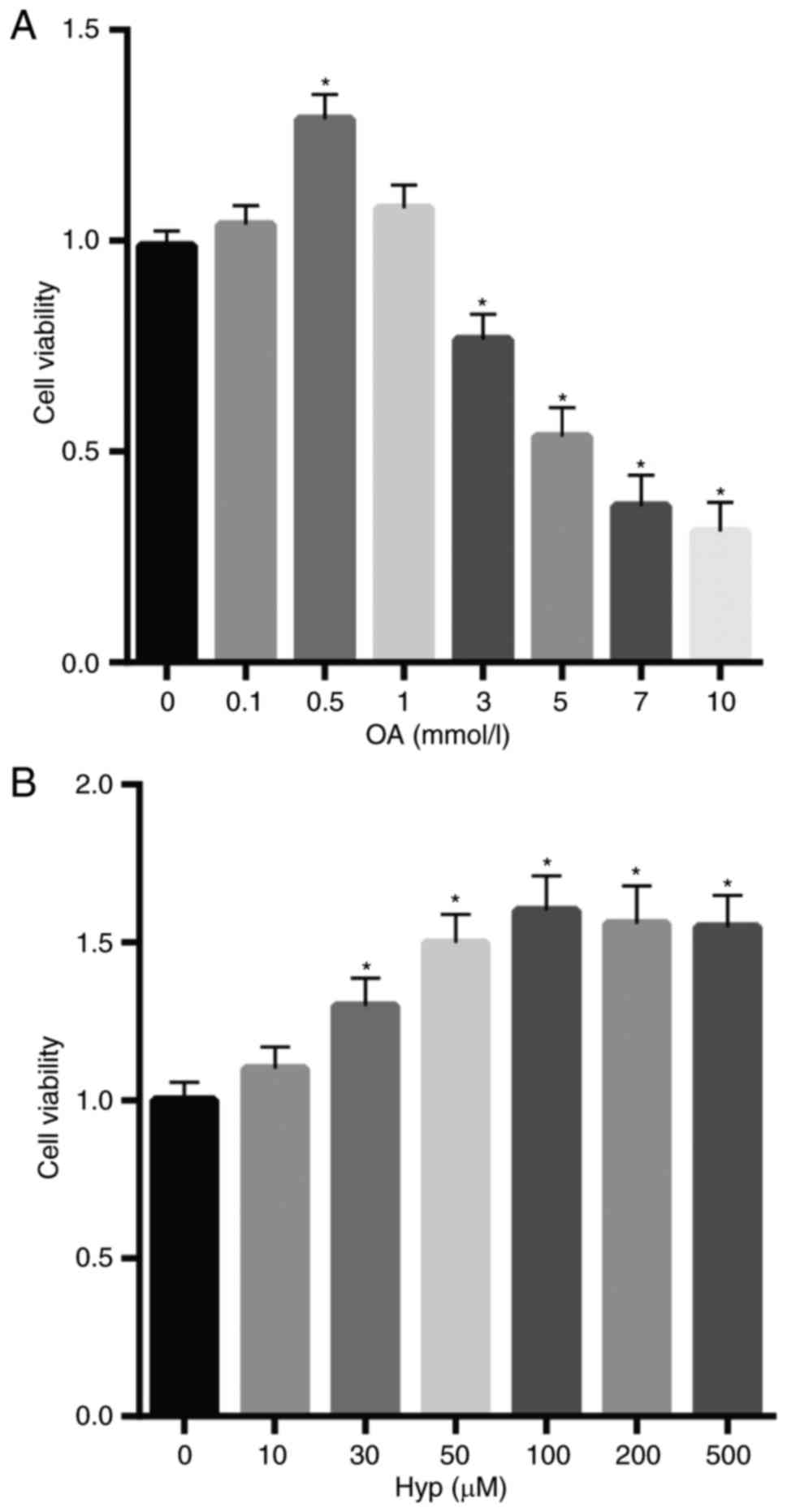
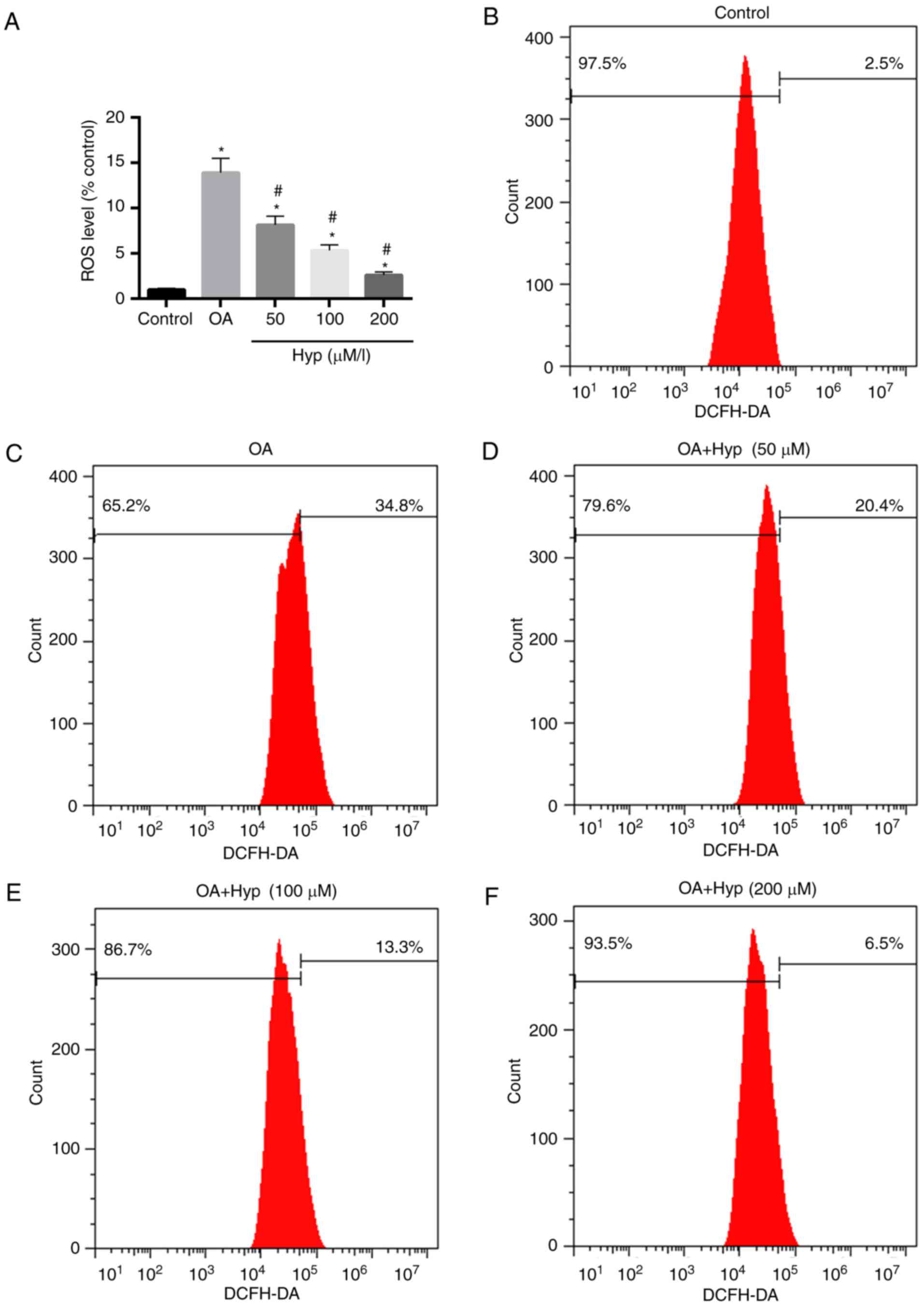
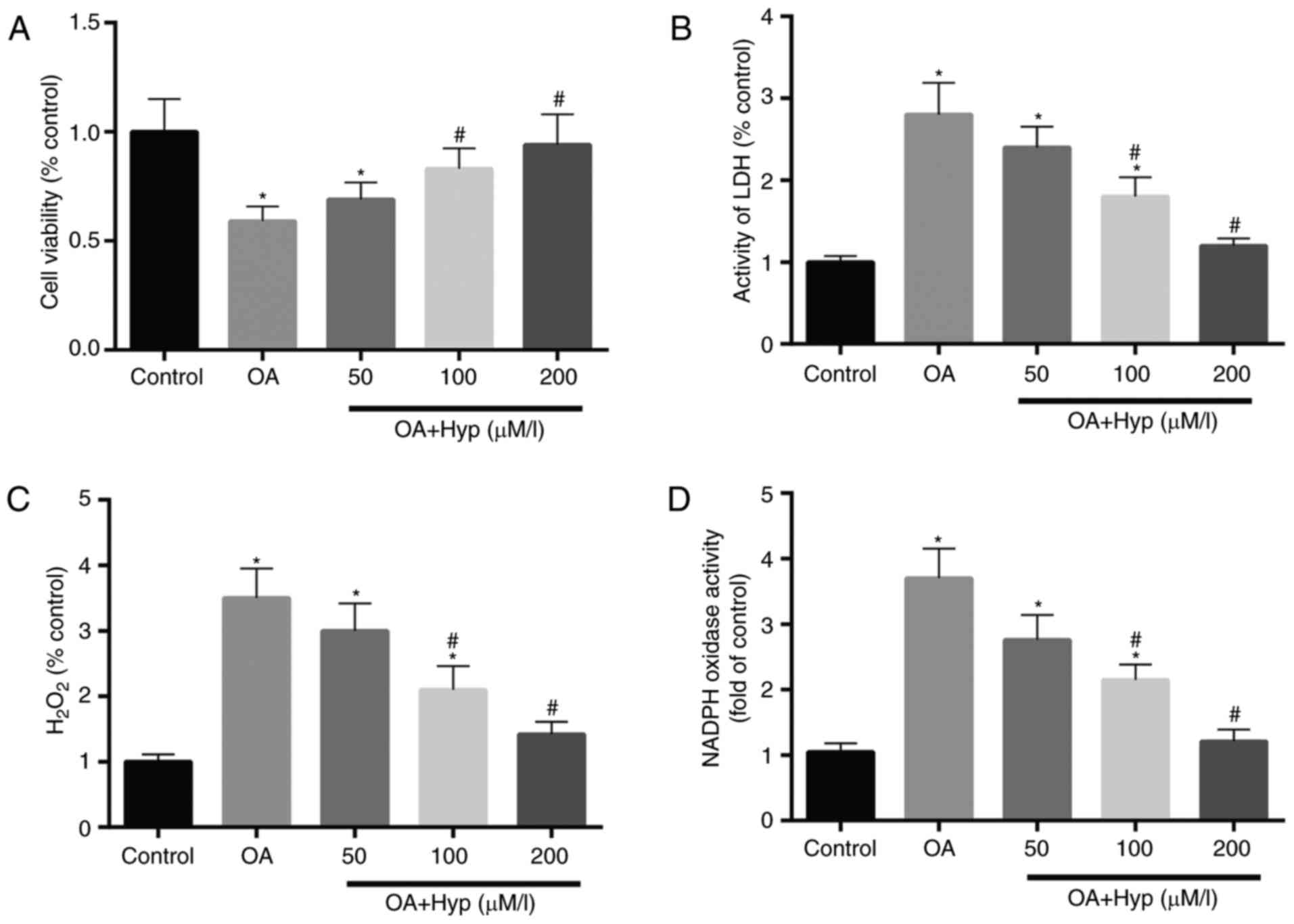
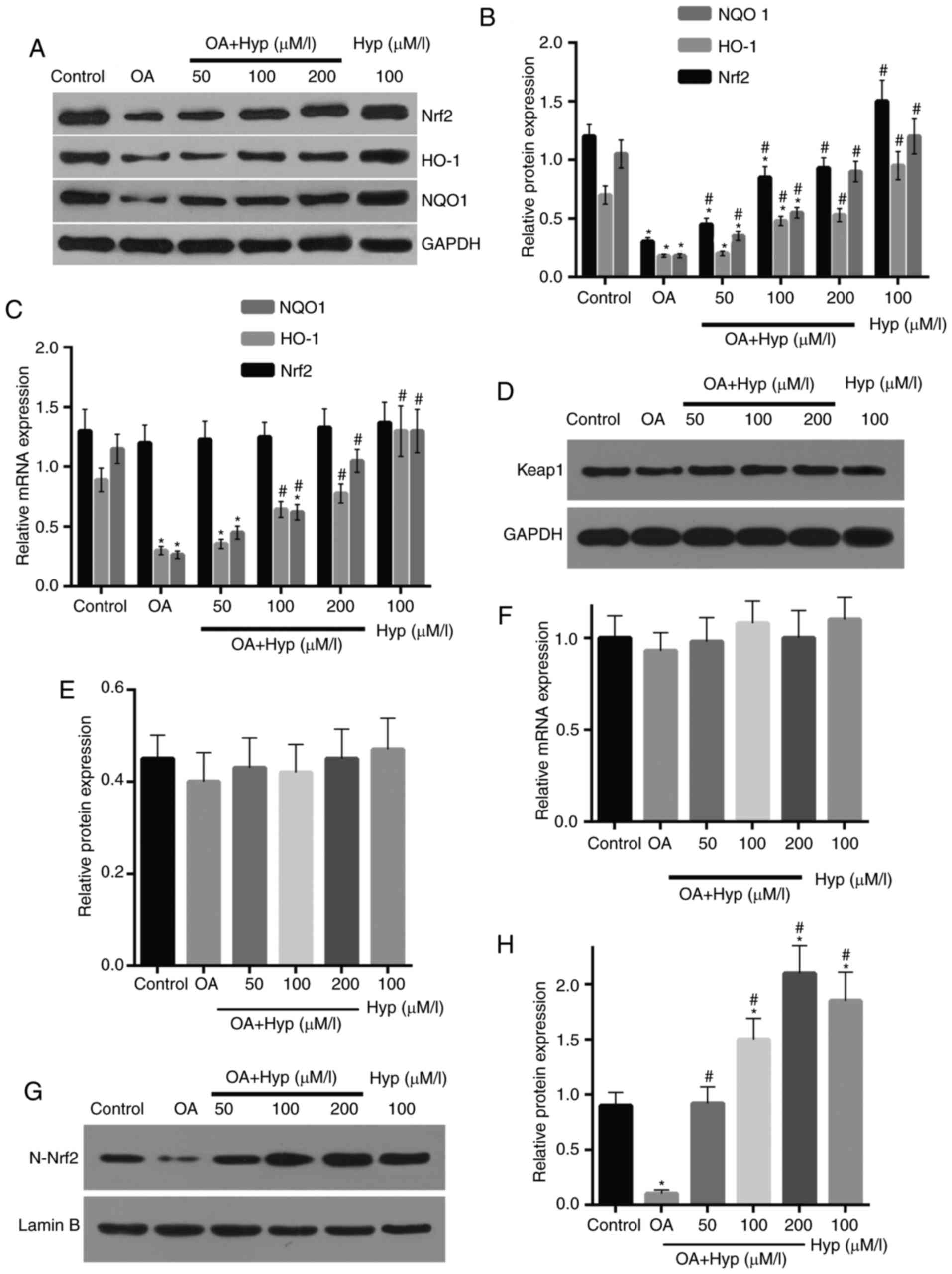
|
1
|
Merchant ML, Cummins TD, Wilkey DW, Salyer
SA, Powell DW, Klein JB and Lederer ED: Proteomic analysis of renal
calculi indicates an important role for inflammatory processes in
calcium stone formation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
295:F1254–F1258. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chauhan Prachi N, Kumar D and Kasana MS:
Medicinal plants of Muzaffarnagar district used in treatment of
urinary tract and kidney stones. Indian J Traditional Knowledge.
8:191–195. 2009.
|
|
3
|
Cervellin G, Comelli I, Comelli D, Meschi
T, Lippi G and Borghi L: Mean temperature and humidity variations,
along with patient age, predict the number of visits for renal
colic in a large urban Emergency Department: Results of a 9-year
survey. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2:31–38. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sorensen MD, Hsi RS, Chi T, Shara N,
Wactawski-Wende J, Kahn AJ, Wang H, Hou L and Stoller ML: Women's
Health Initiative Writing Group: Dietary intake of fiber, fruit,
and vegetables decrease the risk of incident kidney stones in
women: A Women's health initiative (WHI) report. J Urol.
192:1694–1699. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abdi R, Bagley J, Bonventre JV, Brenner
BM, Carpenter CB, Chandraker A, Charytan DM, Christopher KB, Curhan
GC, Denker BM, et al: Diagnosis and Management of Stone Disease.
Nephrology Rounds. 4:2006.
|
|
6
|
Hirose M, Yasui T, Okada A, Hamamoto S,
Shimizu H, Itoh Y, Tozawa K and Kohri K: Renal tubular epithelial
cell injury and oxidative stress induce calcium oxalate crystal
formation in mouse kidney. Int J Urol. 17:83–92. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mckiernan SH, Tuen VC, Baldwin K, Wanagat
J, Djamali A and Aiken JM: Adult-onset calorie restriction delays
the accumulation of mitochondrial enzyme abnormalities in aging rat
kidney tubular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
292:F1751–F1750. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Korolczuk A, Maciejewski M, Czechowska G
Md Phd and Orzeł-Pankowska M: Ultrastructural examination of renal
tubular epithelial cells and hepatocytes in the course of chronic
cyclosporin A treatment-a possible link to oxidative stress.
Ultrastruct Pathol. 37:332–339. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tikoo K, Lau SS and Monks TJ: Histone H3
phosphorylation is coupled to poly-(ADP-ribosylation) during
reactive oxygen species-induced cell death in renal proximal
tubular epithelial cells. Mol Pharmacol. 60:394–402. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sidle EH, Casselman R and Smith GN: Effect
of cigarette smoke on placental antioxidant enzyme expression. Am J
Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 293:R754–R758. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bhakkiyalakshmi E, Shalini D, Sekar TV,
Rajaguru P, Paulmurugan R and Ramkumar KM: Therapeutic potential of
pterostilbene against pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis through Nrf2
mechanism. Br J Pharmacol. 171:1747–1757. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gurjit KB, Inderpal SS, Saini NK, Puar Sk,
Singh G and Bhatti JS: Ameliorative role of melatonin against
cypermethrin induced hepatotoxicity and impaired antioxidant
defense system in Wistar rats. Iosrjournals Org. 8:39–48. 2014.
|
|
13
|
Fujisawa S, Atsumi T, Ishihara M and
Kadoma Y: Cytotoxicity, ROS-generation activity and
radical-scavenging activity of curcumin and related compounds.
Anticancer Res. 24:563–569. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang L, Lv Y, Yao H, Yin L and Shang J:
Curcumin prevents the non-alcoholic fatty hepatitis via
mitochondria protection and apoptosis reduction. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:11503–11509. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miriyala S, Holley AK and St Clair DK:
Mitochondrial superoxide dismutase-signals of distinction.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 11:181–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim SM, Kim YG, Jeong KH, Lee SH, Lee TW,
Ihm CG and Moon JY: Angiotensin II-induced mitochondrial Nox4 is a
major endogenous source of oxidative stress in kidney tubular
cells. PLoS One. 7:e397392012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zsom M, Fülöp T, Zsom L, Baráth A, Maróti
Z and Endreffy E: Genetic polymorphisms and the risk of progressive
renal failure in elderly Hungarian patients. Hemodial Int.
15:501–508. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hiatt RA, Ettinger B, Caan B, Quesenberry
CP Jr, Duncan D and Citron JT: Randomized controlled trial of a low
animal protein, high fiber diet in the prevention of recurrent
calcium oxalate kidney stones. Am J Epidemiol. 144:25–33. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bahmani M, Baharvand-Ahmadi B, Tajeddini
P, Rafieian-Kopaei M and Naghdi N: Identification of medicinal
plants for the treatment of kidney and urinary stones. J Renal Inj
Prev. 5:129–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sharma N, Tanwer BS and Vijayvergia R:
Study of medicinal plants in Aravali regions of Rajasthan for
treatment of Kidney stone and Urinary tract troubles. Int J
PharmTech Res. 3:110–113. 2011.
|
|
21
|
Ji YP, Xia H, Mei JP, Oh MC, Fernando PM,
Kang KA, Ryu YS, Jung U, Kim IG and Hyun JW: Hyperoside Induces
Endogenous Antioxidant System to Alleviate Oxidative Stress. J
Cancer Prev. 21:41–47. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kruse ML, Friedrich M, Arlt A, Röcken C,
Egberts JH, Sebens S and Schäfer H: Colonic Lamina propria
inflammatory cells from patients with IBD induce the nuclear
Factor-E2 related Factor-2 thereby leading to greater proteasome
activity and apoptosis protection in human colonocytes. Inflamm
Bowel Dis. 22:2593–2606. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Park HR and Loch-Caruso R: Protective
effect of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 on inflammatory
cytokine response to brominated diphenyl ether-47 in the
HTR-8/SVneo human first trimester extravillous trophoblast cell
line. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 281:67–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee Y, Shin JM, Jang S, Choi DK, Seo MS,
Kim HR, Sohn KC, Im M, Seo YJ, Lee JH and Kim CD: Role of nuclear
factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) in epidermal differentiation.
Arch Dermatol Res. 306:677–682. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McMahon M, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Chanas SA,
Henderson CJ, McLellan LI, Wolf CR, Cavin C and Hayes JD: The
Cap'n'Collar basic leucine zipper transcription factor Nrf2 (NF-E2
p45-related factor 2) controls both constitutive and inducible
expression of intestinal detoxification and glutathione
biosynthetic enzymes. Cancer Res. 61:3299–3307. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li W, Yu S, Liu T, Kim JH, Blank V, Li H
and Kong AN: Heterodimerization with small Maf proteins enhances
nuclear retention of Nrf2 via masking the NESzip motif. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1783:1847–1856. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cho HY, Reddy SP and Kleeberger SR: Nrf2
defends the lung from oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal.
8:76–87. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pokkunuri ID, Chugh G and Asghar M: Human
kidney-2 cells harbor functional dopamine D1 receptors that require
Giα for Gq/11α signaling. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
305:F560–F567. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Umekawa T, Byer K, Uemura H and Khan SR:
Diphenyleneiodium (DPI) reduces oxalate ion- and calcium oxalate
monohydrate and brushite crystal-induced upregulation of MCP-1 in
NRK 52E cells. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 20:870–878. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xing HY, Liu Y, Chen JH, Sun FJ, Shi HQ
and Xia PY: Hyperoside attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced L02
cell damage via MAPK-dependent Keap1-Nrf2-ARE
signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 410:759–765. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Panopoulos A, Harraz M, Engelhardt JF and
Zandi E: Iron-mediated H2O2 production as a mechanism for cell
type-specific inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced but
not interleukin-1beta-induced IkappaB kinase complex/nuclear
factor-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem. 280:2912–2923. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sun L, Li W, Li W, Xiong L, Li G and Ma R:
Astragaloside IV prevents damage to human mesangial cells through
the inhibition of the NADPH oxidase/ROS/Akt/NF-κB pathway under
high glucose conditions. Int J Mol Med. 34:167–176. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang L, Yue Z, Guo M, Fang L, Bai L, Li X,
Tao Y, Wang S, Liu Q, Zhi D and Zhao H: Dietary flavonoid
hyperoside induces apoptosis of activated human LX-2 hepatic
stellate cell by suppressing canonical NF-κB signaling. Biomed Res
Int. 2016:10685282016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Piao MJ, Kang KA, Zhang R, Ko DO, Wang ZH,
You HJ, Kim HS, Kim JS, Kang SS and Hyun JW: Hyperoside prevents
oxidative damage induced by hydrogen peroxide in lung fibroblast
cells via an antioxidant effect. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1780:1448–1457. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang FQ, Liu M, Li W, Che JP, Wang GC and
Zheng JH: Combination of quercetin and hyperoside inhibits prostate
cancer cell growth and metastasis via regulation of microRNA-21.
Mol Med Rep. 11:1085–1092. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Matsunami T, Sato Y, Hasegawa Y, Ariga S,
Kashimura H, Sato T and Yukawa M: Enhancement of reactive oxygen
species and induction of apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats under hyperbaric oxygen exposure. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 4:255–266. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li J, He C, Tong W, Zou Y, Li D, Zhang C
and Xu W: Tanshinone IIA blocks dexamethasone-induced apoptosis in
osteoblasts through inhibiting Nox4-derived ROS production. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:13695–13706. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vanachayangkul P, Byer K, Khan S and
Butterweck V: An aqueous extract of Ammi visnaga fruits and its
constituents khellin and visnagin prevent cell damage caused by
oxalate in renal epithelial cells. Phytomedicine. 17:653–658. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xing HY, Cai YQ, Wang XF, Wang LL, Li P,
Wang GY and Chen JH: The cytoprotective effect of hyperoside
against oxidative stress is mediated by the Nrf2-ARE signaling
pathway through GSK-3β inactivation. PLoS One. 10:e01451832015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xing HY, Liu Y, Chen JH, Sun FJ, Shi HQ
and Xia PY: Hyperoside attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced L02
cell damage via MAPK-dependent Keap1-Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 410:759–765. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hsieh TC, Lu X, Wang Z and Wu JM:
Induction of quinone reductase NQO1 by resveratrol in human K562
cells involves the antioxidant response element ARE and is
accompanied by nuclear translocation of transcription factor Nrf2.
Med Chem. 2:275–285. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee SB, Kim CY, Lee HJ, Yun JH and Nho CW:
Induction of the phase II detoxification enzyme NQO1 in
hepatocarcinoma cells by lignans from the fruit of Schisandra
chinensis through nuclear accumulation of Nrf2. Planta Med.
75:1314–1318. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ishii Y, Itoh K, Morishima Y, Kimura T,
Kiwamoto T, Iizuka T, Hegab AE, Hosoya T, Nomura A, Sakamoto T, et
al: Transcription factor Nrf2 plays a pivotal role in protection
against elastase-induced pulmonary inflammation and emphysema. J
Immunol. 175:6968–6975. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Itoh K, Mimura J and Yamamoto M: Discovery
of the negative regulator of Nrf2, Keap1: A historical overview.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 13:1665–1678. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|