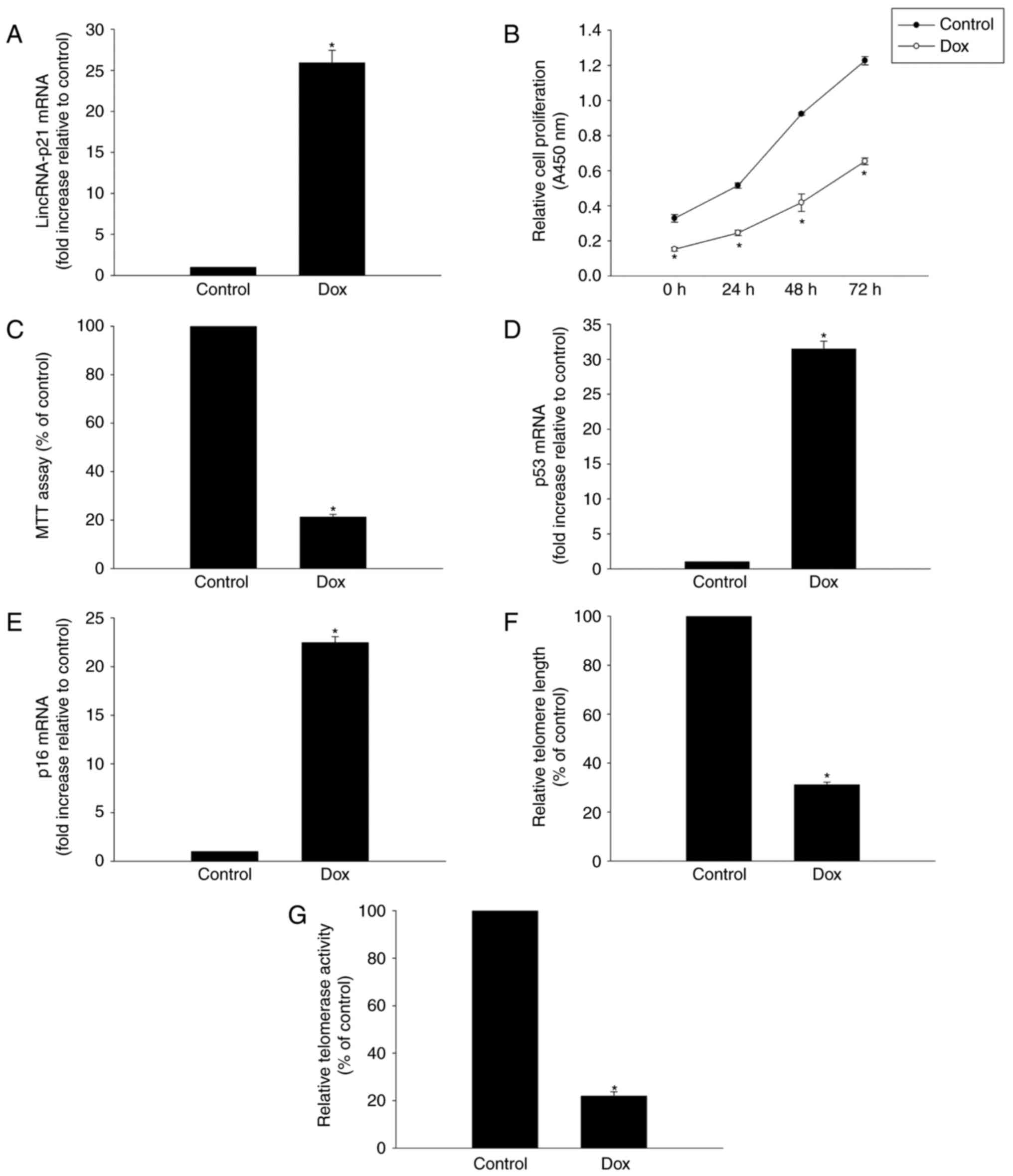
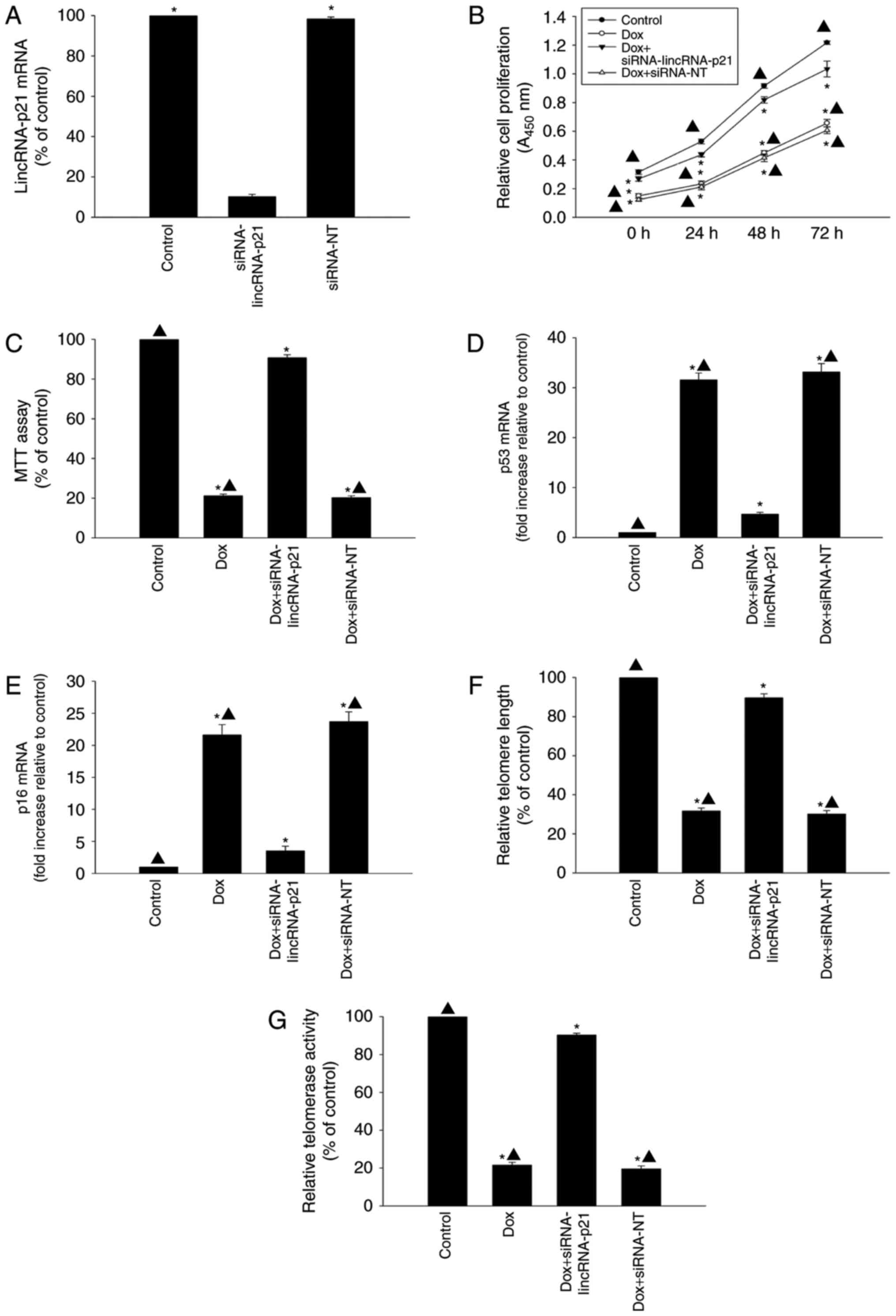
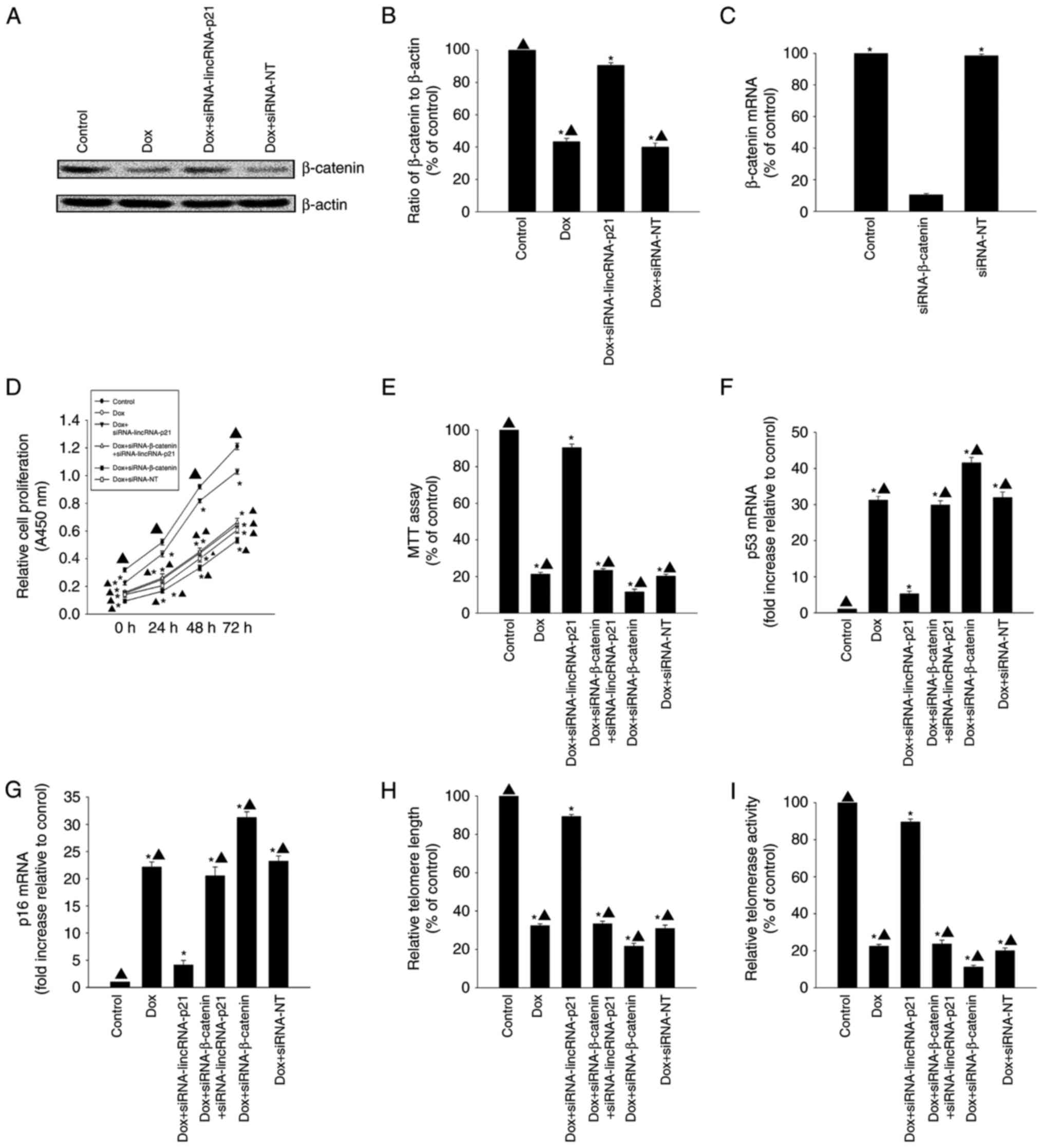
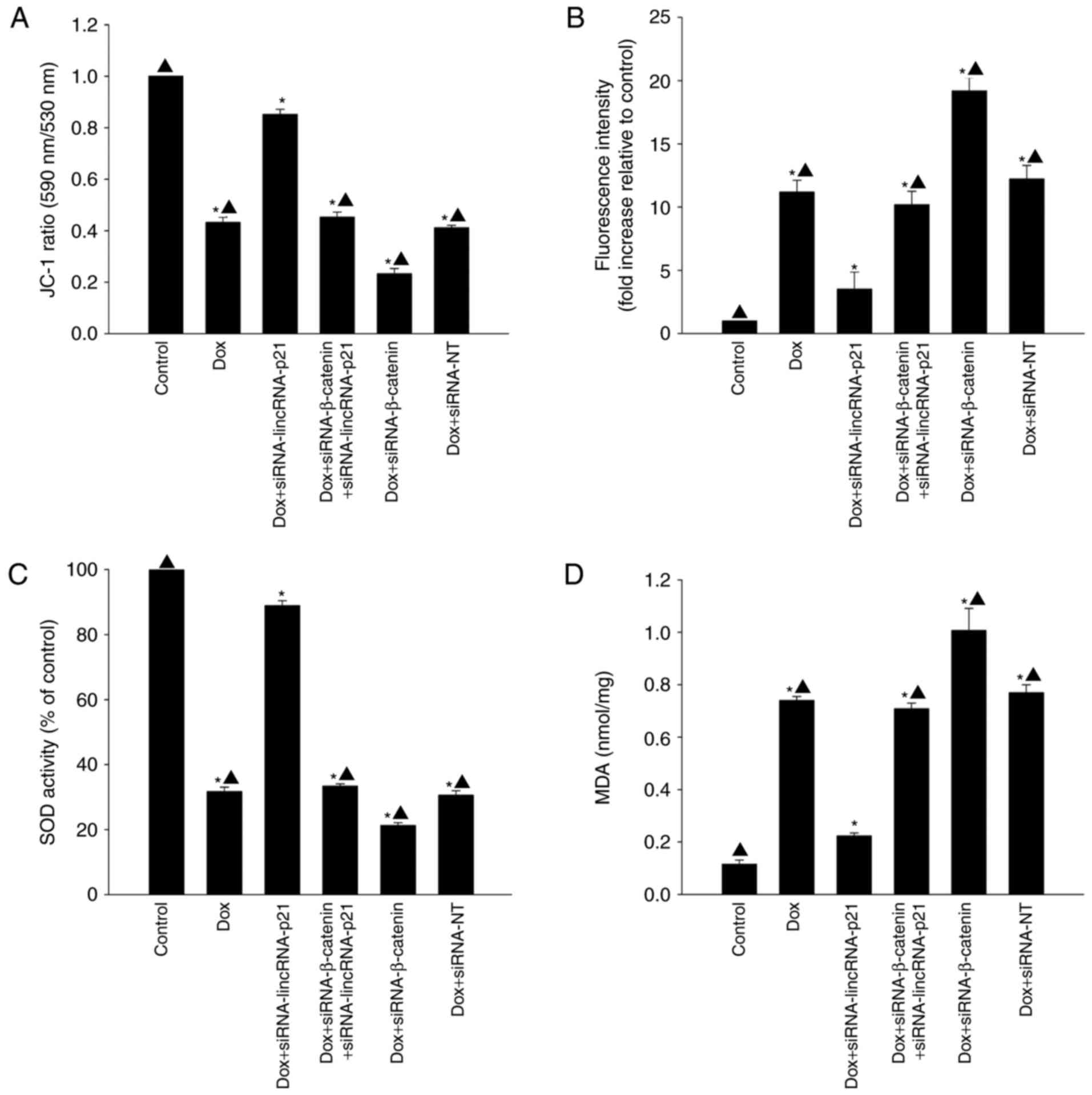
|
1
|
Binaschi M, Bigioni M, Cipollone A, Rossi
C, Goso C, Maggi CA, Capranico G and Animati F: Anthracyclines:
Selected new developments. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents.
1:113–130. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferrans VJ, Clark JR, Zhang J, Yu ZX and
Herman EH: Pathogenesis and prevention of doxorubicin
cardiomyopathy. Tsitologiia. 39:928–937. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kumar S, Marfatia R, Tannenbaum S, Yang C
and Avelar E: Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy 17 years after
chemotherapy. Tex Heart Inst J. 39:424–427. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartlett JJ, Trivedi PC and Pulinilkunnil
T: Autophagic dysregulation in doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 104:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Du WW, Yang W, Chen Y, Wu ZK, Foster FS,
Yang Z, Li X and Yang BB: Foxo3 circular RNA promotes cardiac
senescence by modulating multiple factors associated with stress
and senescence responses. Eur Heart J. 38:1402–1412.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ghosh AK, Rai R, Park KE, Eren M, Miyata
T, Wilsbacher LD and Vaughan DE: A small molecule inhibitor of
PAI-1 protects against doxorubicin-induced cellular senescence.
Oncotarget. 7:72443–72457. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Atianand MK, Cafferey DR and Fitzgerald
KA: Immunobiology of long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Immunol.
35:177–198. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kour S and Rath PC: Age-related expression
of a repeat-rich intergenic long noncoding RNA in the rat brain.
Mol Neurobiol. 54:639–660. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I,
Santini T, Sthandier O, Chinappi M, Tramontano A and Bozzoni I: A
long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning
as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell. 147:358–369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu S, Wang Z, Chen D, Zhang B, Tian RR,
Wu J, Zhang Y, Xu K, Yang LM, Cheng C, et al: Annotation and
cluster analysis of spatiotemporal- and sex-related lncRNA
expression in rhesus macaque brain. Genome Res. 27:1608–1620. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K, Srikantan S, Yang
X, Martindale JL, De S, Huarte M, Zhan M, Becker KG and Gorospe M:
LincRNA-p21 suppresses target mRNA translation. Mol Cell.
47:648–655. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abdelmohsen K and Gorospe M: Noncoding RNA
control of cellular senescence. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA.
6:615–629. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu G, Cai J, Han Y, Chen J, Huang ZP, Chen
C, Cai Y, Huang H, Yang Y, Liu Y, et al: LincRNA-p21 regulates
neointima formation, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation,
apoptosis, and atherosclerosis by enhancing p53 activity.
Circulation. 130:1452–1465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dimitrova N, Zamudio JR, Jong RM, Soukup
D, Resnick R, Sarma K, Ward AJ, Raj A, Lee JT, Sharp PA and Jacks
T: LincRNA-p21 activates p21 in cis to promote Polycomb target gene
expression and to enforce the G1/S checkpoint. Mol Cell.
54:777–790. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schwörer S, Becker F, Feller C, Baig AH,
Köber U, Henze H, Kraus JM, Xin B, Lechel A, Lipka DB, et al:
Epigenetic stress responses induce muscle stem-cell ageing by Hoxa9
developmental signals. Nature. 540:428–432. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakamura T, Hosoyama T, Murakami J, Samura
M, Ueno K, Kurazumi H, Suzuki R, Mikamo A and Hamano K: Age-related
increase in Wnt inhibitor causes a senescence-like phenotype in
human cardiac stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 487:653–659.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang J, Lei ZJ, Guo Y, Wang T, Qin ZY,
Xiao HL, Fan LL, Chen DF, Bian XW, Liu J and Wang B:
miRNA-regulated delivery of lincRNA-p21 suppresses β-catenin
signaling and tumorigenicity of colorectal cancer stem cells.
Oncotarget. 6:37852–37870. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen KH, Chen CH, Wallace CG, Chen YT,
Yang CC, Sung PH, Chiang HJ, Chen YL, Chua S, Yip HK and Cheng JT:
Combined therapy with melatonin and exendin-4 effectively
attenuated the deterioration of renal function in rat cardiorenal
syndrome. Am J Transl Res. 9:214–229. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rodier F and Campisi J: Four faces of
cellular senescence. J Cell Biol. 192:547–556. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Du Q, Zhu B, Zhai Q and Yu B: Sirt3
attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiac hypertrophy and
mitochondrial dysfunction via suppression of Bnip3. Am J Transl
Res. 9:3360–3373. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Przybylska D, Janiszewska D, Goździk A,
Bielak-Zmijewska A, Sunderland P, Sikora E and Mosieniak G: NOX4
downregulation leads to senescence of human vascular smooth muscle
cells. Oncotarget. 7:66429–66443. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zeng Q, Wang Q, Chen X, Xia K, Tang J,
Zhou X, Cheng Y, Chen Y, Huang L, Xiang H, et al: Analysis of
lncRNAs expression in UVB-induced stress responses of melanocytes.
J Dermatol Sci. 81:53–60. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hall JR, Messenger ZJ, Tam HW, Phillips
SL, Recio L and Smart RC: Long noncoding RNA lincRNA-p21 is the
major mediator of UVB-induced and p53-dependent apoptosis in
keratinocytes. Cell Death Dis. 6:e17002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang N, Fu Y, Zhang H, Hui S, Zhu N and
Yang G: LincRNA-p21 activates endoplasmic reticulum stress and
inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:281512015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Crepin T, Carron C, Roubiou C, Gaugler B,
Gaiffe E, Simula-Faivre D, Ferrand C, Tiberghien P, Chalopin JM,
Moulin B, et al: ATG-induced accelerated immune senescence:
Clinical implications in renal transplant recipients. Am J
Transplant. 15:1028–1038. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xia W, Zhang F, Xie C, Jiang M and Hou M:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor confers resistance to
senescence through CD74-dependent AMPK-FOXO3a signaling in
mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang F, Teves SS, Kemp CJ and Henikoff S:
Doxorubicin, DNA torsion, and chromatin dynamics. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1845:84–89. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cardinale D, Colombo A, Bacchiani G,
Tedeschi I, Meroni CA, Veglia F, Civelli M, Lamantia G, Colombo N,
Curigliano G, et al: Early detection of anthracycline
cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy.
Circulation. 131:1981–1988. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Singal PK and Iliskovic N:
Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 339:900–905.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang S, Liu X, Bawa-Khalfe T, Lu LS, Lyu
YL, Liu LF and Yeh ET: Identification of the molecular basis of
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Nat Med. 18:1639–1642. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Suliman HB, Carraway MS, Ali AS, Reynolds
CM, Welty-Wolf KE and Piantadosi CA: The CO/HO system reverses
inhibition of mitochondrial biogenesis and prevents murine
doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. J Clin Invest. 117:3730–3741.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Minotti G, Ronchi R, Salvatorelli E, Menna
P and Cairo G: Doxorubicin irreversibly inactivates iron regulatory
proteins 1 and 2 in cardiomyocytes: Evidence for distinct metabolic
pathways and implications for iron-mediated cardiotoxicity of
antitumor therapy. Cancer Res. 61:8422–8428. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gutschner T and Diederichs S: The
hallmarks of cancer: A long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol.
9:703–719. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Quinodoz S and Guttman M: Long noncoding
RNAs: An emerging link between gene regulation and nuclear
organization. Trends Cell Biol. 24:651–663. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Andersson R, Refsing Andersen P, Valen E,
Core LJ, Bornholdt J, Boyd M, Heick Jensen T and Sandelin A:
Nuclear stability and transcriptional directionality separate
functionally distinct RNA species. Nat Commun. 5:53362014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kalwa M, Hänzelmann S, Otto S, Kuo CC,
Franzen J, Joussen S, Fernandez-Rebollo E, Rath B, Koch C, Hofmann
A, et al: The lncRNA HOTAIR impacts on mesenchymal stem cells via
triple helix formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:10631–10643. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bianchessi V, Badi I, Bertolotti M, Nigro
P, D'Alessandra Y, Capogrossi MC, Zanobini M, Pompilio G, Raucci A
and Lauri A: The mitochondrial lncRNA ASncmtRNA-2 is induced in
aging and replicative senescence in endothelial cells. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 81:62–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim C, Kang D, Lee EK and Lee JS: Long
Noncoding RNAs and RNA-binding proteins in oxidative stress,
cellular senescence and age-related diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:20623842017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lim BK, Xiong D, Dorner A, Youn TJ, Yung
A, Liu TI, Gu Y, Dalton ND, Wright AT, Evans SM, et al:
Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (CAR) mediates
atrioventricular-node function and connexin 45 localization in the
murine heart. J Clin Invest. 118:2758–2770. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yu F, Guo Y, Chen B, Shi L, Dong P, Zhou M
and Zheng J: LincRNA-p21 Inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in
activated hepatic stellate cells via sponging MicroRNA-17-5p. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 41:1970–1980. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim YY, Jee HJ, Um JH, Kim YM, Bae SS and
Yun J: Cooperation between p21 and Akt is required for
p53-dependent cellular senescence. Aging Cell. 16:1094–1103. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Finkel T and Holbrook NJ: Oxidants,
oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature. 408:239–247.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rigaud VO, Ferreira LR, Ayub-Ferreira SM,
Ávila MS, Brandão SM, Cruz FD, Santos MH, Cruz CB, Alves MS, Issa
VS, et al: Circulating miR-1 as a potential biomarker of
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients.
Oncotarget. 8:6994–7002. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ichikawa Y, Ghanefar M, Bayeva M, Wu R,
Khechaduri A, Naga Prasad SV, Mutharasan RK, Naik TJ and Ardehali
H: Cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin is mediated through mitochondrial
iron accumulation. J Clin Invest. 124:617–630. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang D, Lee H, Haspel JA and Jin Y: Long
noncoding RNA FOXD3-AS1 regulates oxidative stress-induced
apoptosis via sponging microRNA-150. FASEB J. 31:4472–4481. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|