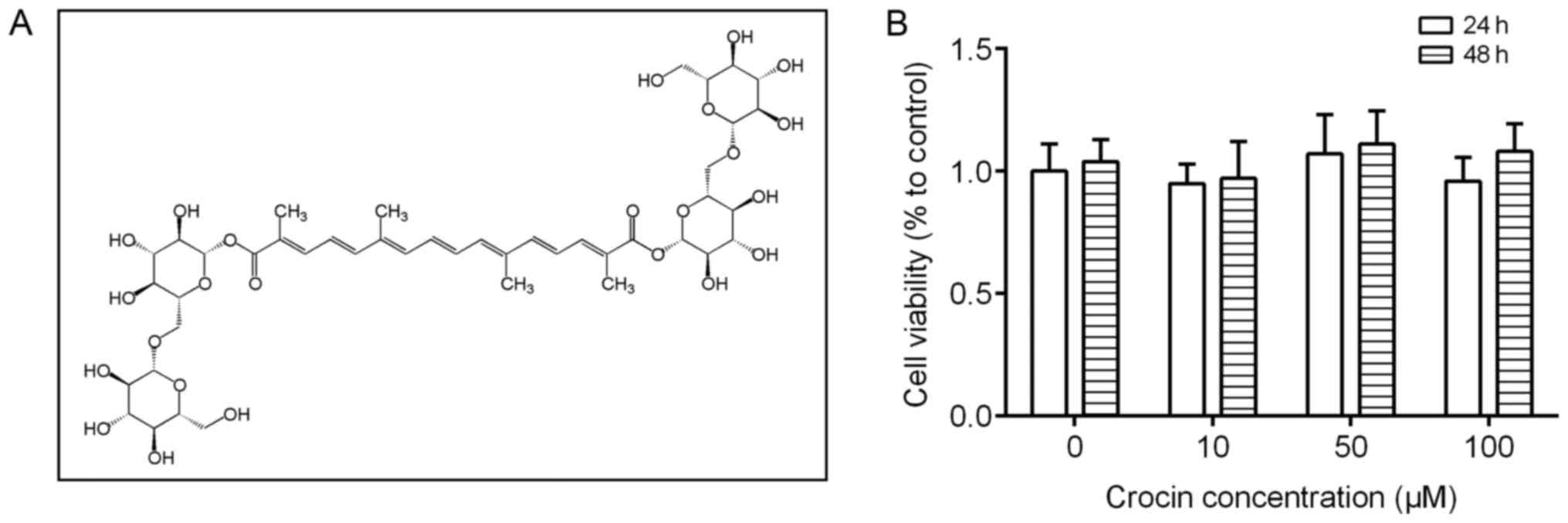
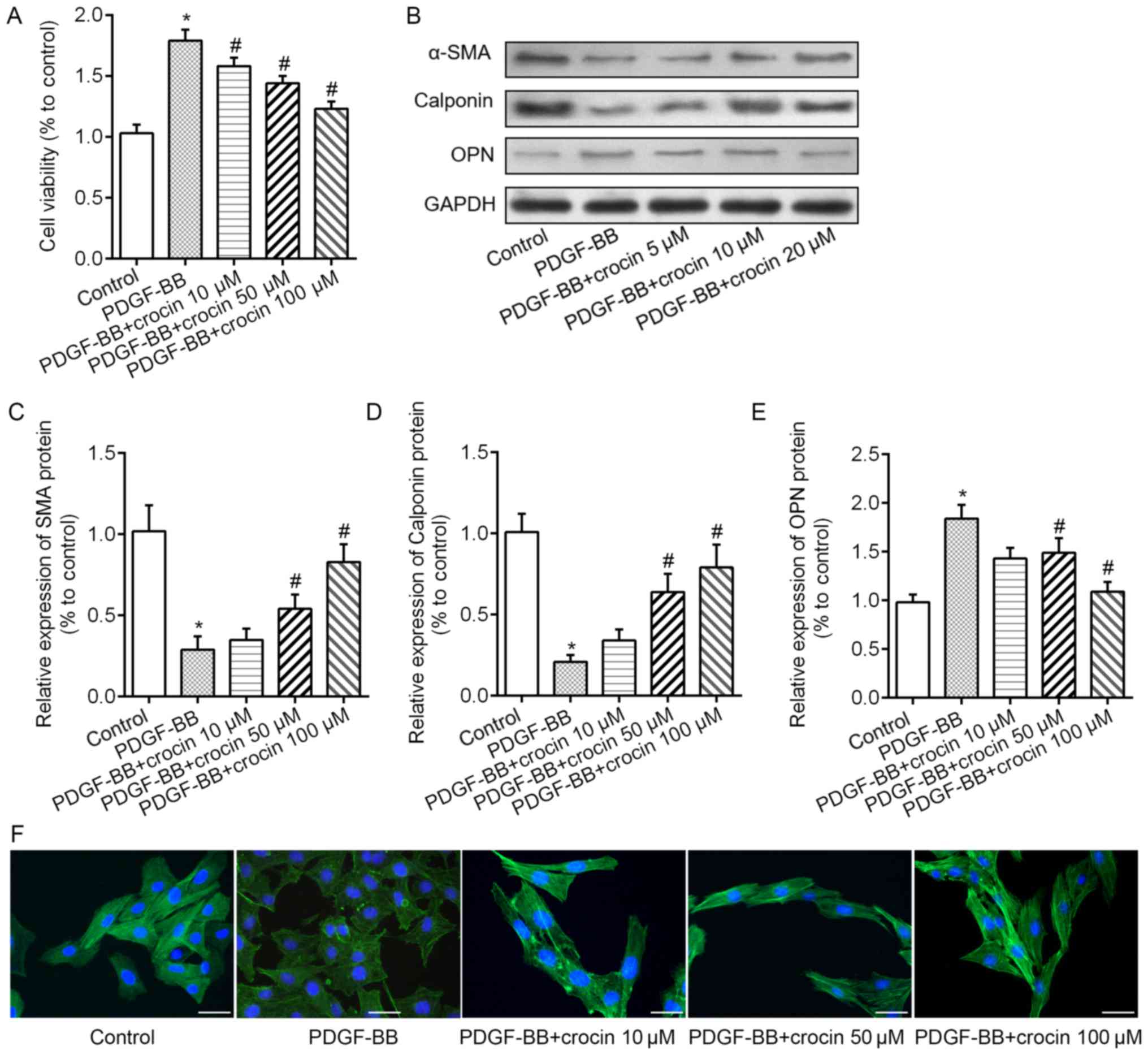
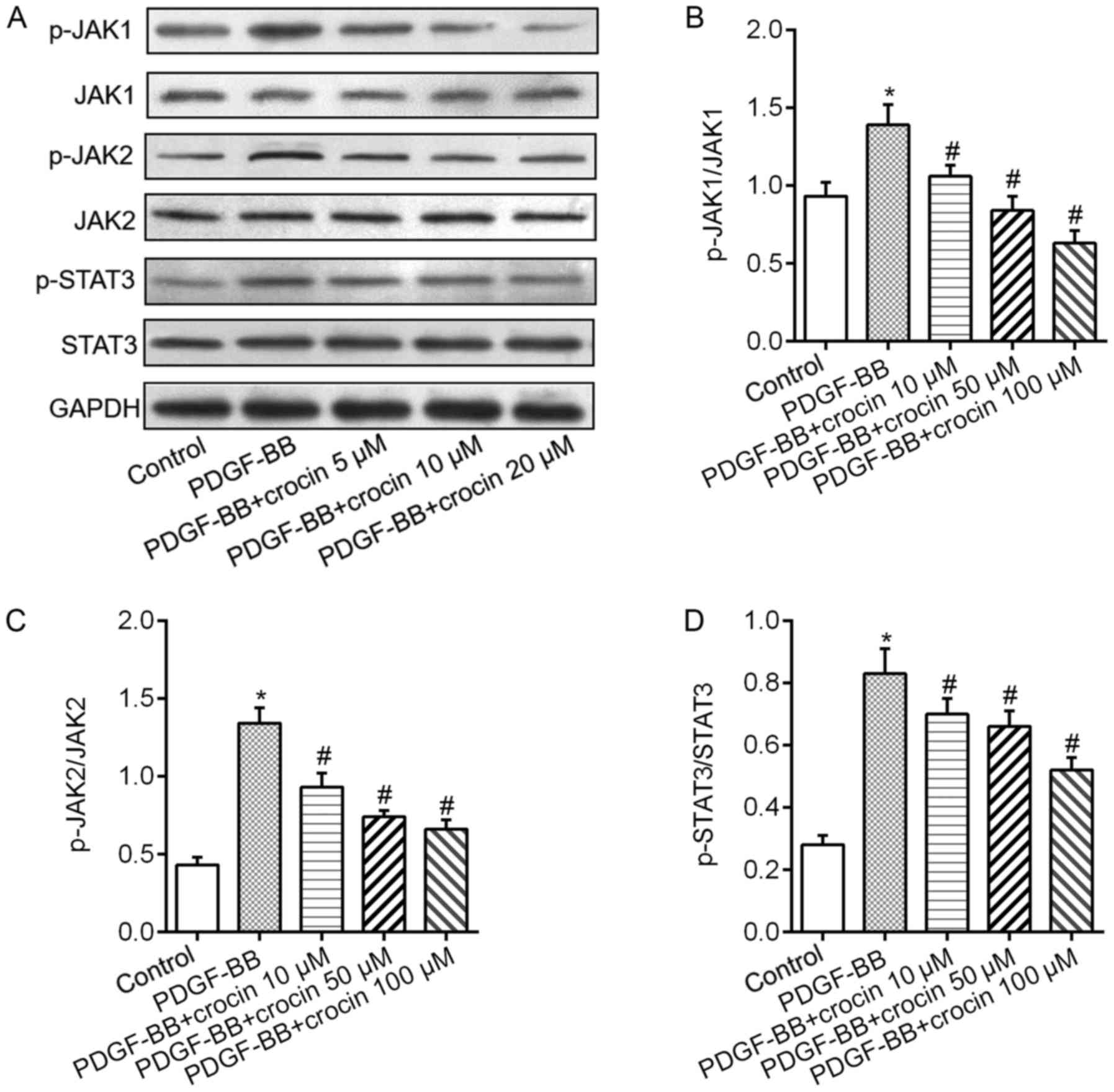
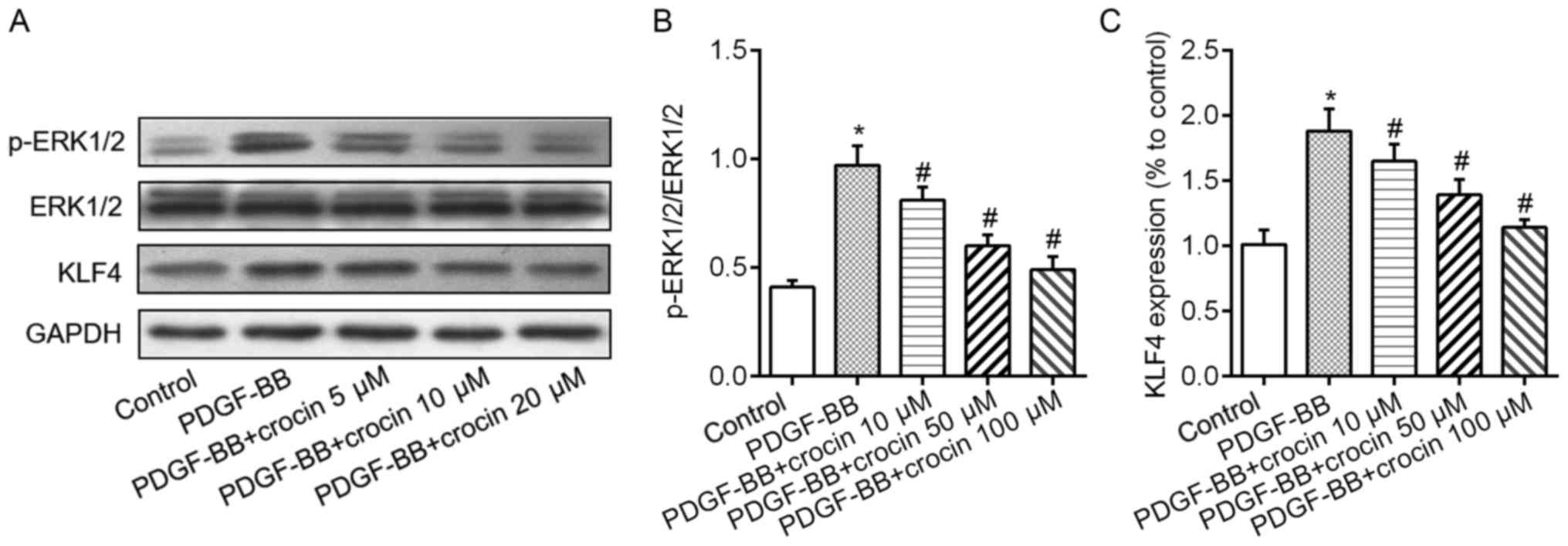
|
1
|
Ding Y, Zhang M, Zhang W, Lu Q, Cai Z,
Song P, Okon IS, Xiao L and Zou MH: AMP-activated protein kinase
alpha 2 deletion induces VSMC phenotypic switching and reduces
features of atherosclerotic plaque stability. Circ Res.
119:718–730. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang F, Chen Q, He S, Yang M, Maguire EM,
An W, Afzal TA, Luong LA, Zhang L and Xiao Q: miRNA-22 is a novel
mediator of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic modulation and
neointima formation. Circulation. pii: CIRCULATIONAHA.117.027799.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yang X, Dong M, Wen H, Liu X, Zhang M, Ma
L, Zhang C, Luan X, Lu H and Zhang Y: MiR-26a contributes to the
PDGF-BB-induced phenotypic switch of vascular smooth muscle cells
by suppressing Smad1. Oncotarget. 8:75844–75853. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li G, Xie N, Yao Y, Zhang Y, Guo J, Feng
Y, Lv F, Xiao RP and Cao CM: Identification of PI3K regulatory
subunit p55γ as a novel inhibitor of vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation and neointimal formation. Cardiovasc Res. 105:75–85.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kaimoto T, Yasuda O, Ohishi M, Mogi M,
Takemura Y, Suhara T, Ogihara T, Fukuo K and Rakugi H: Nifedipine
inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell dedifferentiation via
downregulation of Akt signaling. Hypertension. 56:247–252. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Song IS, Jeong YJ, Park JH, Shim S and
Jang SW: Chebulinic acid inhibits smooth muscle cell migration by
suppressing PDGF-Rβ phosphorylation and inhibiting matrix
metalloproteinase-2 expression. Sci Rep. 7:117972017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rahaiee S, Moini S, Hashemi M and
Shojaosadati SA: Evaluation of antioxidant activities of bioactive
compounds and various extracts obtained from saffron (Crocus
sativus L.): A review. J Food Sci Technol. 52:1881–1888. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Amin A, Hamza AA, Daoud S, Khazanehdari K,
Hrout AA, Baig B, Chaiboonchoe A, Adrian TE, Zaki N and
Salehi-Ashtiani K: Saffron-based crocin prevents early lesions of
liver cancer: In vivo, in vitro and network analyses. Recent Pat
Anticancer Drug Discov. 11:121–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mohammadzadeh L, Hosseinzadeh H, Abnous K
and Razavi BM: Neuroprotective potential of crocin against
malathion-induced motor deficit and neurochemical alterations in
rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 25:4904–4914. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He SY, Qian ZY, Tang FT, Wen N, Xu GL and
Sheng L: Effect of crocin on experimental atherosclerosis in quails
and its mechanisms. Life Sci. 77:907–921. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li J, Lei HT, Cao L, Mi YN, Li S and Cao
YX: Crocin alleviates coronary atherosclerosis via inhibiting lipid
synthesis and inducing M2 macrophage polarization. Int
Immunopharmacol. 55:120–127. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chi J, Meng L, Pan S, Lin H, Zhai X, Liu
L, Zhou C, Jiang C and Guo H: Primary culture of rat aortic
vascular smooth muscle cells: A new method. Med Sci Monit.
23:4014–4020. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liao Y, Hu X, Guo X, Zhang B, Xu W and
Jiang H: Promoting effects of IL-23 on myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion are associated with increased expression of IL-17A and
upregulation of the JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
16:9309–9316. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu N, Xu L, Shi Y, Fang L, Gu H, Wang H,
Ding X and Zhuang S: Pharmacologic targeting ERK1/2 attenuates the
development and progression of hyperuricemic nephropathy in rats.
Oncotarget. 8:33807–33826. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu B, Zhang L, Zhu YH, Zhang YE, Zheng F,
Yang JY, Guo LY, Li XY, Wang L, Tang JM, et al: Mesoderm/mesenchyme
homeobox gene l promotes vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic
modulation and vascular remodeling. Int J Cardiol. 251:82–89. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yan G, Wang Q, Hu S, Wang D, Qiao Y, Ma G,
Tang C and Gu Y: Digoxin inhibits PDGF-BB-induced VSMC
proliferation and migration through an increase in ILK signaling
and attenuates neointima formation following carotid injury. Int J
Mol Med. 36:1001–1011. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park S, Kim JK, Oh CJ, Choi SH, Jeon JH
and Lee IK: Scoparone interferes with STAT3-induced proliferation
of vascular smooth muscle cells. Exp Mol Med. 47:e1452015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Salabei JK, Cummins TD, Singh M, Jones SP,
Bhatnagar A and Hill BG: PDGF-mediated autophagy regulates vascular
smooth muscle cell phenotype and resistance to oxidative stress.
Biochem J. 451:375–388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Simon AR, Takahashi S, Severgnini M,
Fanburg BL and Cochran BH: Role of the JAK-STAT pathway in
PDGF-stimulated proliferation of human airway smooth muscle cells.
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 282:L1296–L1304. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ji Y, Yang X and Su H: Overexpression of
microRNA-375 impedes platelet-derived growth factor-induced
proliferation and migration of human fetal airway smooth muscle
cells by targeting Janus kinase 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 98:69–75.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim B, Lee KY and Park B: Crocin
suppresses constitutively active STAT3 through induction of protein
tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. J Cell Biochem. 118:3290–3298. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liao XH, Wang N, Zhao DW, Zheng DL, Zheng
L, Xing WJ, Ma WJ, Bao LY, Dong J and Zhang TC: STAT3 protein
regulates vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switch by
interaction with myocardin. J Biol Chem. 290:19641–19652. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chang Y, Li JY, Jayakumar T, Hung SH, Lee
WC, Manubolu M, Sheu JR and Hsu MJ: Ketamine, a clinically used
anesthetic, inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via
PP2A-activated PI3K/Akt/ERK inhibition. Int J Mol Sci. 18:pii:
E2545. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen Q, Chen L, Kong D, Shao J, Wu L and
Zheng S: Dihydroartemisinin alleviates bile duct ligation-induced
liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation by interfering
with the PDGF-βR/ERK signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
34:250–258. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gharibi B, Ghuman MS and Hughes FJ: Akt-
and Erk-mediated regulation of proliferation and differentiation
during PDGFRβ-induced MSC self-renewal. J Cell Mol Med.
16:2789–2801. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim JY, Kim KH, Lee WR, An HJ, Lee SJ, Han
SM, Lee KG, Park YY, Kim KS, Lee YS, et al: Apamin inhibits
PDGF-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and
migration through suppressions of activated Akt and Erk signaling
pathway. Vascul Pharmacol. 70:8–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim MO, Kim SH, Cho YY, Nadas J, Jeong CH,
Yao K, Kim DJ, Yu DH, Keum YS, Lee KY, et al: ERK1 and ERK2
regulate embryonic stem cell self-renewal through phosphorylation
of Klf4. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 19:283–290. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kawai-Kowase K and Owens GK: Multiple
repressor pathways contribute to phenotypic switching of vascular
smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 292:C59–C69. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen S, Dong S, Li Z, Guo X, Zhang N, Yu B
and Sun Y: Atorvastatin calcium inhibits PDGF-ββ-induced
proliferation and migration of VSMCs through the G0/G1 cell cycle
arrest and suppression of activated PDGFRβ-PI3K-Akt signaling
cascade. Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:215–228. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen L, Qi Y and Yang X: Neuroprotective
effects of crocin against oxidative stress induced by
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat retina. Ophthalmic Res.
54:157–168. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lari P, Rashedinia M, Abnous K and
Hosseinzadeh H: Crocin improves lipid dysregulation in subacute
diazinon exposure through ERK1/2 pathway in rat liver. Drug Res
(Stuttg). 64:301–305. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang TM, Chen KC, Hsu PY, Lin HF, Wang YS,
Chen CY, Liao YC and Juo SH: microRNA let-7g suppresses
PDGF-induced conversion of vascular smooth muscle cell into the
synthetic phenotype. J Cell Mol Med. 21:3592–3601. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sunaga H, Matsui H, Anjo S, Syamsunarno
MR, Koitabashi N, Iso T, Matsuzaka T, Shimano H, Yokoyama T and
Kurabayashi M: Elongation of long-chain fatty acid family member 6
(Elovl6)-driven fatty acid metabolism regulates vascular smooth
muscle cell phenotype through AMP-activated protein
kinase/krüppel-like factor 4 (AMPK/KLF4) signaling. J Am Heart
Assoc. 5:pii: e004014. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ouyang QF, Han Y, Lin ZH, Xie H, Xu CS and
Xie LD: Fluvastatin upregulates the α 1C subunit of CaV1.2 channel
expression in vascular smooth muscle cells via RhoA and ERK/p38
MAPK pathways. Dis Markers. 2014:2370672014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Feng J, Ge S, Zhang L, Che H and Liang C:
Aortic dissection is associated with reduced polycystin-1
expression, an abnormality that leads to increased ERK
phosphorylation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Histochem.
60:27112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chang C, Zhao Y, Song G and She K:
Resveratrol protects hippocampal neurons against cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury via modulating JAK/ERK/STAT signaling
pathway in rats. J Neuroimmunol. 315:9–14. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ottani A, Giuliani D, Neri L, Calevro A,
Canalini F, Vandini E, Cainazzo MM, Ruberto IA, Barbieri A, Rossi R
and Guarini S: NDP-alpha-MSH attenuates heart and liver responses
to myocardial reperfusion via the vagus nerve and JAK/ERK/STAT
signaling. Eur J Pharmacol. 769:22–32. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ottani A, Galantucci M, Ardimento E, Neri
L, Canalini F, Calevro A, Zaffe D, Novellino E, Grieco P, Giuliani
D and Guarini S: Modulation of the JAK/ERK/STAT signaling in
melanocortin-induced inhibition of local and systemic responses to
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Pharmacol Res. 72:1–8. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wilson JL, Yu J, Taylor L and Polgar P:
Hyperplastic growth of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells from
subjects with pulmonary arterial hypertension is activated through
JNK and p38 MAPK. PLoS One. 10:e01236622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|