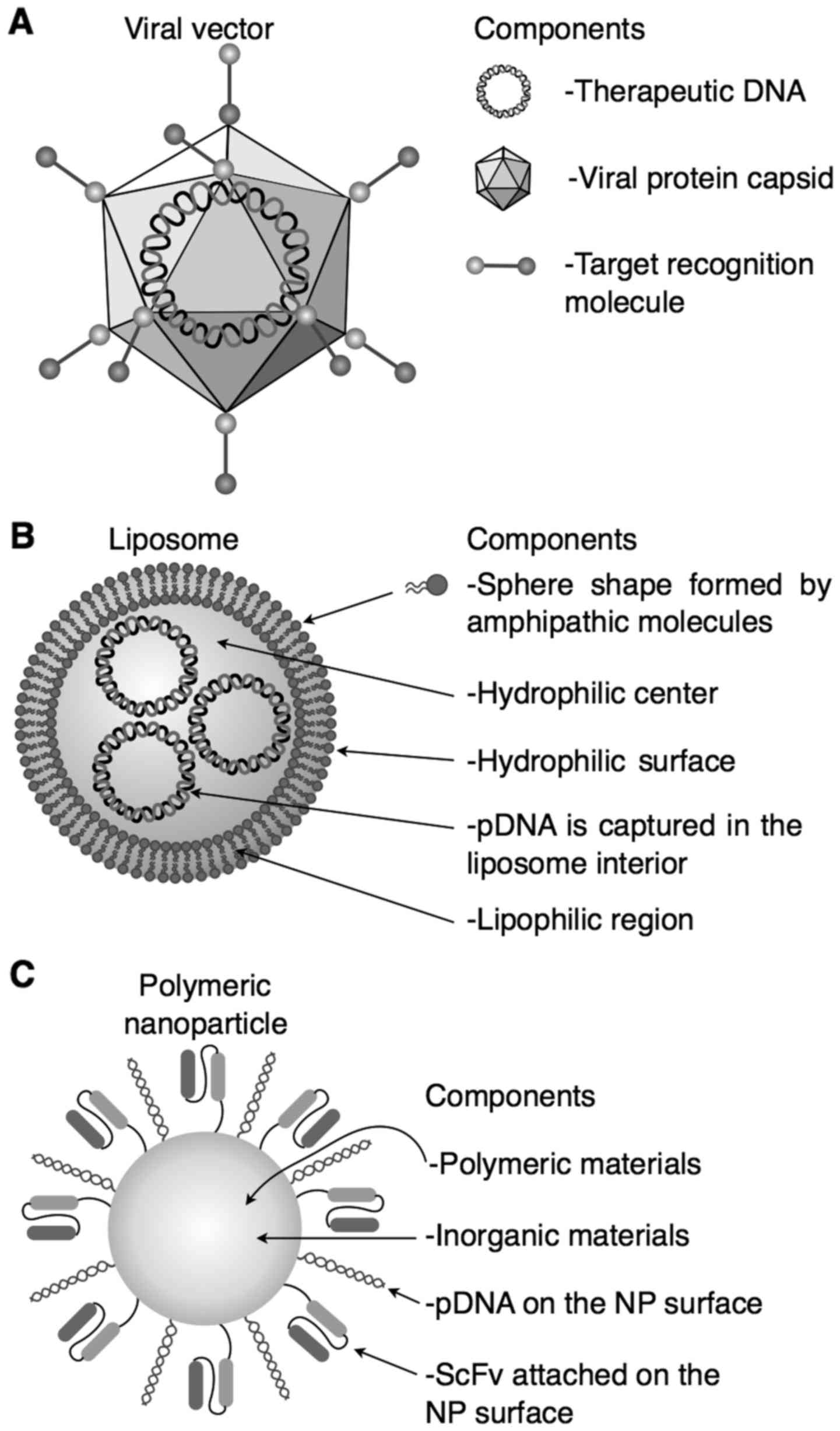
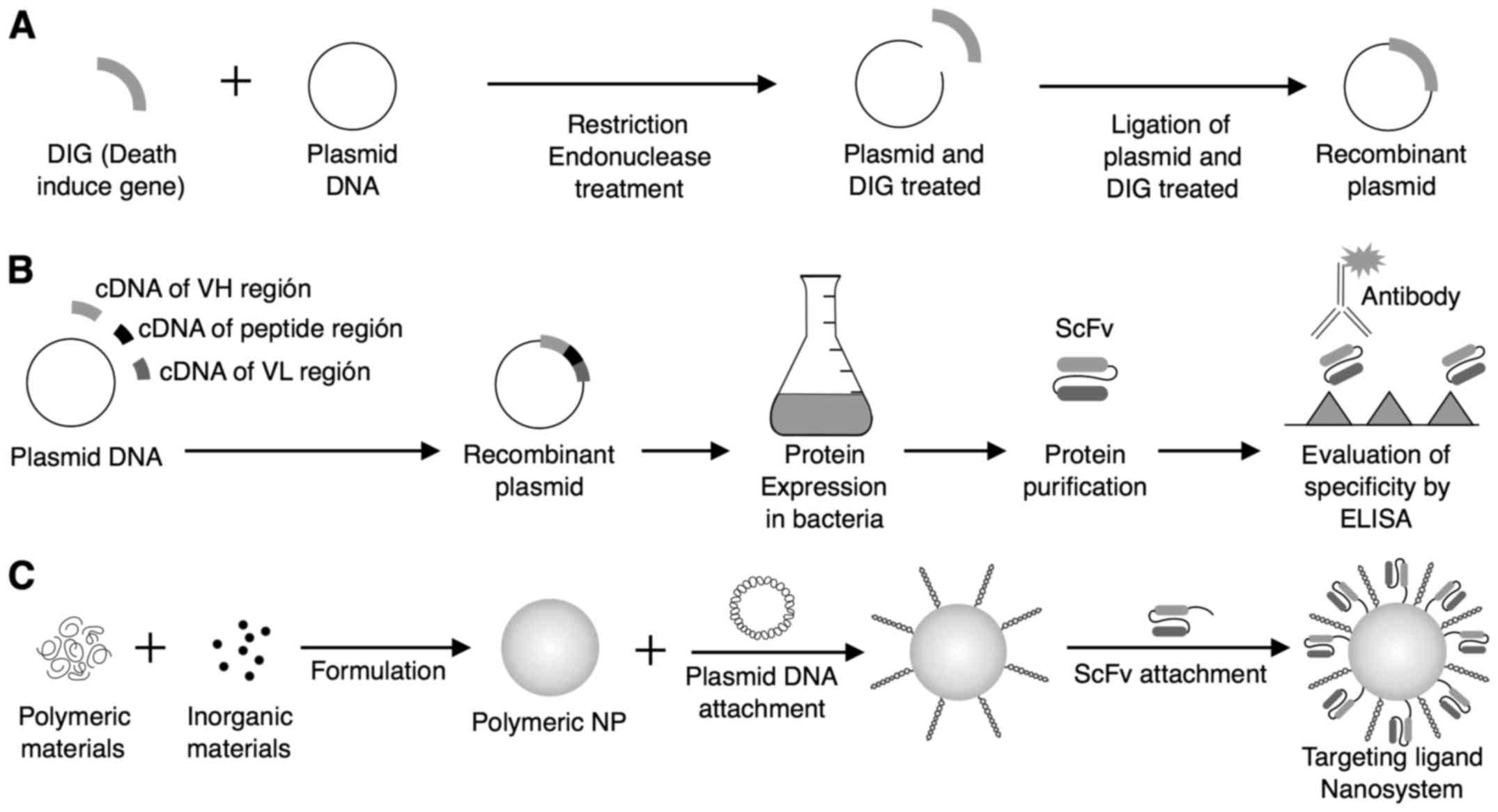
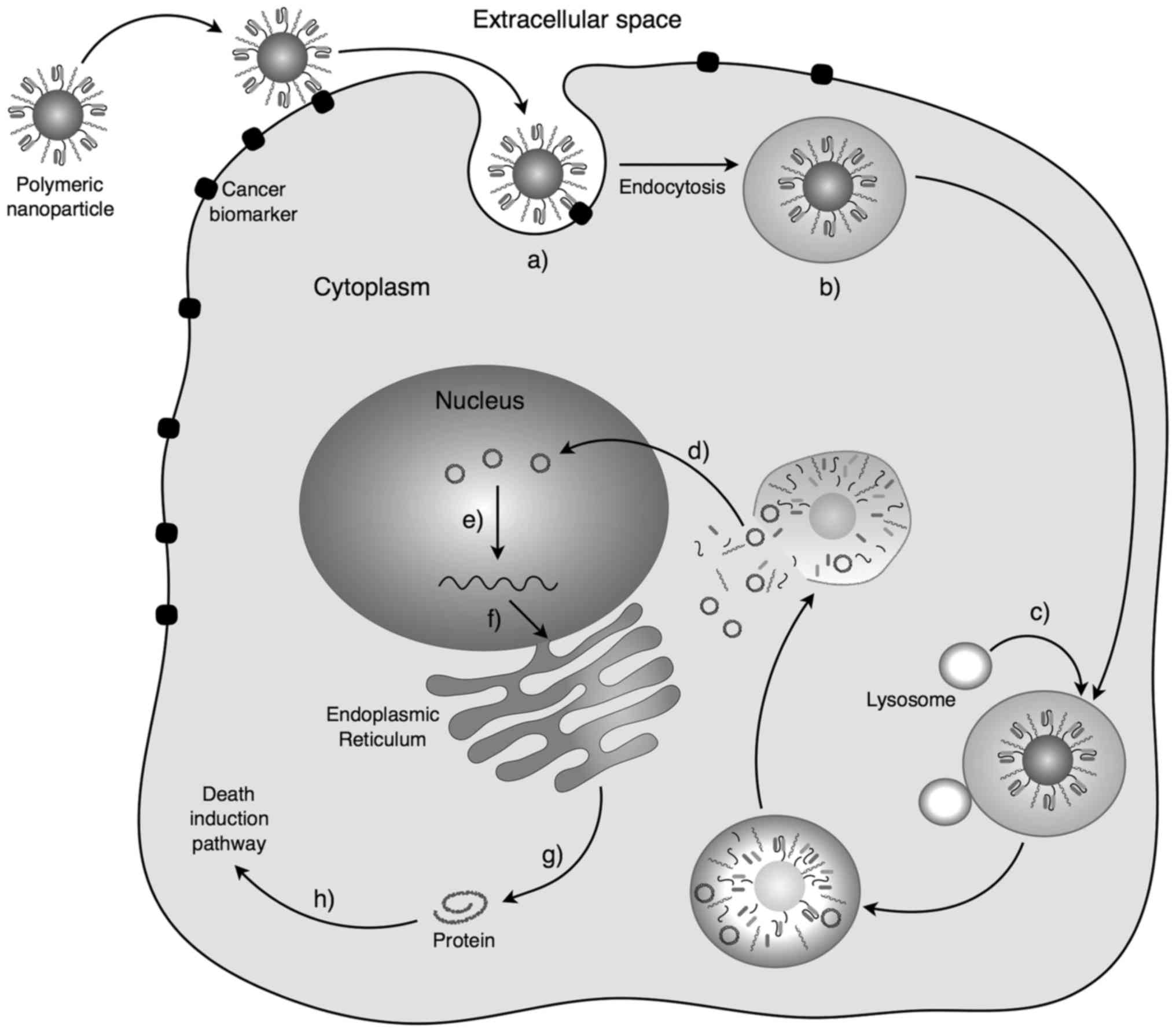
|
1
|
Qin SY, Zhang AQ, Cheng SX, Rong L and
Zhang XZ: Drug self-delivery systems for cancer therapy.
Biomaterials. 112:234–247. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sun NF, Liu ZA, Huang WB, Tian AL and Hu
SY: The research of nanoparticles as gene vector for tumor gene
therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 89:352–357. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van Ramshorst MS, van Werkhoven E, Honkoop
AH, Dezentjé VO, Oving IM, Mandjes IA, Kemper I, Smorenburg CH,
Stouthard JM, Linn SC, et al: Toxicity of dual HER2-blockade with
pertuzumab added to anthracycline versus non-anthracycline
containing chemotherapy as neoadjuvant treatment in HER2-positive
breast cancer: The TRAIN-2 study. Breast. 29:153–159. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vago R, Collico V, Zuppone S, Prosperi D
and Colombo M: Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of suicide genes in
cancer therapy. Pharmacol Res. 111:619–641. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Banerjee SM, MacRobert AJ, Mosse CA,
Periera B, Bown SG and Keshtgar MR: Photodynamic therapy: Inception
to application in breast cancer. Breast. 31:105–113. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sanchez-Dominguez CN, Gallardo-Blanco HL,
Rodriguez-Rodriguez AA, Vela-Gonzalez AV and Sanchez-Dominguez M:
Nanoparticles vs cancer: A multifuncional tool. Curr Top Med Chem.
14:664–675. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu M, Wu J, Shi J and Farokhzad OC:
Nanotechnology for protein delivery: Overview and perspectives. J
Control Release. 240:24–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Beik J, Abed Z, Ghoreishi FS,
Hosseini-Nami S, Mehrzadi S, Shakeri-Zadeh A and Kamrava SK:
Nanotechnology in hyperthermia cancer therapy: From fundamental
principles to advanced applications. J Control Release.
235:205–221. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Amer MH: Gene therapy for cancer: Present
status and future perspective. Mol Cell Ther. 2:272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tolmasky ME: Plasmids. Reference Module in
Life Sciences: Elsevier. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Fang CY, Tsai YD, Lin MC, Wang M, Chen PL,
Chao CN, Huang YL, Chang D and Shen CH: Inhibition of human bladder
cancer growth by a suicide gene delivered by JC polyomavirus
virus-like particles in a mouse model. J Urol. 193:2100–2106. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim HA, Nam K, Lee M and Kim SW:
Hypoxia/hepatoma dual specific suicide gene expression plasmid
delivery using bio-reducible polymer for hepatocellular carcinoma
therapy. J Control Release. 171:1–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lazarus GG and Singh M: In vitro cytotoxic
activity and transfection efficiency of polyethyleneimine
functionalized gold nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.
145:906–911. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pruitt KD, Brown GR, Hiatt SM,
Thibaud-Nissen F, Astashyn A, Ermolaeva O, Farrell CM, Hart J,
Landrum MJ, McGarvey KM, et al: RefSeq: An update on mammalian
reference sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:(Database Issue).
D756–D763. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Luo C, Miao L, Zhao Y, Musetti S, Wang Y,
Shi K and Huang L: A novel cationic lipid with intrinsic antitumor
activity to facilitate gene therapy of TRAIL DNA. Biomaterials.
102:239–248. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Inoue N, Watanabe M, Ishido N, Kodu A,
Maruoka H, Katsumata Y, Hidaka Y and Iwatani Y: Involvement of
genes encoding apoptosis regulatory factors (FAS, FASL, TRAIL,
BCL2, TNFR1 and TNFR2) in the pathogenesis of autoimmune thyroid
diseases. Hum Immunol. 77:944–951. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhan C, Li C, Wei X and Lu W and Lu W:
Toxins and derivatives in molecular pharmaceutics: Drug delivery
and targeted therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 90:101–118. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Glinka EM: Eukaryotic expression vectors
bearing genes encoding cytotoxic proteins for cancer gene therapy.
Plasmid. 68:69–85. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Walsh MJ, Dodd JE and Hautbergue GM:
Ribosome-inactivating proteins: Potent poisons and molecular tools.
Virulence. 15:774–784. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Glinka EM: Eukaryotic expression vectors
containing genes encoding plant proteins for killing of cancer
cells. Cancer Epidemiol. 37:1014–1019. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Malekshah OM, Chen X, Nomani A, Sarkar S
and Hatefi A: Enzyme/prodrug systems for cancer gene therapy. Curr
Pharmacol Rep. 2:299–308. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Duarte S, Carle G, Faneca H, de Lima MC
and Pierrefite-Carle V: Suicide gene therapy in cancer: Where do we
stand now? Cancer Lett. 324:160–170. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karjoo Z, Chen X and Hatefi A: Progress
and problems with the use of suicide genes for targeted cancer
therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 99:113–128. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lila Abu AS, Uehara Y, Ishida T and Kiwada
H: Application of polyglycerol coating to plasmid DNA lipoplex for
the evasion of the accelerated blood clearance phenomenon in
nucleic acid delivery. J Pharm Sci. 103:557–566. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Badrinath N, Heo J and Yoo SY: Viruses as
nanomedicine for cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. 11:4835–4847. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dizaj SM, Jafari S and Khosroushahi AY: A
sight on the current nanoparticle-based gene delivery vectors.
Nanoscale Res Lett. 9:2522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Crespo-Barreda A, Encabo-Berzosa MM,
González-Pastor R, Ortíz-Teba P, Iglesias M, Serrano JL and
Duque-Martin P: Chapter 11-viral and nonviral vectors for in vivo
and ex vivo gene therapies A2-laurence, JeffreyTrans Regenerative
Med Clinic. Boston: Academic Press; pp. 155–177. 2016, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zou W, Liu C, Chen Z and Zhang N:
Preparation and characterization of cationic PLA-PEG nanoparticles
for delivery of plasmid DNA. Nanoscale Res Lett. 4:982–992. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Raju D, Vishwakarma RK, Khan BM, Mehta UJ
and Ahmad A: Biological synthesis of cationic gold nanoparticles
and binding of plasmid DNA. Mater Lett. 129:159–161. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Anselmo AC and Mitragotri S: Nanoparticles
in the clinic. Bioeng Trans Med. 1:10–29. 2016.
|
|
31
|
Gebremedhin S, Singh A, Koons S, Bernt W,
Konopka K and Duzgunes N: Gene delivery to carcinoma cells via
novel non-viral vectors: Nanoparticle tracking analysis and suicide
gene therapy. Eur J Pharm Sci. 60:72–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gao S, Tian H, Xing Z, Zhang D, Guo Y, Guo
Z, Zhu X and Chen X: A non-viral suicide gene delivery system
traversing the blood brain barrier for non-invasive glioma
targeting treatment. J Control Release. 243:357–369. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Eslaminejad T, Nematollahi-Mahani SN and
Ansari M: Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity of the
plasmid EGFP-p53 loaded on pullulan-spermine magnetic
nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater. 402:34–43. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
McBride JW, Massey AS, McCaffrey J,
McCrudden CM, Coulter JA, Dunne NJ, Robson T and McCarthy HO:
Development of TMTP-1 targeted designer biopolymers for gene
delivery to prostate cancer. Int J Pharm. 500:144–153. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang K, Kievit FM and Zhang M:
Nanoparticles for cancer gene therapy: Recent advances, challenges,
and strategies. Pharmacol Res. 114:56–66. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Islam MA, Park TE, Singh B, Maharjan S,
Firdous J, Cho MH, Kang SK, Yun CH, Choi YJ and Cho CS: Major
degradable polycations as carriers for DNA and siRNA. J Control
Release. 193:74–89. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pérez-Herrero E and Fernández-Medarde A:
Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the
future of chemotherapy. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 93:52–79. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bishop CJ, Majewski RL, Guiriba TR, Wilson
DR, Bhise NS, Quiñones-Hinojosa A and Green JJ: Quantification of
cellular and nuclear uptake rates of polymeric gene delivery
nanoparticles and DNA plasmids via flow cytometry. Acta Biomater.
37:120–130. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Guo J, O'Driscoll CM, Holmes JD and Rahme
K: Bioconjugated gold nanoparticles enhance cellular uptake: A
proof of concept study for siRNA delivery in prostate cancer cells.
Int J Pharm. 509:16–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Masood F: Polymeric nanoparticles for
targeted drug delivery system for cancer therapy. Mater Sci Eng C
Mater Biol Appl. 60:569–578. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Carrillo C, Suñé JM, Pérez-Lozano P,
García-Montoya E, Sarrate R, Fàbregas A, Miñarro M and Ticó JR:
Chitosan nanoparticles as non-viral gene delivery systems:
Determination of loading efficiency. Biomed Pharmacother.
68:775–783. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bor G, Mytych J, Zebrowski J, Wnuk M and
Şanli-Mohamed G: Cytotoxic and cytostatic side effects of chitosan
nanoparticles as a non-viral gene carrier. Int J Pharm.
513:431–437. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhou J, Deng W, Wang Y, Cao X, Chen J,
Wang Q, Xu W, Du P, Yu Q, Chen J, et al: Cationic carbon quantum
dots derived from alginate for gene delivery: One-step synthesis
and cellular uptake. Acta Biomater. 42:209–219. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tirkey B, Bhushan B, Kumar Uday S and
Gopinath P: Prodrug encapsulated albumin nanoparticles as an
alternative approach to manifest anti-proliferative effects of
suicide gene therapy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 73:507–515.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shi S, Shi K, Tan L, Qu Y, Shen G, Chu B,
Zhang S, Su X, Li X, Wei Y and Qian Z: The use of cationic
MPEG-PCL-g-PEI micelles for co-delivery of Msurvivin T34A gene and
doxorubicin. Biomaterials. 35:4536–4547. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gaspar VM, Baril P, Costa EC, de
Melo-Diogo D, Foucher F, Queiroz JA, Sousa F, Pichon C and Correia
IJ: Bioreducible poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)-PLA-PEI-SS triblock
copolymer micelles for co-delivery of DNA minicircles and
Doxorubicin. J Control Release. 213:175–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Peng SF, Hsu HK, Lin CC, Cheng YM and Hsu
KH: Novel PEI/Poly-γ-Gutamic Acid Nanoparticles for high efficient
siRNA and Plasmid DNA Co-Delivery. Molecules. 22:pii: E86. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Cocco E, Deng Y, Shapiro EM, Bortolomai I,
Lopez S, Lin K, Bellone S, Cui J, Menderes G, Black JD, et al:
Dual-targeting nanoparticles for in vivo delivery of suicide genes
to chemotherapy-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
16:323–333. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Frede A, Neuhaus B, Klopfleisch R, Walker
C, Buer J, Müller W, Epple M and Westendorf AM: Colonic gene
silencing using siRNA-loaded calcium phosphate/PLGA nanoparticles
ameliorates intestinal inflammation in vivo. J Control Release.
222:86–96. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ohta T, Hashida Y, Higuchi Y, Yamashita F
and Hashida M: In vitro cellular gene delivery employing a novel
composite material of single-walled carbon nanotubes associated
with designed peptides with pegylation. J Pharm Sci. 106:792–802.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shekhar S, Roy A, Hong D and Kumta PN:
Nanostructured silicate substituted calcium phosphate (NanoSiCaPs)
nanoparticles-efficient calcium phosphate based non-viral gene
delivery systems. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 69:486–495.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li Y, Hei M, Xu Y, Qian X and Zhu W:
Ammonium salt modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for dual
intracellular-responsive gene delivery. Int J Pharm. 511:689–702.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
El-Sherbiny IM, Elbaz NM, Sedki M,
Elgammal A and Yacoub MH: Magnetic nanoparticles-based drug and
gene delivery systems for the treatment of pulmonary diseases.
Nanomedicine (Lond). 12:387–402. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sun J, Shi Z, Jia S and Zhang P: The force
analysis for superparamagnetic nanoparticles-based gene delivery in
an oscillating magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater. 427:85–89. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Sun T, Zhang YS, Pang B, Hyun DC, Yang M
and Xia Y: Engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer
therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 53:12320–12344. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Xu X, Ho W, Zhang X, Bertrand N and
Farokhzad O: Cancer nanomedicine: From targeted delivery to
combination therapy. Trends Mol Med. 21:223–232. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yang Y and Yu C: Advances in silica based
nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Nanomedicine.
12:317–332. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Suk JS, Xu Q, Kim N, Hanes J and Ensign
LM: PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug
and gene delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 99:28–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Casettari L, Vllasaliu D, Castagnino E,
Stolnik S, Howdle S and Illum L: PEGylated chitosan derivatives:
Synthesis, characterizations and pharmaceutical applications. Prog
Polym Sci. 37:659–685. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Palacio J, Agudelo NA and Lopez BL:
PEGylation of PLA nanoparticles to improve mucus-penetration and
colloidal stability for oral delivery systems. Curr Opin Chem Eng.
11:14–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Kim J, Kang Y, Tzeng SY and Green JJ:
Synthesis and application of poly (ethylene glycol)-co-poly
(β-amino ester) copolymers for small cell lung cancer gene therapy.
Acta Biomaterialia. 41:293–301. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ahmed S, Sami A and Xiang J: HER2-directed
therapy: Current treatment options for HER2-positive breast cancer.
Breast Cancer. 22:101–116. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhu L, Staley C, Kooby D, El-Rays B, Mao H
and Yang L: Current status of biomarker and targeted nanoparticle
development: The precision oncology approach for pancreatic cancer
therapy. Cancer Lett. 388:139–148. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Grunewald T and Ledermann JA: Targeted
Therapies for Ovarian Cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol.
14:139–152. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
McMahon KM, Scielzo C, Angeloni NL,
Deiss-Yehiely E, Scarfo L, Ranghetti P, Ma S, Kaplan J, Barbaglio
F, Gordon LI, et al: Synthetic high-density lipoproteins as
targeted monotherapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncotarget.
8:11219–11227. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Liu J, Zhao D, He W, Zhang H, Li Z and
Luan Y: Nanoassemblies from amphiphilic cytarabine prodrug for
leukemia targeted therapy. J Colloid Interface Sci. 487:239–249.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Pillai MR, Nanabala R, Joy A, Sasikumar A
and Knapp FF: Radiolabeled enzyme inhibitors and binding agents
targeting PSMA: Effective theranostic tools for imaging and therapy
of prostate cancer. Nucl Med Biol. 43:692–720. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Xie T, Dong B, Yan Y, Hu G and Xu Y:
Association between MMP-2 expression and prostate cancer: A
meta-analysis. Biomed Rep. 4:241–245. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Tarokh Z, Naderi-Manesh H and Nazari M:
Towards prostate cancer gene therapy: Development of a
chlorotoxin-targeted nanovector for toxic (melittin) gene delivery.
Eur J Pharm Sci. 99:209–218. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Sun L, Wu Q, Peng F, Liu L and Gong C:
Strategies of polymeric nanoparticles for enhanced internalization
in cancer therapy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 135:56–72. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Christian CG, Carlos MP, Alejandro MM,
Imelda OA, Oscar ZT, Adriana ME and Perla GC: Development of
antibody-coated magnetite nanoparticles for biomarker
immobilization. Journal of Nanomaterials. 2014:72014.
|
|
72
|
Thorek DL, Elias DR and Tsourkas A:
Comparative analysis of nanoparticle-antibody conjugations:
Carbodiimide versus click chemistry. Mol Imaging. 8:221–229.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Crivianu-Gaita V and Thompson M: Aptamers,
antibody scFv, and antibody Fab' fragments: An overview and
comparison of three of the most versatile biosensor biorecognition
elements. Biosens Bioelectron. 85:32–45. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kim J, Wilson DR, Zamboni CG and Green JJ:
Targeted polymeric nanoparticles for cancer gene therapy. J Drug
Target. 23:627–641. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Cheraghi R, Nazari M, Alipour M, Majidi A
and Hosseinkhani S: Development of a targeted anti-HER2 scFv
chimeric peptide for gene delivery into HER2-positive breast cancer
cells. Int J Pharm. 515:632–643. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Cai Z, Chattopadhyay N, Yang K, Kwon YL,
Yook S, Pignol JP and Reilly RM: 111In-labeled trastuzumab-modified
gold nanoparticles are cytotoxic in vitro to HER2-positive breast
cancer cells and arrest tumor growth in vivo in athymic mice after
intratumoral injection. Nucl Med Biol. 43:818–826. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Yin XB, Wu LQ, Fu HQ, Huang MW, Wang K,
Zhou F, Yu X and Wang KY: Inhibitory effect of humanized
anti-VEGFR-2 ScFv-As2O3-stealth nanoparticles conjugate on growth
of human hepatocellular carcinoma: In vitro and in vivo studies.
Asian Pac J Trop Med. 7:337–343. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Xiangbao Y, Linquan W, Mingwen H, Fan Z,
Kai W, Xin Y, Kaiyang W and Huaqun F: Humanized anti-VEGFR-2
ScFv-As2O3-stealth nanoparticles, an antibody conjugate with potent
and selective anti-hepatocellular carcinoma activity. Biomed
Pharmacother. 68:597–602. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|