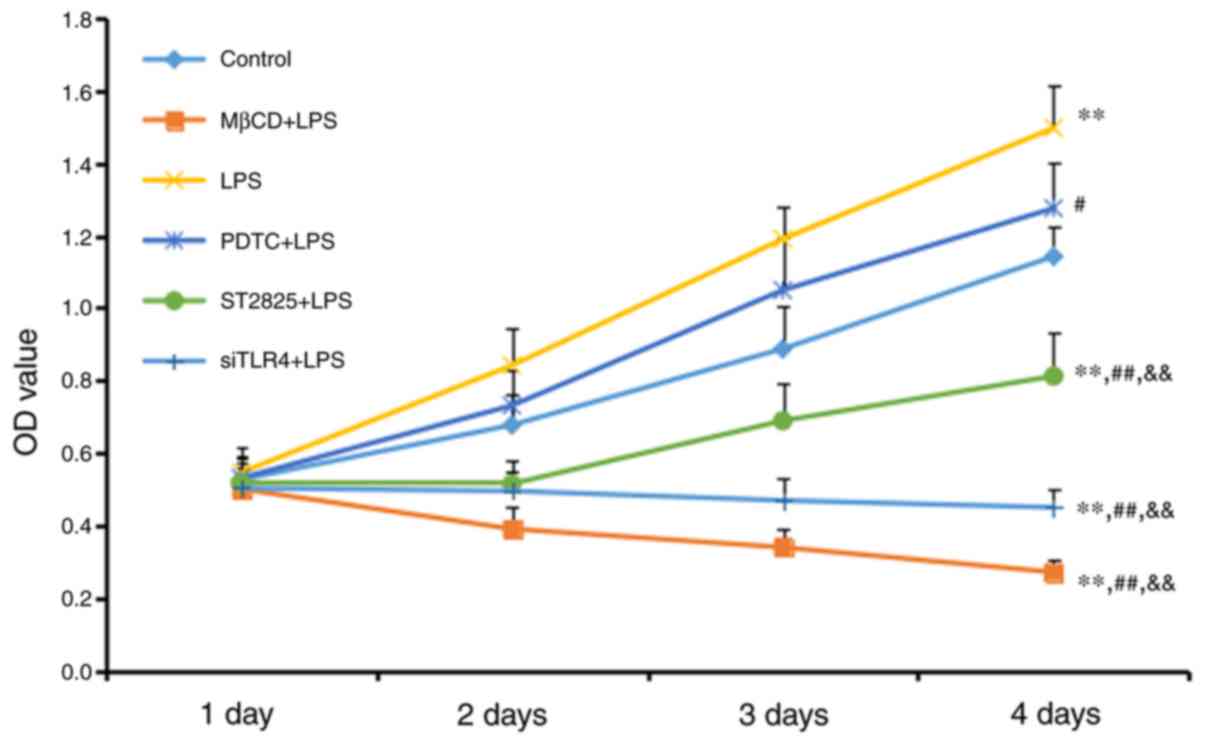
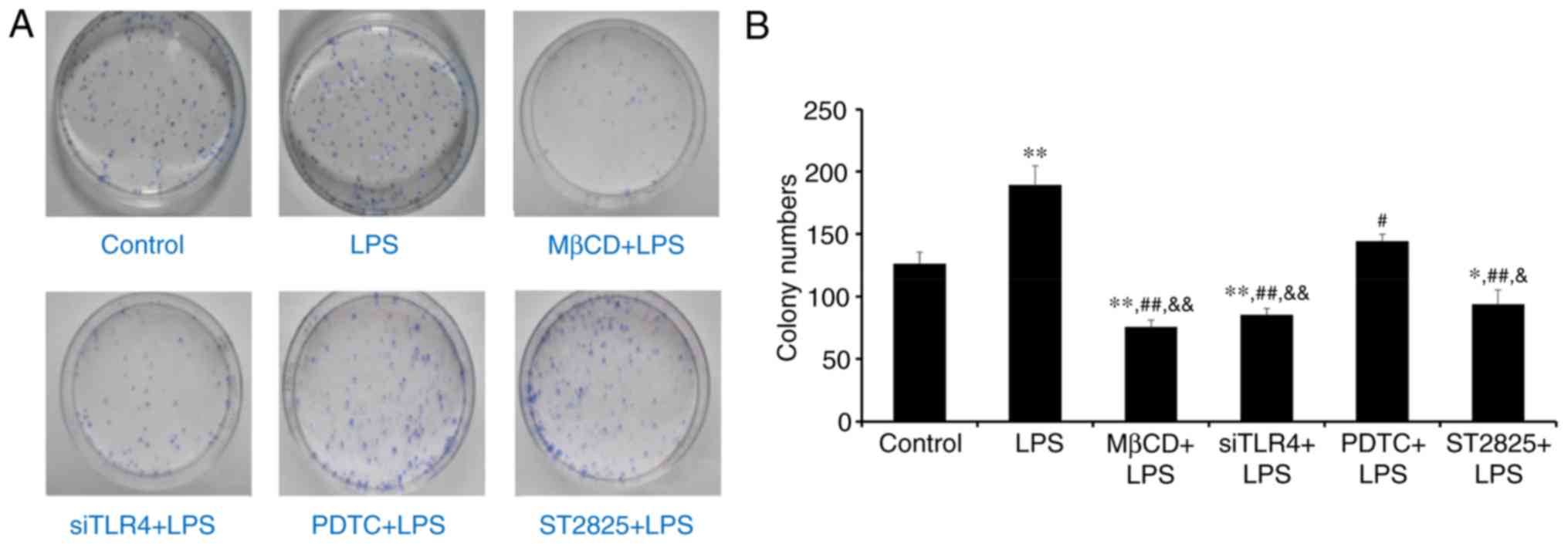
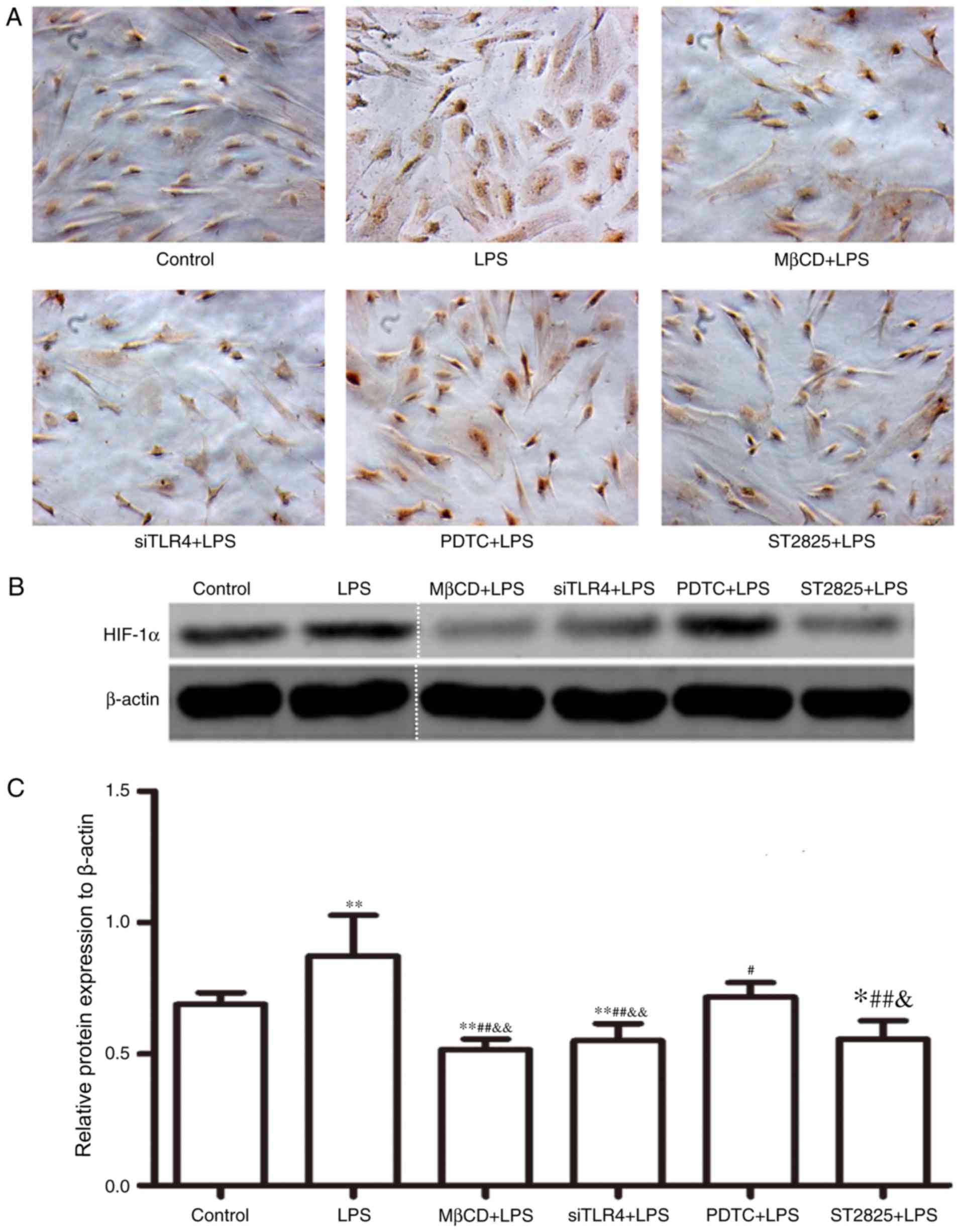
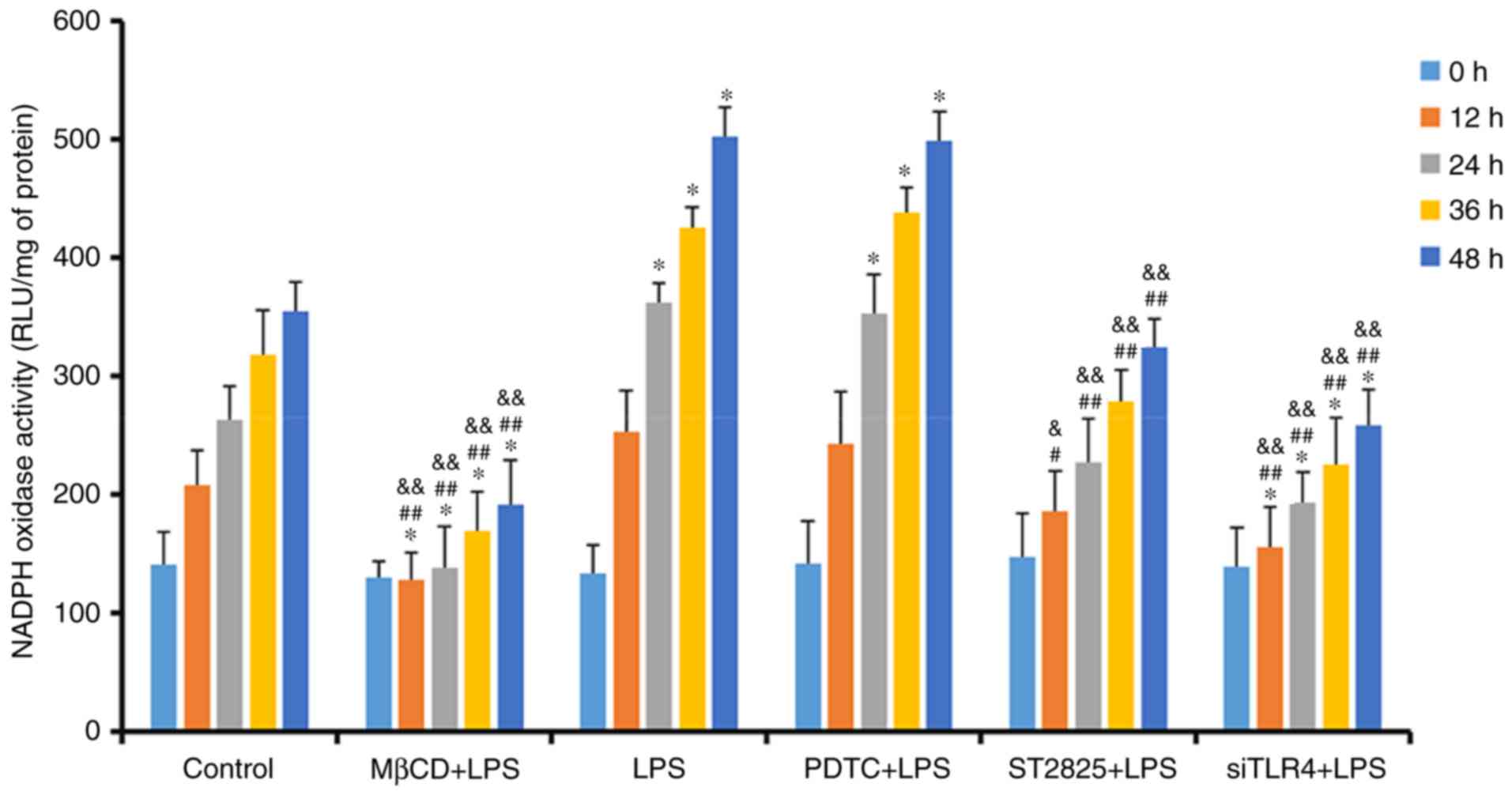
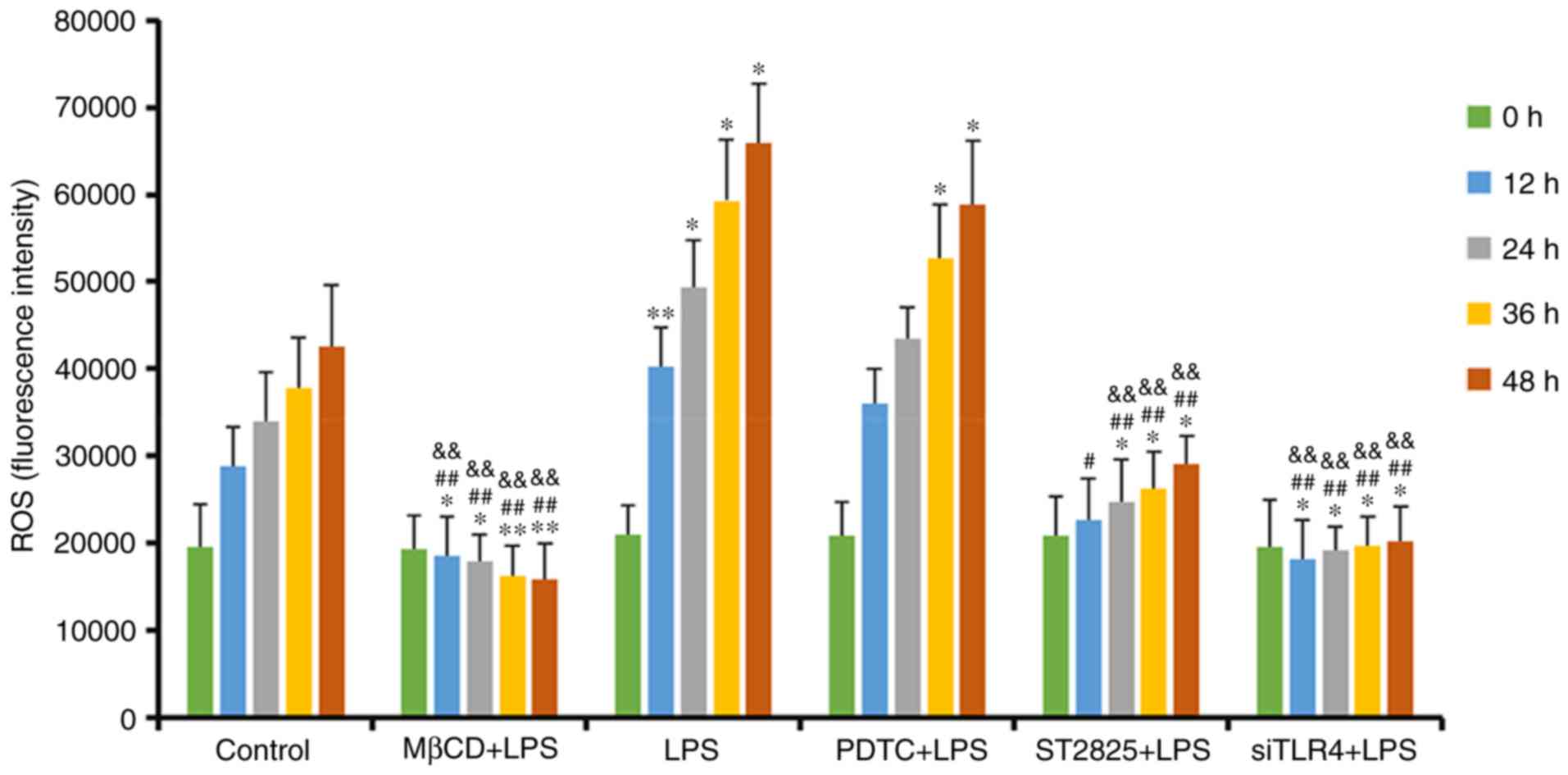
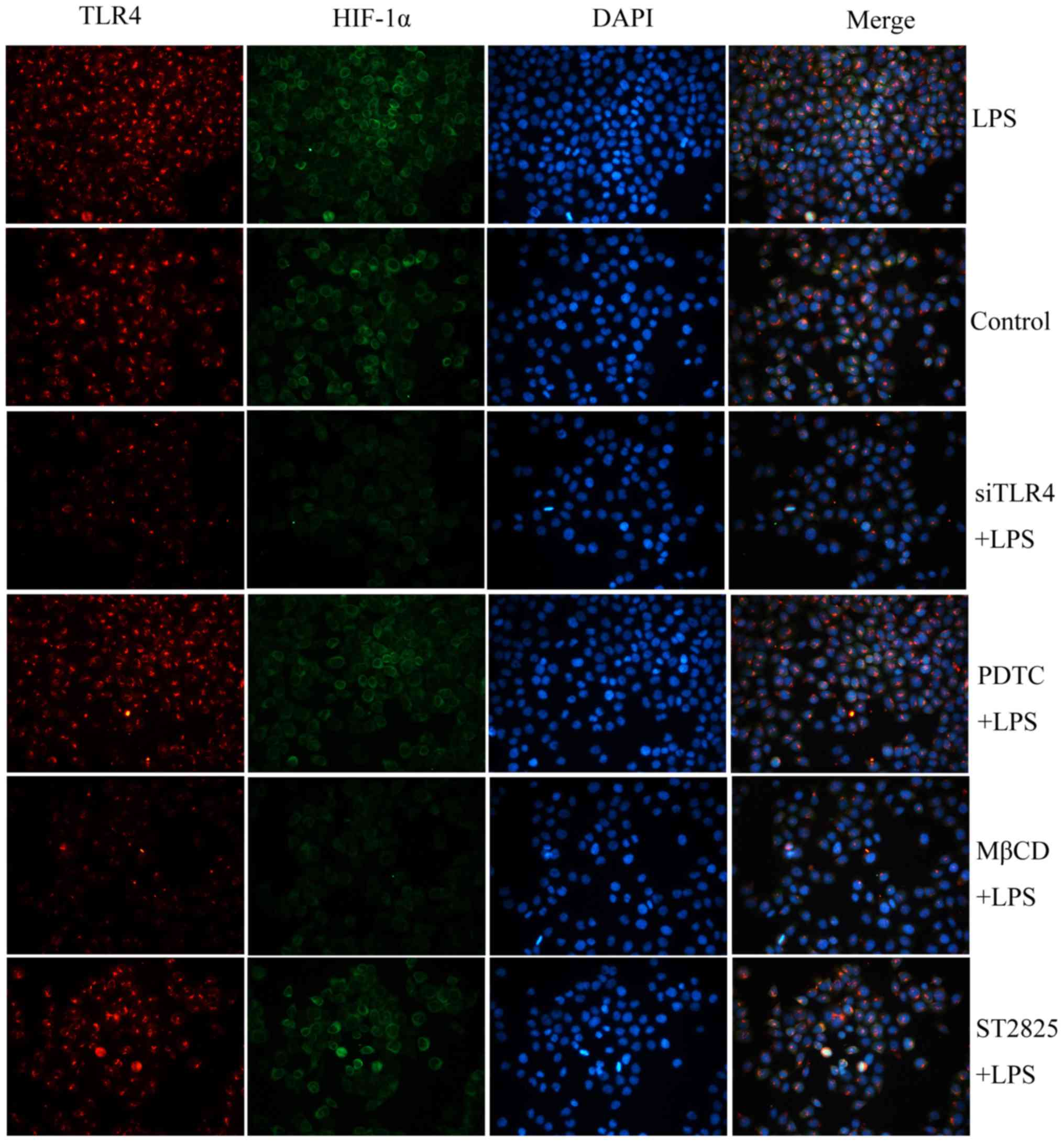
|
1
|
Wei KR, Chen WQ, Zhang SW, Zheng RS, Wang
YN and Liang ZH: Epidemiology of uterine corpus cancer in some
cancer registering areas of China from 2003–2007. Zhonghua Fu Chan
Ke Za Zhi. 47:445–451. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sharma N, Akhade AS and Qadri A: Src
kinases central to T-cell receptor signaling regulate TLR-activated
innate immune responses from human T cells. Innate Immun.
22:238–244. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Galli R, Starace D, Busà R, Angelini DF,
Paone A, De Cesaris P, Filippini A, Sette C, Battistini L, Ziparo E
and Riccioli A: TLR stimulation of prostate tumor cells induces
chemokine-mediated recruitment of specific immune cell types. J
Immunol. 184:6658–6669. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Molteni M, Marabella D, Orlandi C and
Rossetti C: Melanoma cell lines are responsive in vitro to
lipopolysaccharide and express TLR-4. Cancer Lett. 235:75–83. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
MacRedmond R, Greene C, Taggart CC,
McElvaney N and O'Neill S: Respiratory epithelial cells require
Toll-like receptor 4 for induction of human beta-defensin 2 by
lipopolysaccharide. Respir Res. 6:1162005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oblak A and Jerala R: Toll-like receptor 4
activation in cancer progression and therapy. Clin Dev Immunol.
2011:6095792011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Roxburgh CS and McMillan DC: The role of
the in situ local inflammatory response in predicting recurrence
and survival in patients with primary operable colorectal cancer.
Cancer Treat Rev. 38:451–466. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Woo JK, Kang JH, Jang YS, Ro S, Cho JM,
Kim HM, Lee SJ and Oh SH: Evaluation of preventive and therapeutic
activity of novel non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, CG100649,
in colon cancer: Increased expression of TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand receptors enhance the apoptotic response
to combination treatment with TRAIL. Oncol Rep. 33:1947–1955. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Goto Y, Arigami T, Kitago M, Nguyen SL,
Narita N, Ferrone S, Ferrone S, Morton DL, Irie RF and Hoon DS:
Activation of Toll-like receptors 2, 3, and 4 on human melanoma
cells induces inflammatory factors. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3642–3653.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu L and Chen S: Toll-like receptors
expressed in tumor cells: Targets for therapy. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 57:1271–1278. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nishimura M and Naito S: Tissue-specific
mRNA expression profiles of human toll-like receptors and related
genes. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:886–892. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Y, Weng Y, Shi Y, Xia X, Wang S and
Duan H: Expression and functional analysis of Toll-like receptor 4
in human cervical carcinoma. J Membr Biol. 247:591–599. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song J, Fan HJ, Li H, Ding H, Lv Q and Hou
SK: Zingerone ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney
injury by inhibiting Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway. Eur J
Pharmacol. 772:108–114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fessler MB and Parks JS: Intracellular
lipid flux and membrane microdomains as organizing principles in
inflammatory cell signaling. J Immunol. 187:1529–1535. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Semenza GL: Targeting HIF-1 for cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:721–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nishi H, Sasaki T, Nagamitsu Y, Terauchi
F, Nagai T, Nagao T and Isaka K: Hypoxia inducible factor-1
mediates upregulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator
receptor gene transcription during hypoxia in cervical cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 35:992–998. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Myllyharju J and Koivunen P:
Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl 4-hydroxylases: Common and specific
roles. Biol Chem. 394:435–448. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yatabe N, Kyo S, Maida Y, Nishi H,
Nakamura M, Kanaya T, Tanaka M, Isaka K, Ogawa S and Inoue M:
HIF-1-mediated activation of telomerase in cervical cancer cells.
Oncogene. 23:3708–3715. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jing S, Xu Q, Jing S, Zhao Z, Zhao Z, Wu
F, Liu Q, Cheng Y and Wang J: Effect of silencing HIF-1α by RNA
interference on adhesion and invasion of the human nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cell line CNE-1. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke
Za Zhi. 50:929–933. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tong Y, Yang H, Xu X, Ruan J, Liang M, Wu
J and Luo B: Effect of a hypoxic microenvironment after
radiofrequency ablation on residual hepatocellular cell migration
and invasion. Cancer Sci. 108:753–762. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang JH, Wang ZR, Jiang L, Bao Y and
Cheng YX: Mechanism of anti-tumor effect of HIF-1alpha silencing on
cervical cancer in nude mice. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi.
31:820–825. 2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peyssonnaux C, Cejudo-Martin P, Doedens A,
Zinkernagel AS, Johnson RS and Nizet V: Cutting edge: Essential
role of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha in development of
lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis. J Immunol. 178:7516–7519. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheng YX, Hu M, Chen L, Huang JL, Xia LB,
Li BS, Zhou LM and Hong L: The mechanism of lipid raft mediating
chemoresistance of cervical cancer. Saudi Med J. 33:508–514.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Niecknig H, Tug S, Reyes BD, Kirsch M,
Fandrey J and Berchner-Pfannschmidt U: Role of reactive oxygen
species in the regulation of HIF-1 by prolyl hydroxylase 2 under
mild hypoxia. Free Radic Res. 46:705–717. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cheng Y, Chen G, Hong L, Zhou L, Hu M, Li
B, Huang J, Xia L and Li C: How does hypoxia inducible factor-1α
participate in enhancing the glycolysis activity in cervical
cancer? Ann Diagn Pathol. 17:305–311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cheng YX, Qi XY, Huang JL, Hu M, Zhou LM,
Li BS and Xu XX: Toll-like receptor 4 signaling promotes the
immunosuppressive cytokine production of human cervical cancer. Eur
J Gynaecol Oncol. 33:291–294. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Feng Z, Wang Z, Yang M, Zhou L and Bao Y:
Polysaccharopeptide exerts immunoregulatory effects via
MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 82:201–207.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Carlson CG, Stein L, Dole E, Potter RM and
Bayless D: Agents which inhibit NF-κB signaling block spontaneous
contractile activity and negatively influence survival of
developing myotubes. J Cell Physiol. 231:788–797. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sághy É, Szőke É, Payrits M, Helyes Z,
Börzsei R, Erostyák J, Jánosi TZ, Sétáló G Jr and Szolcsányi J:
Evidence for the role of lipid rafts and sphingomyelin in
Ca2+-gating of Transient Receptor Potential channels in
trigeminal sensory neurons and peripheral nerve terminals.
Pharmacol Res. 100:101–106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhan Z, Xie X, Cao H, Zhou X, Zhang XD,
Fan H and Liu Z: Autophagy facilitates TLR4- and TLR3-triggered
migration and invasion of lung cancer cells through the promotion
of TRAF6 ubiquitination. Autophagy. 10:257–268. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu L, Wang L, Li M, Zhong J, Wang Z and
Chen S: Expression of toll-like receptor 4 is downregulated during
progression of cervical neoplasia. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
59:1021–1028. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Szczepanski MJ, Czystowska M, Szajnik M,
Harasymczuk M, Boyiadzis M, Kruk-Zagajewska A, Szyfter W, Zeromski
J and Whiteside TL: Triggering of Toll-like receptor 4 expressed on
human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma promotes tumor
development and protects the tumor from immune attack. Cancer Res.
69:3105–3113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang B, Zhao J, Li H, He KL, Chen Y, Chen
SH, Mayer L, Unkeless JC and Xiong H: Toll-like receptors on tumor
cells facilitate evasion of immune surveillance. Cancer Res.
65:5009–5014. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang EL, Qian ZR, Nakasono M, Tanahashi T,
Yoshimoto K, Bando Y, Kudo E, Shimada M and Sano T: High expression
of Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88 signals
correlates with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer.
102:908–915. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Iovine B, Guardia F, Irace C and
Bevilacqua MA: l-carnosine dipeptide overcomes acquired resistance
to 5-fluorouracil in HT29 human colon cancer cells via
downregulation of HIF1-alpha and induction of apoptosis. Biochimie.
127:196–204. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Acker T, Fandrey J and Acker H: The good,
the bad and the ugly in oxygen-sensing: ROS, cytochromes and
prolyl-hydroxylases. Cardiovasc Res. 71:195–207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nishi K, Oda T, Takabuchi S, Oda S, Fukuda
K, Adachi T, Semenza GL, Shingu K and Hirota K: LPS induces
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation in macrophage-differentiated
cells in a reactive oxygen species-dependent manner. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 10:983–995. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tewari R, Choudhury SR, Ghosh S, Mehta VS
and Sen E: Involvement of TNFα-induced TLR4-NF-κB and TLR4-HIF-1α
feed-forward loops in the regulation of inflammatory responses in
glioma. Journal of Molecular Medicine. 2012.90(1): 67–80.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lai FB, Liu WT, Jing YY, Yu GF, Han ZP,
Yang X, Zeng JX, Zhang HJ, Shi RY, Li XY, et al: Lipopolysaccharide
supports maintaining the stemness of CD133(+) hepatoma cells
through activation of the NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway. Cancer Lett.
378:131–141. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Patra SK: Dissecting lipid raft
facilitated cell signaling pathways in cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1785:182–206. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wickström SA, Alitalo K and Keski-Oja J:
Endostatin associates with lipid rafts and induces reorganization
of the actin cytoskeleton via down-regulation of RhoA activity. J
Biol Chem. 278:37895–37901. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chansrichavala P, Chantharaksri U, Sritara
P, Ngaosuwankul N and Chaiyaroj SC: Atorvastatin affects TLR4
clustering via lipid raft modulation. Int Immunopharmacol.
10:892–899. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Das S, Alhasson F, Dattaroy D, Pourhoseini
S, Seth RK, Nagarkatti M, Nagarkatti PS, Michelotti GA, Diehl AM,
Kalyanaraman B and Chatterjee S: NADPH oxidase-derived
peroxynitrite drives inflammation in mice and human nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis via TLR4-Lipid raft recruitment. Am J Pathol.
185:1944–1957. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gorudko IV, Mukhortava AV, Caraher B, Ren
M, Cherenkevich SN, Kelly GM and Timoshenko AV: Lectin-induced
activation of plasma membrane NADPH oxidase in cholesterol-depleted
human neutrophils. Arch Biochem Biophys. 516:173–181. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bieberich E: It's a lipid's world:
Bioactive lipid metabolism and signaling in neural stem cell
differentiation. Neurochem Res. 37:1208–1229. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Eum SY, Andras I, Hennig B and Toborek M:
NADPH oxidase and lipid raft-associated redox signaling are
required for PCB153-induced upregulation of cell adhesion molecules
in human brain endothelial cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
240:299–305. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gribar SC, Anand RJ, Sodhi CP and Hackam
DJ: The role of epithelial Toll-like receptor signaling in the
pathogenesis of intestinal inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 83:493–498.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tanaka T, Legat A, Adam E, Steuve J, Gatot
JS, Vandenbranden M, Ulianov L, Lonez C, Ruysschaert JM, Muraille
E, et al: DiC14-amidine cationic liposomes stimulate myeloid
dendritic cells through Toll-like receptor 4. Eur J Immunol.
38:1351–1357. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kim D and Kim JY: Anti-CD14 antibody
reduces LPS responsiveness via TLR4 internalization in human
monocytes. Mol Immunol. 57:210–215. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Campbell JS, Riehle KJ, Brooling JT, Bauer
RL, Mitchell C and Fausto N: Proinflammatory cytokine production in
liver regeneration is Myd88-dependent, but independent of Cd14,
Tlr2, and Tlr4. J Immunol. 176:2522–2528. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|