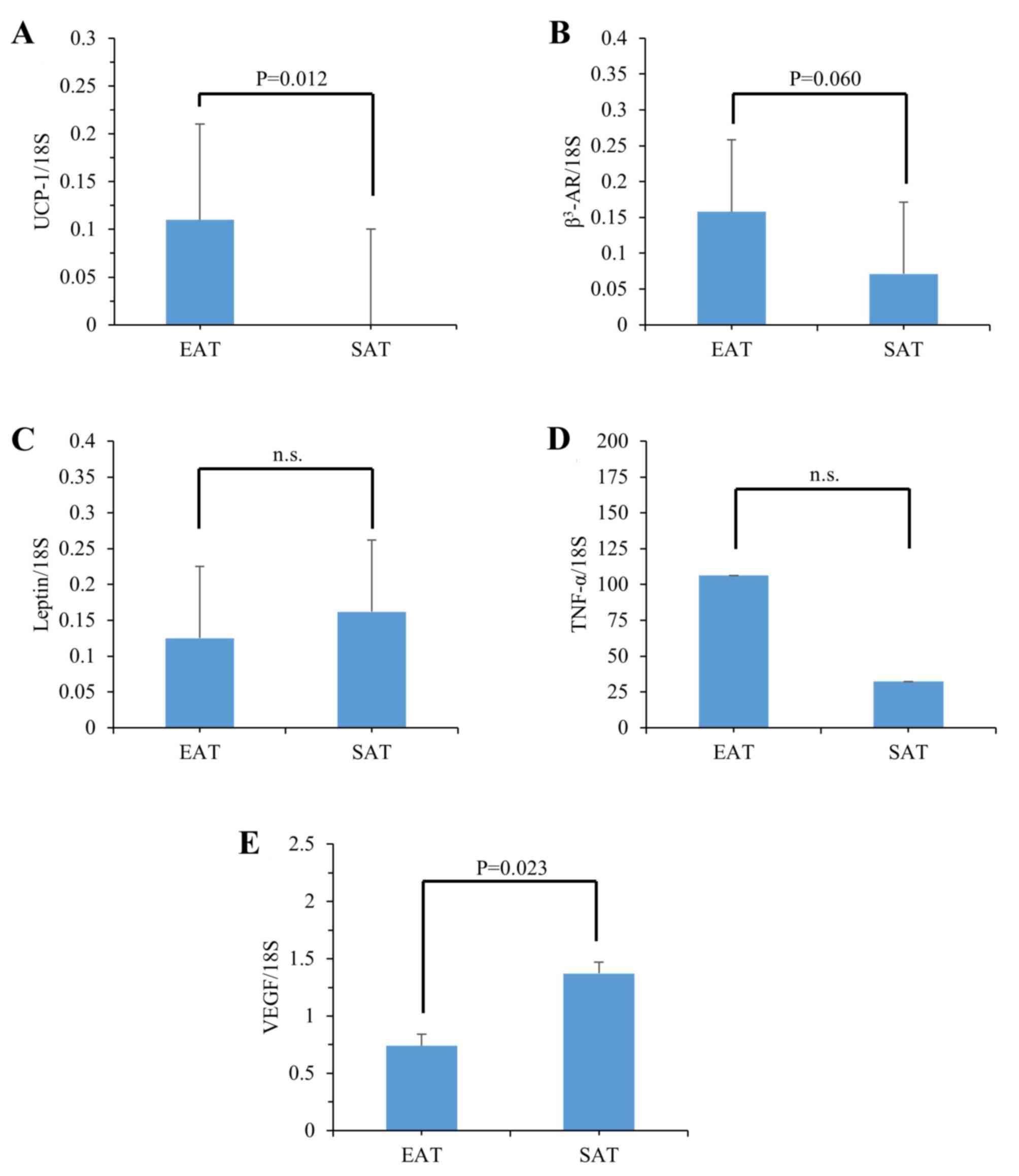
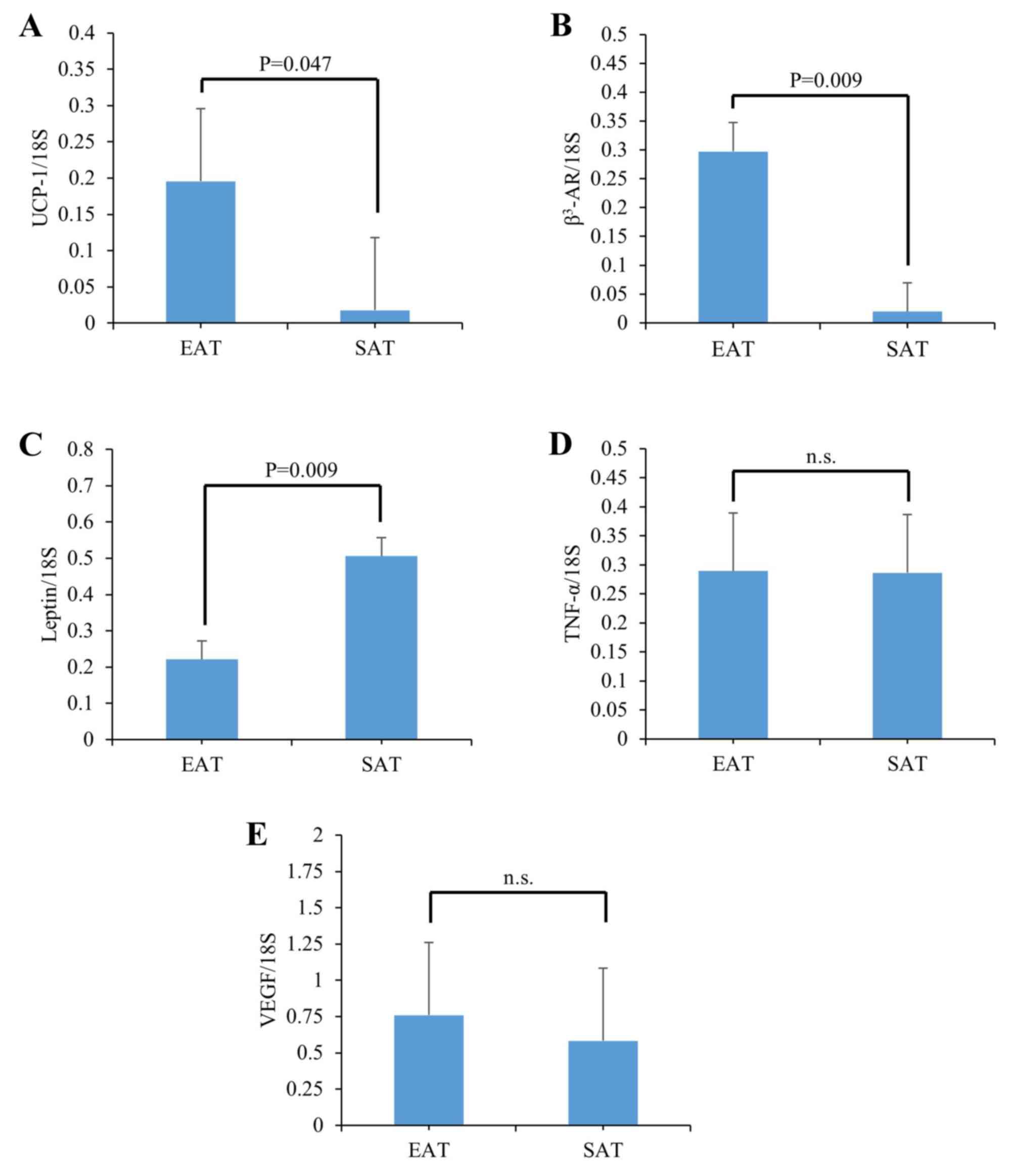
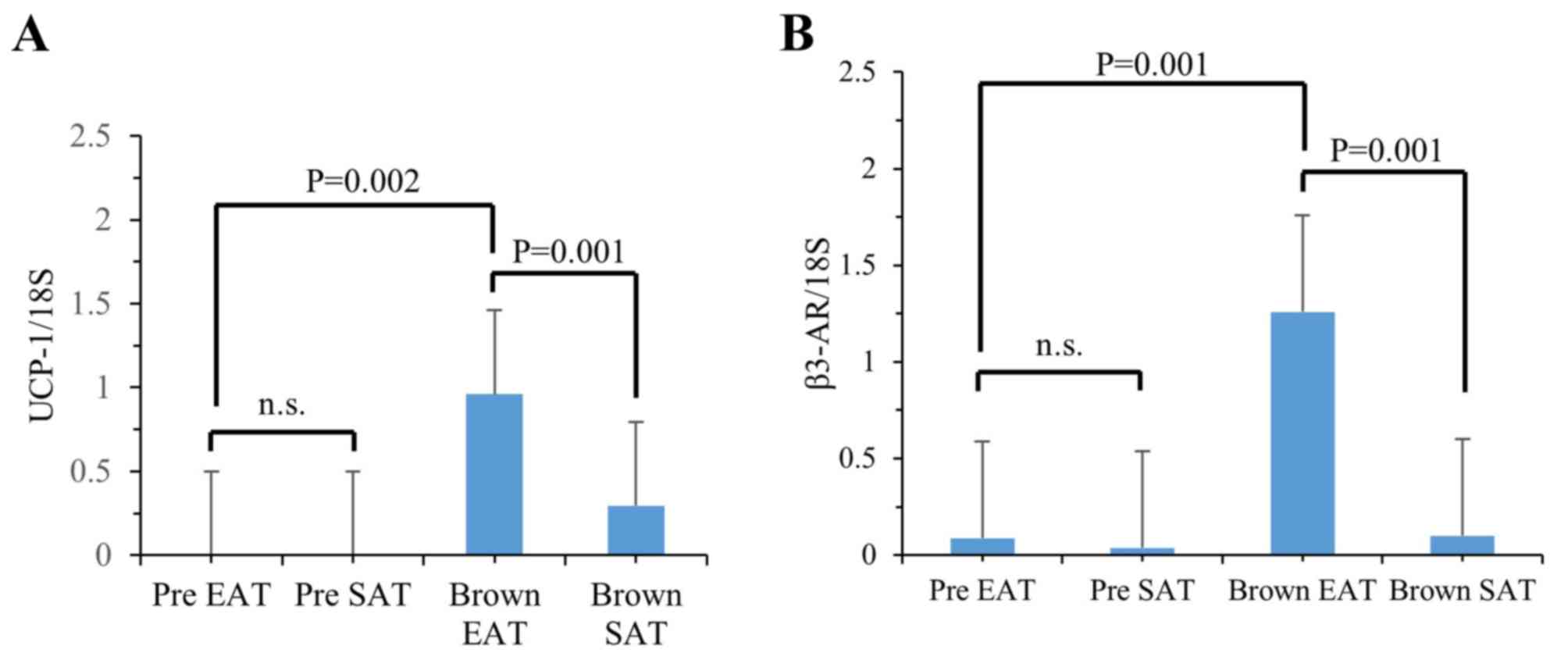
|
1
|
Bostrom P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A,
Ye L, Lo JC, Rasbach KA, Boström EA, Choi JH, Long JZ, et al: A
PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of
white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 481:463–468. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cypess AM, Lehman S, Williams G, Tal I,
Rodman D, Goldfine AB, Kuo FC, Palmer EL, Tseng YH, Doria A, et al:
Identification and importance of brown adipose tissue in adult
humans. N Engl J Med. 360:1509–1517. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zingaretti MC, Crosta F, Vitali A,
Guerrieri M, Frontini A, Cannon B, Nedergaard J and Cinti S: The
presence of UCP1 demonstrates that metabolically active adipose
tissue in the neck of adult humans truly represents brown adipose
tissue. FASEB J. 23:3113–3120. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ouellet V, Routhier-Labadie A, Bellemare
W, Lakhal-Chaieb L, Turcotte E, Carpentier AC and Richard D:
Outdoor temperature, age, sex, body mass index and diabetic status
determine the prevalence, mass and glucose-uptake activity of
18F-FDG-detected BAT in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
96:192–199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Whittle AJ, Jiang M, Peirce V, Relat J,
Virtue S, Ebinuma H, Fukamachi I, Yamaguchi T, Takahashi M, Murano
T, et al: Soluble LR11/SorLA represses thermogenesis in adipose
tissue and correlates with BMI in humans. Nat Commun. 6:89512015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iacobellis G, Corradi D and Sharma AM:
Epicardial adipose tissue: Anatomic, biomolecular and clinical
relationships with the heart. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med.
2:536–543. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Marchington JM, Mattacks CA and Pond CM:
Adipose tissue in the mammalian heart and pericardium: Structure,
foetal development and biochemical properties. Comp Biochem Physiol
B. 94:225–232. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mattacks CA and Pond CM: Site-specific and
sex differences in the rates of fatty acid/triacylglycerol
substrate cycling in adipose, tissue and muscle of sedentary and
exercised dwarf hamsters (Phodopus sungorus). Int J Obes.
12:585–597. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iacobellis G: Local and systemic effects
of the multifaceted epicardial adipose tissue depot. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 11:363–371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chechi K and Richard D: Thermogenic
potential and physiological relevance of human epicardial adipose
tissue. Int J Obes Suppl. 5 Suppl 1:S28–S34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sacks HS, Fain JN, Bahouth SW, Ojha S,
Frontini A, Budge H, Cinti S and Symonds ME: Adult epicardial fat
exhibits beige features. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 98:E1448–E1455.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Terai K, Jiang M, Tokuyama W, Murano T,
Takada N, Fujimura K, Ebinuma H, Kishimoto T, Hiruta N, Schneider
WJ and Bujo H: Levels of soluble LR11/SorLA are highly increased in
the bile of patients with biliary tract and pancreatic cancers.
Clin Chim Acta. 457:130–136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Committee of the Japan Diabetes Society on
the Diagnostic Criteria of Diabetes Mellitus, . Seino Y, Nanjo K,
Tajima N, Kadowaki T, Kashiwagi A, Araki E, Ito C, Inagaki N,
Iwamoto Y, et al: Report of the committee on the classification and
diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig.
1:212–228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shimamoto K, Ando K, Fujita T, Hasebe N,
Higaki J, Horiuchi M, Imai Y, Imaizumi T, Ishimitsu T, Ito M, et
al: The japanese society of hypertension guidelines for the
management of hypertension (JSH 2014). Hypertens Res. 37:253–390.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Teramoto T, Sasaki J, Ishibashi S, Birou
S, Daida H, Dohi S, Egusa G, Hiro T, Hirobe K, Iida M, et al:
Diagnostic criteria for dyslipidemia. J Atheroscler Thromb.
20:655–660. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Imai E, Matsuo S, Makino H, Watanabe T,
Akizawa T, Nitta K, Iimuro S, Ohashi Y and Hishida A: CKD-JAC Study
Group: Chronic kidney disease japan cohort (CKD-JAC) study: Design
and methods. Hypertens Res. 31:1101–1107. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Examination Committee of Criteria for
‘Obesity Disease’ in Japan; Japan Society for the Study of Obesity:
New criteria for ‘obesity disease’ in Japan. Circ J. 66:987–992.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sarin S, Wenger C, Marwaha A, Qureshi A,
Go BD, Woomert CA, Clark K, Nassef LA and Shirani J: Clinical
significance of epicardial fat measured using cardiac multislice
computed tomography. Am J Cardiol. 102:767–771. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Borkan GA, Gerzof SG, Robbins AH, Hults
DE, Silbert CK and Silbert JE: Assessment of abdominal fat content
by computed tomography. Am J Clin Nutr. 36:172–177. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sacks HS: Weight loss in obesity reduces
epicardial fat thickness; so what? J Appl Physiol (1985). 106:1–2.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rabkin SW and Campbell H: Comparison of
reducing epicardial fat by exercise, diet or bariatric surgery
weight loss strategies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes
Rev. 16:406–415. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Foppa M, Pond KK, Jones DB, Schneider B,
Kissinger KV and Manning WJ: Subcutaneous fat thickness, but not
epicardial fat thickness, parallels weight reduction three months
after bariatric surgery: A cardiac magnetic resonance study. Int J
Cardiol. 168:4532–4533. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Willens HJ, Byers P, Chirinos JA, Labrador
E, Hare JM and de Marchena E: Effects of weight loss after
bariatric surgery on epicardial fat measured using
echocardiography. Am J Cardiol. 99:1242–1245. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Doucet E, St-Pierre S, Almeras N, Alméras
N, Imbeault P, Mauriège P, Pascot A, Després JP and Tremblay A:
Reduction of visceral adipose tissue during weight loss. Eur J Clin
Nutr. 56:297–304. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stallone DD, Stunkard AJ, Wadden TA,
Foster GD, Boorstein J and Arger P: Weight loss and body fat
distribution: A feasibility study using computed tomography. Int J
Obes. 15:775–780. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|