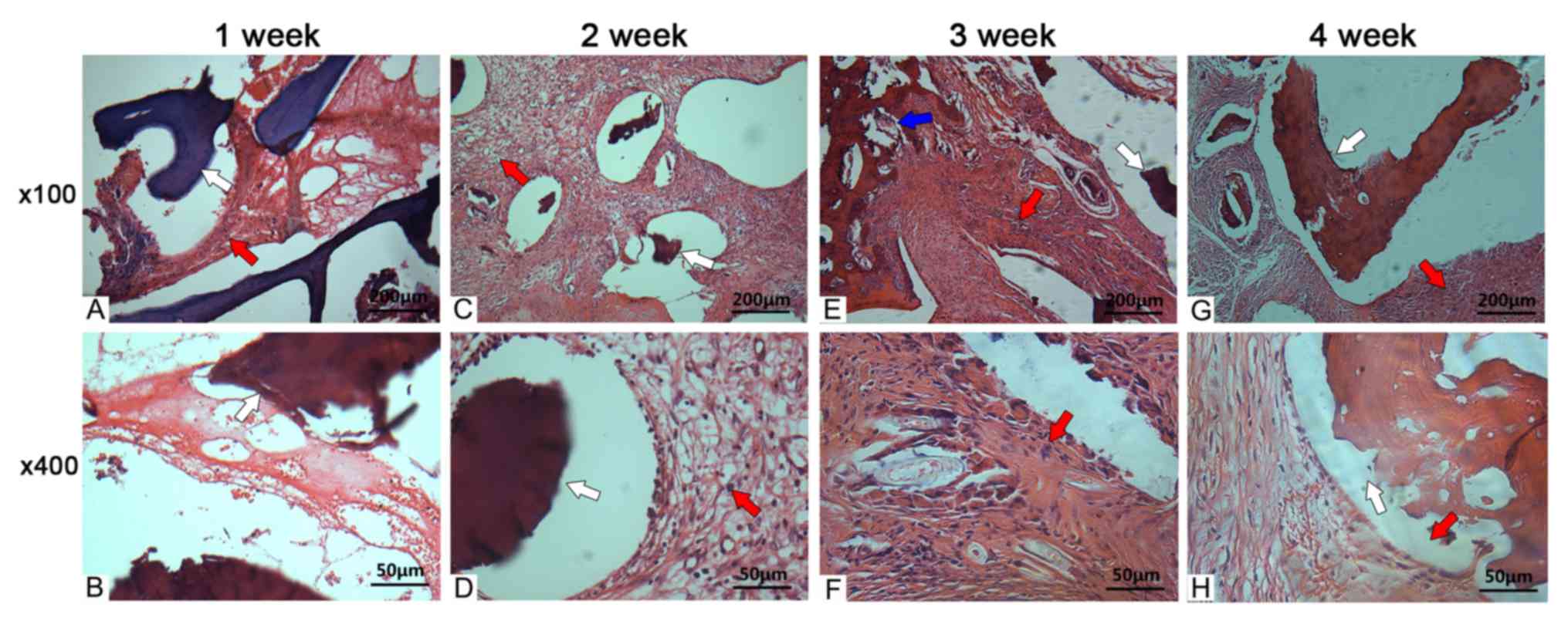
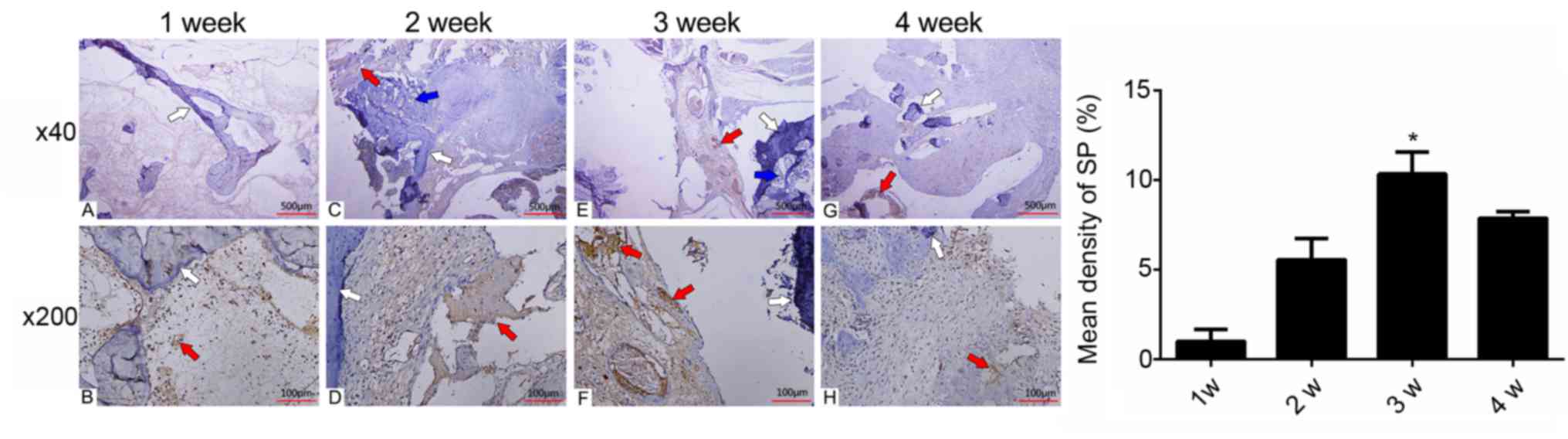
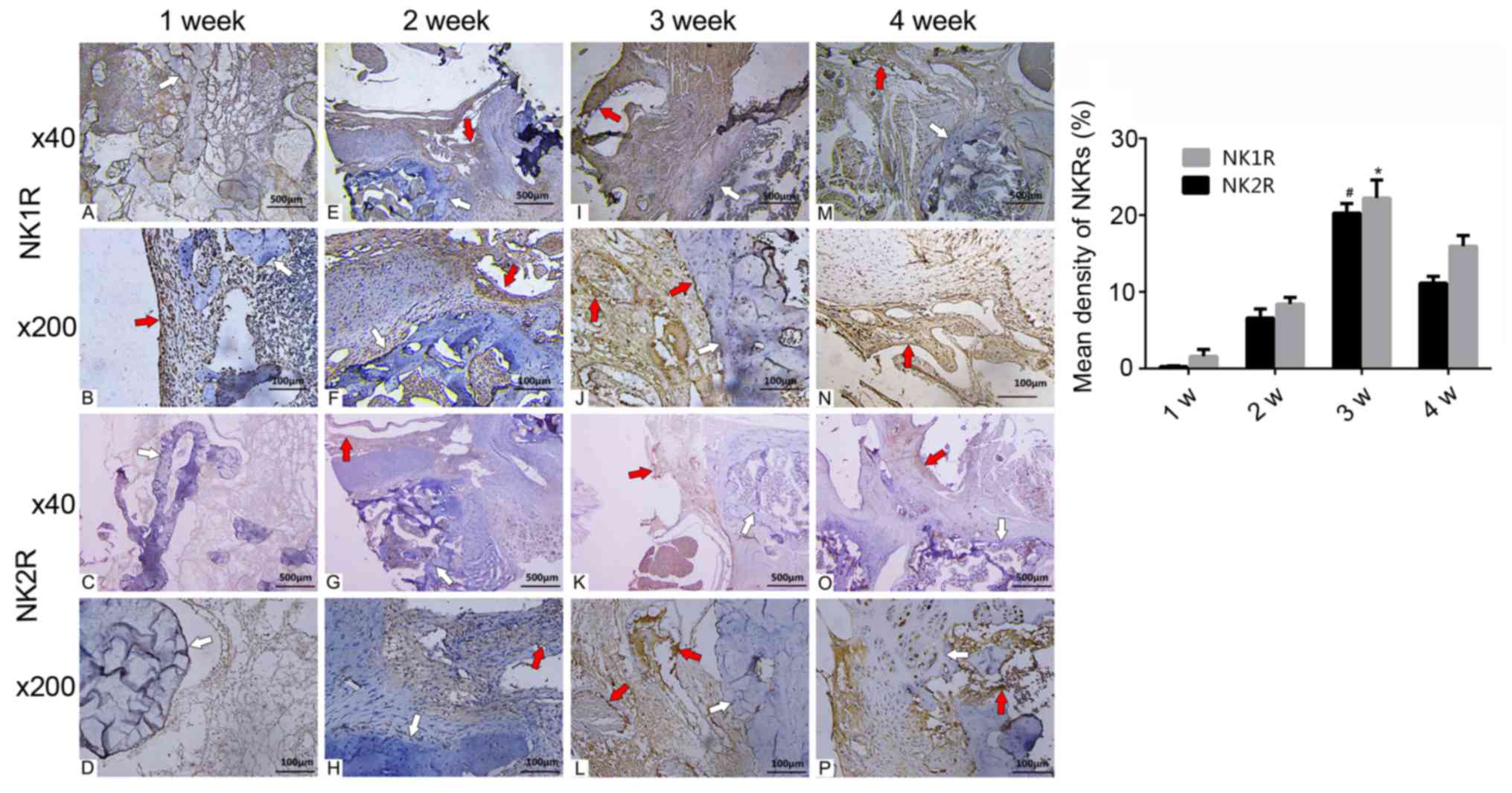
|
1
|
Kreinest M, Rillig J, Grützner PA, Küffer
M, Tinelli M and Matschke S: Analysis of complications and
perioperative data after open or percutaneous dorsal
instrumentation following traumatic spinal fracture of the thoracic
and lumbar spine: A retrospective cohort study including 491
patients. Eur Spine J. 26:1535–1540. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang Z, Liu Z, Zhu Z and Qiu Y: Spinal
epidural lipomatosis-an easily ignored secondary intraspinal
disorder in spinal kyphotic deformities. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.
18:1122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meshkini A, Salehpour F, Rezakhah A,
Mirzaei F, Kazemzadeh M and Naseri Alavi SA: Textiloma: A case of
foreign body mimicking a spinal tumor. Spine. 42:E1272–E1274. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bowles RD and Setton LA: Biomaterials for
intervertebral disc regeneration and repair. Biomaterials.
129:54–67. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Patel VV, Andersson GB, Garfin SR, Resnick
DL and Block JE: Utilization of CT scanning associated with complex
spine surgery. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 18:522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y, Xu J, Ruan YC, Yu MK, O'laughlin
M, Wise H, Chen D, Tian L, Shi D, Wang J, et al: Implant-derived
magnesium induces local neuronal production of CGRP to improve
bone-fracture healing in rats. Nat Med. 22:1160–1169. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lenza M, Belloti JC, Andriolo RB and
Faloppa F: Conservative interventions for treating middle third
clavicle fractures in adolescents and adults. Cochrane Database
Syst Rev: CD007121. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hrabovszky E, Borsay BÁ, Rácz K, Herczeg
L, Ciofi P, Bloom SR, Ghatei MA, Dhillo WS and Liposits Z:
Substance P immunoreactivity exhibits frequent colocalization with
kisspeptin and neurokinin B in the human infundibular region. PLoS
One. 8:e723692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mistrova E, Kruzliak P and Chottova
Dvorakova M: Role of substance P in the cardiovascular system.
Neuropeptides. 58:41–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dionne RA, Max MB, Gordon SM, Parada S,
Sang C, Gracely RH, Sethna NF and Maclean DB: The substance P
receptor antagonist CP-99,994 reduces acute postoperative pain.
Clin Pharmacol Ther. 64:562–568. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wei T, Guo TZ, Li WW, Kingery WS and Clark
JD: Acute versus chronic phase mechanisms in a rat model of CRPS. J
Neuroinflammation. 13:142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mander K, Harford-Wright E, Lewis KM and
Vink R: Advancing drug therapy for brain tumours: A current review
of the pro-inflammatory peptide substance P and its antagonists as
anti-cancer agents. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov. 9:110–121. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fan TP, Hu DE, Guard S, Gresham GA and
Watling KJ: Stimulation of angiogenesis by substance P and
interleukin-1 in the rat and its inhibition by NK1 or interleukin-1
receptor antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 110:43–49. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hong HS, Lee J, Lee E, Kwon YS, Lee E, Ahn
W, Jiang MH, Kim JC and Son Y: A new role of substance P as an
injury-inducible messenger for mobilization of CD29+
stromal-like cells. Nat Med. 15:425–435. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grässel SG: The role of peripheral nerve
fibers and their neurotransmitters in cartilage and bone physiology
and pathophysiology. Arthritis Res Ther. 16:4852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Muñoz M and Coveñas R: Involvement of
substance P and the NK-1 receptor in human pathology. Amino Acids.
46:1727–1750. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Seegers HC, Hood VC, Kidd BL, Cruwys SC
and Walsh DA: Enhancement of angiogenesis by endogenous substance P
release and neurokinin-1 receptors during neurogenic inflammation.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 306:8–12. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Szczesny G: Fracture healing and its
disturbances. A literature review. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil.
17:437–454. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li J, Ahmed M, Bergstrom J, Ackermann P,
Stark A and Kreicbergs A: Occurrence of substance P in bone repair
under different load comparison of straight and angulated fracture
in rat tibia. J Orthop Res. 28:1643–1650. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pavlovic S, Daniltchenko M, Tobin DJ,
Hagen E, Hunt SP, Klapp BF, Arck PC and Peters EM: Further
exploring the brain-skin connection: Stress worsens dermatitis via
substance P-dependent neurogenic inflammation in mice. J Invest
Dermatol. 128:434–446. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Onuoha GN: Circulating sensory peptide
levels within 24 h of human bone fracture. Peptides. 22:1107–1110.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wei T, Li WW, Guo TZ, Zhao R, Wang L,
Clark DJ, Oaklander AL, Schmelz M and Kingery WS: Post-junctional
facilitation of Substance P signaling in a tibia fracture rat model
of complex regional pain syndrome type I. Pain. 144:278–286. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Eglezos A, Giuliani S, Viti G and Maggi
CA: Direct evidence that capsaicin-induced plasma protein
extravasation is mediated through tachykinin NK1 receptors. Eur J
Pharmacol. 209:277–279. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fu S, Jin D, Liu S, Wang L, Wang Z, Mei G,
Zou ZL, Wu JQ and Xu ZY: Protective effect of neuropeptide
substance P on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells against apoptosis
induced by serum deprivation. Stem Cells Int. 2015:2703282015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
El Karim IA, Linden GJ, Irwin CR and Lundy
FT: Neuropeptides regulate expression of angiogenic growth factors
in human dental pulp fibroblasts. J Endod. 35:829–833. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ytteborg E, Torgersen JS, Pedersen ME,
Helland SJ, Grisdale-Helland B and Takle H: Exercise induced
mechano-sensing and substance P mediated bone modeling in Atlantic
salmon. Bone. 53:259–268. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aro H: Effect of nerve injury on fracture
healing. Callus formation studied in the rat. Acta Orthop Scand.
56:233–237. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Niedermair T, Kuhn V, Doranehgard F,
Stange R, Wieskötter B, Beckmann J, Salmen P, Springorum HR, Straub
RH, Zimmer A, et al: Absence of substance P and the sympathetic
nervous system impact on bone structure and chondrocyte
differentiation in an adult model of endochondral ossification.
Matrix Biol. 38:22–35. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Amadesi S, Reni C, Katare R, Meloni M,
Oikawa A, Beltrami AP, Avolio E, Cesselli D, Fortunato O, Spinetti
G, et al: Role for substance p-based nociceptive signaling in
progenitor cell activation and angiogenesis during ischemia in mice
and in human subjects. Circulation. 125(1774–1786): S1–S19. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kohara H, Tajima S, Yamamoto M and Tabata
Y: Angiogenesis induced by controlled release of neuropeptide
substance P. Biomaterials. 31:8617–8625. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Artese L, Rubini C, Ferrero G, Fioroni M,
Santinelli A and Piattelli A: Vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF) expression in healthy and inflamed human dental pulps. J
Endod. 28:20–23. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tran-Hung L, Laurent P, Camps J and About
I: Quantification of angiogenic growth factors released by human
dental cells after injury. Arch Oral Biol. 53:9–13. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Krishnan V and Davidovitch Z: On a path to
unfolding the biological mechanisms of orthodontic tooth movement.
J Dent Res. 88:597–608. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ziche M, Morbidelli L, Pacini M, Geppetti
P, Alessandri G and Maggi CA: Substance P stimulates
neovascularization in vivo and proliferation of cultured
endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 40:264–278. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ziche M, Morbidelli L, Masini E, Amerini
S, Granger HJ, Maggi CA, Geppetti P and Ledda F: Nitric oxide
mediates angiogenesis in vivo and endothelial cell growth and
migration in vitro promoted by substance P. J Clin Invest.
94:2036–2044. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kusumbe AP, Ramasamy SK and Adams RH:
Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel
subtype in bone. Nature. 507:323–328. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xu X, Wang F, Yang Y, Zhou X, Cheng Y, Wei
X and Li M: LIPUS promotes spinal fusion coupling proliferation of
type H microvessels in bone. Sci Rep. 6:201162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chandrasekhar KS, Zhou H, Zeng P, Alge D,
Li W, Finney BA, Yoder MC and Li J: Blood vessel wall-derived
endothelial colony-forming cells enhance fracture repair and bone
regeneration. Calcif Tissue Int. 89:347–357. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|