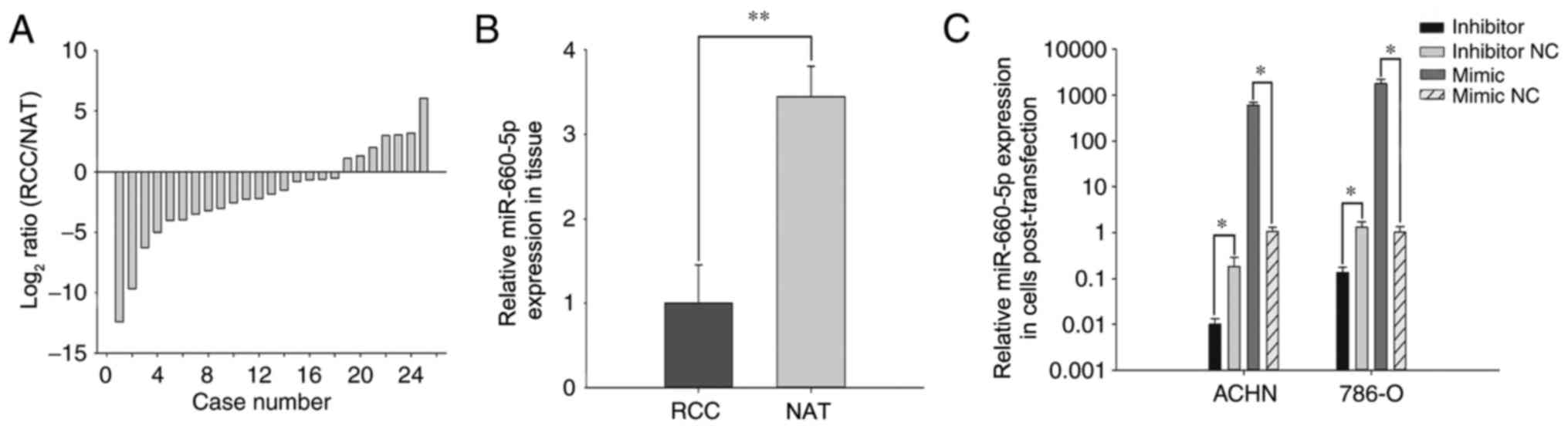
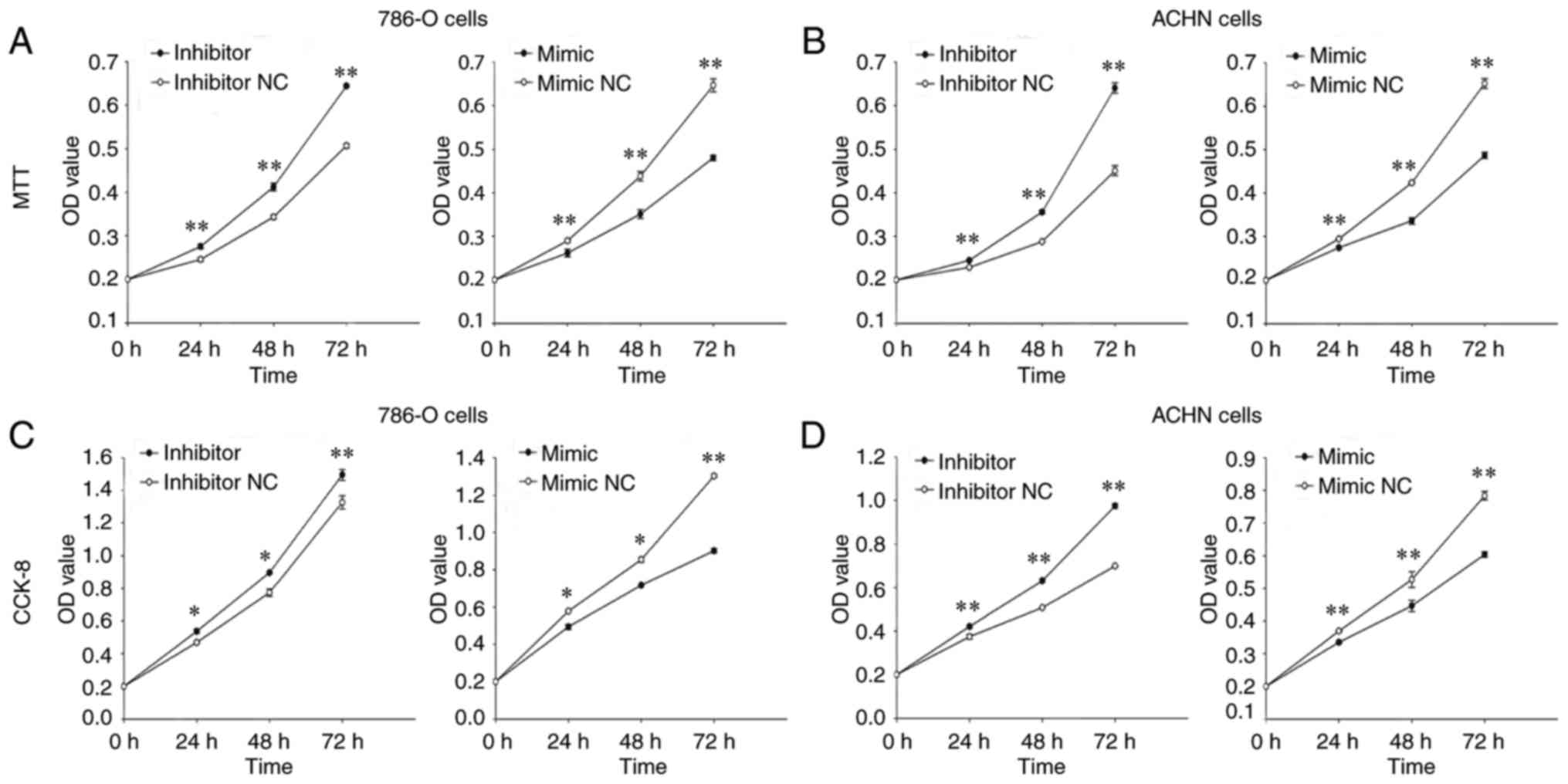
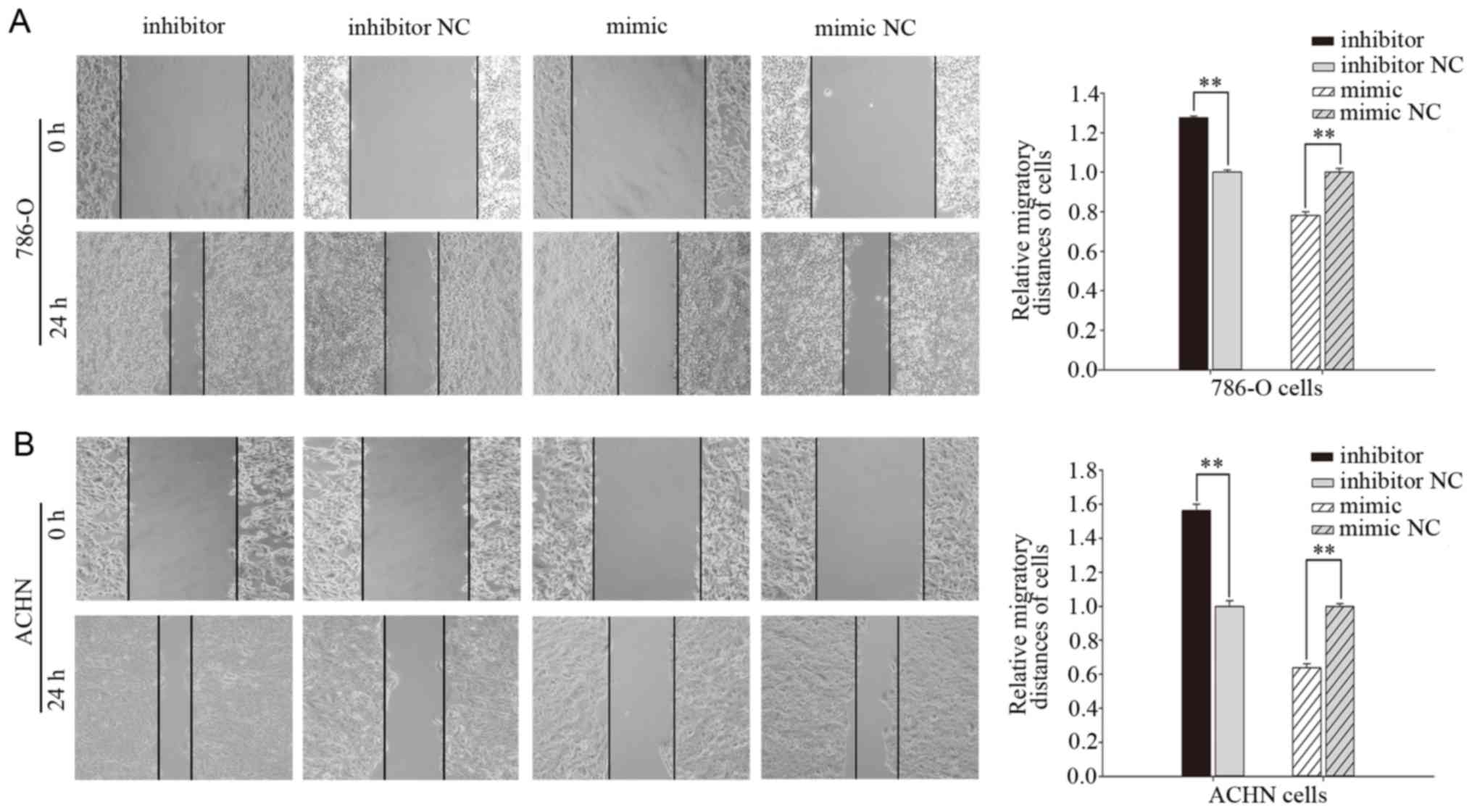
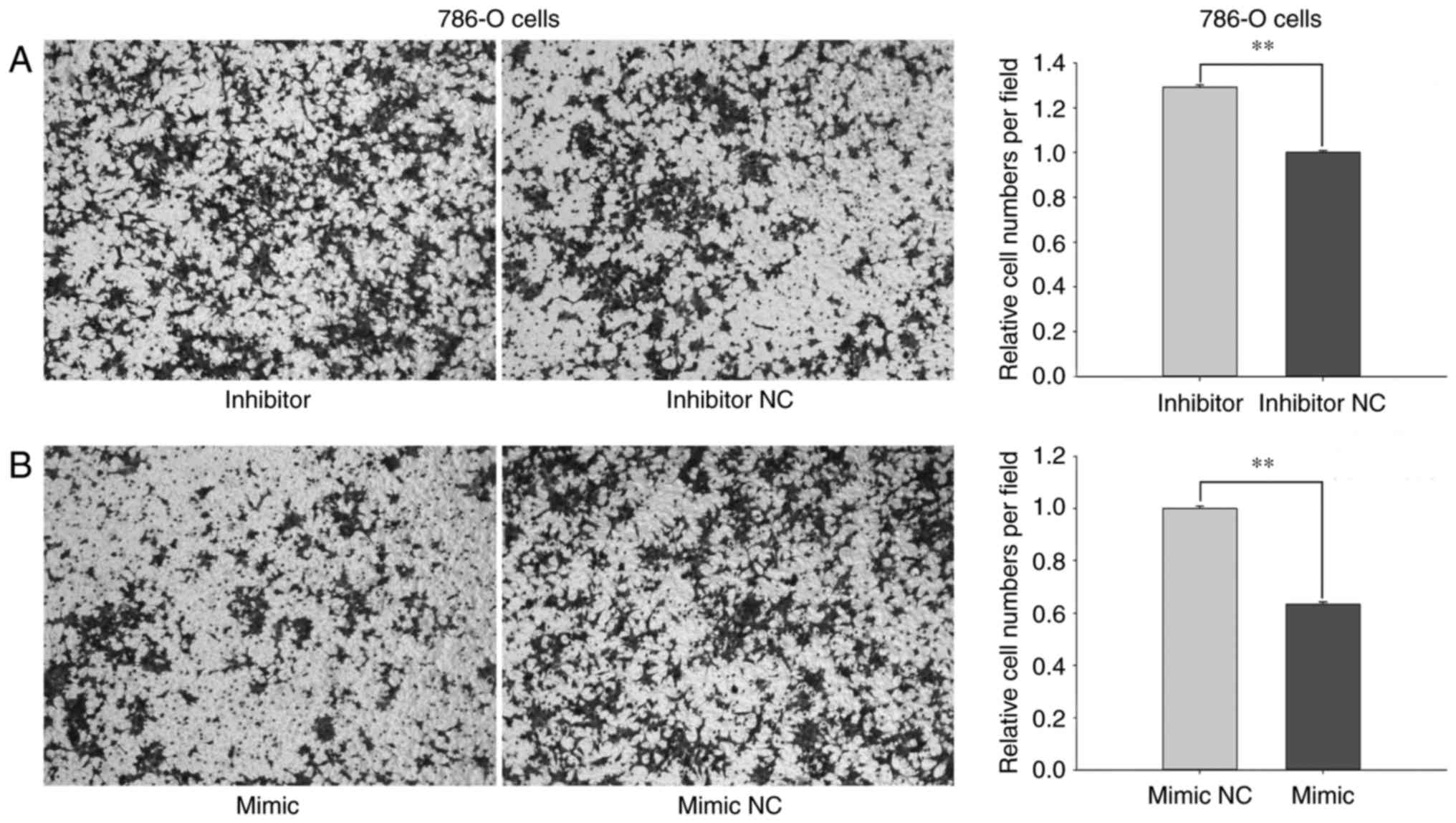
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yan Y, Yang FQ, Zhang HM, Che J and Zheng
JH: Up-regulation of flotillin-2 is associated with renal cell
carcinoma progression. Tumour Biol. 35:10479–10486. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Patel C, Ahmed A and Ellsworth P: Renal
cell carcinoma: A reappraisal. Urol Nurs. 32:182–191. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rini BI, Campbell SC and Escudier B: Renal
cell carcinoma. Lancet. 373:1119–1132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yin B, Zeng Y, Wang X, Liu G, Zhang M and
Song Y: Expression and clinical significance of cancer-testis genes
in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:4112–4119. 2014.
|
|
7
|
Escudier B, Porta C, Schmidinger M,
Rioux-Leclercq N, Bex A, Khoo V, Gruenvald V and Horwich A: ESMO
Guidelines Committee: Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO clinical practice
guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 27
Suppl 5:v58–v68. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Rendon RA, Kapoor A, Breau R, Leveridge M,
Feifer A, Black PC and So A: Surgical management of renal cell
carcinoma: Canadian kidney cancer forum consensus. Can Urol Assoc
J. 8:E398–E412. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Yim NH, Jung YP, Kim A, Kim T and Ma JY:
Induction of apoptotic cell death by betulin in multidrug-resistant
human renal carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 34:1058–1064. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hong MH, Kim HS, Kim C, Ahn JR, Chon HJ,
Shin SJ, Ahn JB, Chung HC and Rha SY: Treatment outcomes of
sunitinib treatment in advanced renal cell carcinoma patients: A
single cancer center experience in Korea. Cancer Res Treat.
41:67–72. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Carthew RW and Sontheimer EJ: Origins and
mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 136:642–655. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E: Gene
silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of translational repression
and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet. 12:99–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010.
|
|
15
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Shenouda SK and Alahari SK: MicroRNA
function in cancer: Oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 28:369–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Guil S and Esteller M: DNA methylomes,
histone codes and miRNAs: Tying it all together. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 41:87–95. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Fortunato O, Boeri M, Moro M, Verri C,
Mensah M, Conte D, Caleca L, Roz L, Pastorino U and Sozzi G:
Mir-660 is downregulated in lung cancer patients and its
replacement inhibits lung tumorigenesis by targeting MDM2-p53
interaction. Cell Death Dis. 5:e15642014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Krishnan P, Ghosh S, Wang B, Li D,
Narasimhan A, Berendt R, Graham K, Mackey JR, Kovalchuk O and
Damaraju S: Next generation sequencing profiling identifies
miR-574-3p and miR-660-5p as potential novel prognostic markers for
breast cancer. BMC Genomics. 16:7352015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Navarro A, Diaz T, Tovar N, Pedrosa F,
Tejero R, Cibeira MT, Magnano L, Rosiñol L, Monzó M, Bladé J and de
Larrea Fernández C: A serum microRNA signature associated with
complete remission and progression after autologous stem-cell
transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma. Oncotarget.
6:1874–1883. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Ferrer G, Navarro A, Hodgson K, Aymerich
M, Pereira A, Baumann T, Monzo M, Moreno C and Montserrat E:
MicroRNA expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia developing
autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 54:2016–2022. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tang K and Xu H: Prognostic value of
meta-signature miRNAs in renal cell carcinoma: An integrated miRNA
expression profiling analysis. Sci Rep. 5:102722015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Ge YZ, Wu R, Xin H, Zhu M, Lu TZ, Liu H,
Xu Z, Yu P, Zhao YC, Li MH, et al: A tumor-specific microRNA
signature predicts survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 141:1291–1299. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Martinez-Salamanca JI, Huang WC, Millán I,
Bertini R, Bianco FJ, Carballido JA, Ciancio G, Hernández C,
Herranz F, Haferkamp A, et al: Prognostic impact of the 2009
UICC/AJCC TNM staging system for renal cell carcinoma with venous
extension. Eur Urol. 59:120–127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Su Z, Chen D, Zhang E, Li Y, Yu Z, Shi M,
Jiang Z, Ni L, Yang S, Gui Y, et al: MicroRNA-509-3p inhibits
cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting the
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 8 oncogene in renal
cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 12:1535–1543. 2015.
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Murai M and Oya M: Renal cell carcinoma:
Etiology, incidence and epidemiology. Curr Opin Urol. 14:229–233.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rasmussen F: Metastatic renal cell cancer.
Cancer Imaging. 13:374–380. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Li Y, Chen D, Li Y, Jin L, Liu J, Su Z, Qi
Z, Shi M, Jiang Z, Gui Y, et al: Identification of miR-130b as an
oncogene in renal cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 13:1902–1908. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yu Z, Chen D, Su Z, Li Y, Yu W, Zhang Q,
Yang L, Li C, Yang S, Ni L, et al: miR-886-3p upregulation in clear
cell renal cell carcinoma regulates cell migration, proliferation
and apoptosis by targeting PITX1. Int J Mol Med. 34:1409–1416.
2014.
|
|
31
|
Chen D, Li Y, Yu Z, Su ZYW, Li Y, Yang S,
Gui Y, Ni L and Lai Y: Upregulated microRNA-16 as an oncogene in
renal cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 12:1399–1404. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Li Y, Chen D, Jin L, Su Z, Liu J,
Duan H, Li X, Qi Z, Shi M, et al: miR-30a-5p in the tumorigenesis
of renal cell carcinoma: A tumor suppressive microRNA. Mol Med Rep.
13:4085–4094. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jin L, Li Y, Liu J, Yang S, Gui Y, Mao X,
Nie G and Lai Y: Tumor suppressor miR-149-5p is associated with
cellular migration, proliferation and apoptosis in renal cell
carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 13:5386–5392. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chen D, Li Y, Su Z, Yu Z, Yu W, Li Y, Gui
Y, Yang S and Lai Y: Identification of miR-125a-5p as a tumor
suppressor of renal cell carcinoma, regulating cellular
proliferation, migration and apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 11:1278–1283.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Paydas S, Acikalin A, Ergin M, Celik H,
Yavuz B and Tanriverdi K: Micro-RNA (miRNA) profile in Hodgkin
lymphoma: Association between clinical and pathological variables.
Med Oncol. 33:342016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Qin Q, Wang X, Yan N, Song RH, Cai TT,
Zhang W, Guan LJ, Muhali FS and Zhang JA: Aberrant expression of
miRNA and mRNAs in lesioned tissues of Graves' disease. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 35:1934–1942. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bye A, Røsjø H, Nauman J, Silva GJ,
Follestad T, Omland T and Wisløff U: Circulating microRNAs predict
future fatal myocardial infarction in healthy individuals-The HUNT
study. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 97:162–168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li H, Fan J, Yin Z, Wang F, Chen C and
Wang DW: Identification of cardiac-related circulating microRNA
profile in human chronic heart failure. Oncotarget. 7:33–45. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|