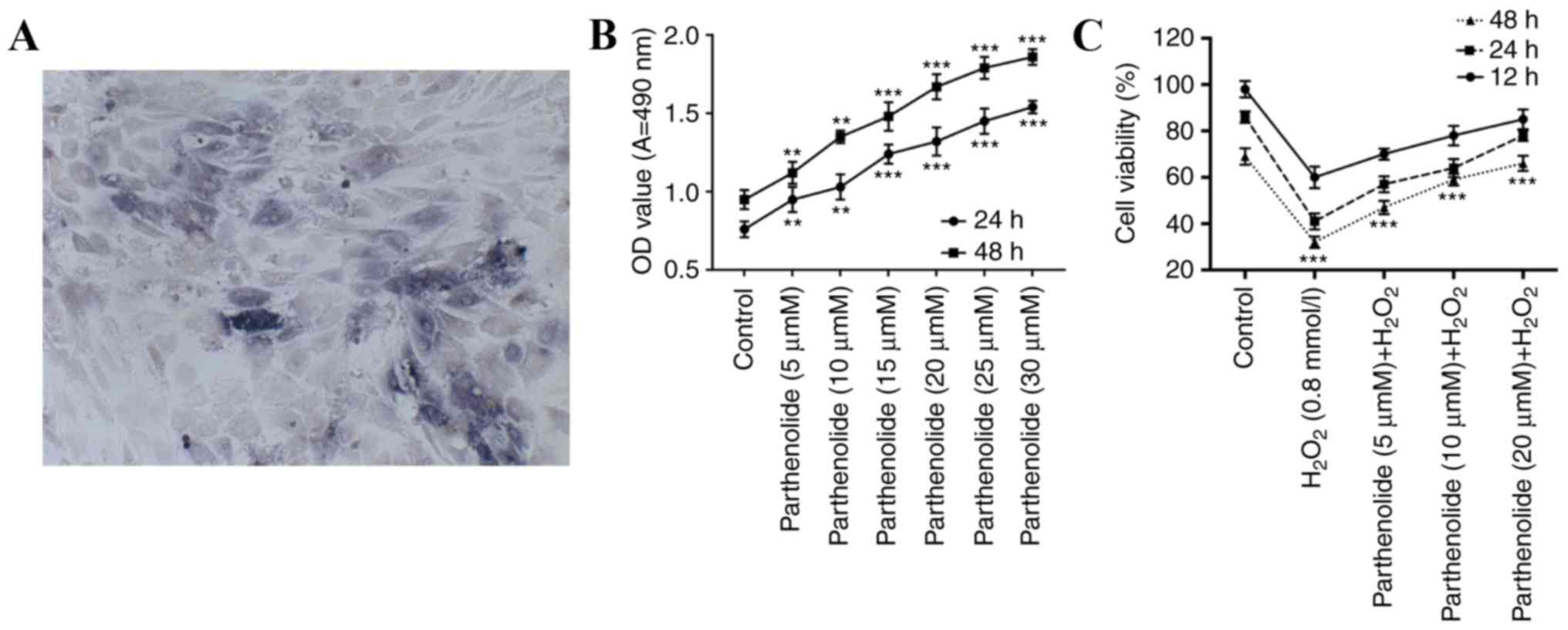
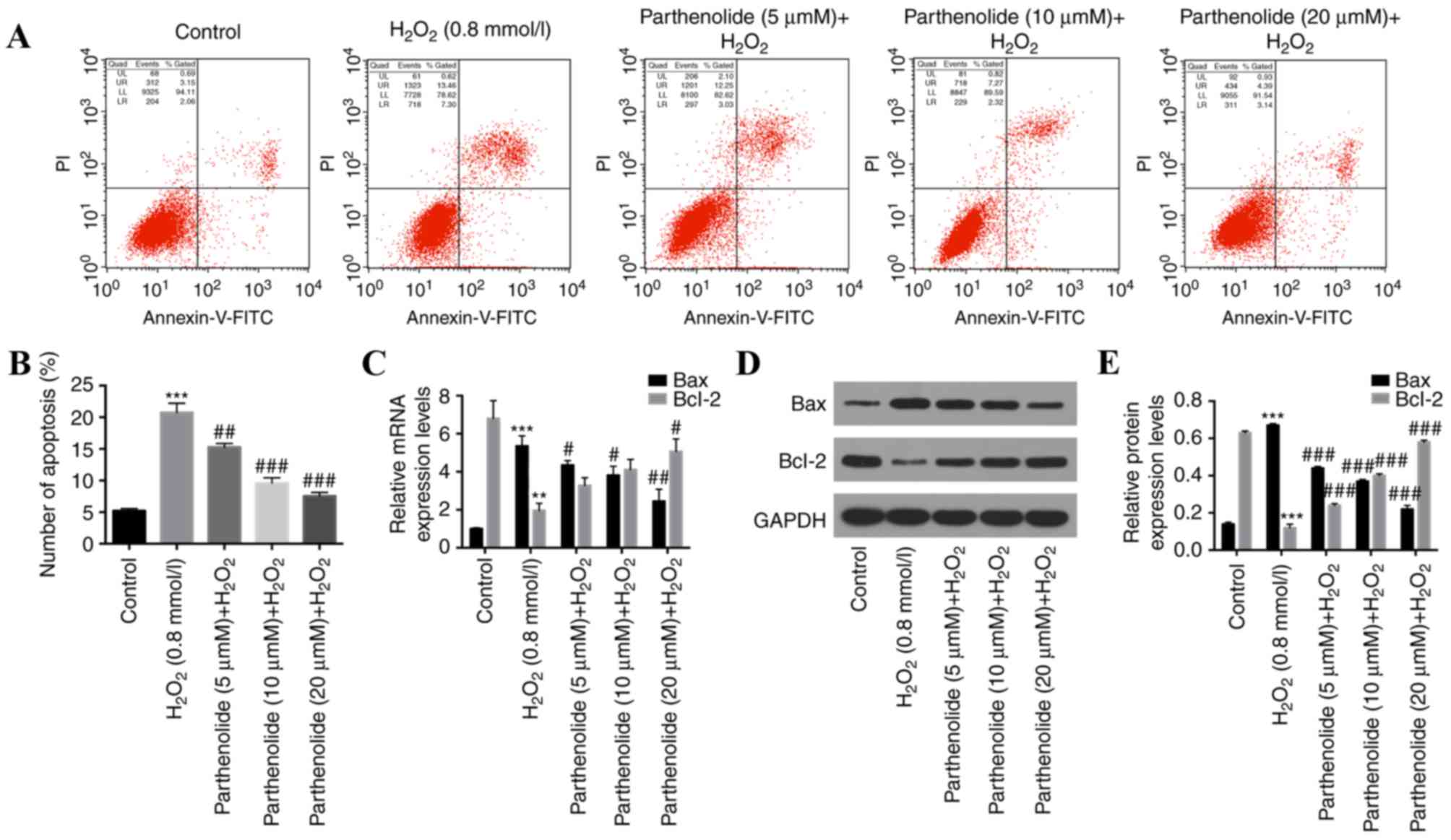
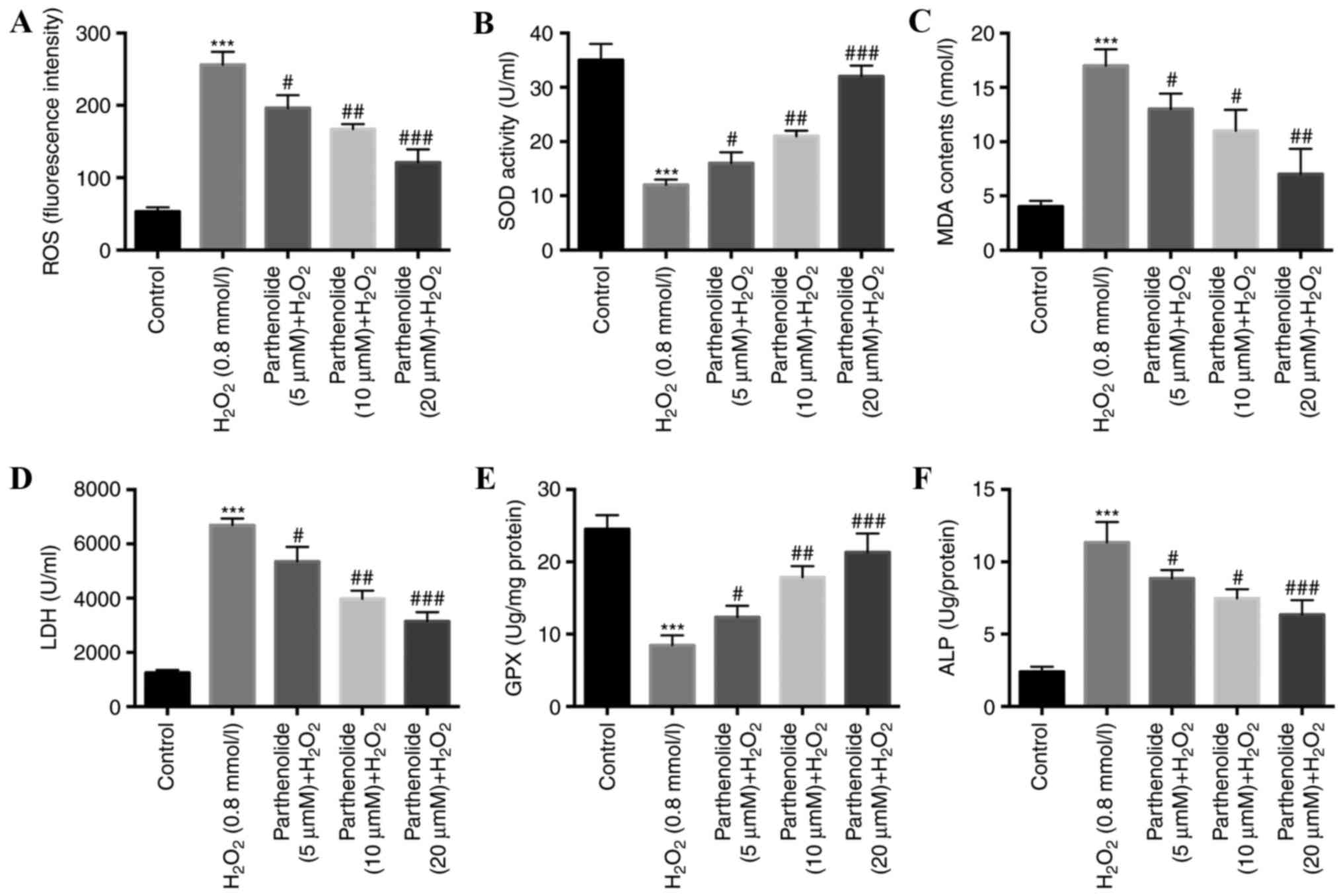
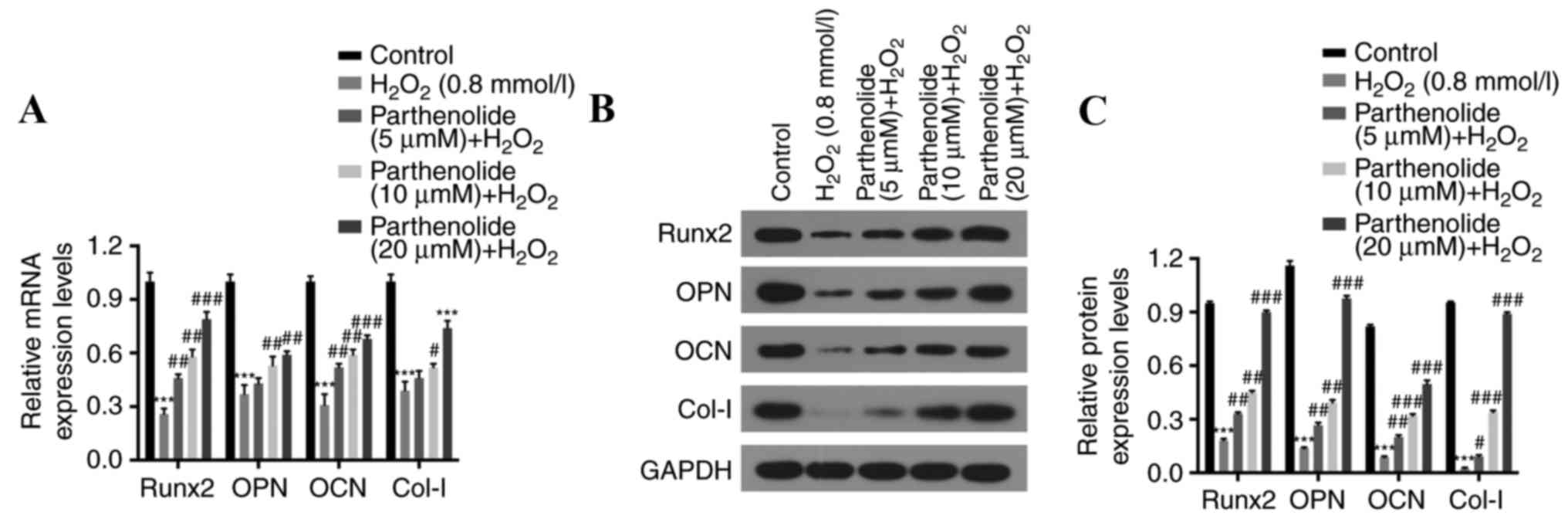
|
1
|
Marengoni A, Rizzuto D, Wang HX, Winblad B
and Fratiglioni L: Patterns of chronic multimorbidity in the
elderly population. J Am Geriatr Soc. 57:225–230. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carmeliet G, Dermauw V and Bouillon R:
Vitamin D signaling in calcium and bone homeostasis: A delicate
balance. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 29:621–631. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reid IR, Bristow SM and Bolland MJ:
Calcium supplements: Benefits and risks. J Int Med. 278:354–368.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ströhle A, Hadji P and Hahn A: Calcium and
bone health-goodbye, calcium supplements? Climacteric. 18:702–714.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Davidovich P, Kearney CJ and Martin SJ:
Inflammatory outcomes of apoptosis, necrosis and necroptosis. Biol
Chem. 395:1163–1171. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kamogashira T, Fujimoto C and Yamasoba T:
Reactive oxygen species, apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in
hearing loss. Biomed Res Int. 2015:6172072015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baek KH, Oh KW, Lee WY, Lee SS, Kim MK,
Kwon HS, Rhee EJ, Han JH, Song KH, Cha BY, et al: Association of
oxidative stress with postmenopausal osteoporosis and the effects
of hydrogen peroxide on osteoclast formation in human bone marrow
cell cultures. Calcif Tissue Int. 87:226–235. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mackinnon ES, Rao AV and Rao LG: Dietary
restriction of lycopene for a period of one month resulted in
significantly increased biomarkers of oxidative stress and bone
resorption in postmenopausal women. J Nutr Health Aging.
15:133–138. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Callaway DA and Jiang JX: Reactive oxygen
species and oxidative stress in osteoclastogenesis, skeletal aging
and bone diseases. J Bone Miner Metab. 33:359–370. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hamada Y, Fujii H and Fukagawa M: Role of
oxidative stress in diabetic bone disorder. Bone. 45 Suppl
1:S35–S38. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vela L, Contel M, Palomera L, Azaceta G
and Marzo I: Iminophosphorane-organogold (III) complexes induce
cell death through mitochondrial ROS production. J Inorg Biochem.
105:1306–1313. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
D'Amico E, Factor-Litvak P, Santella RM
and Mitsumoto H: Clinical perspective on oxidative stress in
sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Free Radic Biol Med.
65:509–527. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ling F, Niu R, Hatakeyama H, Goto Y,
Shibata T and Yoshida M: Reactive oxygen species stimulate
mitochondrial allele segregation toward homoplasmy in human cells.
Mol Biol Cell. 27:1684–1693. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Majid AS, Yin ZQ and Ji D: Sulphur
antioxidants inhibit oxidative stress induced retinal ganglion cell
death by scavenging reactive oxygen species but influence nuclear
factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 signalling pathway differently.
Biol Pharm Bull. 36:1095–1110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Romiszewska A and Nowak-Stępniowska A:
Photodynamic reaction and oxidative stress-influence of the
photodynamic effect on the activity antioxidant enzymes. Postepy
Biochemii. 60:355–364. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
She C, Zhu LQ, Zhen YF, Wang XD and Dong
QR: Activation of AMPK protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced
osteoblast apoptosis through autophagy induction and NADPH
maintenance: New implications for osteonecrosis treatment? Cell
Signal. 26:1–8. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Harachikuma M, Watanabe S and Satooka H:
Involvement of aquaporin-3 in epidermal growth factor receptor
signaling via H2O2 transport in cancer cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 471:603–609. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Holmström KM and Finkel T: Cellular
mechanisms and physiological consequences of redox-dependent
signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:411–421. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yue Q, Gao G, Zou G, Yu H and Zheng X:
Natural products as adjunctive treatment for pancreatic cancer:
Recent trends and advancements. Biomed Res Int. 2017:84125082017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun J, Zhang C, Bao YL, Wu Y, Chen ZL, Yu
CL, Huang YX, Sun Y, Zheng LH, Wang X and Li YX:
Parthenolide-induced apoptosis, autophagy and suppression of
proliferation in HepG2 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:4897–4902. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Uchibori R, Tsukahara T, Ohmine K and
Ozawa K: Cancer gene therapy using mesenchymal stem cells. Int J
Hematol. 99:377–382. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou J, Zhang H, Gu P, Bai J, Margolick JB
and Zhang Y: NF-kappaB pathway inhibitors preferentially inhibit
breast cancer stem-like cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
111:419–427. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Diamanti P, Cox CV, Moppett JP and Blair
A: Parthenolide eliminates leukemia-initiating cell populations and
improves survival in xenografts of childhood acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Blood. 121:1384–1393. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Al Fatlawi AA, Al-Fatlawi AA, Irshad M,
Rahisuddin and Ahmad A: Effect of parthenolide on growth and
apoptosis regulatory genes of human cancer cell lines. Pharm Biol.
53:104–109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sang WK, Park ES and Lee CS: Parthenolide
induces apoptosis by activating the mitochondrial and death
receptor pathways and inhibits FAK-mediated cell invasion. Mol Cell
Biochem. 385:133–144. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shen Y, Guo W, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Zhong L
and Zhu Y: Protective Effects of hydrogen sulfide in hypoxic human
umbilical vein endothelial cells: A possible mitochondria-dependent
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 14:13093–13108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mccord JM and Fridovich I: Superoxide
dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J
Biol Chem. 244:6049–6055. 1969.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cabaud PG and Wroblewski F: Colorimetric
measurement of lactic dehydrogenase activity of body fluids. Am J
Clin Pathol. 30:234–236. 1958. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maseko T, Howell K, Dunshea FR and Ng K:
Selenium-enriched Agaricus bisporus increases expression and
activity of glutathione peroxidase-1 and expression of glutathione
peroxidase-2 in rat colon. Food Chem. 146:327–333. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Can M, Guven B, Bektas S and Arikan I:
Oxidative stress and apoptosis in preeclampsia. Tissue Cell.
46:477–481. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jain S, Webster TJ, Sharma A and Basu B:
Intracellular reactive oxidative stress, cell proliferation and
apoptosis of Schwann cells on carbon nanofibrous substrates.
Biomaterials. 34:4891–4901. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vaz CV, Marques R, Maia CJ and Socorro S:
Aging-associated changes in oxidative stress, cell proliferation
and apoptosis are prevented in the prostate of transgenic rats
overexpressing regucalcin. Transl Res. 166:693–705. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yen YH, Farooqi AA, Li KT, Butt G, Tang
JY, Wu CY, Cheng YB, Hou MF and Chang HW: Methanolic extracts of
solieria robusta inhibits proliferation of oral cancer ca9-22 cells
via apoptosis and oxidative stress. Molecules. 19:18721–18732.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Simon HU, Hajyehia A and Levischaffer F:
Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction.
Apoptosis. 5:415–418. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yee C, Yang W and Hekimi S: The intrinsic
apoptosis pathway mediates the pro-longevity response to
mitochondrial ROS in C. elegans. Cell. 157:8972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sharma SS and Dietz KJ: The relationship
between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant
Sci. 14:43–50. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sivaramakrishnan V, Shilpa PN, Kumar VR
and Devaraj SN: Attenuation of N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced
hepatocellular carcinogenesis by a novel flavonol-Morin. Chem Biol
Interact. 171:79–88. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang Z, Feng Z, Wu G, Bai S, Yan D and
Zhao Y: In vitro studies on human periodontal ligament stem cell
sheets enhanced by enamel matrix derivative. Colloids Surf B
Biointerfaces. 141:102–111. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rosen CJ and Bouxsein ML: Mechanisms of
Disease: is osteoporosis the obesity of bone? Nat Clin Pract
Rheumatol. 2:35–43. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xie G, Schepetkin IA and Quinn MT:
Immunomodulatory activity of acidic polysaccharides isolated from
Tanacetum vulgare L. Int Immunopharmacol. 7:1639–1650. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tiuman TS, Uedanakamura T, DA Cortez
Garcia, Filho Dias BP, Morgado-Díaz JA, de Souza W and Nakamura CV:
Antileishmanial activity of parthenolide, a sesquiterpene lactone
isolated from tanacetum parthenium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
49:176–182. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mathema VB, Koh YS, Thakuri BC and
Sillanpää M: Parthenolide, a sesquiterpene lactone, expresses
multiple anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activities.
Inflammation. 35:560–565. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Valko M, Morris H and Cronin MT: Metals,
toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem. 12:1161–1208. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM and Samali
A: Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.
EMBO Rep. 7:880–885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Manna SK, Sarkar S, Barr J, Wise K,
Barrera EV, Jejelowo O, Rice-Ficht AC and Ramesh GT: Single-walled
carbon nanotube induces oxidative stress and activates nuclear
transcription factor-κB in human keratinocytes. Nano Lett.
5:1676–1684. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Manolagas SC: From estrogen-centric to
aging and oxidative stress: A revised perspective of the
pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 31:266–300. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Doshi SB and Agarwal A: The role of
oxidative stress in menopause. J Midlife Health. 4:140–146.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kim Y, You Y, Yoon HG, Lee YH, Kim K, Lee
J, Kim MS, Kim JC and Jun W: Hepatoprotective effects of fermented
Curcuma longa L. on carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative stress
in rats. Food Chem. 151:148–153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pajak B, Gajkowska B and Orzechowski A:
Molecular basis of parthenolide-dependent proapoptotic activity in
cancer cells. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 46:129–135. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wyrębska A, Gach K and Janecka A: Combined
effect of parthenolide and various anti-cancer drugs or anticancer
candidate substances on malignant cells in vitro and in vivo. Mini
Rev Med Chem. 14:222–228. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kim JH, Liu L, Lee SO, Kim YT, You KR and
Kim DG: Susceptibility of cholangiocarcinoma cells to
parthenolide-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 65:6312–6320. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fang LJ, Shao XT, Wang S, Lu GH, Tao X and
Zhou JY: Sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide markedly enhances
sensitivity of human A549 cells to low-dose oxaliplatin via
inhibition of NF-κB activation and induction of apoptosis. Planta
Med. 76:258–264. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kim SL, Liu YC, Park YR, Seo SY, Kim SH,
Kim IH, Lee SO, Lee ST, Kim DG and Kim SW: Parthenolide enhances
sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to TRAIL by inducing death
receptor 5 and promotes TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Int J Oncol.
46:1121–1130. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Michaeloudes C, Mercado N, Clarke C,
Bhavsar PK, Adcock IM, Barnes PJ and Chung KF: Bromodomain and
extraterminal proteins suppress NF-E2-related factor 2-mediated
antioxidant gene expression. J Immunol. 192:4913–4920. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Paul MK, Bisht B, Darmawan DO, Chiou R, Ha
VL, Wallace WD, Chon AT, Hegab AE, Grogan T, Elashoff DA, et al:
Dynamic changes in intracellular ROS levels regulate airway basal
stem cell homeostasis through Nrf2-dependent Notch signaling. Cell
Stem Cell. 15:199–214. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ma Q: Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and
toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 53:401–426. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|