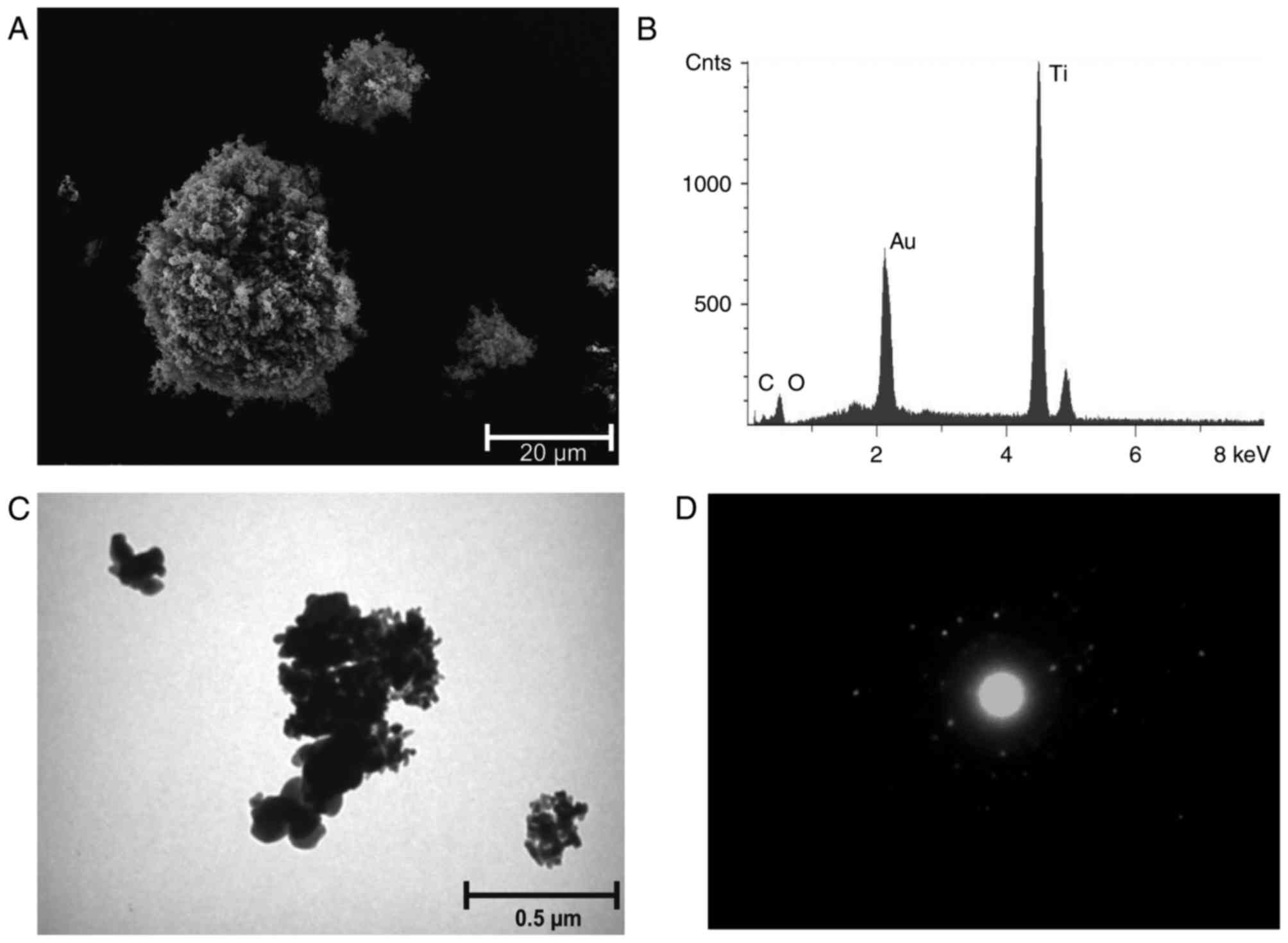
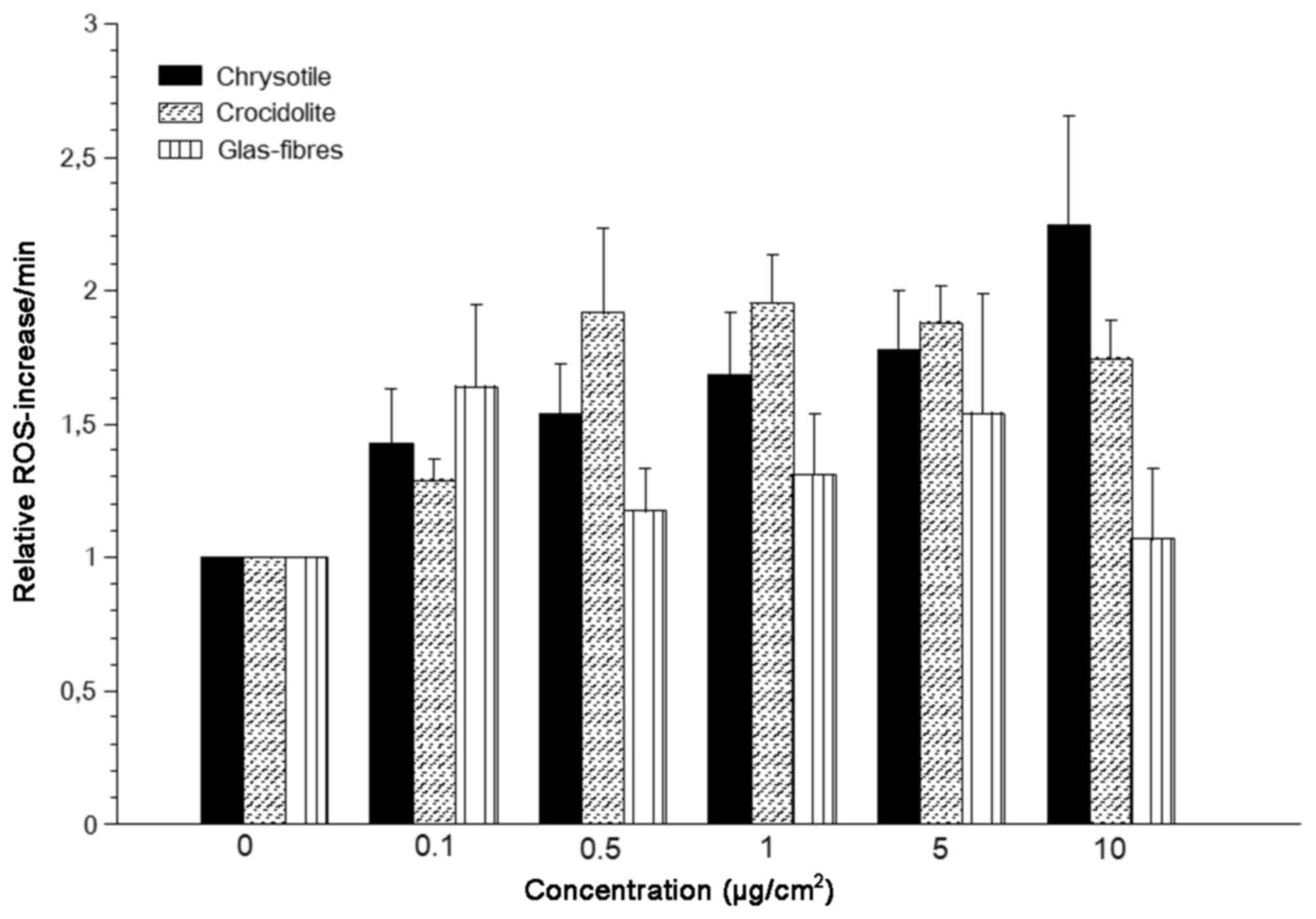
|
1
|
Roesslein M, Hirsch C, Kaiser JP, Krug HF
and Wick P: Comparability of in vitro tests for bioactive
nanoparticles: A common assay to detect reactive oxygen species as
an example. Int J Mol Sci. 14:24320–24337. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Held P: An Introduction to Reactive Oxygen
Species. Measurement of ROS in CellsWhite Paper. BioTek
Instruments, Inc.; Winooski, VT: 2015
|
|
3
|
Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L and Li N: Toxic
potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science. 311:622–627.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu Y, Rahlfs S, Mersch-Sundermann V and
Becker K: Resveratrol modulates mRNA transcripts of genes related
to redox metabolism and cell proliferation in non-small-cell lung
carcinoma cells. Biol Chem. 388:207–219. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu J and Holmgren A: The thioredoxin
antioxidant system. Free Radic Biol Med. 66:75–87. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Becker K, Gromer S, Schirmer RH and Müller
S: Thioredoxin reductase as a pathophysiological factor and drug
target. Eur J Biochem. 267:6118–6125. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xiao GG, Wang M, Li N, Loo JA and Nel AE:
Use of proteomics to demonstrate a hierarchical oxidative stress
response to diesel exhaust particle chemicals in a macrophage cell
line. J Biol Chem. 278:50781–50790. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Oberdörster G, Oberdörster E and
Oberdörster J: Nanotoxicology: An emerging discipline evolving from
studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect.
113:823–839. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Phaniendra A, Jestadi DB and Periyasamy L:
Free radicals: Properties, sources, targets, and their implication
in various diseases. Indian J Clin Biochem. 30:11–26. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Murphy MP, Holmgren A, Larsson NG,
Halliwell B, Chang CJ, Kalyanaraman B, Rhee SG, Thornalley PJ,
Partridge L, Gems D, et al: Unraveling the biological roles of
reactive oxygen species. Cell Metab. 13:361–366. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Federico A, Morgillo F, Tuccillo C,
Ciardiello F and Loguercio C: Chronic inflammation and oxidative
stress in human carcinogenesis. Int J Cancer. 121:2381–2386. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rapisarda V, Loreto C, Ledda C, Musumeci
G, Bracci M, Santarelli L, Renis M, Ferrante M and Cardile V:
Cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and genotoxicity induced by glass
fibers on human alveolar epithelial cell line A549. Toxicol In
Vitro. 29:551–557. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Knaapen AM, Borm PJ, Albrecht C and Schins
RP: Inhaled particles and lung cancer. Part A: Mechanisms. Int J
Cancer. 109:799–809. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
DFG: List of MAK and BAT valuesList of MAK
and BAT Values 2016: Permanent Senate Commission for the
Investigation of Health Hazards of Chemical Compounds in the Work
Area. Report No. 52. Wiley-VCH; Weinheim: 2016
|
|
15
|
Walter D: Primary
particles-Agglomerates-Aggregates. In: NanomaterialsDeutsche
Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) (ed). Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.
KGaA.; Weinheim: pp. 9–24. 2013
|
|
16
|
Stone V, Johnston H and Clift MJ: Air
pollution, ultrafine and nanoparticle toxicology: Cellular and
molecular interactions. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 6:331–340. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oberdörster G: Pulmonary effects of
inhaled ultrafine particles. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 74:1–8.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mossman BT and Churg A: Mechanisms in the
pathogenesis of asbestosis and silicosis. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 157:1666–1680. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kamp DW: Asbestos-induced lung diseases:
An update. Transl Res. 153:143–152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shukla A, MacPherson MB, Hillegass J,
Ramos-Nino ME, Alexeeva V, Vacek PM, Bond JP, Pass HI, Steele C and
Mossman BT: Alterations in gene expression in human mesothelial
cells correlate with mineral pathogenicity. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 41:114–123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Robledo R and Mossman B: Cellular and
molecular mechanisms of asbestos-induced fibrosis. J Cell Physiol.
180:158–166. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lemaire I and Ouellet S: Distinctive
profile of alveolar macrophage-derived cytokine release induced by
fibrogenic and nonfibrogenic mineral dusts. J Toxicol Environ
Health. 47:465–478. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kamp DW and Weitzman SA: The molecular
basis of asbestos induced lung injury. Thorax. 54:638–652. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Riedel E: Allgemeine und Anorganische
Chemie. Walter de Gruyter; Berlin, New York: 1999
|
|
25
|
Wang J and Fan Y: Lung injury induced by
TiO2 nanoparticles depends on their structural features: Size,
shape, crystal phases, and surface coating. Int J Mol Sci.
15:22258–22278. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liochev SL: The role of iron-sulfur
clusters in in vivo hydroxyl radical production. Free Radic Res.
25:369–384. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liochev SI and Fridovich I: The relative
importance of HO* and ONOO-in mediating the toxicity of O*-. Free
Radic Biol Med. 26:777–778. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liochev SI and Fridovich I: The
Haber-Weiss cycle-70 years later: An alternative view. Redox Rep.
7(55–57): 59–60. 2002.
|
|
29
|
Schneider J, Walter D, Brückel B and
Rödelsperger K: Primary particles and their agglomerate formation
as modifying risk factors of nonfibrous nanosized dust. J Toxicol
Environ Health A. 76:131–141. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Helmig S, Dopp E, Wenzel S, Walter D and
Schneider J: Induction of altered mRNA expression profiles caused
by fibrous and granular dust. Mol Med Rep. 9:217–228. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Walter D: Characterization of synthetic
hydrous hematite pigments. Thermochimica Acta. 445:195–199. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Rhodes JM: Introduction to Patricle
Technology. 2nd edition. John Wiley & Sons Ltd.; Chichester:
2008, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Helmig S, Hadzaad B, Döhrel J and
Schneider J: Relative quantification of Cytochrome P450 1B1 gene
expression in peripheral leukocytes using lightcycler. Cancer
Genomics Proteomics. 6:13–17. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rödelsperger K, Brückel B, Podhorsky S and
Schneider J: Charakterisierung von ultrafeinen Partikeln für den
Arbeitsschutz-Teil 2. Bundesanstalt für Arbeitsschutz und
Arbeitsmedizin, Dortmund/Berlin/Dresden. 2009.https://www.baua.de/DE/Angebote/Publikationen/Berichte/F2075.pdf?__blob=publicationFile
|
|
36
|
Simon-Deckers A, Gouget B, Mayne-L'hermite
M, Herlin-Boime N, Reynaud C and Carrière M: In vitro investigation
of oxide nanoparticle and carbon nanotube toxicity and
intracellular accumulation in A549 human pneumocytes. Toxicology.
253:137–146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiang J, Oberdörster G, Elder A, Gelein R,
Mercer P and Biswas P: Does nanoparticle activity depend upon size
and crystal phase? Nanotoxicology. 2:33–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ertl G and Knözinger H: Handbook of
Heterogeneous Catalysis. Wiley-VCH; Weinheim: 1997, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sayes CM, Wahi R, Kurian PA, et al:
Correlating nanoscale titania structure with toxicity: a
cytotoxicity and inflammatory response study with human dermal
fibroblasts and human lung epithelial cells. Toxicol Sci.
92:174–185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Khan MI, Mohammad A, Patil G, Naqvi SA,
Chauhan LK and Ahmad I: Induction of ROS, mitochondrial damage and
autophagy in lung epithelial cancer cells by iron oxide
nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 33:1477–1488. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wottrich R, Diabaté S and Krug HF:
Biological effects of ultrafine model particles in human
macrophages and epithelial cells in mono- and co-culture. Int J Hyg
Environ Health. 207:353–361. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Freyria FS, Bonelli B, Tomatis M, et al:
Hematite nanoparticles larger than 90 nm show no sign of toxicity
in terms of lactate dehydrogenase release, nitric oxide generation,
apoptosis, and comet assay in murine alveolar macrophages and human
lung epithelial cells. Chem Res Toxicol. 25:850–861. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Karlsson HL, Cronholm P, Gustafsson J and
Moller L: Copper oxide nanoparticles are highly toxic: a comparison
between metal oxide nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. Chem Res
Toxicol. 21:1726–1732. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Herzog E, Byrne HJ, Davoren M, Casey A,
Duschl A and Oostingh GJ: Dispersion medium modulates oxidative
stress response of human lung epithelial cells upon exposure to
carbon nanomaterial samples. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 236:276–281.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Baldys A, Pande P, Mosleh T, Park SH and
Aust AE: Apoptosis induced by crocidolite asbestos in human lung
epithelial cells involves inactivation of Akt and MAPK pathways.
Apoptosis. 12:433–447. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Otsuki T, Maeda M, Murakami S, Hayashi H,
Miura Y, Kusaka M, Nakano T, Fukuoka K, Kishimoto T, Hyodoh F, et
al: Immunological effects of silica and asbestos. Cell Mol Immunol.
4:261–268. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zelko IN, Mariani TJ and Folz RJ:
Superoxide dismutase multigene family: A comparison of the CuZn-SOD
(SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures,
evolution, and expression. Free Radic Biol Med. 33:337–349. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Eckelman BP, Salvesen GS and Scott FL:
Human inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: Why XIAP is the black sheep
of the family. EMBO Rep. 7:988–994. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Caballero-López MJ, Nieto-Diaz M, Yunta M,
Reigada D, Muñoz-Galdeano T, Del Águila Á, Navarro-Ruíz R,
Pita-Thomas W, Lindholm D and Maza RM: XIAP interacts with and
regulates the activity of FAF1. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1864:1335–1348. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|