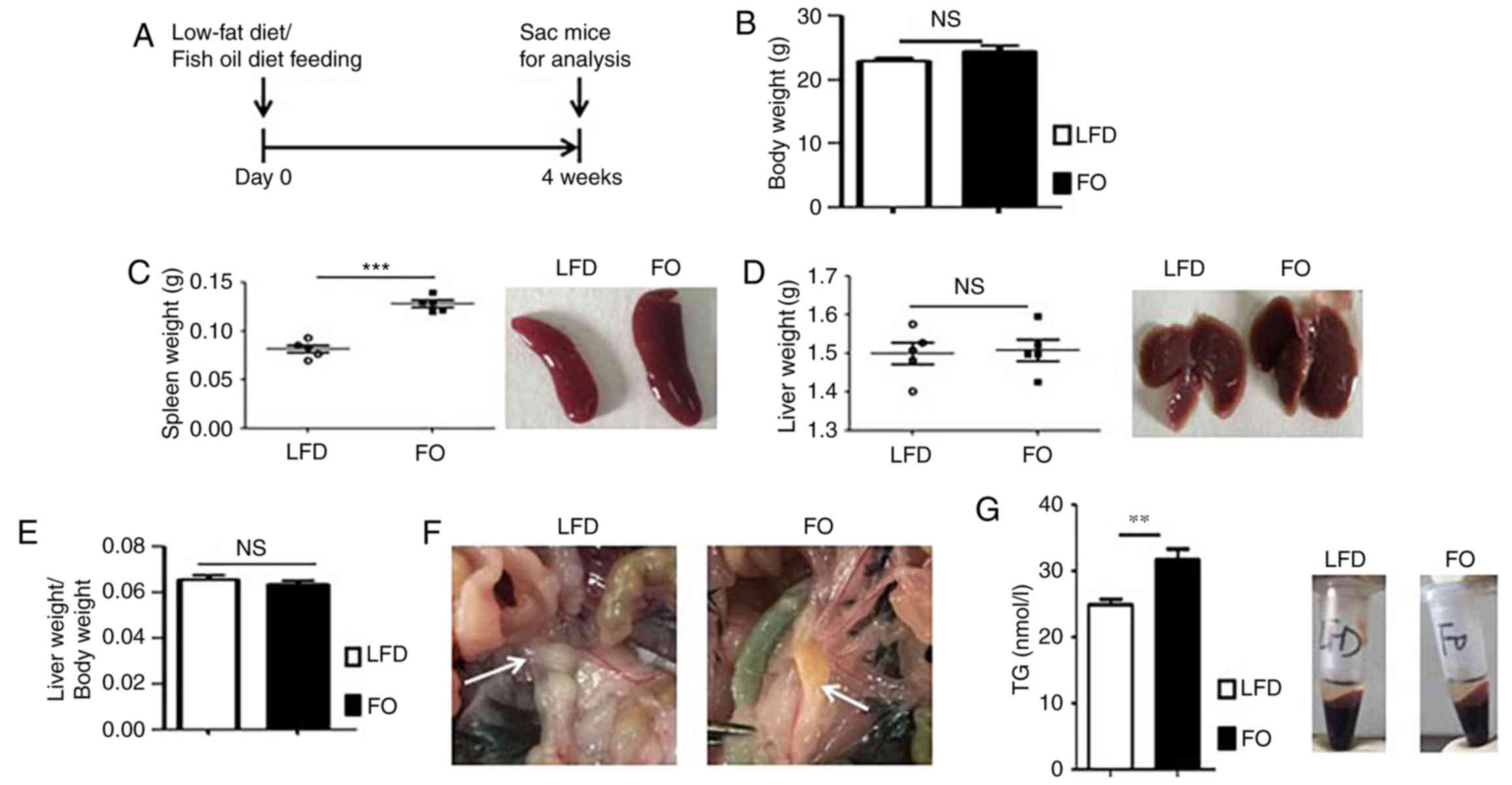
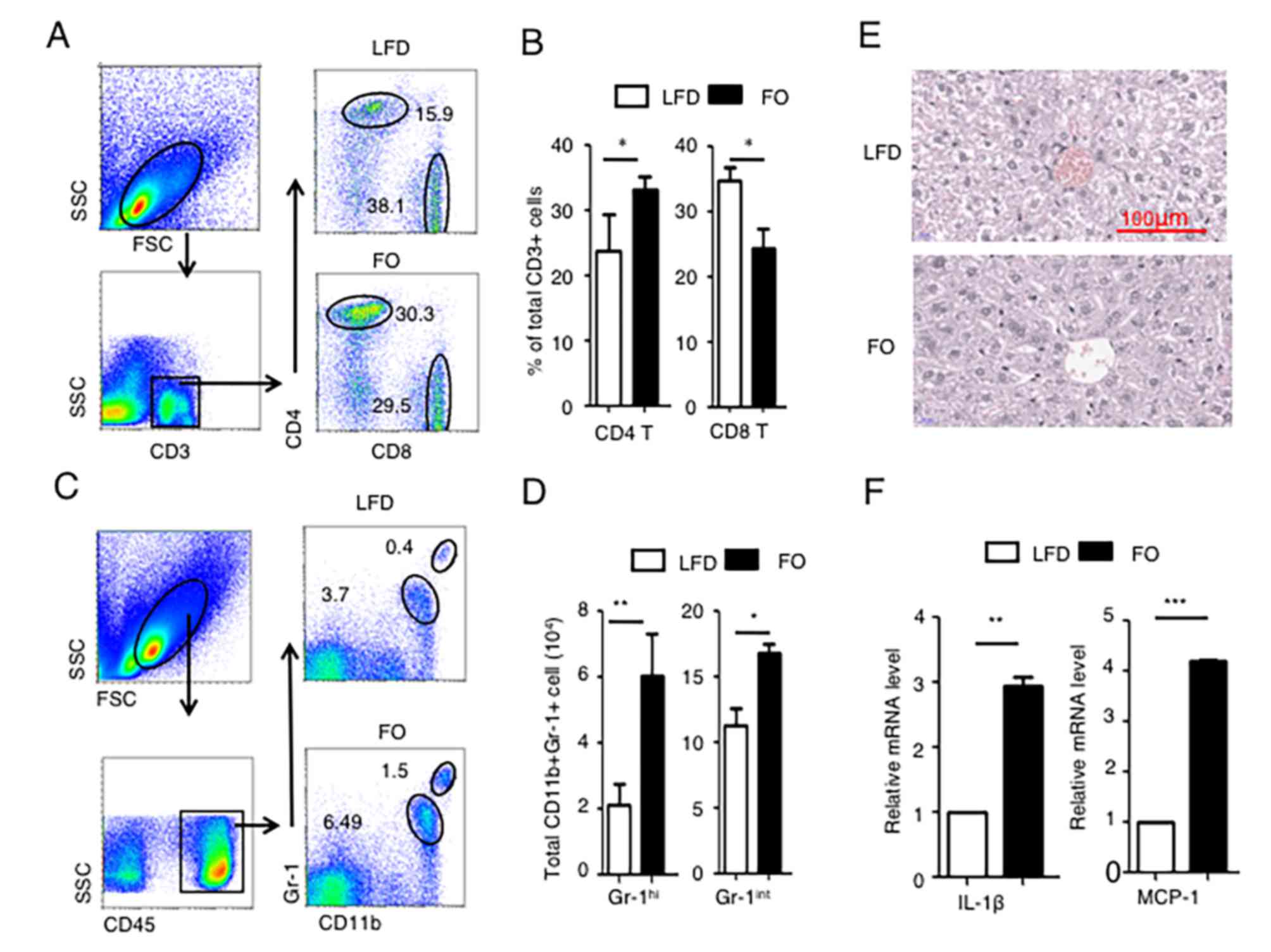
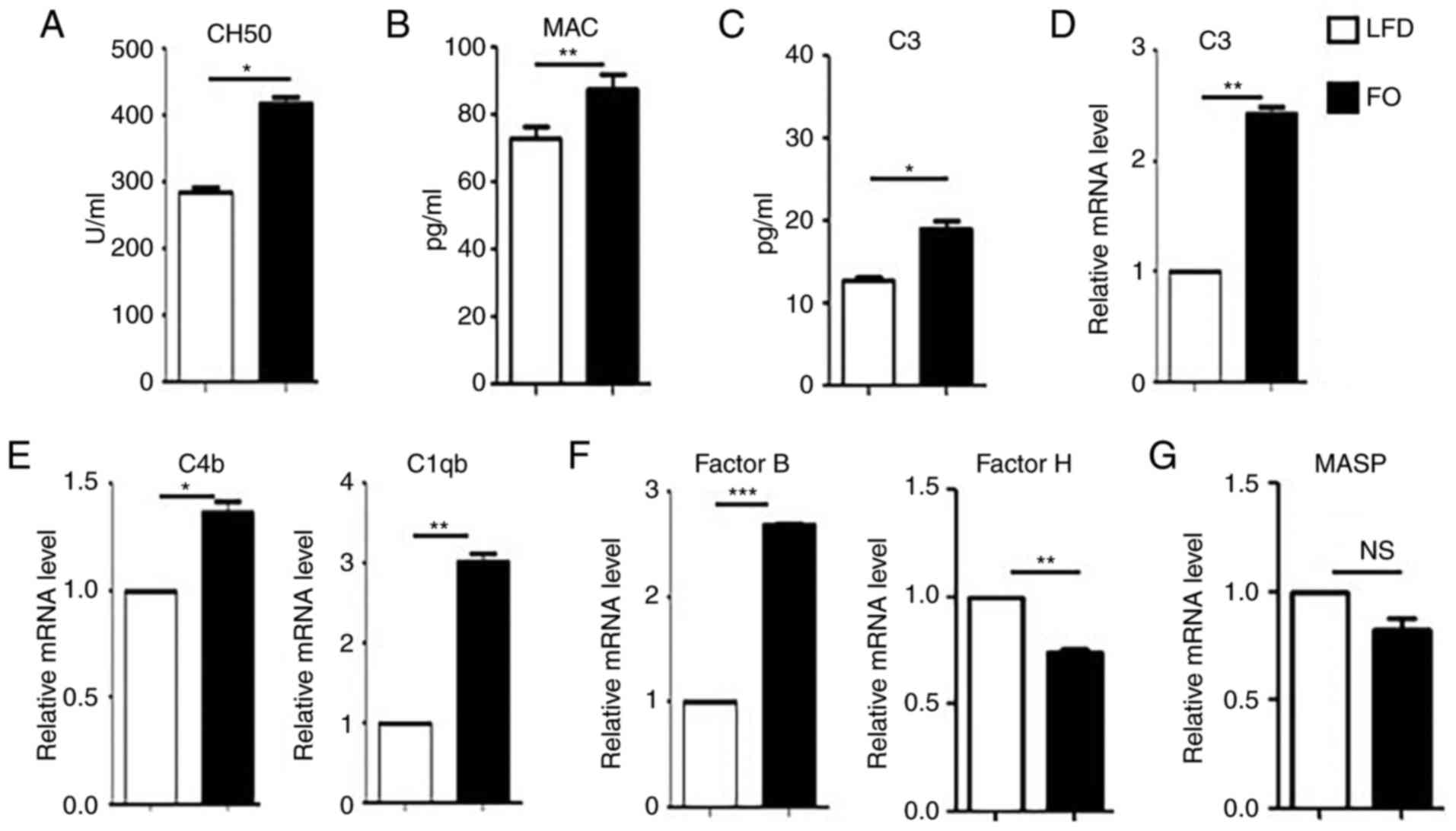
|
1
|
Banchereau J and Steinman RM: Dendritic
cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 392:245–252. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Austyn JM: Death, destruction, danger and
dendritic cells. Nat Med. 5:1232–1233. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Iwasaki A and Medzhitov R: Regulation of
adaptive immunity by the innate immune system. Science.
327:291–295. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cruvinel Wde M, Mesquita D Jr, Araújo JA,
Catelan TT, de Souza AW, da Silva NP and Andrade LE: Immune
system-part I. Fundamentals of innate immunity with emphasis on
molecular and cellular mechanisms of inflammatory response. Rev
Bras Reumatol. 50:434–461. 2010.(In English, Portuguese).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Walport MJ: Complement. First of two
parts. N Engl J Med. 344:1058–1066. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Arbore G, West EE, Spolski R, Robertson
AAB, Klos A, Rheinheimer C, Dutow P, Woodruff TM, Yu ZX, O'Neill
LA, et al: T helper 1 immunity requires complement-driven NLRP3
inflammasome activity in CD4+ T cells. Science.
352:aad12102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cravedi P, van der Touw W and Heeger PS:
Complement regulation of T-cell alloimmunity. Semin Nephrol.
33:565–574. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Martin M and Blom AM: Complement in
removal of the dead-balancing inflammation. Immunol Rev.
274:218–232. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ricklin D, Hajishengallis G, Yang K and
Lambris JD: Complement: A key system for immune surveillance and
homeostasis. Nat Immunol. 11:785–797. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Suresh R, Chandrasekaran P, Sutterwala FS
and Mosser DM: Complement-mediated ‘bystander’ damage initiates
host NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J Cell Sci. 129:1928–1939.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu HQ, Qiu Y, Mu Y, Zhang XJ, Liu L, Hou
XH, Zhang L, Xu XN, Ji AL, Cao R, et al: A high ratio of dietary
n-3/n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids improves obesity-linked
inflammation and insulin resistance through suppressing activation
of TLR4 in SD rats. Nutr Res. 33:849–858. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Serini S, Piccioni E, Merendino N and
Calviello G: Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids as inducers of
apoptosis: Implications for cancer. Apoptosis. 14:135–152. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shoelson SE, Lee J and Goldfine AB:
Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 116:1793–1801.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kalupahana NS, Claycombe KJ and
Moustaid-Moussa N: (n-3) Fatty acids alleviate adipose tissue
inflammation and insulin resistance: Mechanistic insights. Adv
Nutr. 2:304–316. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cooke AA, Connaughton RM, Lyons CL,
McMorrow AM and Roche HM: Fatty acids and chronic low grade
inflammation associated with obesity and the metabolic syndrome.
Eur J Pharmacol. 785:207–214. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vlaicu SI, Tatomir A, Boodhoo D, Vesa S,
Mircea PA and Rus H: The role of complement system in adipose
tissue-related inflammation. Immunol Res. 64:653–664. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lim J, Iyer A, Suen JY, Seow V, Reid RC,
Brown L and Fairlie DP: C5aR and C3aR antagonists each inhibit
diet-induced obesity, metabolic dysfunction and adipocyte and
macrophage signaling. FASEB J. 27:822–831. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hillian AD, McMullen MR, Sebastian BM,
Roychowdhury S, Kashyap SR, Schauer PR, Kirwan JP, Feldstein AE and
Nagy LE: Mice lacking C1q are protected from high fat diet-induced
hepatic insulin resistance and impaired glucose homeostasis. J Biol
Chem. 288:22565–22575. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bavia L, Cogliati B, Dettoni JB, Ferreira
Alves VA and Isaac L: The complement component C5 promotes liver
steatosis and inflammation in murine non-alcoholic liver disease
model. Immunol Lett. 177:53–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Alvarez-Curto E and Milligan G: Metabolism
meets immunity: The role of free fatty acid receptors in the immune
system. Biochem Pharmacol. 114:3–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Viggiano E, Mollica MP, Lionetti L,
Cavaliere G, Trinchese G, De Filippo C, Chieffi S, Gaita M,
Barletta A, De Luca B, et al: Effects of an high-fat diet enriched
in lard or in fish oil on the hypothalamic amp-activated protein
kinase and inflammatory mediators. Front Cell Neurosci. 10:1502016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Poreba M, Mostowik M, Siniarski A,
Golebiowska-Wiatrak R, Malinowski KP, Haberka M, Konduracka E,
Nessler J, Undas A and Gajos G: Treatment with high-dose n-3 PUFAs
has no effect on platelet function, coagulation, metabolic status
or inflammation in patients with atherosclerosis and type 2
diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 16:502017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kremer JM: Fish oil and inflammation-A
fresh look. J Rheumatol. 44:713–716. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xia S, Li X, Cheng L, Han M, Zhang M, Liu
X, Xu H, Zhang M, Shao Q and Qi L: Chronic intake of high fish oil
diet induces myeloid-derived suppressor cells to promote tumor
growth. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 63:663–673. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xia S, Li XP, Cheng L, Han MT, Zhang MM,
Shao QX, Xu HX and Qi L: Fish oil-rich diet promotes hematopoiesis
and alters hematopoietic niche. Endocrinology. 156:2821–2830. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xia S, Guo Z, Xu X, Yi H, Wang Q and Cao
X: Hepatic microenvironment programs hematopoietic progenitor
differentiation into regulatory dendritic cells, maintaining liver
tolerance. Blood. 112:3175–3185. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xia S, Sha H, Yang L, Ji Y,
Ostrand-Rosenberg S and Qi L: Gr-1+ CD11b+ myeloid-derived
suppressor cells suppress inflammation and promote insulin
sensitivity in obesity. J Biol Chem. 286:23591–23599. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gao B, Jeong WI and Tian Z: Liver: An
organ with predominant innate immunity. Hepatology. 47:729–736.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ricklin D, Reis ES, Mastellos DC, Gros P
and Lambris JD: Complement component C3-The ‘Swiss Army Knife’ of
innate immunity and host defense. Immunol Rev. 274:33–58. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Morgan BP and Gasque P: Extrahepatic
complement biosynthesis: Where, when and why? Clin Exp Immunol.
107:1–7. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Marsh JE, Zhou W and Sacks SH: Local
tissue complement synthesis-fine tuning a blunt instrument. Arch
Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 49 Suppl 1:S41–S46. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Alper CA, Johnson AM, Birtch AG and Moore
FD: Human C′3: Evidence for the liver as the primary site of
synthesis. Science. 163:286–288. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Morris KM, Aden DP, Knowles BB and Colten
HR: Complement biosynthesis by the human hepatoma-derived cell line
HepG2. J Clin Invest. 70:906–913. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Walport MJ: Complement. Second of two
parts. N Engl J Med. 344:1140–1144. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Arlaud GJ, Biro A and Ling WL:
Enzymatically modified low-density lipoprotein is recognized by c1q
and activates the classical complement pathway. J Lipids.
2011:3760922011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Arbore G and Kemper C: A novel
‘complement-metabolism-inflammasome axis’ as a key regulator of
immune cell effector function. Eur J Immunol. 46:1563–1573. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Samstad EO, Niyonzima N, Nymo S, Aune MH,
Ryan L, Bakke SS, Lappegård KT, Brekke OL, Lambris JD, Damås JK, et
al: Cholesterol crystals induce complement-dependent inflammasome
activation and cytokine release. J Immunol. 192:2837–2845. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Haeffner-Cavaillon N, Cavaillon JM, Laude
M and Kazatchkine MD: C3a(C3adesArg) induces production and release
of interleukin 1 by cultured human monocytes. J Immunol.
139:794–799. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bavia L, de Castro IA, Cogliati B, Dettoni
JB, Alves VA and Isaac L: Complement C5 controls liver lipid
profile, promotes liver homeostasis and inflammation in C57BL/6
genetic background. Immunobiology. 221:822–832. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Listenberger LL, Han X, Lewis SE, Cases S,
Farese RV Jr, Ory DS and Schaffer JE: Triglyceride accumulation
protects against fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 100:pp. 3077–3082. 2003; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|