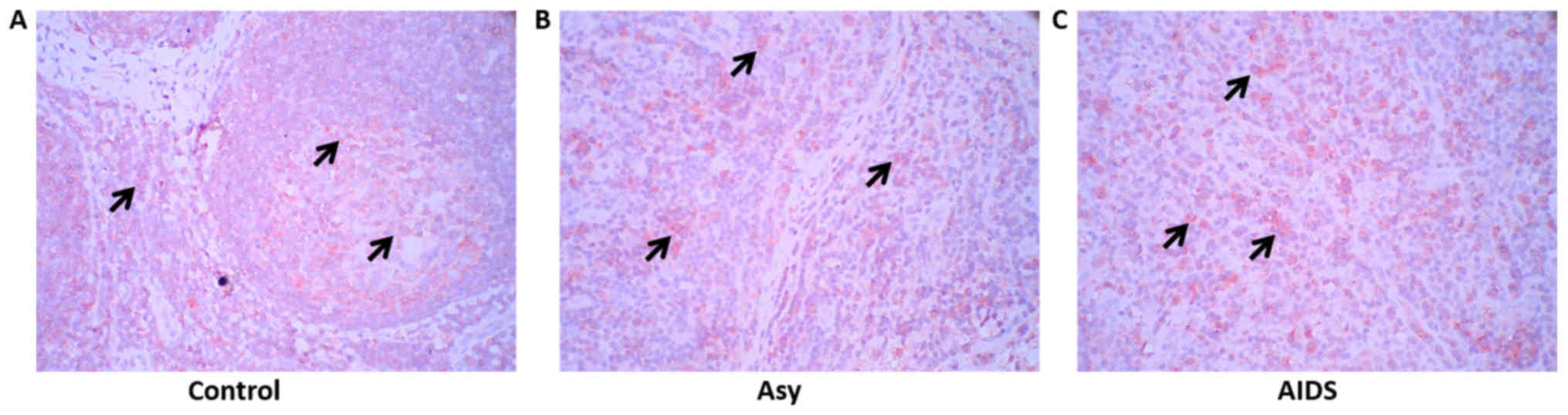
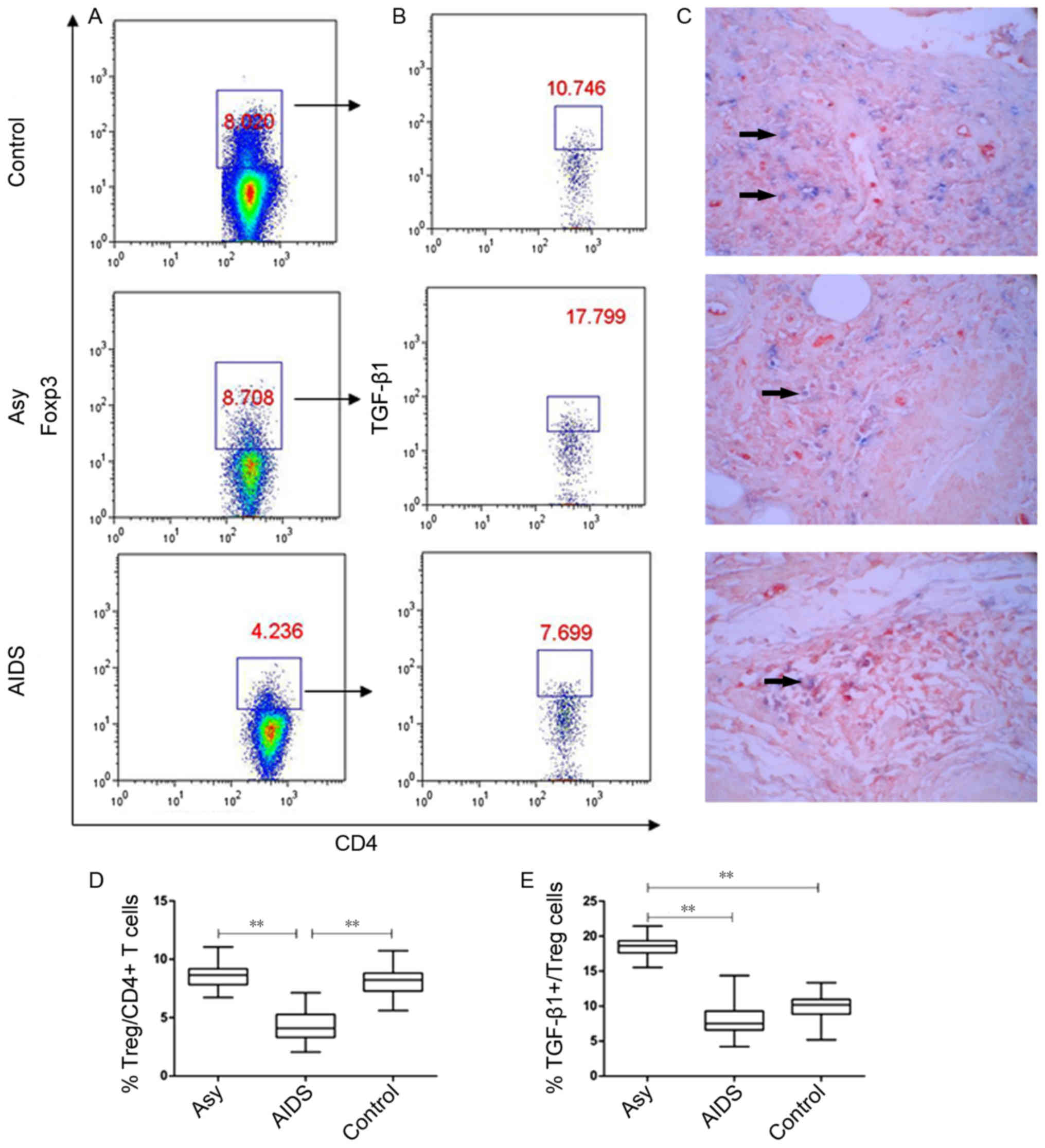
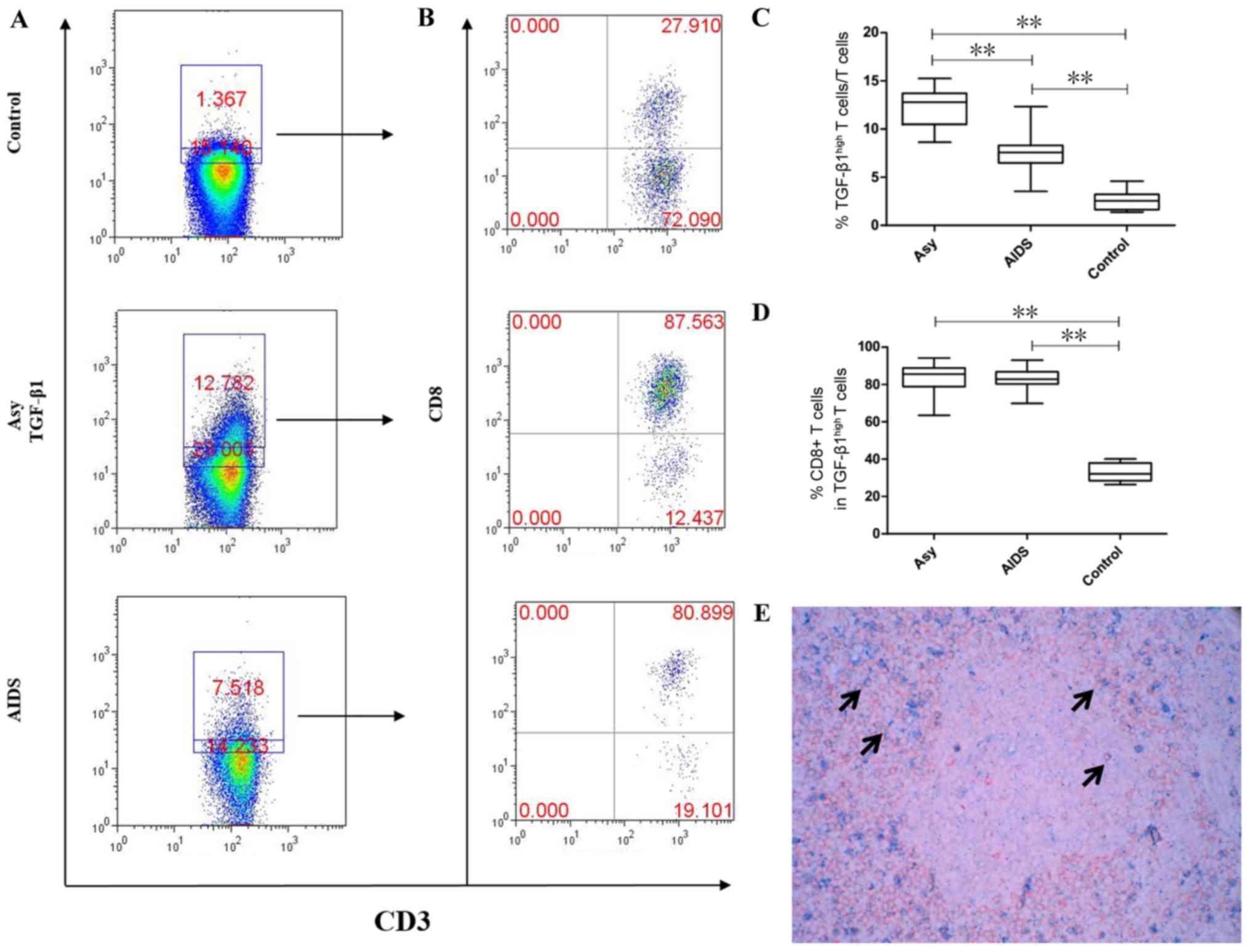
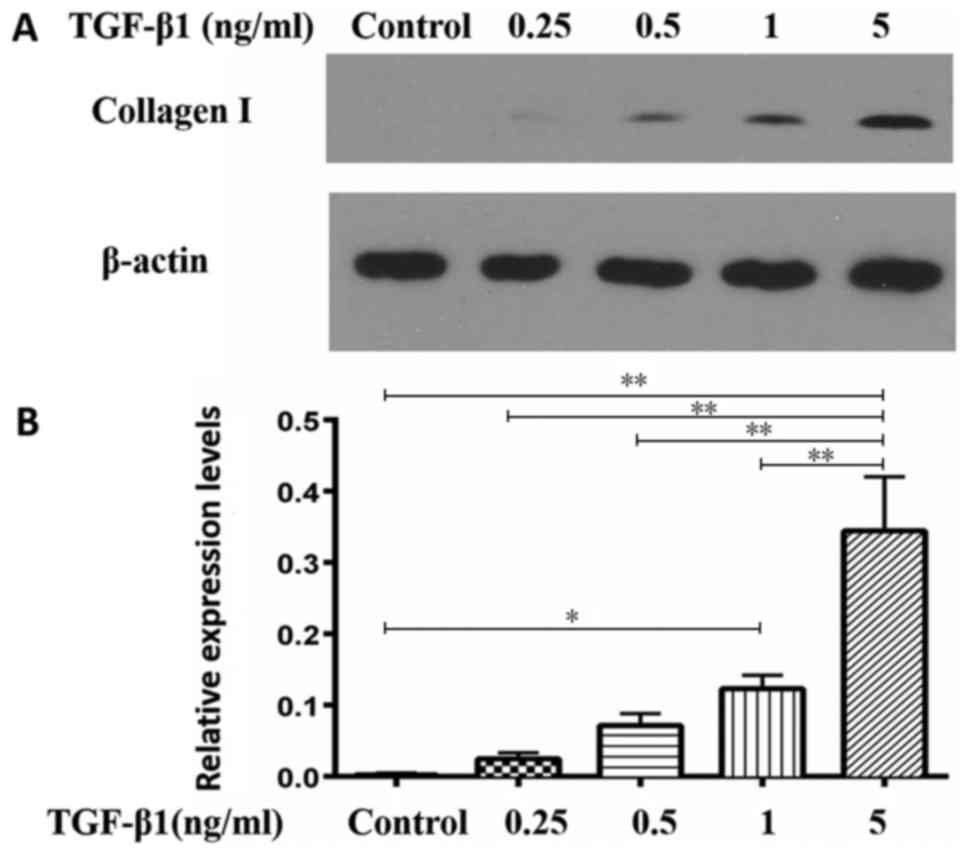
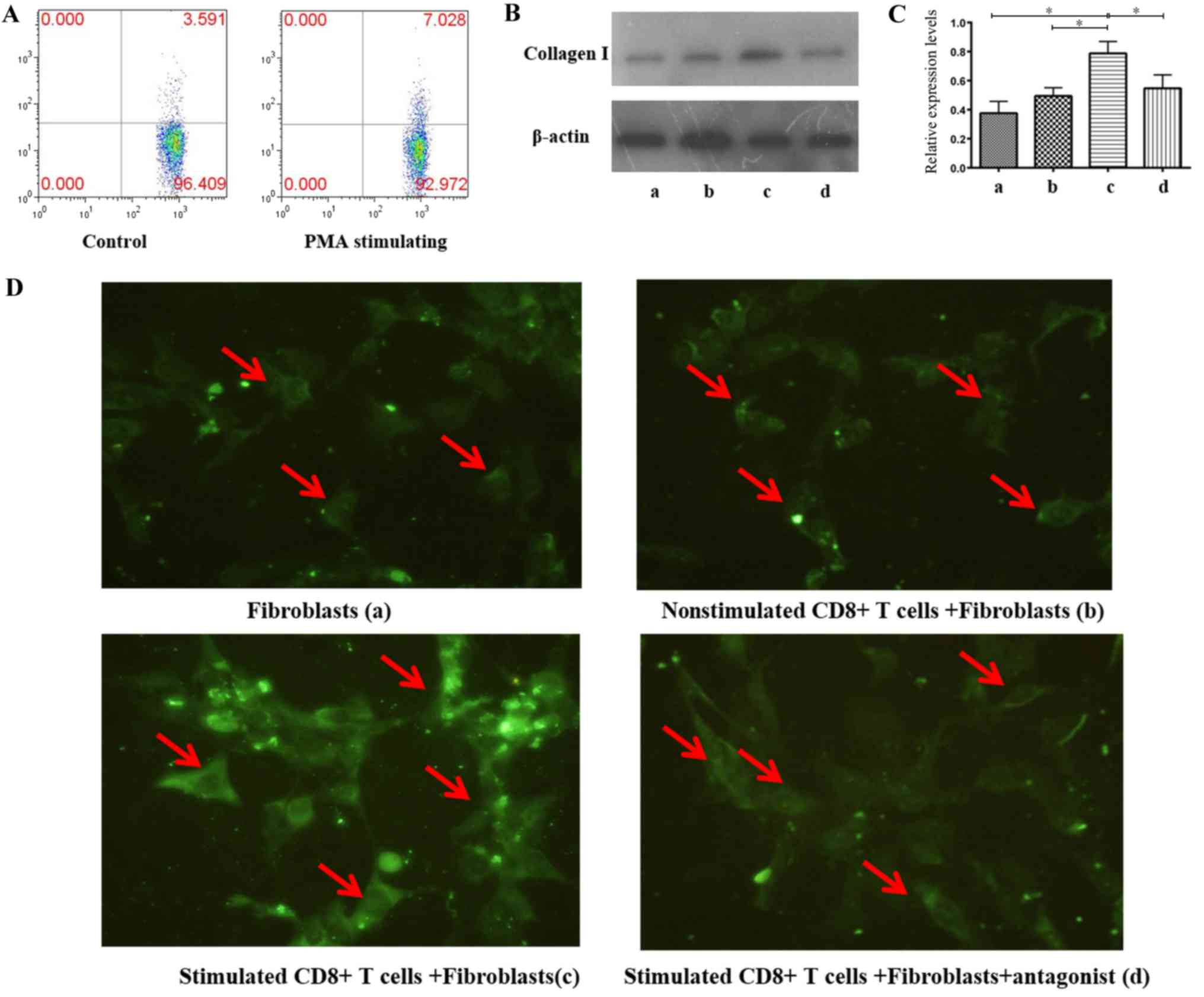
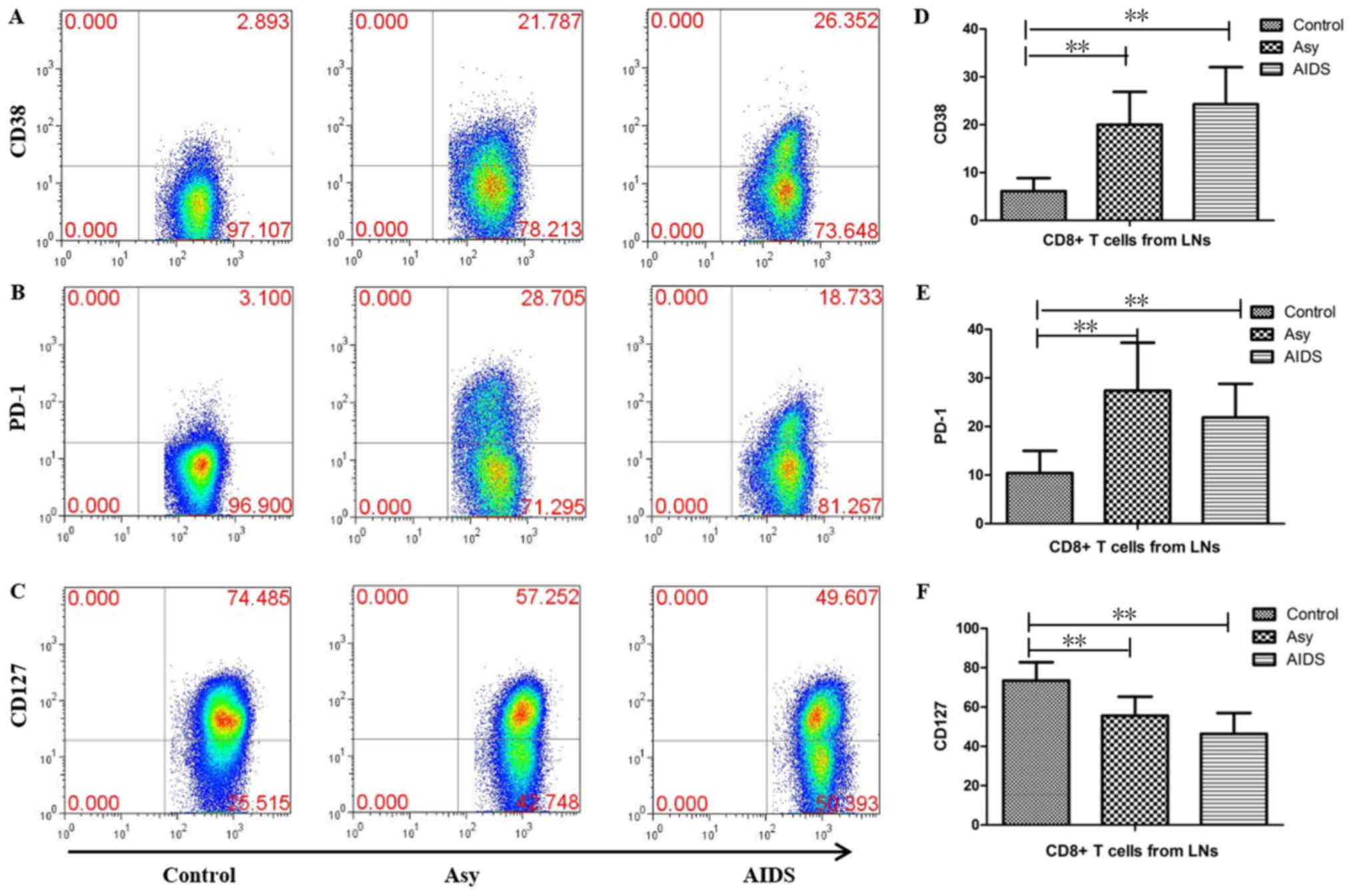
|
1
|
Gandhi RT, Chen BK, Straus SE, Dale JK,
Lenardo MJ and Baltimore D: HIV-1 directly kills CD4+ T cells by a
Fas-independent mechanism. J Exp Med. 187:1113–1122. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zinkernagel RM: Are HIV-specific CTL
responses salutary or pathogenic? Curr Opin Immunol. 7:462–470.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McCune JM: The dynamics of CD4+ T-cell
depletion in HIV disease. Nature. 410:974–979. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dion ML, Poulin JF, Bordi R, Sylvestre M,
Corsini R, Kettaf N, Dalloul A, Boulassel MR, Debré P, Routy JP, et
al: HIV infection rapidly induces and maintains a substantial
suppression of thymocyte proliferation. Immunity. 21:757–768. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McCune JM, Loftus R, Schmidt DK, Carroll
P, Webster D, Swor-Yim LB, Francis IR, Gross BH and Grant RM: High
prevalence of thymic tissue in adults with human immunodeficiency
virus-1 infection. J Clin Invest. 101:2301–2308. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brenchley JM, Price DA and Douek DC: HIV
disease: Fallout from a mucosal catastrophe? Nat Immunol.
7:235–239. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Grossman Z, Meier-Schellersheim M, Paul WE
and Picker LJ: Pathogenesis of HIV infection: What the virus spares
is as important as what it destroys. Nat Med. 12:289–295. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Derdeyn CA and Silvestri G: Viral and host
factors in the pathogenesis of HIV infection. Curr Opin Immunol.
17:366–373. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Drayton DL, Liao S, Mounzer RH and Ruddle
NH: Lymphoid organ development: From ontogeny to neogenesis. Nat
Immunol. 7:344–353. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Angeli V, Ginhoux F, Llodrà J, Quemeneur
L, Frenette PS, Skobe M, Jessberger R, Merad M and Randolph GJ: B
cell-driven lymphangiogenesis in inflamed lymph nodes enhances
dendritic cell mobilization. Immunity. 24:203–215. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bajénoff M, Egen JG, Koo LY, Laugier JP,
Brau F, Glaichenhaus N and Germain RN: Stromal cell networks
regulate lymphocyte entry, migration, and territoriality in lymph
nodes. Immunity. 25:989–1001. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Allan RS, Waithman J, Bedoui S, Jones CM,
Villadangos JA, Zhan Y, Lew AM, Shortman K, Heath WR and Carbone
FR: Migratory dendritic cells transfer antigen to a lymph
node-resident dendritic cell population for efficient CTL priming.
Immunity. 25:153–162. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Link A, Vogt TK, Favre S, Britschgi MR,
Acha-Orbea H, Hinz B, Cyster JG and Luther SA: Fibroblastic
reticular cells in lymph nodes regulate the homeostasis of naive T
cells. Nat Immunol. 8:1255–1265. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Urban ML, Manenti L and Vaglio A:
Fibrosis-a common pathway to organ injury and failure. N Engl J
Med. 373:95–96. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Denton CP and Abraham DJ: Transforming
growth factor-beta and connective tissue growth factor: Key
cytokines in scleroderma pathogenesis. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
13:505–511. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li MO, Wan YY, Sanjabi S, Robertson AK and
Flavell RA: Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of immune
responses. Ann Rev Immunol. 24:99–146. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kehrl JH, Roberts AB, Wakefield LM,
Jakowlew S, Sporn MB and Fauci AS: Transforming growth factor beta
is an important immunomodulatory protein for human B lymphocytes. J
Immunol. 137:3855–3860. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Esplugues E, Sancho D, Vega-Ramos J,
Martínez C, Syrbe U, Hamann A, Engel P, Sánchez-Madrid F and
Lauzurica P: Enhanced antitumor immunity in mice deficient in CD69.
J Exp Med. 197:1093–1106. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gray JD, Hirokawa M, Ohtsuka K and Horwitz
DA: Generation of an inhibitory circuit involving CD8+ T cells,
IL-2, and NK cell-derived TGF-beta: Contrasting effects of anti-CD2
and anti-CD3. J Immunol. 160:2248–2254. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang W, He T, Wang Q, Li X, Wei J, Hou X,
Zhang B, Huang L and Wang L: Interleukin-1 receptor-associated
kinase-2 genetic variant rs708035 increases NF-κB activity through
promoting TRAF6 ubiquitination. J Biol Chem. 289:12507–12519. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Estes JD, Wietgrefe S, Schacker T,
Southern P, Beilman G, Reilly C, Milush JM, Lifson JD, Sodora DL,
Carlis JV and Haase AT: Simian immunodeficiency virus-induced
lymphatic tissue fibrosis is mediated by transforming growth factor
beta 1-positive regulatory T cells and begins in early infection. J
Infect Dis. 195:551–561. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schacker TW, Nguyen PL, Beilman GJ,
Wolinsky S, Larson M, Reilly C and Haase AT: Collagen deposition in
HIV-1 infected lymphatic tissues and T cell homeostasis. J Clin
Invest. 110:1133–1139. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Diaz A, Alós L, León A, Mozos A, Caballero
M, Martinez A, Plana M, Gallart T, Gil C, Leal M, et al: Factors
associated with collagen deposition in lymphoid tissue in long-term
treated HIV-infected patients. AIDS. 24:2029–2039. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Diaz A, García F, Mozos A, Caballero M,
León A, Martinez A, Gil C, Plana M, Gallart T, Gatell JM and Alós
L: Lymphoid tissue collagen deposition in HIV-infected patients
correlates with the imbalance between matrix metalloproteinases and
their inhibitors. J Infect Dis. 203:810–813. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Estes JD: Role of collagen deposition in
lymphatic tissues and immune reconstruction during HIV-1 and SIV
infections. Current HIV/AIDS Rep. 6:29–35. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Schacker TW, Brenchley JM, Beilman GJ,
Reilly C, Pambuccian SE, Taylor J, Skarda D, Larson M, Douek DC and
Haase AT: Lymphatic tissue fibrosis is associated with reduced
numbers of naive CD4+ T cells in human immunodeficiency virus type
1 infection. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 13:556–560. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nies-Kraske E, Schacker TW, Condoluci D,
Orenstein J, Brenchley J, Fox C, Daucher M, Dewar R, Urban E, Hill
B, et al: Evaluation of the pathogenesis of decreasing CD4(+) T
cell counts in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected
patients receiving successfully suppressive antiretroviral therapy.
J Infect Dis. 199:1648–1656. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zeng M, Smith AJ, Wietgrefe SW, Southern
PJ, Schacker TW, Reilly CS, Estes JD, Burton GF, Silvestri G,
Lifson JD, et al: Cumulative mechanisms of lymphoid tissue fibrosis
and T cell depletion in HIV-1 and SIV infections. J Clin Invest.
121:998–1008. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeng M, Southern PJ, Reilly CS, Beilman
GJ, Chipman JG, Schacker TW and Haase AT: Lymphoid tissue damage in
HIV-1 infection depletes naive T cells and limits T cell
reconstitution after antiretroviral therapy. PLoS Pathog.
8:e10024372012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Estes JD, Haase AT and Schacker TW: The
role of collagen deposition in depleting CD4+ T cells and limiting
reconstitution in HIV-1 and SIV infections through damage to the
secondary lymphoid organ niche. Semin Immunol. 20:181–186. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shull MM, Ormsby I, Kier AB, Pawlowski S,
Diebold RJ, Yin M, Allen R, Sidman C, Proetzel G, Calvin D, et al:
Targeted disruption of the mouse transforming growth factor-beta 1
gene results in multifocal inflammatory disease. Nature.
359:693–699. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kulkarni AB, Huh CG, Becker D, Geiser A,
Lyght M, Flanders KC, Roberts AB, Sporn MB, Ward JM and Karlsson S:
Transforming growth factor beta 1 null mutation in mice causes
excessive inflammatory response and early death. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 90:770–774. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Furuya Y, Furuya AK, Roberts S, Sanfilippo
AM, Salmon SL and Metzger DW: Prevention of influenza virus-induced
immunopathology by TGF-β produced during allergic asthma. PLoS
Pathog. 11:e10051802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tang B, Böttinger EP, Jakowlew SB, Bagnall
KM, Mariano J, Anver MR, Letterio JJ and Wakefield LM: Transforming
growth factor-beta1 is a new form of tumor suppressor with true
haploid insufficiency. Nat Med. 4:802–807. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ziv E, Cauley J, Morin PA, Saiz R and
Browner WS: Association between the T29->C polymorphism in the
transforming growth factor beta1 gene and breast cancer among
elderly white women: The Study of Osteoporotic Fractures. JAMA.
285:2859–2863. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kushiyama Y, Fukuda R, Suetsugu H,
Kazumori H, Ishihara S, Adachi K and Kinoshita Y: Site-dependent
production of transforming growth factor beta1 in colonic mucosa:
Its possible role in tumorigenesis of the colon. J Lab Clin Med.
136:201–208. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Oh SP, Seki T, Goss KA, Imamura T, Yi Y,
Donahoe PK, Li L, Miyazono K, ten Dijke P, Kim S and Li E: Activin
receptor-like kinase 1 modulates transforming growth factor-beta 1
signaling in the regulation of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 97:2626–2631. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Estes JD: Pathobiology of
HIV/SIV-associated changes in secondary lymphoid tissues. Immunol
Rev. 254:65–77. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lang KS, Recher M, Navarini AA, Harris NL,
Löhning M, Junt T, Probst HC, Hengartner H and Zinkernagel RM:
Inverse correlation between IL-7 receptor expression and CD8 T cell
exhaustion during persistent antigen stimulation. Eur J Immunol.
35:738–745. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Agata Y, Kawasaki A, Nishimura H, Ishida
Y, Tsubata T, Yagita H and Honjo T: Expression of the PD-1 antigen
on the surface of stimulated mouse T and B lymphocytes. Int
Immunol. 8:765–772. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Velu V, Titanji K, Zhu B, Husain S,
Pladevega A, Lai L, Vanderford TH, Chennareddi L, Silvestri G,
Freeman GJ, et al: Enhancing SIV-specific immunity in vivo by PD-1
blockade. Nature. 458:206–210. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim HJ, Verbinnen B, Tang X, Lu L and
Cantor H: Inhibition of follicular T-helper cells by CD8(+)
regulatory T cells is essential for self tolerance. Nature.
467:328–332. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim HJ, Barnitz RA, Kreslavsky T, Brown
FD, Moffett H, Lemieux ME, Kaygusuz Y, Meissner T, Holderried TA,
Chan S, et al: Stable inhibitory activity of regulatory T cells
requires the transcription factor Helios. Science. 350:334–339.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kim HJ and Cantor H: Regulation of
self-tolerance by Qa-1-restricted CD8(+) regulatory T cells. Semin
Immunol. 23:446–452. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lu L, Kim HJ, Werneck MB and Cantor H:
Regulation of CD8+ regulatory T cells: Interruption of the
NKG2A-Qa-1 interaction allows robust suppressive activity and
resolution of autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:19420–19425. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jiang H, Canfield SM, Gallagher MP, Jiang
HH, Jiang Y, Zheng Z and Chess L: HLA-E-restricted regulatory
CD8(+) T cells are involved in development and control of human
autoimmune type 1 diabetes. J Clin Invest. 120:3641–3650. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
He R, Hou S, Liu C, Zhang A, Bai Q, Han M,
Yang Y, Wei G, Shen T, Yang X, et al: Follicular CXCR5-expressing
CD8(+) T cells curtail chronic viral infection. Nature.
537:412–428. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mylvaganam GH, Rios D, Abdelaal HM, Iyer
S, Tharp G, Mavigner M, Hicks S, Chahroudi A, Ahmed R, Bosinger SE,
et al: Dynamics of SIV-specific CXCR5+ CD8 T cells during chronic
SIV infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:1976–1981. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fuschiotti P, Larregina AT, Ho J,
Feghali-Bostwick C and Medsger TA Jr: Interleukin-13-producing CD8+
T cells mediate dermal fibrosis in patients with systemic
sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 65:236–246. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|