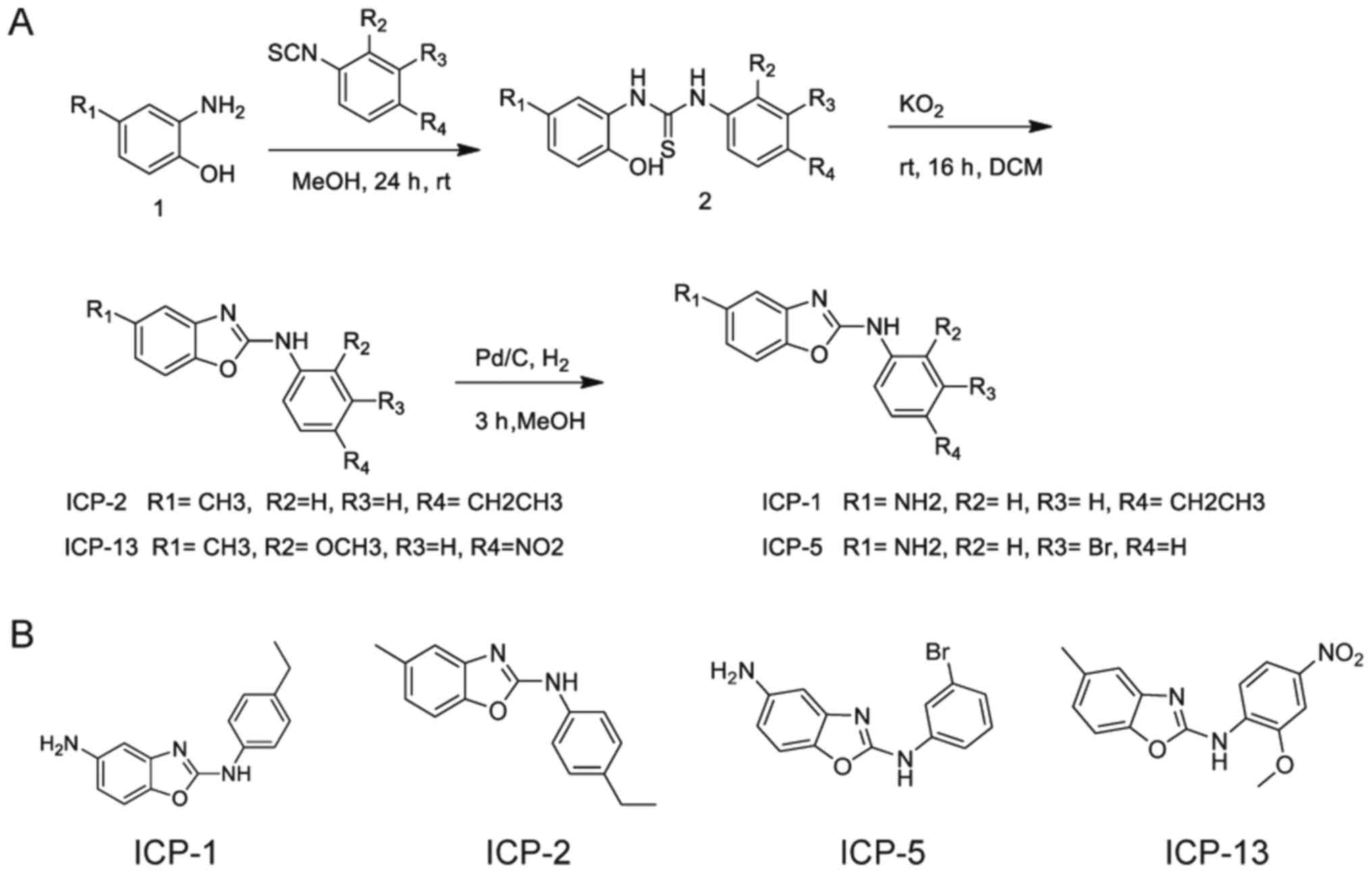
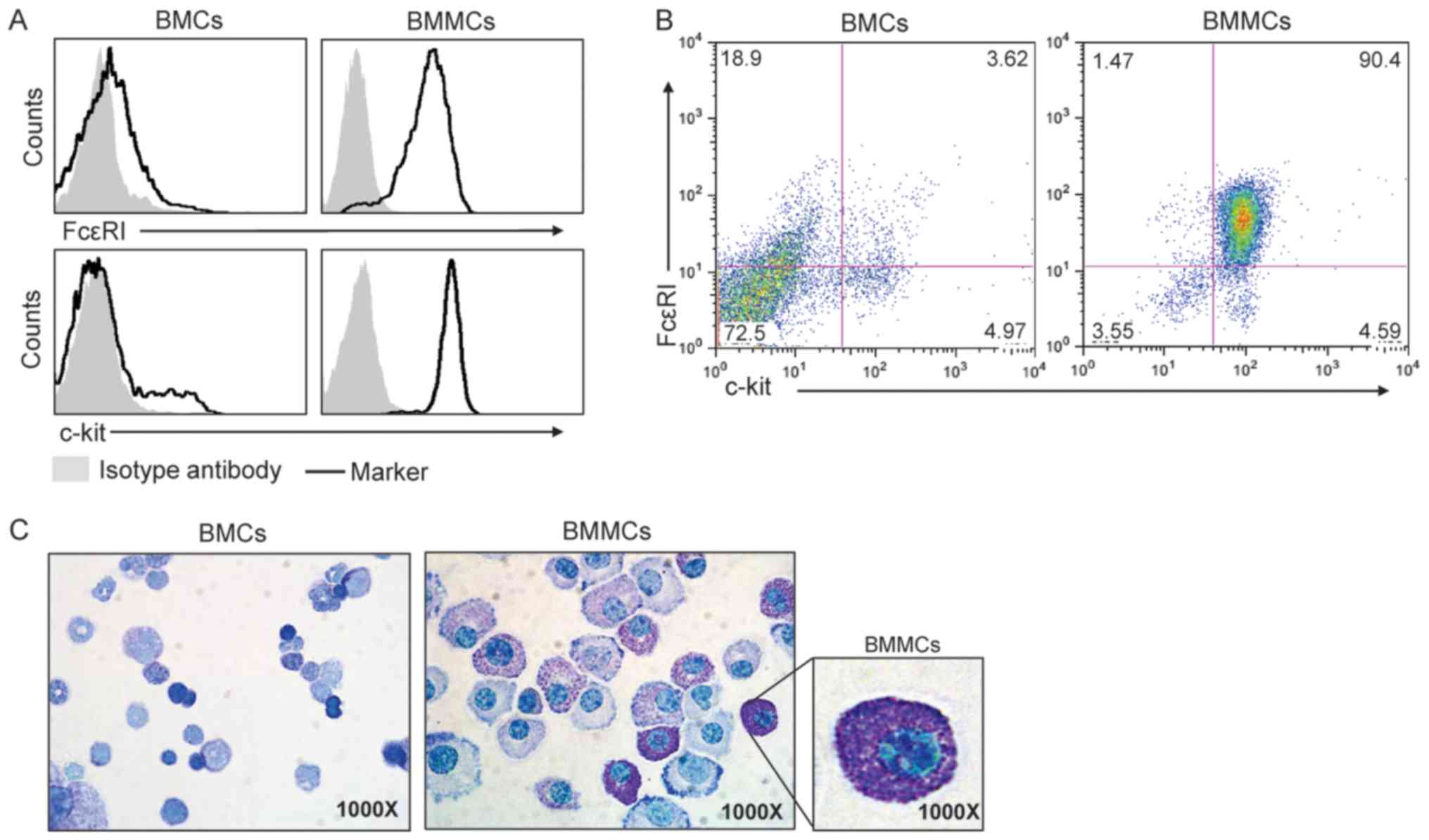
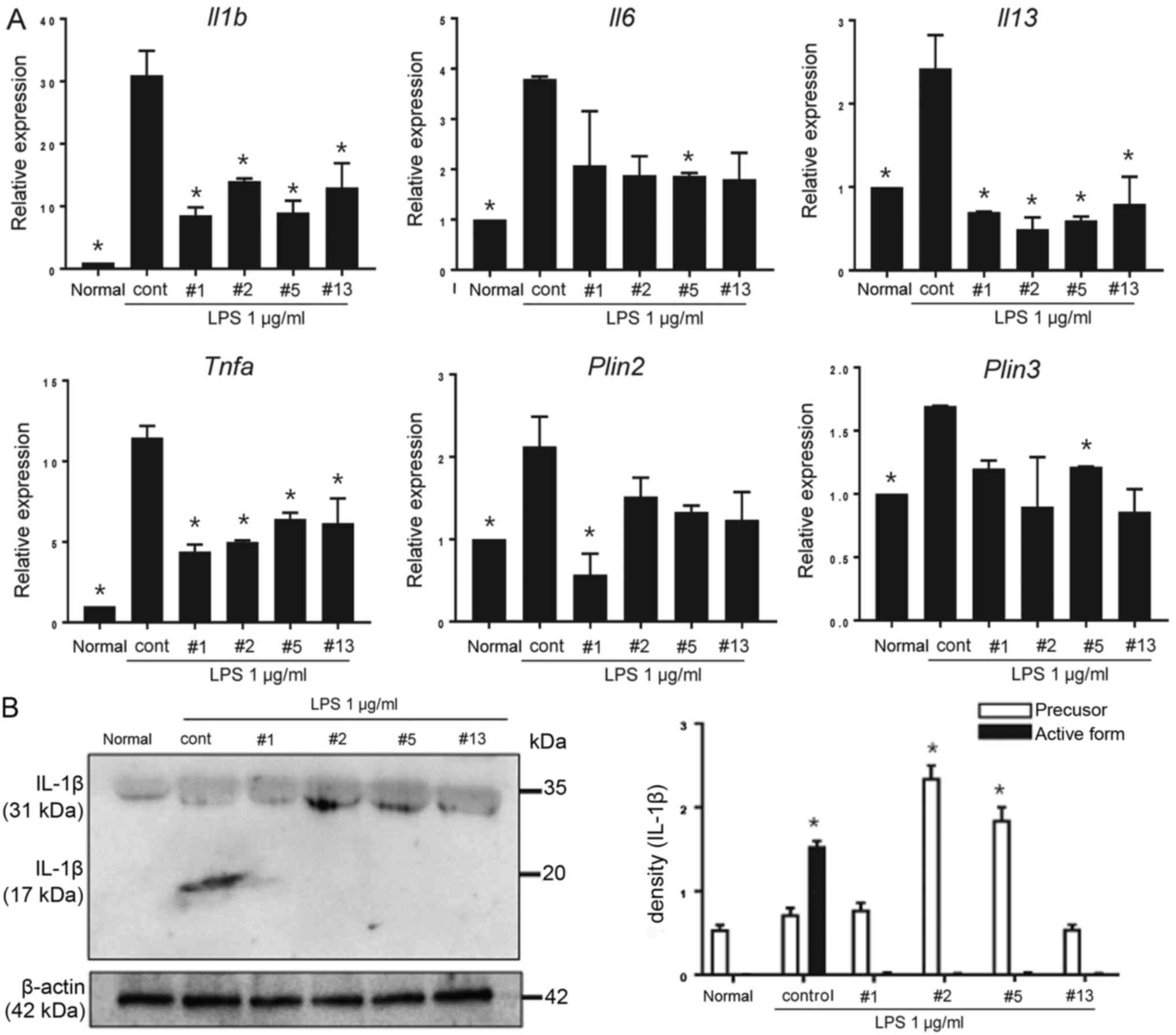
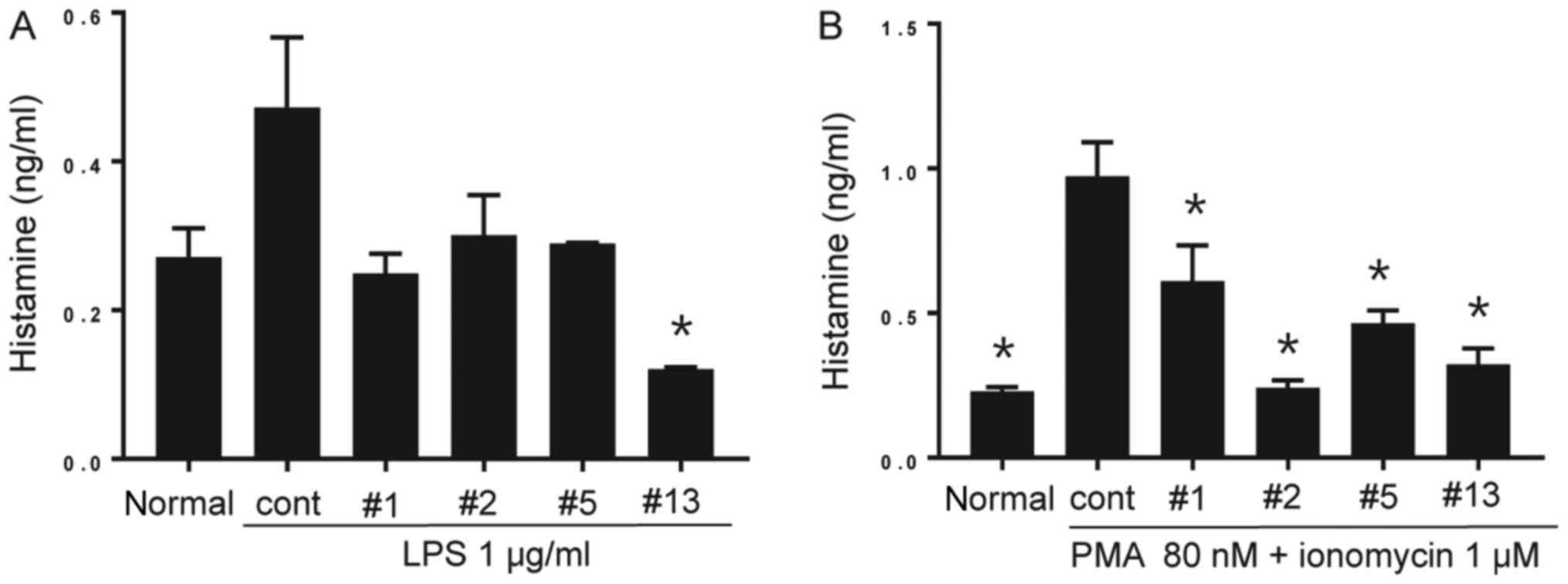
|
1
|
Sismanopoulos N, Delivanis DA,
Alysandratos KD, Angelidou A, Therianou A, Kalogeromitros D and
Theoharides TC: Mast cells in allergic and inflammatory diseases.
Curr Pharm Des. 18:2261–2277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wernersson S and Pejler G: Mast cell
secretory granules: Armed for battle. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:478–494.
2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yamashita M and Nakayama T: Progress in
allergy signal research on mast cells: Regulation of allergic
airway inflammation through toll-like receptor 4-mediated
modification of mast cell function. J Pharmacol Sci. 106:332–335.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Masuda A, Yoshikai Y, Aiba K and
Matsuguchi T: Th2 cytokine production from mast cells is directly
induced by lipopolysaccharide and distinctly regulated by c-Jun
N-terminal kinase and p38 pathways. J Immunol. 169:3801–3810. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Murakami D, Yamada H, Yajima T, Masuda A,
Komune S and Yoshikai Y: Lipopolysaccharide inhalation exacerbates
allergic airway inflammation by activating mast cells and promoting
Th2 responses. Clin Exp Allergy. 37:339–347. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nigo YI, Yamashita M, Hirahara K,
Shinnakasu R, Inami M, Kimura M, Hasegawa A, Kohno Y and Nakayama
T: Regulation of allergic airway inflammation through Toll-like
receptor 4-mediated modification of mast cell function. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 103:pp. 2286–2291. 2006; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shiba E, Izawa K, Kaitani A, Isobe M,
Maehara A, Uchida K, Maeda K, Nakano N, Ogawa H, Okumura K, et al:
Ceramide-CD300f binding inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced skin
inflammation. J Biol Chem. 292:2924–2932. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kuhn H and O'Donnell VB: Inflammation and
immune regulation by 12/15-lipoxygenases. Prog Lipid Res.
45:334–356. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han H, Liang X, Ekberg M, Kritikou JS,
Brunnström Å, Pelcman B, Matl M, Miao X, Andersson M, Yuan X, et
al: Human 15-lipoxygenase-1 is a regulator of dendritic-cell
spreading and podosome formation. FASEB J. 31:491–504. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Claesson HE: On the biosynthesis and
biological role of eoxins and 15-lipoxygenase-1 in airway
inflammation and Hodgkin lymphoma. Prostaglandins Other Lipid
Mediat. 89:120–125. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ro M, Lee AJ and Kim JH:
5-/12-lipoxygenase-linked cascade contributes to the IL-33-induced
synthesis of IL-13 in mast cells, thus promoting asthma
development. Allergy. 73:350–360. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mashima R and Okuyama T: The role of
lipoxygenases in pathophysiology; new insights and future
perspectives. Redox Biol. 6:297–310. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song H, Oh SR, Lee HK, Han G, Kim JH,
Chang HW, Doh KE, Rhee HK and Choo HY: Synthesis and evaluation of
benzoxazole derivatives as 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors. Bioorg Med
Chem. 18:7580–7585. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee JH, An MH, Choi EH, Choo HYP and Han
G: A facile synthesis of 2-acyl and 2-alkylaminobenzimidazoles for
5-lipoxygenase inhibitors. Heterocycles. 70:571–580. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yoon JH, Song H, Kim SW, Han G and Choo
HYP: A facile synthesis of 2-aminothiazolo [5,4-b]pyridines and
2-aminobenzoxazoles via cyclization of thioureas. Heterocycles.
65:2729–2740. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim D, Won HY, Hwang ES, Kim YK and Choo
HP: Synthesis of benzoxazole derivatives as interleukin-6
antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem. 25:3127–3134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chiba N, Masuda A, Yoshikai Y and
Matsuguchi T: Ceramide inhibits LPS-induced production of IL-5,
IL-10, and IL-13 from mast cells. J Cell Physiol. 213:126–136.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hochdörfer T, Tiedje C, Stumpo DJ,
Blackshear PJ, Gaestel M and Huber M: LPS-induced production of
TNF-α and IL-6 in mast cells is dependent on p38 but independent of
TTP. Cell Signal. 25:1339–1347. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sandig H and Bulfone-Paus S: TLR signaling
in mast cells: Common and unique features. Front Immunol.
3:1852012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lopes DEM, Jabr CL, Dejani NN, Saraiva AC,
de Aquino SG, Medeiros AI and Junior CR: Inhibition of
5-lipoxygenase (5-Lo) attenuates inflammation and bone resorption
in lipopolysaccharide (Lps)-induced periodontal disease. J
Periodontol. 1–18. 2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rossaint J, Nadler JL, Ley K and Zarbock
A: Eliminating or blocking 12/15-lipoxygenase reduces neutrophil
recruitment in mouse models of acute lung injury. Crit Care.
16:R1662012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee SJ, Seo KW and Kim CD: LPS increases
5-LO expression on monocytes via an activation of Akt-Sp1/NF-αB
pathways. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 19:263–268. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
D'Avila H, Maya-Monteiro CM and Bozza PT:
Lipid bodies in innate immune response to bacterial and parasite
infections. Int Immunopharmacol. 8:1308–1315. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bozza PT, Bakker-Abreu I, Navarro-Xavier
RA and Bandeira-Melo C: Lipid body function in eicosanoid
synthesis: An update. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids.
85:205–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dichlberger A, Schlager S, Lappalainen J,
Käkelä R, Hattula K, Butcher SJ, Schneider WJ and Kovanen PT: Lipid
body formation during maturation of human mast cells. J Lipid Res.
52:2198–2208. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakamura Y, Franchi L, Kambe N, Meng G,
Strober W and Núñez G: Critical role for mast cells in
interleukin-1β-driven skin inflammation associated with an
activating mutation in the nlrp3 protein. Immunity. 37:85–95. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shoji N, Yoshida A, Yu Z, Endo Y and
Sasano T: Lipopolysaccharide stimulates histamine-forming enzyme
(histidine decarboxylase) activity in murine dental pulp and
gingiva. Arch Oral Biol. 51:856–860. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hershko AY and Rivera J: Mast cell and T
cell communication; amplification and control of adaptive immunity.
Immunol Lett. 128:98–104. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kambayashi T, Allenspach EJ, Chang JT, Zou
T, Shoag JE, Reiner SL, Caton AJ and Koretzky GA: Inducible MHC
class II expression by mast cells supports effector and regulatory
T cell activation. J Immunol. 182:4686–4695. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Espinosa E and Valitutti S: New roles and
controls of mast cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 50:39–47. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nakamura Y and Kambe N: Linkage of
bacterial colonization of skin and the urticaria-like rash of
NLRP3-mediated autoinflammatory syndromes through mast cell-derived
TNF-α. J Dermatol Sci. 71:83–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cho KA and Kang PB: PLIN2 inhibits
insulin-induced glucose uptake in myoblasts through the activation
of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Int J Mol Med. 36:839–844. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wisastra R and Dekker FJ: Inflammation,
cancer and oxidative lipoxygenase activity are intimately linked.
Cancers (Basel). 6:1500–1521. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Werz O: Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase
product synthesis by natural compounds of plant origin. Planta Med.
73:1331–1357. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pettersen D, Davidsson Ö and Whatling C:
Recent advances for FLAP inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
25:2607–2612. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|