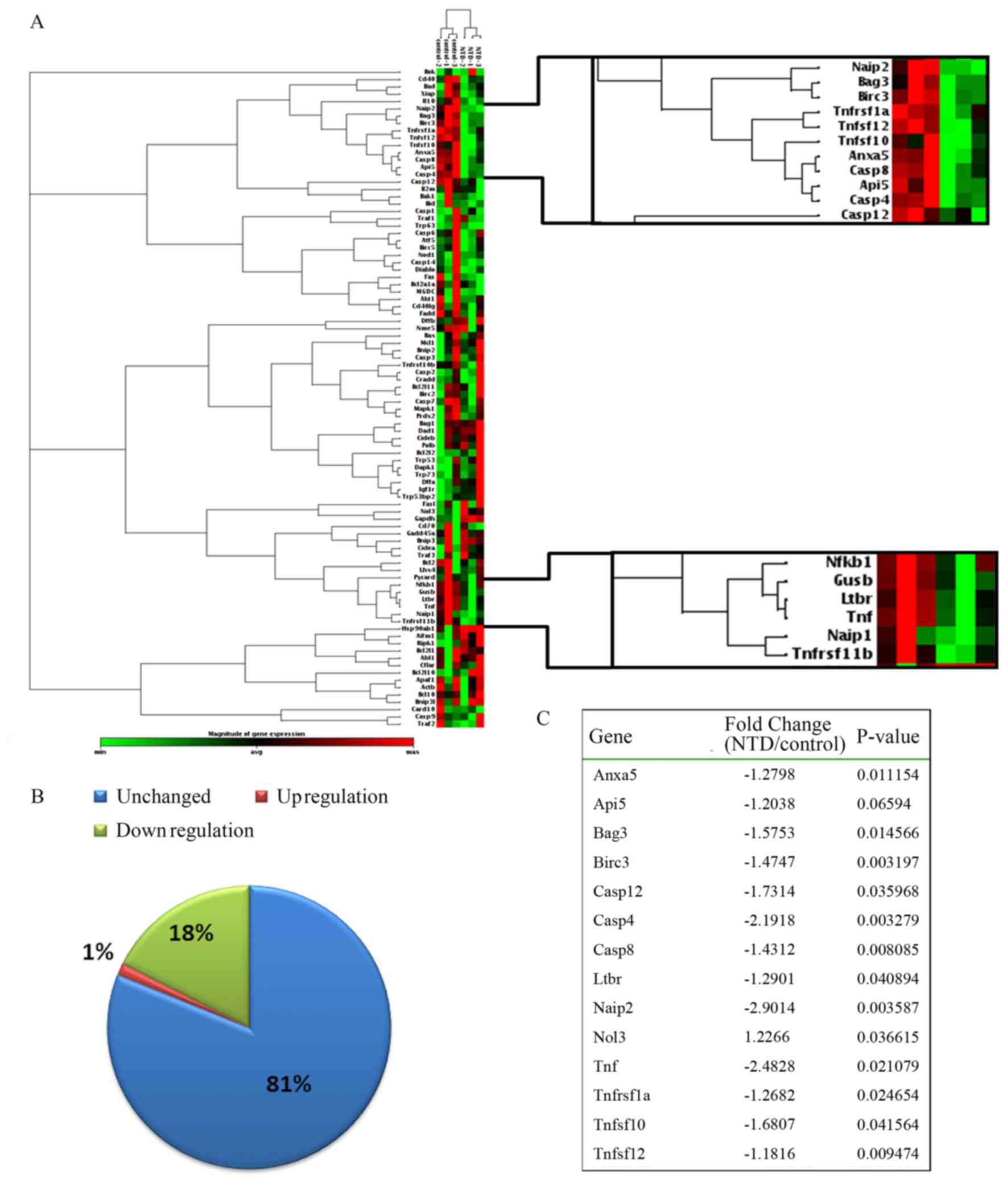
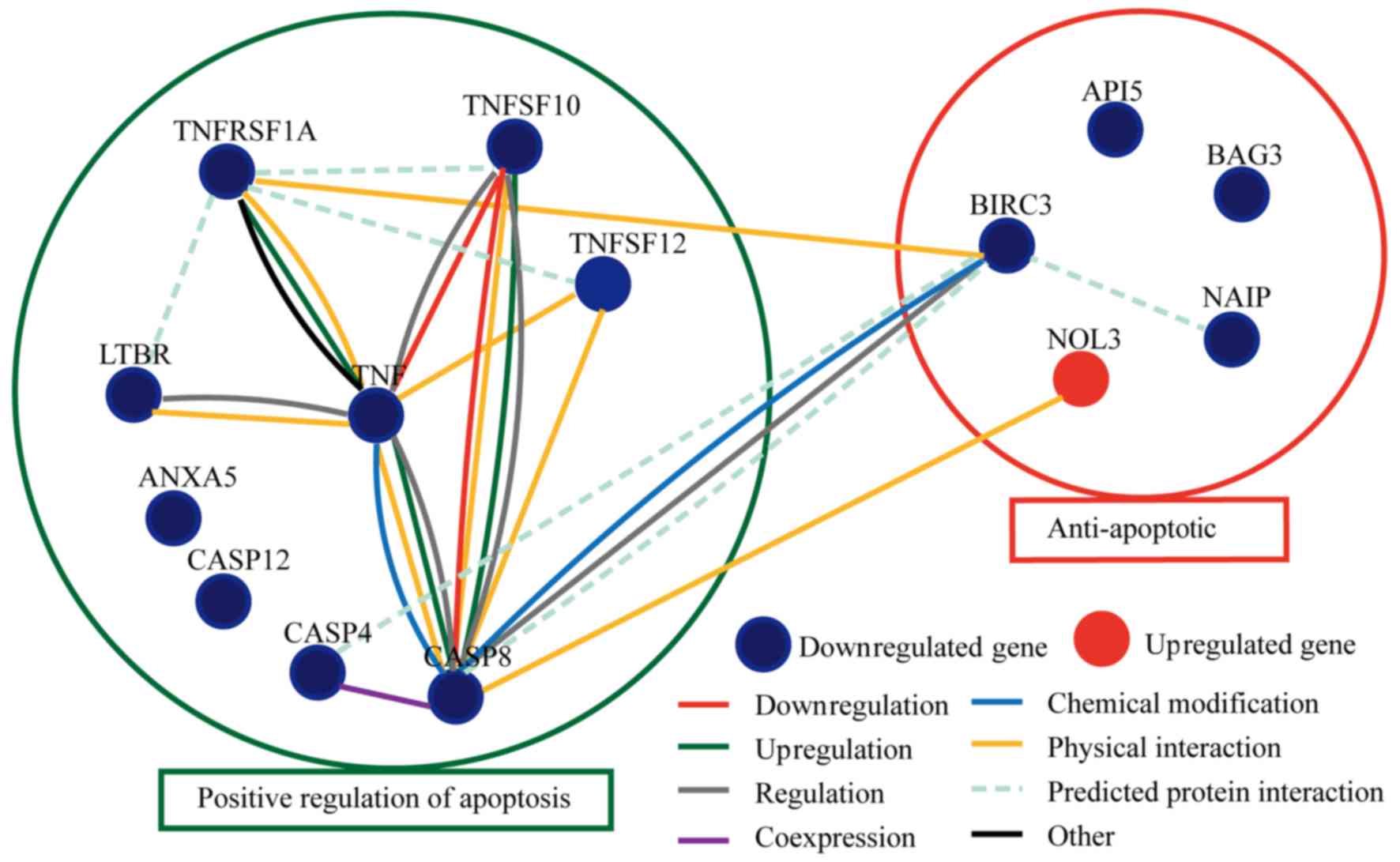
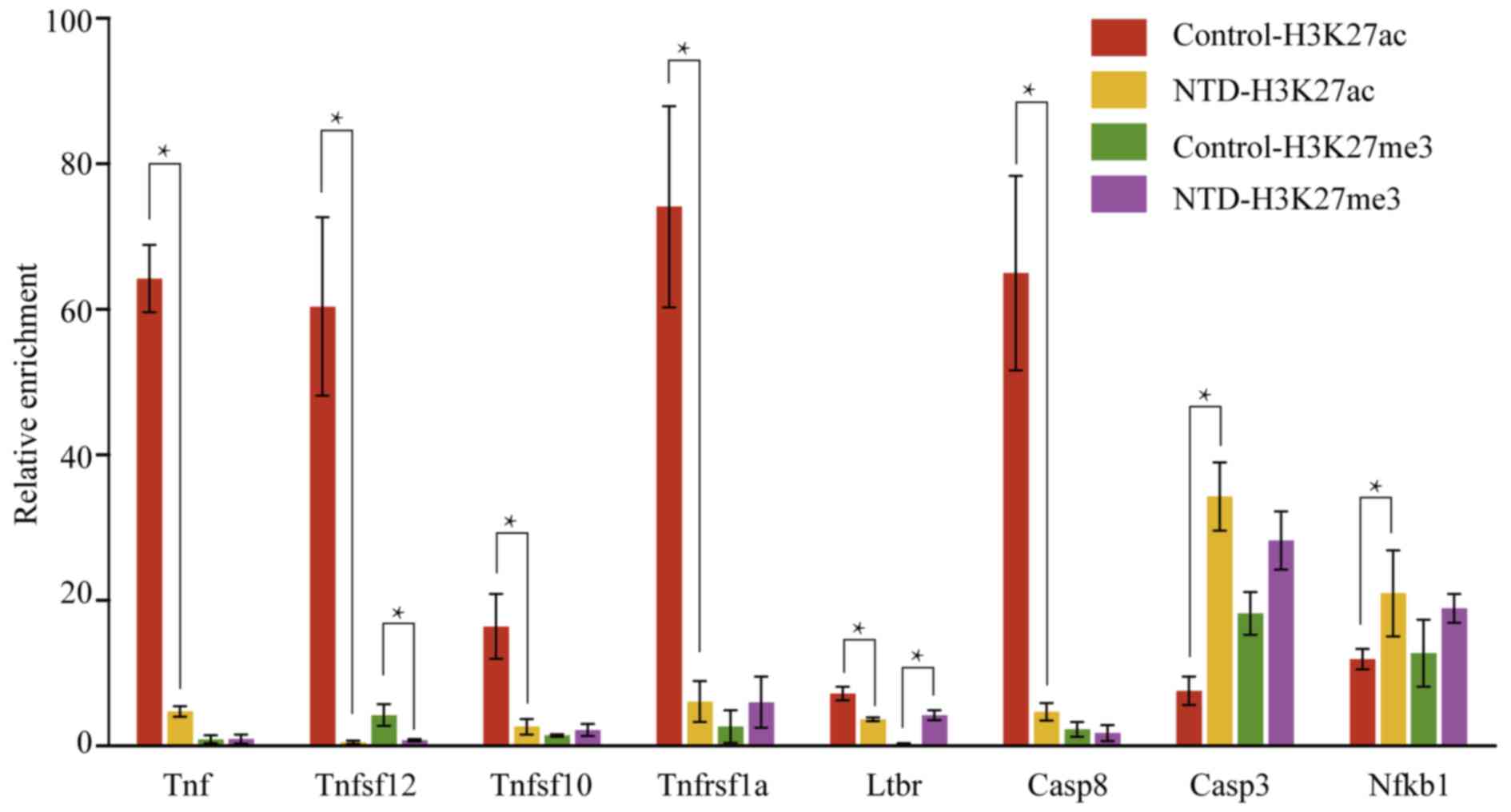
|
1
|
Williams J, Mai CT, Mulinare J, Isenburg
J, Flood TJ, Ethen M, Frohnert B and Kirby RS: Centers for Disease
Control and Prevention: Updated estimates of neural tube defects
prevented by mandatory folic Acid fortification-United States,
1995–2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 64:1–5. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li Z, Ren A, Zhang L, Ye R, Li S, Zheng J,
Hong S, Wang T and Li Z: Extremely high prevalence of neural tube
defects in a 4-county area in Shanxi Province, China. Birth Defects
Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 76:237–240. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hansler A, Chen Q, Gray JD, Ross ME,
Finnell RH and Gross SS: Untargeted metabolite profiling of murine
embryos to reveal metabolic perturbations associated with neural
tube closure defects. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol.
100:623–632. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Copp AJ, Greene ND and Murdoch JN: The
genetic basis of mammalian neurulation. Nat Rev Genet. 4:784–793.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maden M, Gale E and Zile M: The role of
vitamin A in the development of the central nervous system. J Nutr.
128 2 Suppl:471S–475S. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wei X, Li H, Miao J, Zhou F, Liu B, Wu D,
Li S, Wang L, Fan Y, Wang W and Yuan Z: Disturbed apoptosis and
cell proliferation in developing neuroepithelium of lumbo-sacral
neural tubes in retinoic acid-induced spina bifida aperta in rat.
Int J Dev Neurosci. 30:375–381. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Alles AJ and Sulik KK: Retinoic
acid-induced spina bifida: Evidence for a pathogenetic mechanism.
Development. 108:73–81. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ha M, Ng DW, Li WH and Chen ZJ:
Coordinated histone modifications are associated with gene
expression variation within and between species. Genome Res.
21:590–598. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rada-Iglesias A, Bajpai R, Swigut T,
Brugmann SA, Flynn RA and Wysocka J: A unique chromatin signature
uncovers early developmental enhancers in humans. Nature.
470:279–283. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Balmer NV, Weng MK, Zimmer B, Ivanova VN,
Chambers SM, Nikolaeva E, Jagtap S, Sachinidis A, Hescheler J,
Waldmann T and Leist M: Epigenetic changes and disturbed neural
development in a human embryonic stem cell-based model relating to
the fetal valproate syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 21:4104–4114. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Copp AJ and Greene ND: Genetics and
development of neural tube defects. J Pathol. 220:217–230.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang L, Wang F, Guan J, Le J, Wu L, Zou J,
Zhao H, Pei L, Zheng X and Zhang T: Relation between
hypomethylation of long interspersed nucleotide elements and risk
of neural tube defects. Am J Clin Nutr. 91:1359–1367. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Q, Xue P, Li H, Bao Y, Wu L, Chang
S, Niu B, Yang F and Zhang T: Histone modification mapping in human
brain reveals aberrant expression of histone H3 lysine 79
dimethylation in neural tube defects. Neurobiol Dis. 54:404–413.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen S, Bai B, Wang X, Li H and Zhang T:
Retinoic acid induced neural tube defects in C57 mice in a
dose-dependent and time-specific way. Chin J Birth Health Heredity.
126–128. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Martin DA, Siegel RM, Zheng L and Lenardo
MJ: Membrane oligomerization and cleavage activates the caspase-8
(FLICE/MACHalpha1) death signal. J Biol Chem. 273:4345–4349. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mahmood Z and Shukla Y: Death receptors:
Targets for cancer therapy. Exp Cell Res. 316:887–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Varfolomeev EE, Schuchmann M, Luria V,
Chiannilkulchai N, Beckmann JS, Mett IL, Rebrikov D, Brodianski VM,
Kemper OC, Kollet O, et al: Targeted disruption of the mouse
Caspase 8 gene ablates cell death induction by the TNF receptors,
Fas/Apo1, and DR3 and is lethal prenatally. Immunity. 9:267–276.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sakamaki K, Inoue T, Asano M, Sudo K,
Kazama H, Sakagami J, Sakata S, Ozaki M, Nakamura S, Toyokuni S, et
al: Ex vivo whole-embryo culture of caspase-8-deficient embryos
normalize their aberrant phenotypes in the developing neural tube
and heart. Cell Death Differ. 9:1196–1206. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dubrez-Daloz L, Dupoux A and Cartier J:
IAPs: More than just inhibitors of apoptosis proteins. Cell Cycle.
7:1036–1046. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tanabe Y and Jessell TM: Diversity and
pattern in the developing spinal cord. Science. 274:1115–1123.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Smith JL and Schoenwolf GC: Neurulation:
Coming to closure. Trends Neurosci. 20:510–517. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Colas JF and Schoenwolf GC: Towards a
cellular and molecular understanding of neurulation. Dev Dyn.
221:117–145. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sherif ZA: Caspase activation and aberrant
cell growth in a p53(+/+) cell line from a Li-Fraumeni syndrome
family. Genet Res Int. 2015:7892012015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nicotera P: Development and death of
neurons: Sealed by a common fate? Cell Death Differ. 9:1277–1278.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hidalgo A and Ffrench-Constant C: The
control of cell number during central nervous system development in
flies and mice. Mech Dev. 120:1311–1325. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
De Zio D, Giunta L, Corvaro M, Ferraro E
and Cecconi F: Expanding roles of programmed cell death in
mammalian neurodevelopment. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 16:281–294. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Massa V, Savery D, Ybot-Gonzalez P,
Ferraro E, Rongvaux A, Cecconi F, Flavell R, Greene ND and Copp AJ:
Apoptosis is not required for mammalian neural tube closure. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:8233–8238. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Salvesen GS and Ashkenazi A: Snapshot:
Caspases. Cell. 147:476.e12011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Naruse I and Keino H: Apoptosis in the
developing CNS. Prog Neurobiol. 47:135–155. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kuida K, Haydar TF, Kuan CY, Gu Y, Taya C,
Karasuyama H, Su MS, Rakic P and Flavell RA: Reduced apoptosis and
cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation in mice lacking caspase 9.
Cell. 94:325–337. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kuida K, Zheng TS, Na S, Kuan C, Yang D,
Karasuyama H, Rakic P and Flavell RA: Decreased apoptosis in the
brain and premature lethality in CPP32-deficient mice. Nature.
384:368–372. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cecconi F, Alvarez-Bolado G, Meyer BI,
Roth KA and Gruss P: Apaf1 (CED-4 homolog) regulates programmed
cell death in mammalian development. Cell. 94:727–737. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hakem R, Hakem A, Duncan GS, Henderson JT,
Woo M, Soengas MS, Elia A, de la Pompa JL, Kagi D, Khoo W, et al:
Differential requirement for caspase 9 in apoptotic pathways in
vivo. Cell. 94:339–352. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rodriguez-Leon J, Merino R, Macias D,
Gañan Y, Santesteban E and Hurle JM: Retinoic acid regulates
programmed cell death through BMP signalling. Nat Cell Biol.
1:125–126. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Boutzen H, Saland E, Larrue C, de Toni F,
Gales L, Castelli FA, Cathebas M, Zaghdoudi S, Stuani L, Kaoma T,
et al: Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutations prime the all-trans
retinoic acid myeloid differentiation pathway in acute myeloid
leukemia. J Exp Med. 213:483–497. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Graham A, Francis-West P, Brickell P and
Lumsden A: The signalling molecule BMP4 mediates apoptosis in the
rhombencephalic neural crest. Nature. 372:684–686. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sulik KK and Dehart DB:
Retinoic-acid-induced limb malformations resulting from apical
ectodermal ridge cell death. Teratology. 37:527–537. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu WJ, Zhang T, Guo QL, Liu CY and Bai
YQ: Effect of ATRA on the expression of HOXA5 gene in K562 cells
and its relationship with cell cycle and apoptosis. Mol Med Rep.
13:4221–4228. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Holm KL, Indrevaer RL, Myklebust JH,
Kolstad A, Moskaug JØ, Naderi EH and Blomhoff HK: Myeloid cell
leukaemia 1 has a vital role in retinoic acid-mediated protection
of Toll-like receptor 9-stimulated B-cells from spontaneous and DNA
damage-induced apoptosis. Immunology. 149:62–73. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hnisz D, Abraham BJ, Lee TI, Lau A,
Saint-André V, Sigova AA, Hoke HA and Young RA: Super-enhancers in
the control of cell identity and disease. Cell. 155:934–947. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Creyghton MP, Cheng AW, Welstead GG,
Kooistra T, Carey BW, Steine EJ, Hanna J, Lodato MA, Frampton GM,
Sharp PA, et al: Histone H3K27ac separates active from poised
enhancers and predicts developmental state. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:21931–21936. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hayashi-Takanaka Y, Yamagata K, Wakayama
T, Stasevich TJ, Kainuma T, Tsurimoto T, Tachibana M, Shinkai Y,
Kurumizaka H, Nozaki N and Kimura H: Tracking epigenetic histone
modifications in single cells using Fab-based live endogenous
modification labeling. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:6475–6488. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|