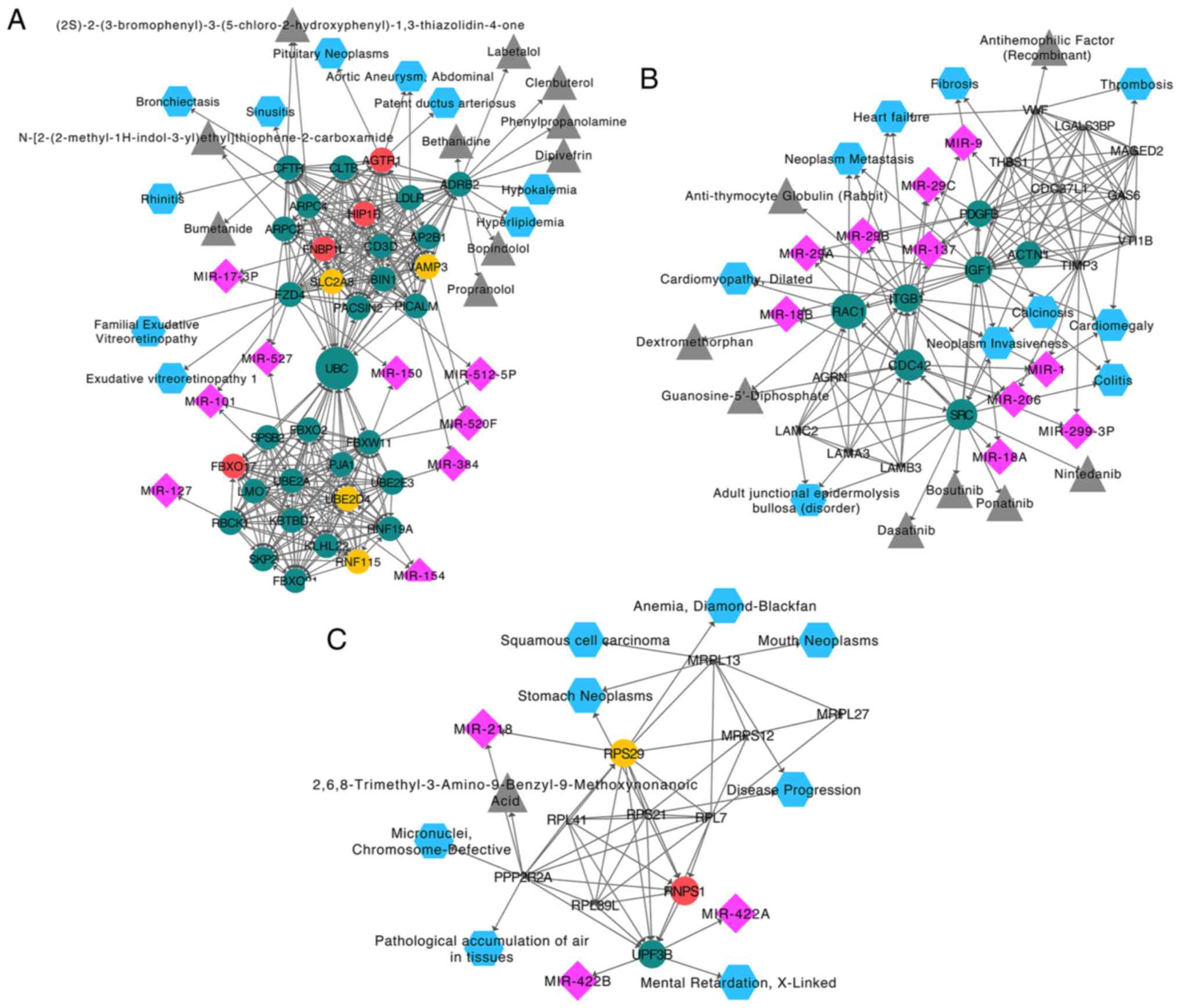
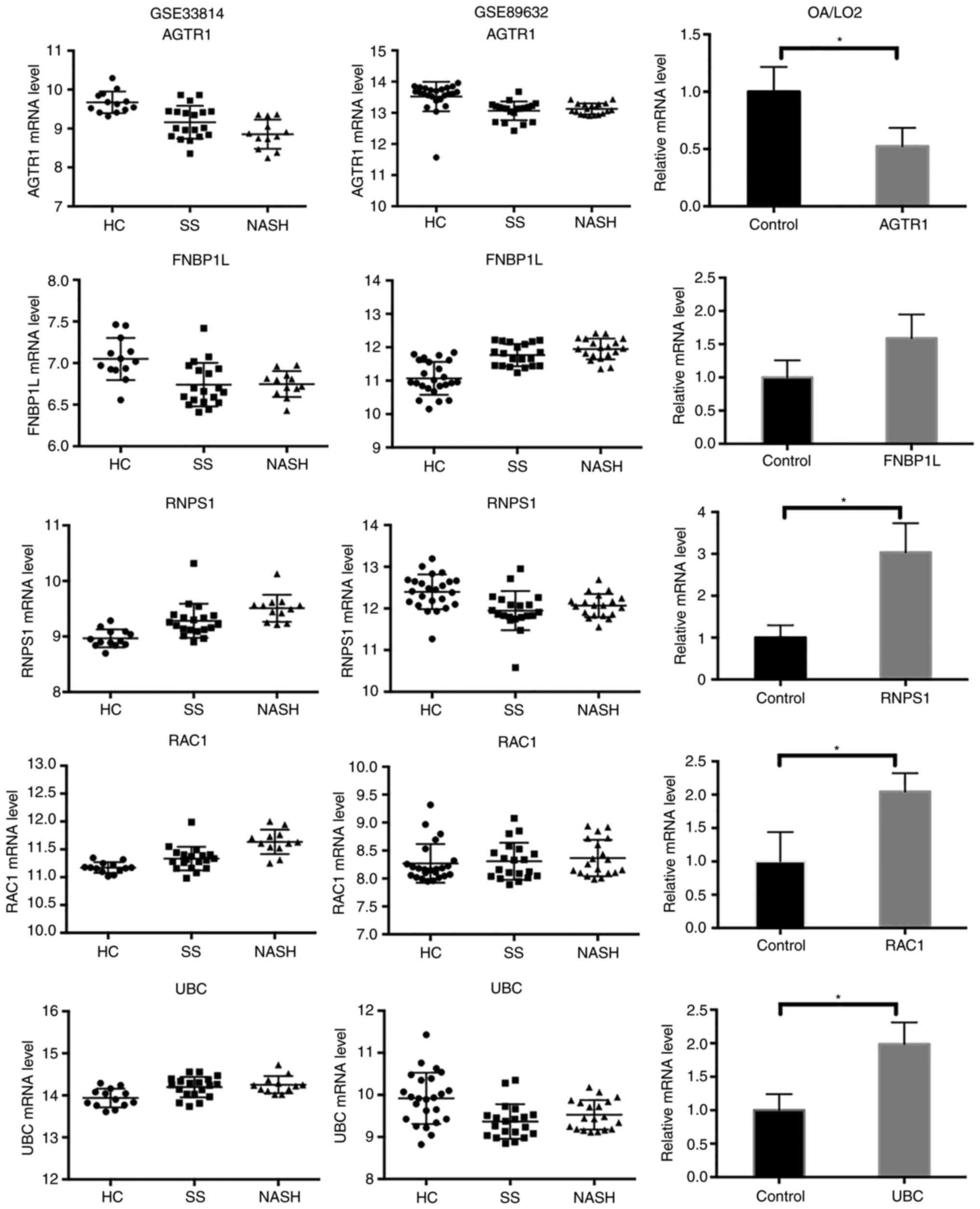
|
1
|
Lewis JR and Mohanty SR: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: A review and update. Dig Dis Sci. 55:560–578.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Starmann J, Fälth M, Spindelböck W, Lanz
KL, Lackner C, Zatloukal K, Trauner M and Sültmann H: Gene
expression profiling unravels cancer-related hepatic molecular
signatures in steatohepatitis but not in steatosis. PLoS One.
7:e465842012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lonardo A, Byrne CD, Caldwell SH,
Cortez-Pinto H and Targher G: Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence,
incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 64:1388–1389. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arendt BM, Comelli EM, Ma DW, Lou W,
Teterina A, Kim T, Fung SK, Wong DK, McGilvray I, Fischer SE and
Allard JP: Altered hepatic gene expression in nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease is associated with lower hepatic n-3 and n-6
polyunsaturated fatty acids. Hepatology. 61:1565–1578. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sookoian S, Castaño G, Gianotti TF, Gemma
C, Rosselli MS and Pirola CJ: Genetic variants in STAT3 are
associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cytokine.
44:201–206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Min HK, Mirshahi F, Verdianelli A, Pacana
T, Patel V, Park CG, Choi A, Lee JH, Park CB, Ren S and Sanyal AJ:
Activation of the GP130-STAT3 axis and its potential implications
in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 308:G794–G803. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miele L, Beale G, Patman G, Nobili V,
Leathart J, Grieco A, Abate M, Friedman SL, Narla G, Bugianesi E,
Day CP and Reeves HL: The Kruppel-like factor 6 genotype is
associated with fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Gastroenterology. 135:282–291.e1. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Seo YS, Kim JH, Jo NY, Choi KM, Baik SH,
Park JJ, Kim JS, Byun KS, Bak YT, Lee CH, et al: PPAR agonists
treatment is effective in a nonalcoholic fatty liver disease animal
model by modulating fatty-acid metabolic enzymes. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 23:102–109. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sazci A, Ergul E, Aygun C, Akpinar G,
Senturk O and Hulagu S: Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene
polymorphisms in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Cell Biochem Funct. 26:291–296. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun MY, Zhang L, Shi SL and Lin JN:
Associations between Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR)
Polymorphisms and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) risk: A
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 11:e01543372016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Edgar R, Domrachev M and Lash AE: Gene
expression omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array
data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:207–210. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
R Core Team: R: A Language and Environment
for Statistical ComputingR Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Vienna: 2011, http://www.R-project.org/
|
|
13
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID gene functional classification tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:(Database Issue). D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bandettini WP, Kellman P, Mancini C,
Booker OJ, Vasu S, Leung SW, Wilson JR, Shanbhag SM, Chen MY and
Arai AE: MultiContrast Delayed Enhancement (MCODE) improves
detection of subendocardial myocardial infarction by late
gadolinium enhancement cardiovascular magnetic resonance: A
clinical validation study. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 14:832012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang B, Kirov S and Snoddy J: WebGestalt:
An integrated system for exploring gene sets in various biological
contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:(Web Server Issue). W741–W748.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang B, Li L, Fu J, Yu P, Gong D, Zeng C
and Zeng Z: Effects of long-chain and medium-chain fatty acids on
apoptosis and oxidative stress in human liver cells with steatosis.
J Food Sci. 81:H794–H800. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
An S, Zhao LP, Shen LJ, Wang S, Zhang K,
Qi Y, Zheng J, Zhang XJ, Zhu XY, Bao R, et al: USP18 protects
against hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance via its
deubiquitinating activity. Hepatology. 66:1866–1884. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Raaz D, Herrmann M, Ekici AB, Klinghammer
L, Lausen B, Voll RE, Leusen JH, van de Winkel JG, Daniel WG, Reis
A and Garlichs CD: FcgammaRIIa genotype is associated with acute
coronary syndromes as first manifestation of coronary artery
disease. Atherosclerosis. 205:512–516. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang SK, Jung Y, Kim H, Hong M, Ye BD and
Song K: Association of FCGR2A, JAK2 or HNF4A variants with
ulcerative colitis in Koreans. Dig Liver Dis. 43:856–861. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Asano K, Matsushita T, Umeno J, Hosono N,
Takahashi A, Kawaguchi T, Matsumoto T, Matsui T, Kakuta Y, Kinouchi
Y, et al: A genome-wide association study identifies three new
susceptibility loci for ulcerative colitis in the Japanese
population. Nat Genet. 41:1325–1329. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chandrashekaran V, Seth RK, Dattaroy D,
Alhasson F, Ziolenka J, Carson J, Berger FG, Kalyanaraman B, Diehl
AM and Chatterjee S: HMGB1-RAGE pathway drives peroxynitrite
signaling-induced IBD-like inflammation in murine nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Redox Biol. 13:8–19. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shulman GI: Cellular mechanisms of insulin
resistance. J Clin Invest. 106:171–176. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kumar R, Prakash S, Chhabra S, Singla V,
Madan K, Gupta SD, Panda SK, Khanal S and Acharya SK: Association
of pro-inflammatory cytokines, adipokines & oxidative stress
with insulin resistance & non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Indian J Med Res. 136:229–236. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Valenti L, Rametta R, Dongiovanni P,
Maggioni M, Fracanzani AL, Zappa M, Lattuada E, Roviaro G and
Fargion S: Increased expression and activity of the transcription
factor FOXO1 in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Diabetes.
57:1355–1362. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Plat AW, Stoffers HE, de Leeuw PW, van
Schayck CP, Soomers FL, Kester AD, Aretz K and Kroon AA: The
association between arterial stiffness and the angiotensin II type
1 receptor (A1166C) polymorphism is influenced by the use of
cardiovascular medication. J Hypertens. 27:69–75. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jourdan T, Szanda G, Rosenberg AZ, Tam J,
Earley BJ, Godlewski G, Cinar R, Liu Z, Liu J, Ju C, et al:
Overactive cannabinoid 1 receptor in podocytes drives type 2
diabetic nephropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:E5420–E5428.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kagawa T, Takao T, Horino T, Matsumoto R,
Inoue K, Morita T and Hashimoto K: Angiotensin II receptor blocker
inhibits tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced cell damage in human
renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Nephrology (Carlton).
13:309–315. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yoneda M, Hotta K, Nozaki Y, Endo H,
Uchiyama T, Mawatari H, Iida H, Kato S, Fujita K, Takahashi H, et
al: Association between angiotensin II type 1 receptor
polymorphisms and the occurrence of nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. Liver Int. 29:1078–1085. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mayeda A, Badolato J, Kobayashi R, Zhang
MQ, Gardiner EM and Krainer AR: Purification and characterization
of human RNPS1: A general activator of pre-mRNA splicing. EMBO J.
18:4560–4570. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schwerk C, Prasad J, Degenhardt K,
Erdjument-Bromage H, White E, Tempst P, Kidd VJ, Manley JL, Lahti
JM and Reinberg D: ASAP, a novel protein complex involved in RNA
processing and apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 23:2981–2990. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huett A, Ng A, Cao Z, Kuballa P, Komatsu
M, Daly MJ, Podolsky DK and Xavier RJ: A novel hybrid yeast-human
network analysis reveals an essential role for FNBP1L in
antibacterial autophagy. J Immunol. 182:4917–4930. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chander H, Brien CD, Truesdell P, Watt K,
Meens J, Schick C, Germain D and Craig AW: Toca-1 is suppressed by
p53 to limit breast cancer cell invasion and tumor metastasis.
Breast Cancer Res. 16:34132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Murray JI, Whitfield ML, Trinklein ND,
Myers RM, Brown PO and Botstein D: Diverse and specific gene
expression responses to stresses in cultured human cells. Mol Biol
Cell. 15:2361–2374. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ryu KT, Maehr R, Gilchrist CA, Long MA,
Bouley DM, Mueller B, Ploegh HL and Kopito RR: The mouse
polyubiquitin gene UbC is essential for fetal liver development,
cell-cycle progression and stress tolerance. EMBO J. 26:2693–2706.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu J, Li Z, Ren X, Dong M, Li J, Shi X,
Zhang Y, Xie W, Sun Z, Liu X and Dai Q: Investigation of pathogenic
genes in chinese sporadic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients by
whole exome sequencing. Sci Rep. 5:166092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Frasa MA, Maximiano FC, Smolarczyk K,
Francis RE, Betson ME, Lozano E, Goldenring J, Seabra MC, Rak A,
Ahmadian MR and Braga VM: Armus is a Rac1 effector that inactivates
Rab7 and regulates E-cadherin degradation. Curr Biol. 20:198–208.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Oka T, Ihara S and Fukui Y: Cooperation of
DEF6 with activated Rac in regulating cell morphology. J Biol Chem.
282:2011–2018. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sharma M, Urano F and Jaeschke A: Cdc42
and Rac1 are major contributors to the saturated fatty
acid-stimulated JNK pathway in hepatocytes. J Hepatol. 56:192–198.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Carroll CL, Stoltz P, Schramm CM and
Zucker AR: Beta2-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms affect response
to treatment in children with severe asthma exacerbations. Chest.
135:1186–1192. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kao WT, Yen YC and Lung FW: The effects of
beta2 adrenergic receptor gene polymorphism in lipid profiles.
Lipids Health Dis. 7:202008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang Q, Liu Y, Fu Q, Xu B, Zhang Y, Kim S,
Tan R, Barbagallo F, West T, Anderson E, et al: Inhibiting
insulin-mediated β2-adrenergic receptor activation prevents
diabetes-associated cardiac dysfunction. Circulation. 135:73–88.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Huang S, Yang Z, Ma Y, Yang Y and Wang S:
miR-101 enhances cisplatin-induced DNA damage through decreasing
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate levels by directly
repressing Tp53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator
expression in prostate cancer cells. DNA Cell Biol. 36:303–310.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Qian L, Zhang W, Lei B, He A, Ye L, Li X
and Dong X: MicroRNA-101 regulates T-cell acute lymphoblastic
leukemia progression and chemotherapeutic sensitivity by targeting
Notch1. Oncol Rep. 36:2511–2516. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jin C, Zhang X, Sun M, Zhang Y, Zhang G
and Wang B: Clinical implications of the coexpression of SRC1 and
NANOG in HER-2-overexpressing breast cancers. Onco Targets Ther.
9:5483–5488. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Laschi M, Bernardini G, Geminiani M,
Manetti F, Mori M, Spreafico A, Campanacci D, Capanna R, Schenone
S, Botta M and Santucci A: Differentially activated Src kinase in
chemo-naïve human primary osteosarcoma cells and effects of a Src
kinase inhibitor. Biofactors. 43:801–811. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhu K, Liu L, Zhang J, Wang Y, Liang H,
Fan G, Jiang Z, Zhang CY, Chen X and Zhou G: MiR-29b suppresses the
proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells by targeting
CDK6. Protein Cell. 7:434–444. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fang JH, Zhou HC, Zeng C, Yang J, Liu Y,
Huang X, Zhang JP, Guan XY and Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-29b suppresses
tumor angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis by regulating matrix
metalloproteinase 2 expression. Hepatology. 54:1729–1740. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang J, Chu E, Chen H, Man K, Go M, Huang
X, Lan H, Sung J and Yu J: microRNA-29b prevents liver fibrosis by
attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation and inducing apoptosis
through targeting PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget. 6:7325–7338.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang X, Dong J, He Y, Zhao M, Liu Z, Wang
N, Jiang M, Zhang Z, Liu G, Liu H, et al: miR-218 inhibited tumor
angiogenesis by targeting ROBO1 in gastric cancer. Gene. 615:42–49.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Dong R, Zheng Y, Chen G, Zhao R, Zhou Z
and Zheng S: miR-222 overexpression may contribute to liver
fibrosis in biliary atresia by targeting PPP2R2A. J Pediatr
Gastroenterol Nutr. 60:84–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kuo YC, Huang KY, Yang CH, Yang YS, Lee WY
and Chiang CW: Regulation of phosphorylation of Thr-308 of Akt,
cell proliferation, and survival by the B55alpha regulatory subunit
targeting of the protein phosphatase 2A holoenzyme to Akt. J Biol
Chem. 283:1882–1892. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|