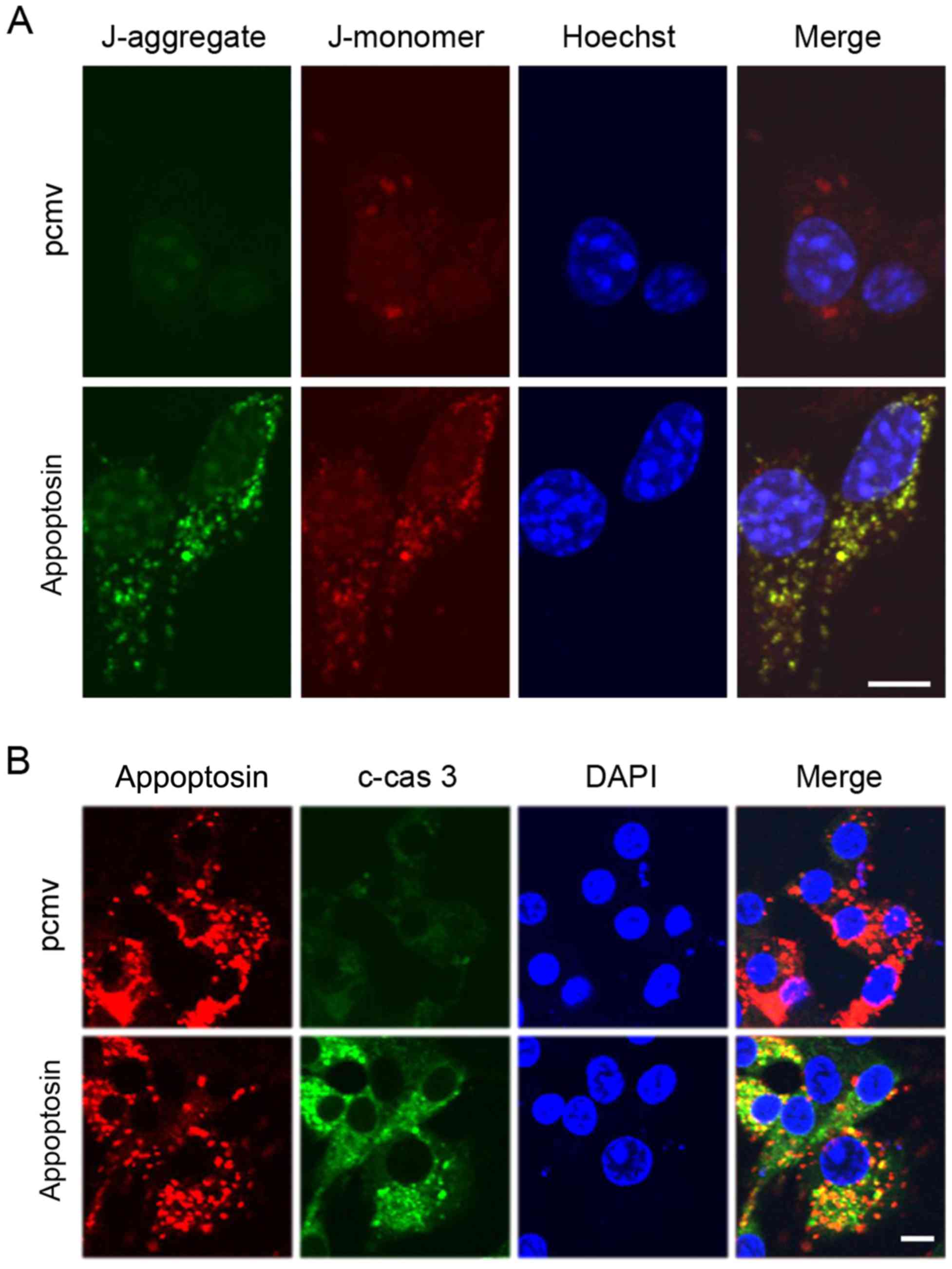
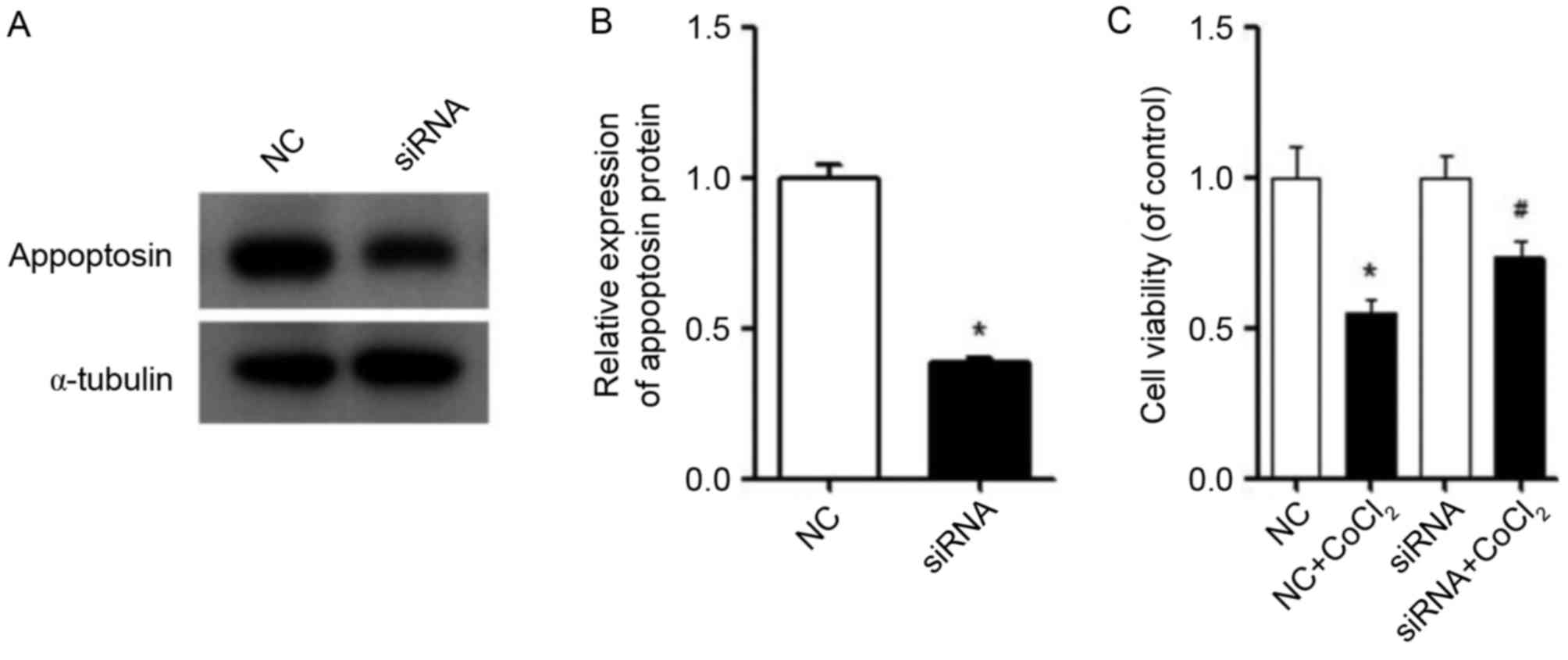
|
1
|
Chiang JL, Kirkman MS, Laffel LM and
Peters AL: Type 1 Diabetes Sourcebook Authors: Type 1 diabetes
through the life span: A position statement of the American
Diabetes Association. Diabetes care. 37:2034–2054. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
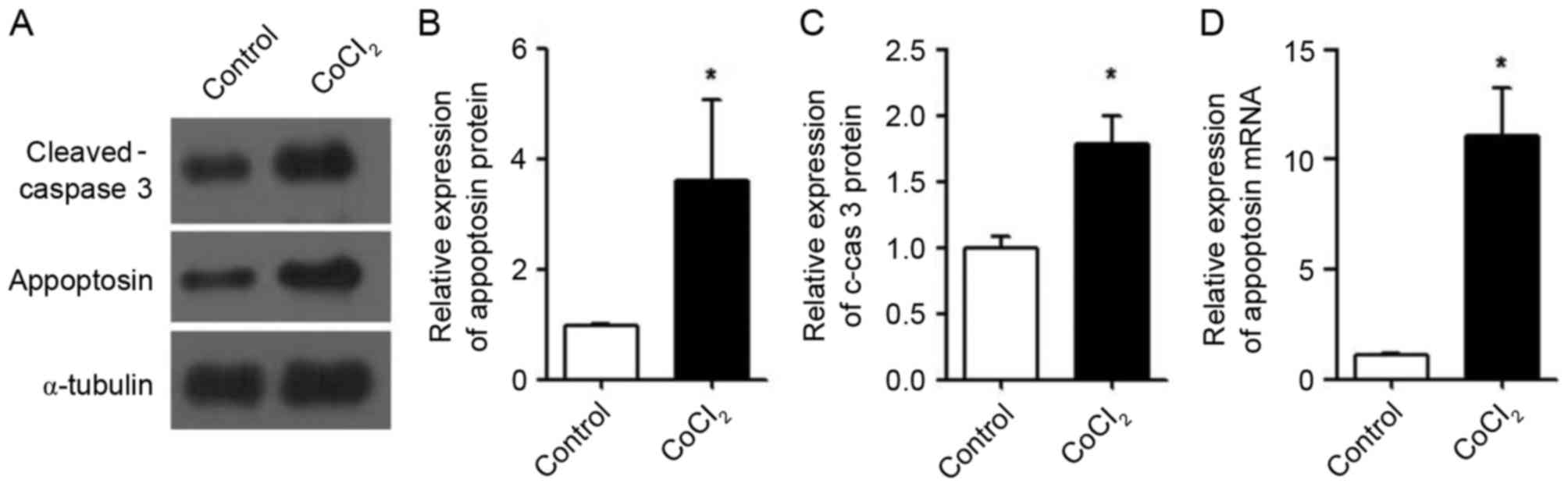
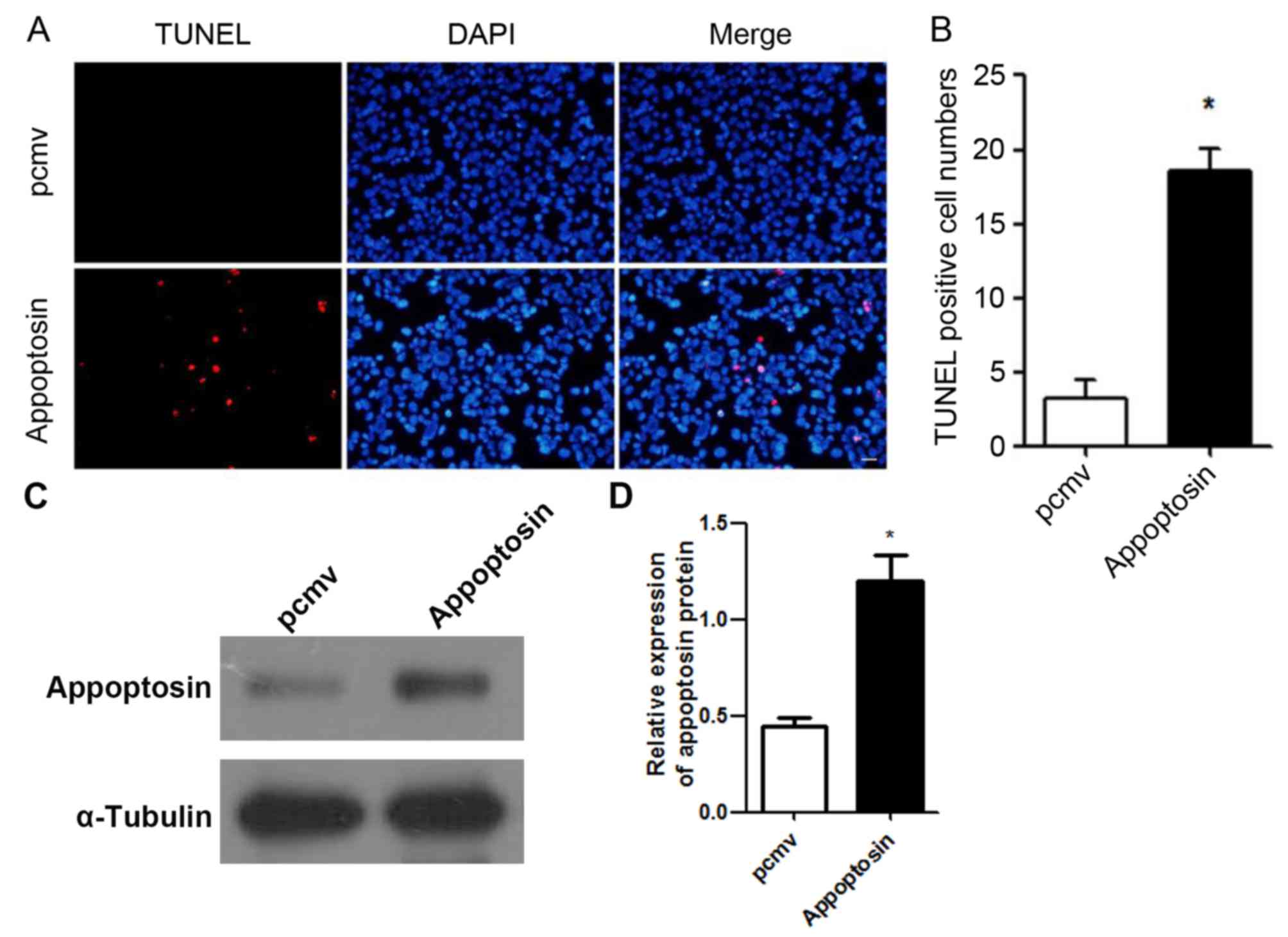
|
Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T,
Wang L, Jiang Y, Dai M, Lu J, et al: Prevalence and control of
diabetes in Chinese adults. Jama. 310:948–959. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
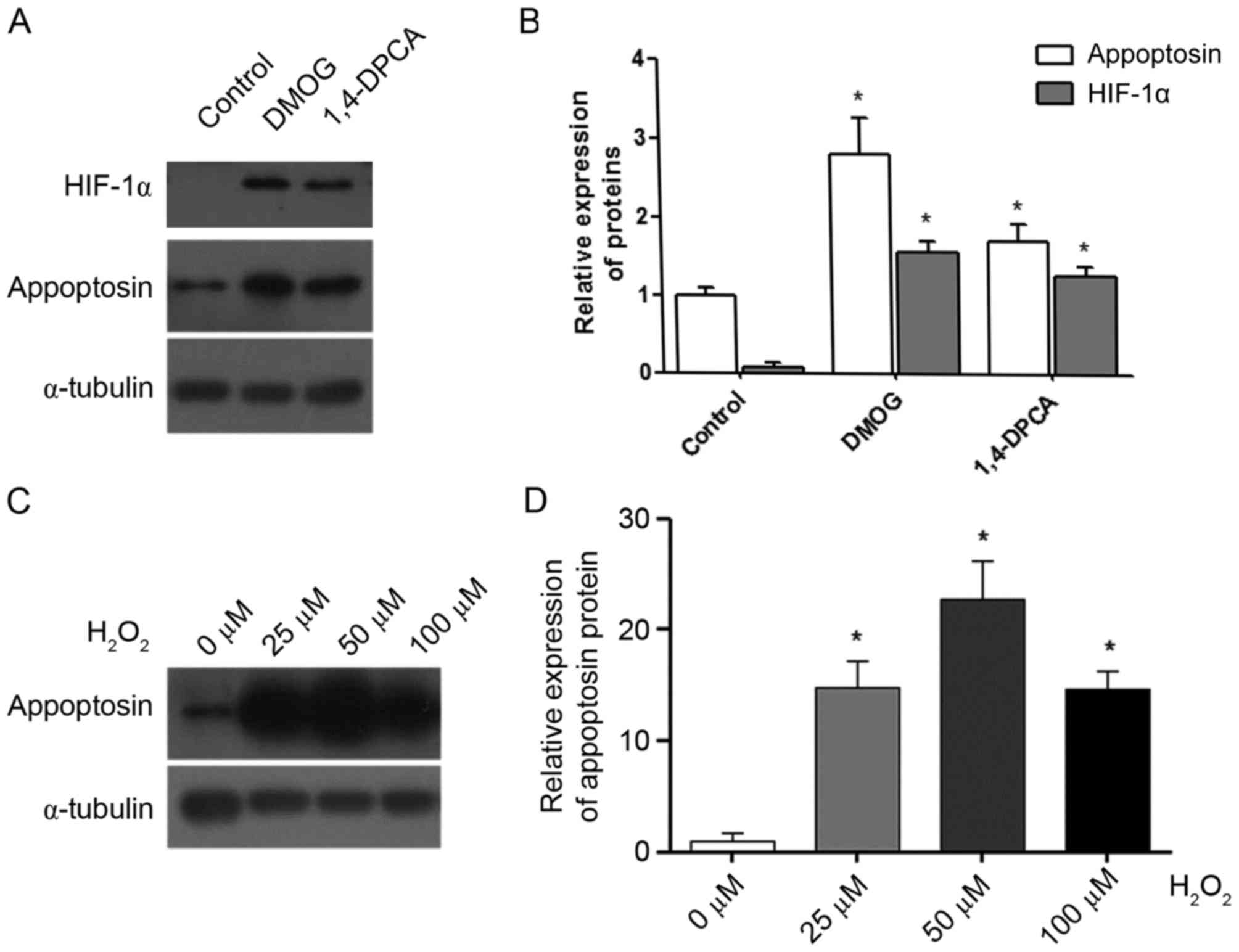
|
|
3
|
Atkinson MA, Eisenbarth GS and Michels AW:
Type 1 diabetes. Lancet. 383:69–82. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ryan EA, Lakey JR, Rajotte RV, Korbutt GS,
Kin T, Imes S, Rabinovitch A, Elliott JF, Bigam D, Kneteman NM, et
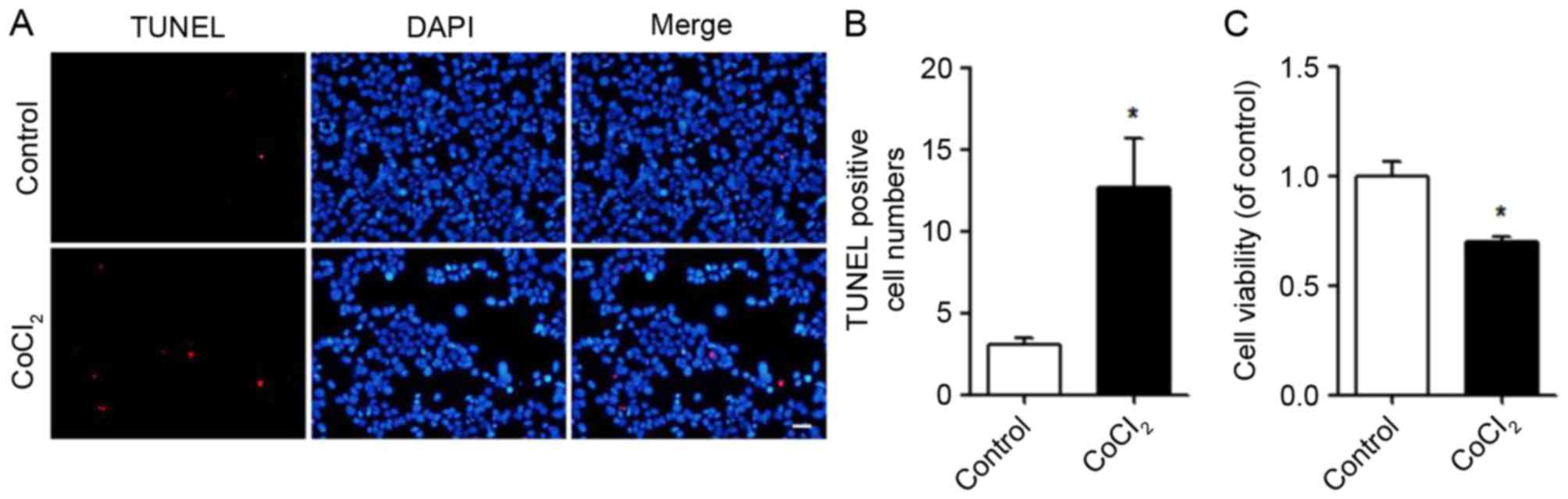
al: Clinical outcomes and insulin secretion after islet
transplantation with the Edmonton protocol. Diabetes. 50:710–719.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bruni A, Gala-Lopez B, Pepper AR,
Abualhassan NS and Shapiro AJ: Islet cell transplantation for the
treatment of type 1 diabetes: Recent advances and future
challenges. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 7:211–223. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shapiro AJ, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, Korbutt GS,
Toth E, Warnock GL, Kneteman NM and Rajotte RV: Islet
transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus
using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J
Med. 343:230–238. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ludwig B, Rotem A, Schmid J, Weir GC,
Colton CK, Brendel MD, Neufeld T, Block NL, Yavriyants K, Steffen
A, et al: Improvement of islet function in a bioartificial pancreas
by enhanced oxygen supply and growth hormone releasing hormone
agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 109:pp. 5022–5027. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ryan EA, Paty BW, Senior PA, Bigam D,
Alfadhli E, Kneteman NM, Lakey JR and Shapiro AM: Five-year
follow-up after clinical islet transplantation. Diabetes.
54:2060–2069. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng CW, Villani V, Buono R, Wei M, Kumar
S, Yilmaz OH, Cohen P, Sneddon JB, Perin L and Longo VD:
Fasting-mimicking diet promotes ngn3-driven β-cell regeneration to
reverse diabetes. Cell. 168:775–788.e712. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang H, Zhang YW, Chen Y, Huang X, Zhou
F, Wang W, Xian B, Zhang X, Masliah E, Chen Q, et al: Appoptosin is
a novel pro-apoptotic protein and mediates cell death in
neurodegeneration. J Neurosci. 32:15565–15576. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang C, Shi Z, Zhang L, Zhou Z, Zheng X,
Liu G, Bu G, Fraser PE, Xu H and Zhang YW: Appoptosin interacts
with mitochondrial outer-membrane fusion proteins and regulates
mitochondrial morphology. J Cell Sci. 129:994–1002. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao Y, Tseng IC, Heyser CJ, Rockenstein
E, Mante M, Adame A, Zheng Q, Huang T, Wang X, Arslan PE, et al:
Appoptosin-mediated caspase cleavage of tau contributes to
progressive supranuclear palsy pathogenesis. Neuron. 87:963–975.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zheng KM, Zhang J, Zhang Cl, Zhang YW and
Chen XC: Curcumin inhibits appoptosin-induced apoptosis via
upregulating heme oxygenase-1 expression in SH-SY5Y cells. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 36:544–552. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Piret JP, Mottet D, Raes M and Michiels C:
CoCl2, a chemical inducer of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and hypoxia
reduce apoptotic cell death in hepatoma cell line HepG2. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 973:443–447. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sano M, Minamino T, Toko H, Miyauchi H,
Orimo M, Qin Y, Akazawa H, Tateno K, Kayama Y, Harada M, et al:
p53-induced inhibition of Hif-1 causes cardiac dysfunction during
pressure overload. Nature. 446:4442007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yuan Y, Hilliard G, Ferguson T and
Millhorn DE: Cobalt inhibits the interaction between
hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha and von Hippel-Lindau protein by
direct binding to hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha. J Biol Chem.
278:15911–15916. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI,
Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, von Kriegsheim A, Hebestreit HF, Mukherji
M, Schofield CJ, et al: Targeting of HIF-α to the von Hippel-Lindau
Ubiquitylation Complex by O2-Regulated Prolyl Hydroxylation.
Science. 292:468–472. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bruick RK and Mcknight SL: A conserved
family of prolyl-4-Hydroxylases that modify HIF. Science.
294:1337–1340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando
J, Ohh M, Salic A, Asara JM, Lane WS and Kaelin WG Jr: HIFalpha
targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation:
Implications for O2 sensing. Science. 292:464–468. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheung EC, Ludwig RL and Vousden KH:
Mitochondrial localization of TIGAR under hypoxia stimulates HK2
and lowers ROS and cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:pp.
20491–20496. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Franklin TJ, Morris WP, Edwards PN, Large
MS and Stephenson R: Inhibition of prolyl 4-hydroxylase in vitro
and in vivo by members of a novel series of phenanthrolinones.
Biochem J. 353:333–338. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Banerji B, Conejogarcia A, Mcneill LA,
McDonough A, Buck MR, Hewitson KS, Oldham NJ and Schofield CJ: The
inhibition of factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor (FIH) by
beta-oxocarboxylic acids. Chem Commun (Camb). 5438–5440. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Litmanovitz I, Bar-Yoseph F, Lifshitz Y,
Davidson K, Eliakim A, Regev RH and Nemet D: Reduced crying in term
infants fed high beta-palmitate formula: A double-blind randomized
clinical trial. BMC Pediatr. 14:1522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li Z, Shangguan Z, Liu Y, Wang J, Li X,
Yang S and Liu S: Puerarin protects pancreatic β-cell survival via
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Mol Endocrinol. 53:71–79. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zheng X, Zheng X, Wang X, Ma Z, Gupta
Sunkari V, Botusan I, Takeda T, Björklund A, Inoue M, Catrina SB,
et al: Acute hypoxia induces apoptosis of pancreatic β-cell by
activation of the unfolded protein response and upregulation of
CHOP. Cell Death Dis. 3:e3222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fang Y, Zhang Q, Tan J, Li L, An X and Lei
P: Intermittent hypoxia-induced rat pancreatic β-cell apoptosis and
protective effects of antioxidant intervention. Nutr Diabetes.
4:e1312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yildirim Ö: The effect of vitamin C and
cobalt supplementation on antioxidant status in healthy and
diabetic rats. African J Biotechnol. 8:2009.
|
|
29
|
Leonard SS, Harris GK and Shi X:
Metal-induced oxidative stress and signal transduction. Free
Radical Biol Med. 37:1921–1942. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sato Y, Endo H, Okuyama H, Takeda T,
Iwahashi H, Imagawa A, Yamagata K, Shimomura I and Inoue M:
Cellular hypoxia of pancreatic beta-cells due to high levels of
oxygen consumption for insulin secretion in vitro. J Biol Chem.
286:12524–12532. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Carlsson PO, Liss P, Andersson A and
Jansson L: Measurements of oxygen tension in native and
transplanted rat pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 47:1027–1032. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cantley J, Selman C, Shukla D, Abramov AY,
Forstreuter F, Esteban MA, Claret M, Lingard SJ, Clements M, Harten
SK, et al: Deletion of the von Hippel-Lindau gene in pancreatic
beta cells impairs glucose homeostasis in mice. J Clin Invest.
119:125–135. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang W, Upshaw L, Strong DM, Robertson RP
and Reems J: Increased oxygen consumption rates in response to high
glucose detected by a novel oxygen biosensor system in non-human
primate and human islets. J Endocrinol. 185:445–455. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|