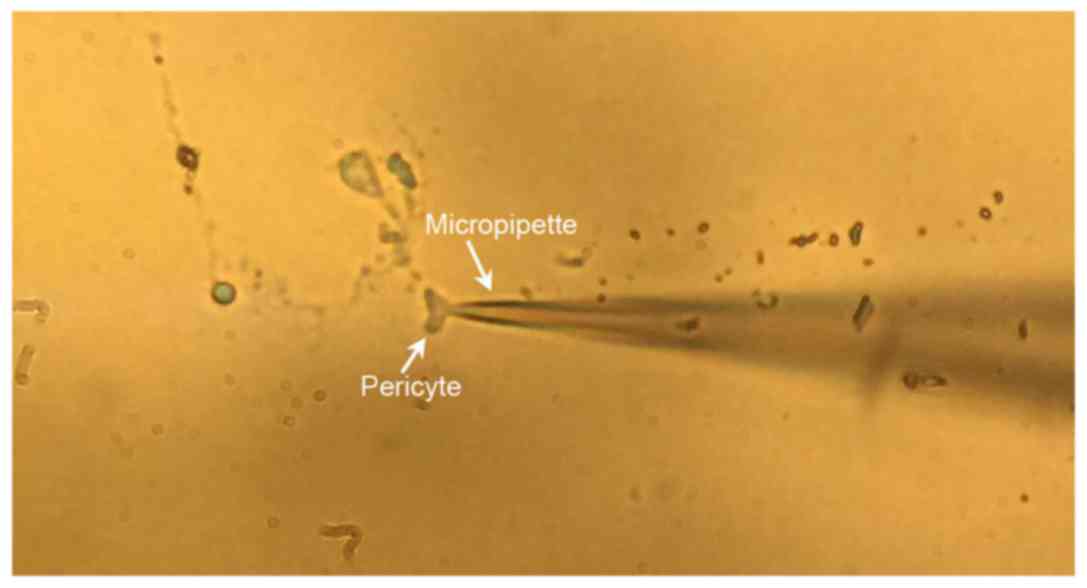
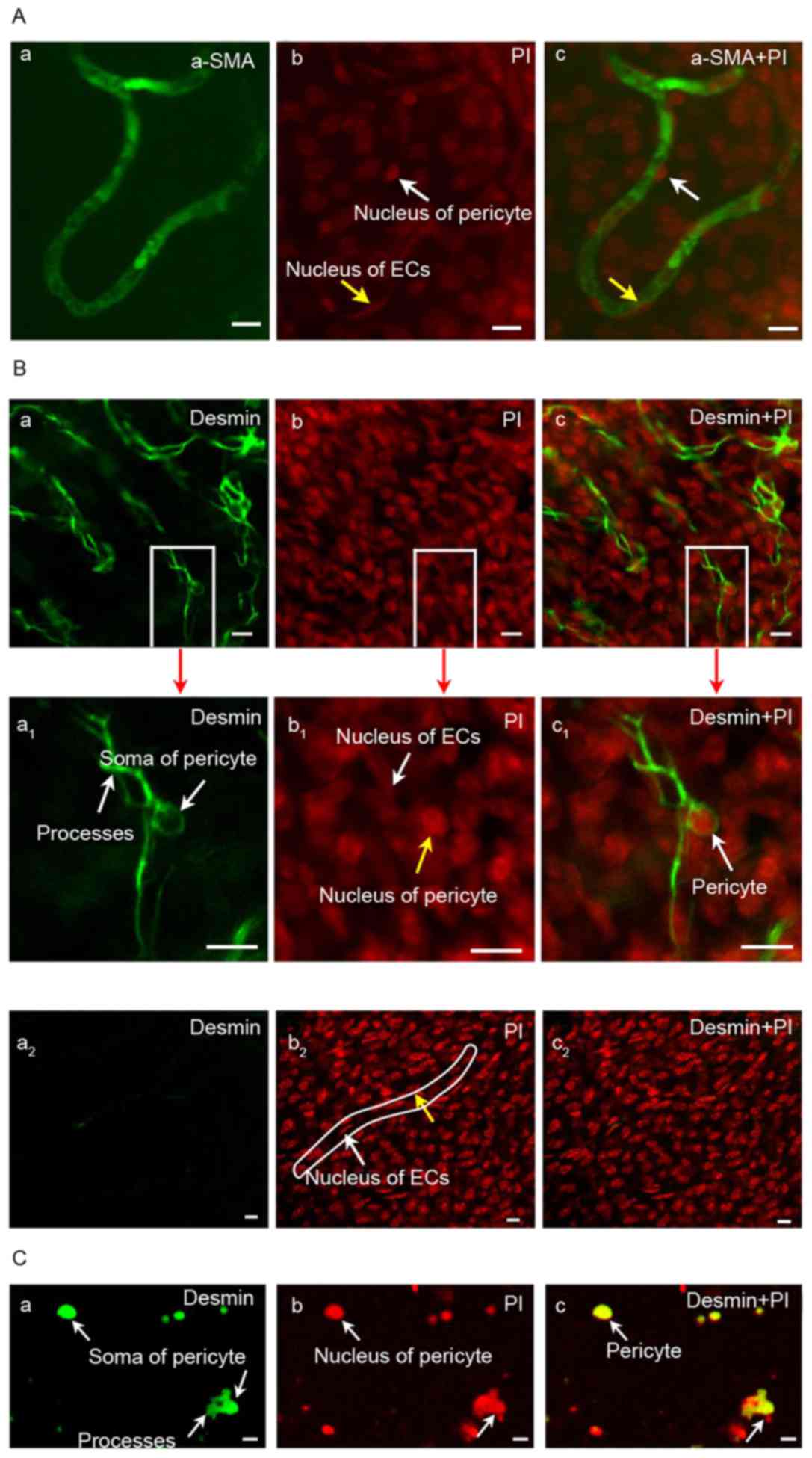
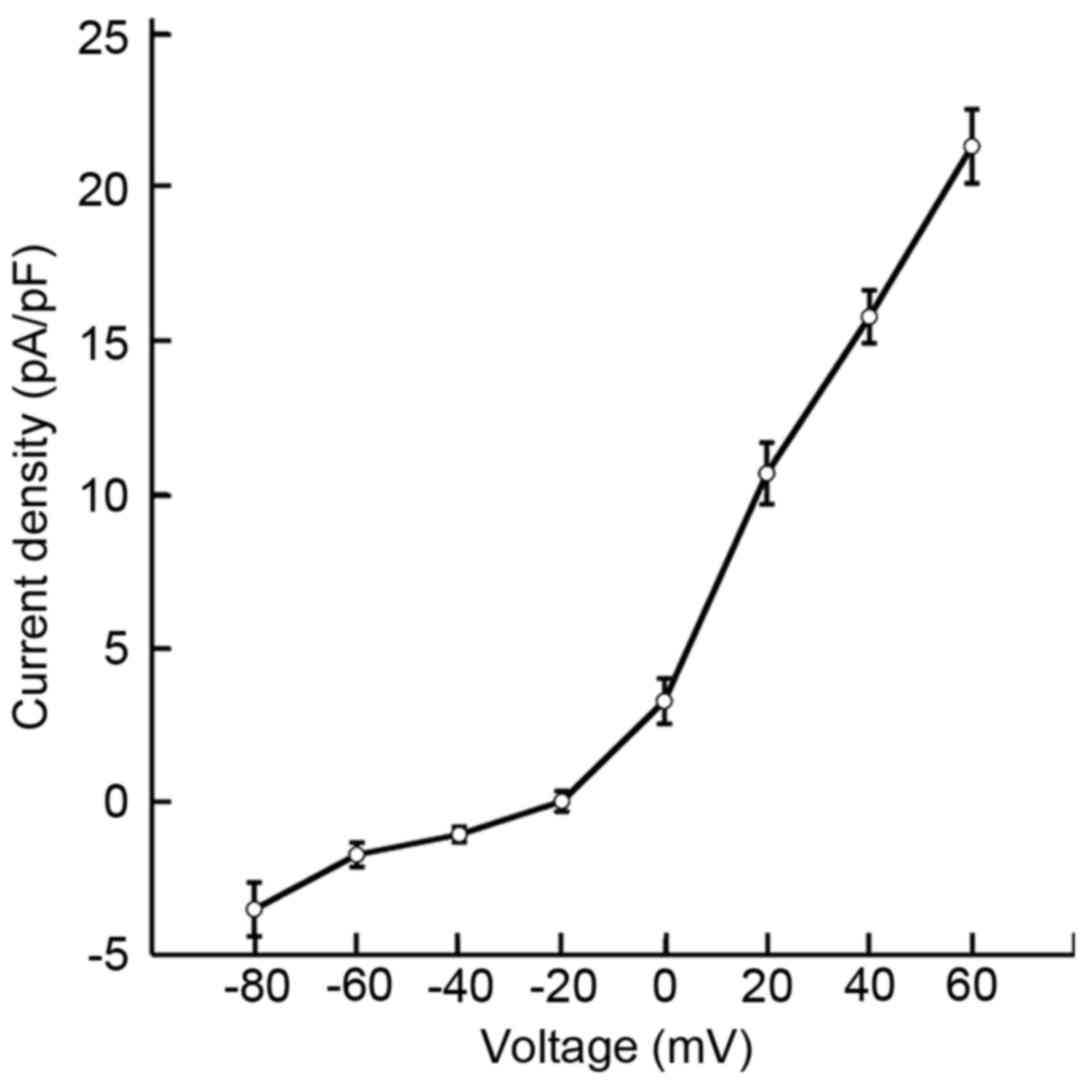
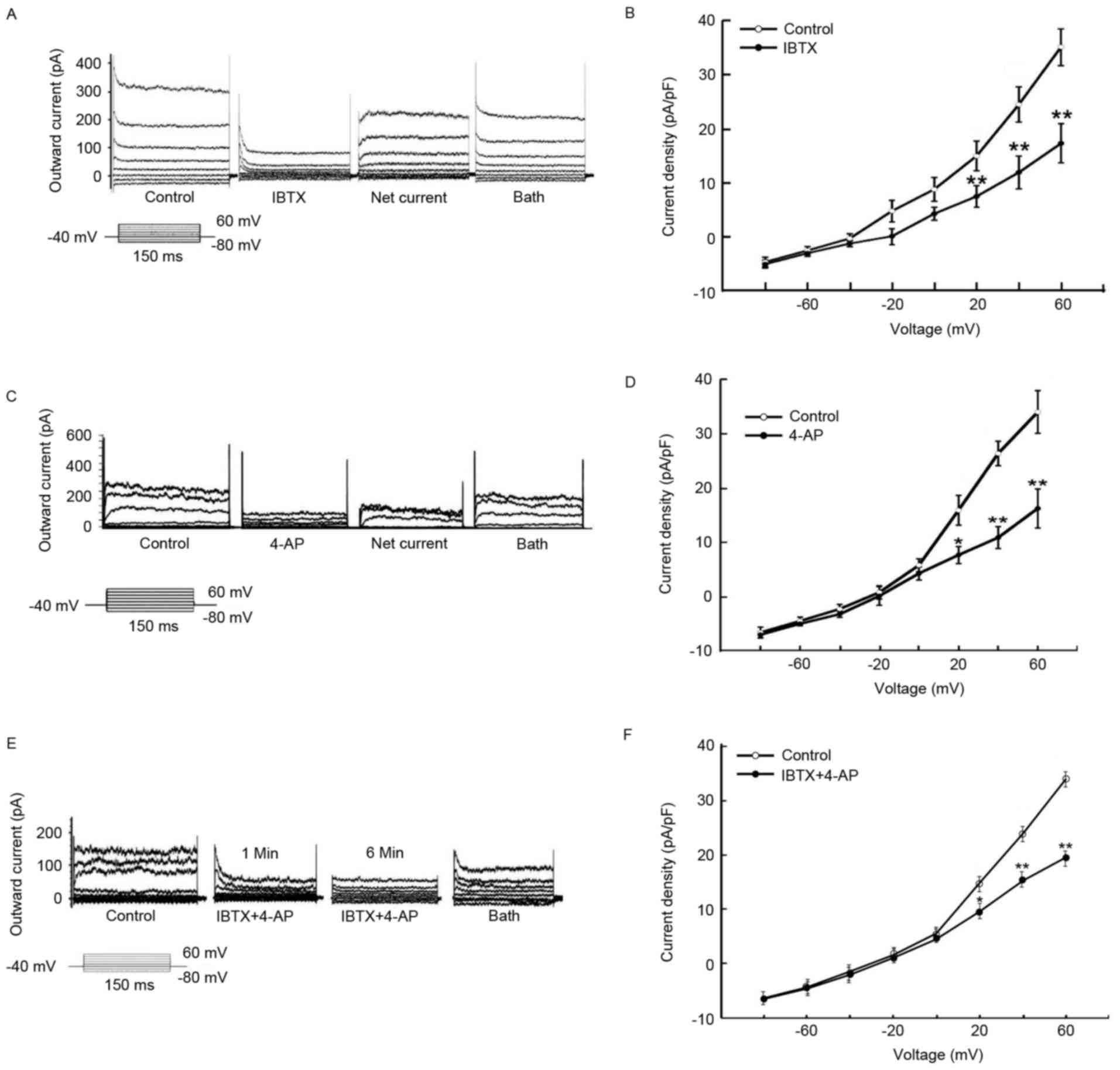
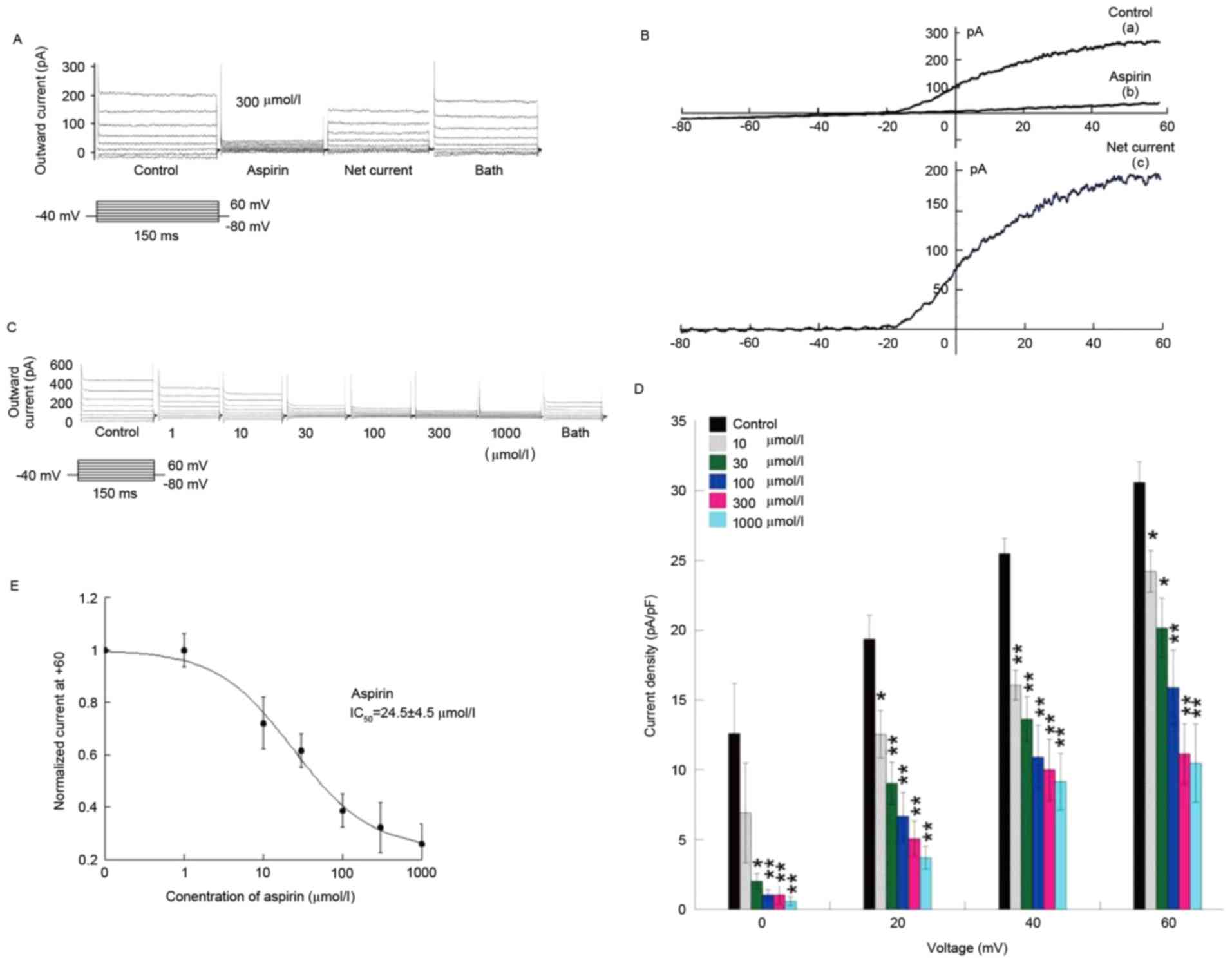
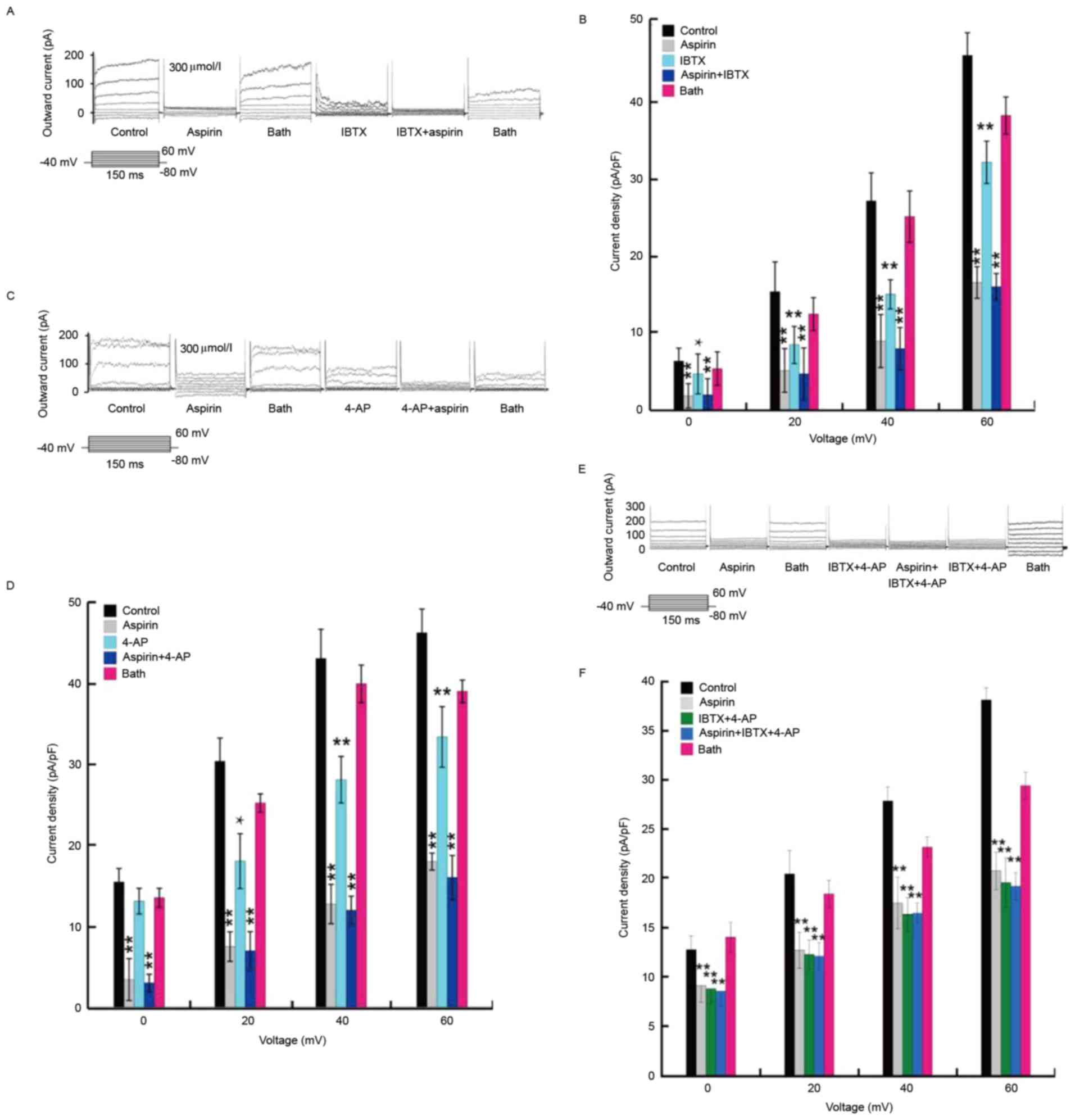
|
1
|
Arai S, Kinouchi H, Akabane A, Owada Y,
Kamii H, Kawase M and Yoshimoto T: Induction of brain-derived
neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and the receptor trk B mRNA following
middle cerebral artery occlusion in rat. Neurosci Lett. 211:57–60.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Uetsuka S, Ogata G, Nagamori S, Isozumi N,
Nin F, Yoshida T, Komune S, Kitahara T, Kikkawa Y, Inohara H, et
al: Molecular architecture of the stria vascularis membrane
transport system, which is essential for physiological functions of
the mammalian cochlea. Eur J Neurosci. 42:1984–2002. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li L, Ma KT, Zhao L, Si JQ, Zhang ZS, Zhu
H and Li J: Niflumic acid hyperpolarizes smooth muscle cells via
calcium-activated potassium channel in spiral modiolar artery of
guinea pigs. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:789–799. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li L, Ma KT, Zhao L, Shi WY, Li XZ, Zhang
ZS and Si JQ: The characteristics of resting membrane potential on
smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells in guinea pigs cochlea
spiral artery. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 28:128–132.
2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li L, Ma KT, Zhao L and Si JQ: Niflumic
acid hyperpolarizes the smooth muscle cells by opening BK(Ca)
channels through ryanodine-sensitive Ca(2+) release in spiral
modiolar artery. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 60:743–750. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma KT, Li XZ, Li L, Zhang ZP, Zhao L, Zhu
H and Si JQ: Comparison of electrophysiological properties of
vascular smooth muscle cells in different arterioles in guinea pig.
Sheng Li Xue Bao. 62:421–426. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang YZ, Liu ZJ, Li L, Fan P, Si JQ, Zhao
L, Ma KT, Zhu L and Gao WJ: Effects of chloride channel blockers on
excitatory junction potentials in smooth muscle cells of cochlear
spiral modiolar artery in guinea pigs. Sheng Li Xue Bao.
58:456–462. 2006.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang ZP, Li XZ, Si JQ, et al: Effects of
acute hypoxia on electrophysiological properties of VSMCs in
guinea-pig spiral modiolar artery. Chin J Mod Med. 21:3979–3983.
2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Fetoni AR, Ferraresi A, Picciotti P,
Gaetani E, Paludetti G and Troiani D: Noise induced hearing loss
and vestibular dysfunction in the guinea pig. Int J Audiol.
48:804–810. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Spicer SS and Schulte BA: Pathologic
changes of presbycusis begin in secondary processes and spread to
primary processes of strial marginal cells. Hear Res. 205:225–240.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fetoni AR, Picciotti PM, Paludetti G and
Troiani D: Pathogenesis of presbycusis in animal models: A review.
Exp Gerontol. 46:413–425. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dai M, Nuttall A, Yang Y and Shi X:
Visualization and contractile activity of cochlear pericytes in the
capillaries of the spiral ligament. Hear Res. 254:100–107. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shi X: Physiopathology of the cochlear
microcirculation. Hear Res. 282:10–24. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Suzuki Y, Inoue T and Ra C: NSAIDs,
mitochondria and calcium signaling: Special focus on
aspirin/salicylates. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 3:1594–1613. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sheppard A, Hayes SH, Chen GD, Ralli M and
Salvi R: Review of salicylate-induced hearing loss, neurotoxicity,
tinnitus and neuropathophysiology. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital.
34:79–93. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Swanson RA, Morton MT, Tsao-Wu G, Savalos
RA, Davidson C and Sharp FR: A semiautomated method for measuring
brain infarct volume. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 10:290–293. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Thomas WE: Brain macrophages: On the role
of pericytes and perivascular cells. Brain Res Brain Res Rev.
31:42–57. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
U.S. National Institutes of Health, .
Laboratory animal welfare: Public health service policy on humane
care and use of laboratory animals by awardee institutions; notice.
Fed Regist. 50:19584–19585. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nicosia RF and Villaschi S: Rat aortic
smooth muscle cells become pericytes during angiogenesis in vitro.
Lab Invest. 73:658–666. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma KT, Li XZ, Li L, Zhang ZP, Zhao L, Zhu
H and Si JQ: Comparison of electrophysiological properties of
vascular smooth muscle cells in different arterioles in guinea pig.
Sheng Li Xue Bao. 62:421–426. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu XL, Liu YX, Zhong BG, Ma HF, Jiang P
and Zhang XY: Effects of salicylate on voltage-gated calcium
channels in rat hippocampal neurons. Chin Pharmacol Bull. 1–1270.
2014.
|
|
22
|
Liu YX, et al: Inhibition of sodium
salicylate on delayed rectifier potassium channels in rat auditory
cortex neurons. Chin Pharmacol Bull. 4:482–486. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|