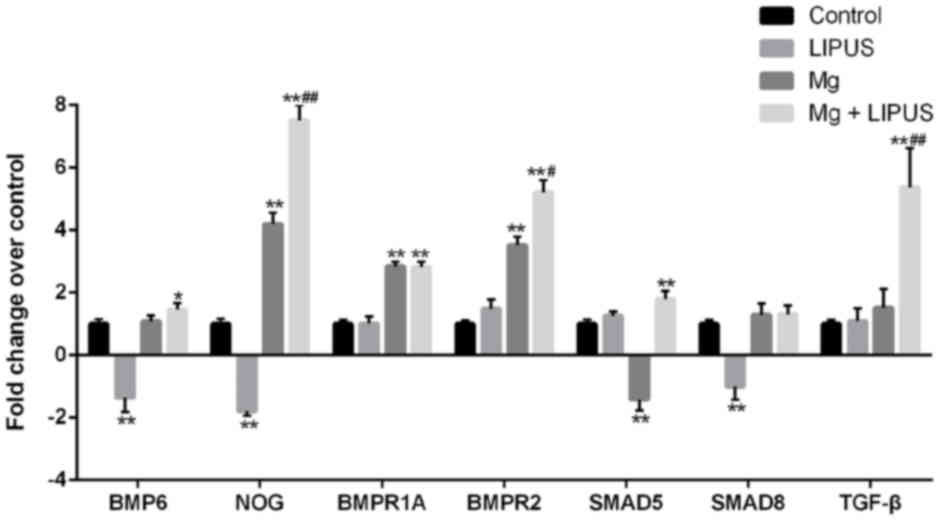
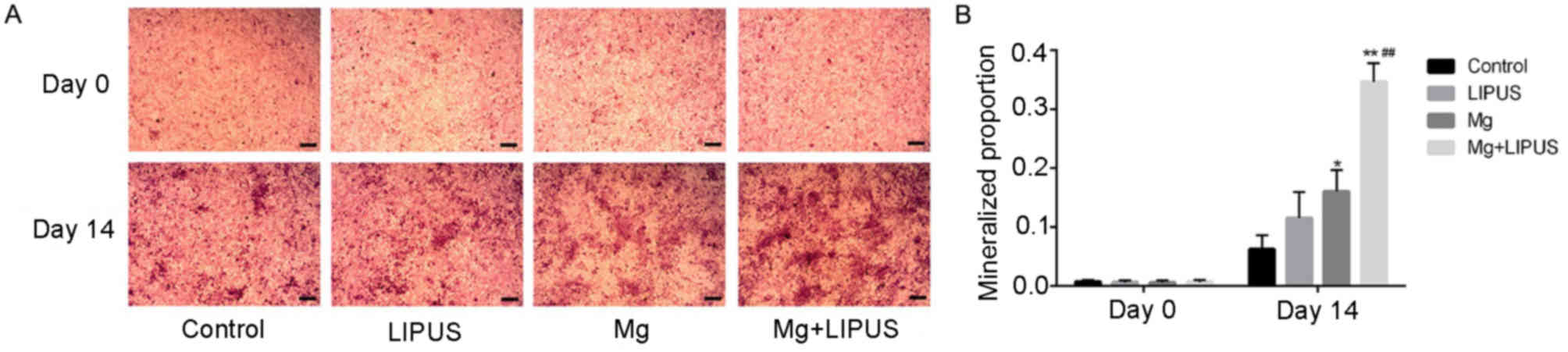
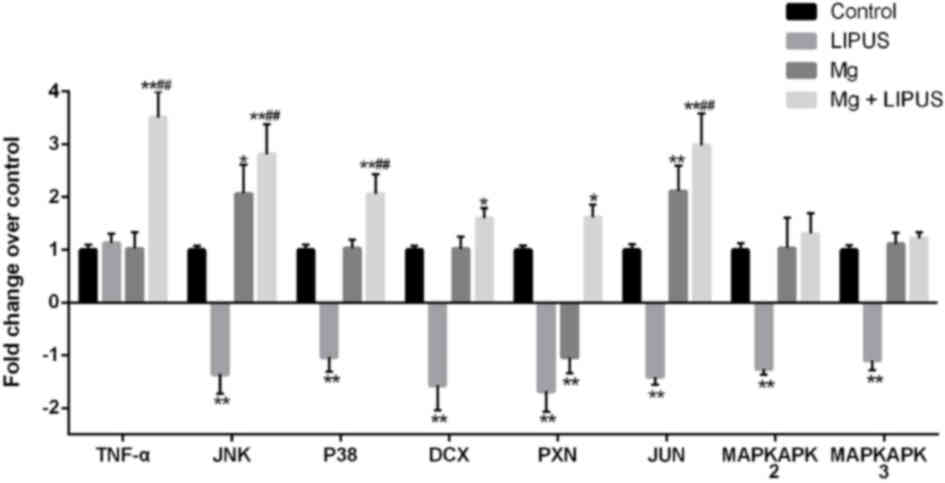
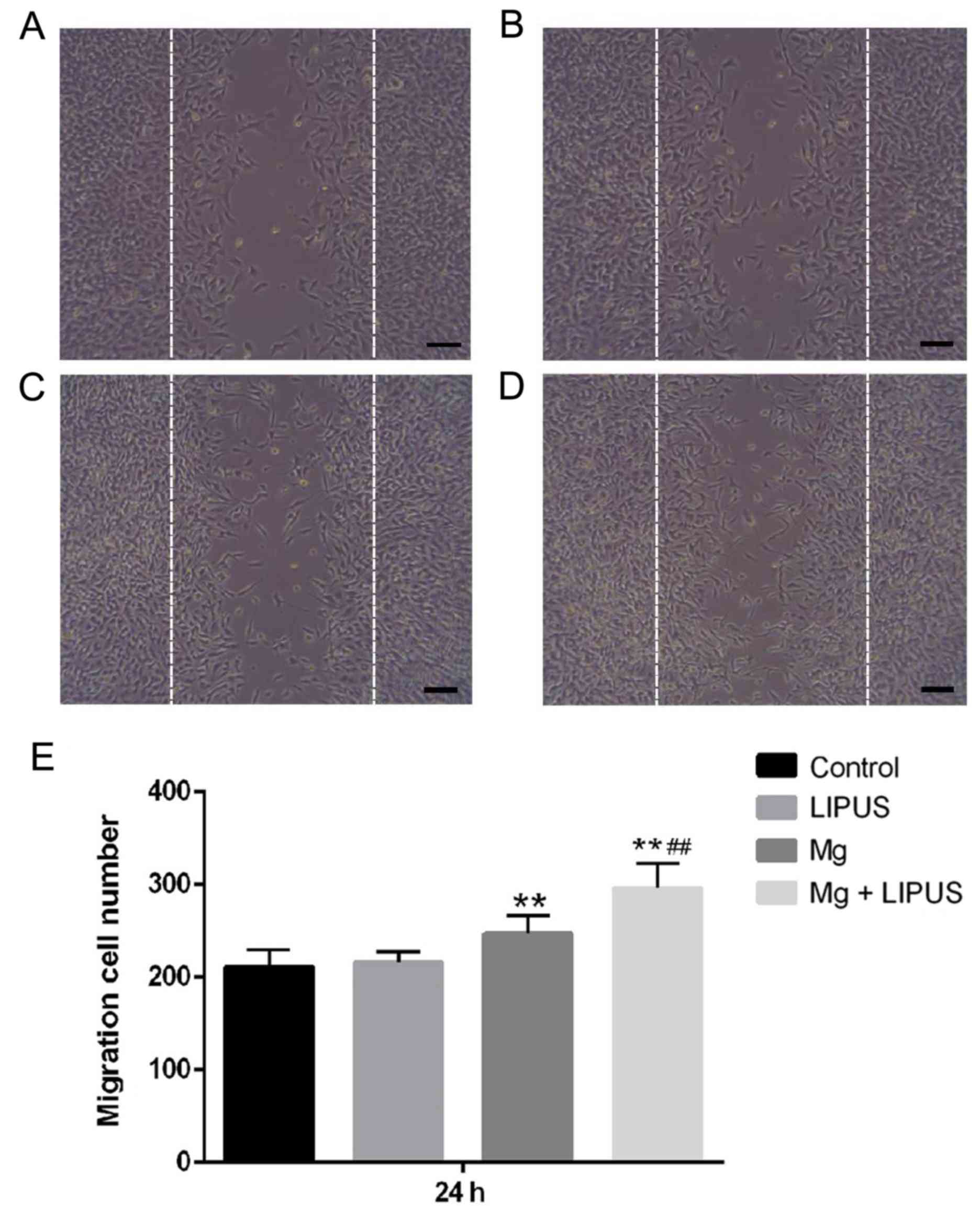
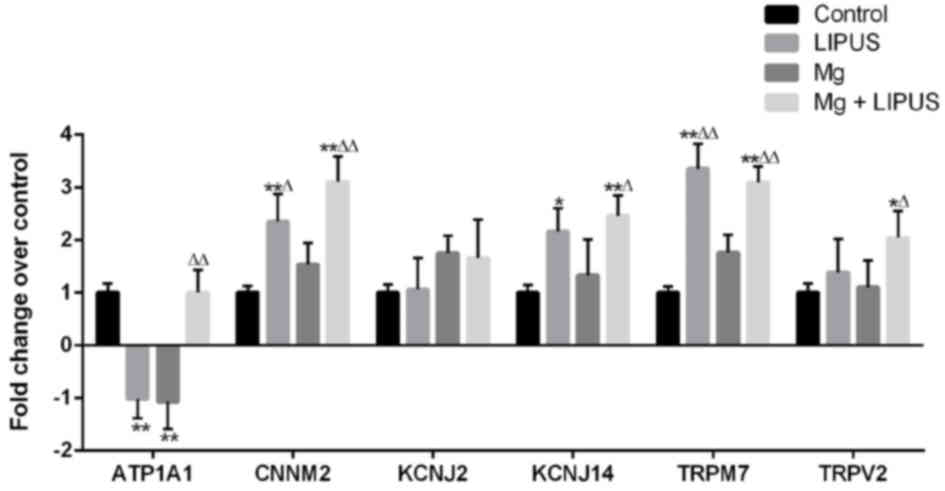
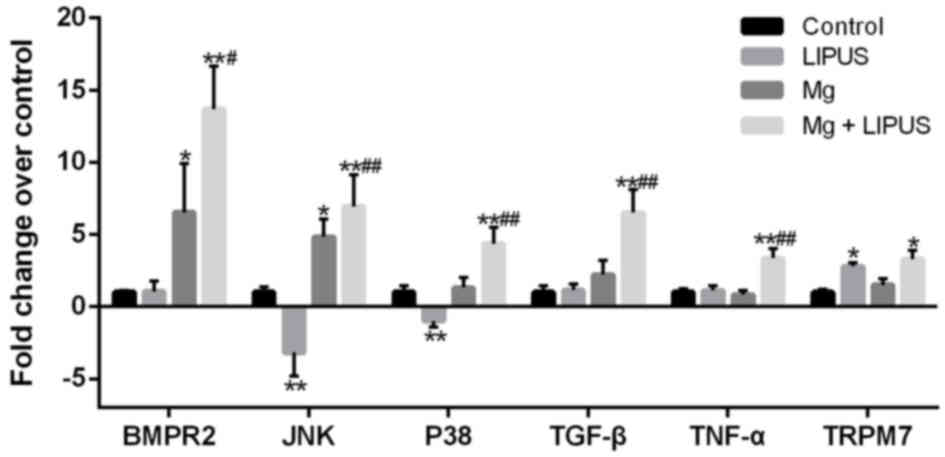
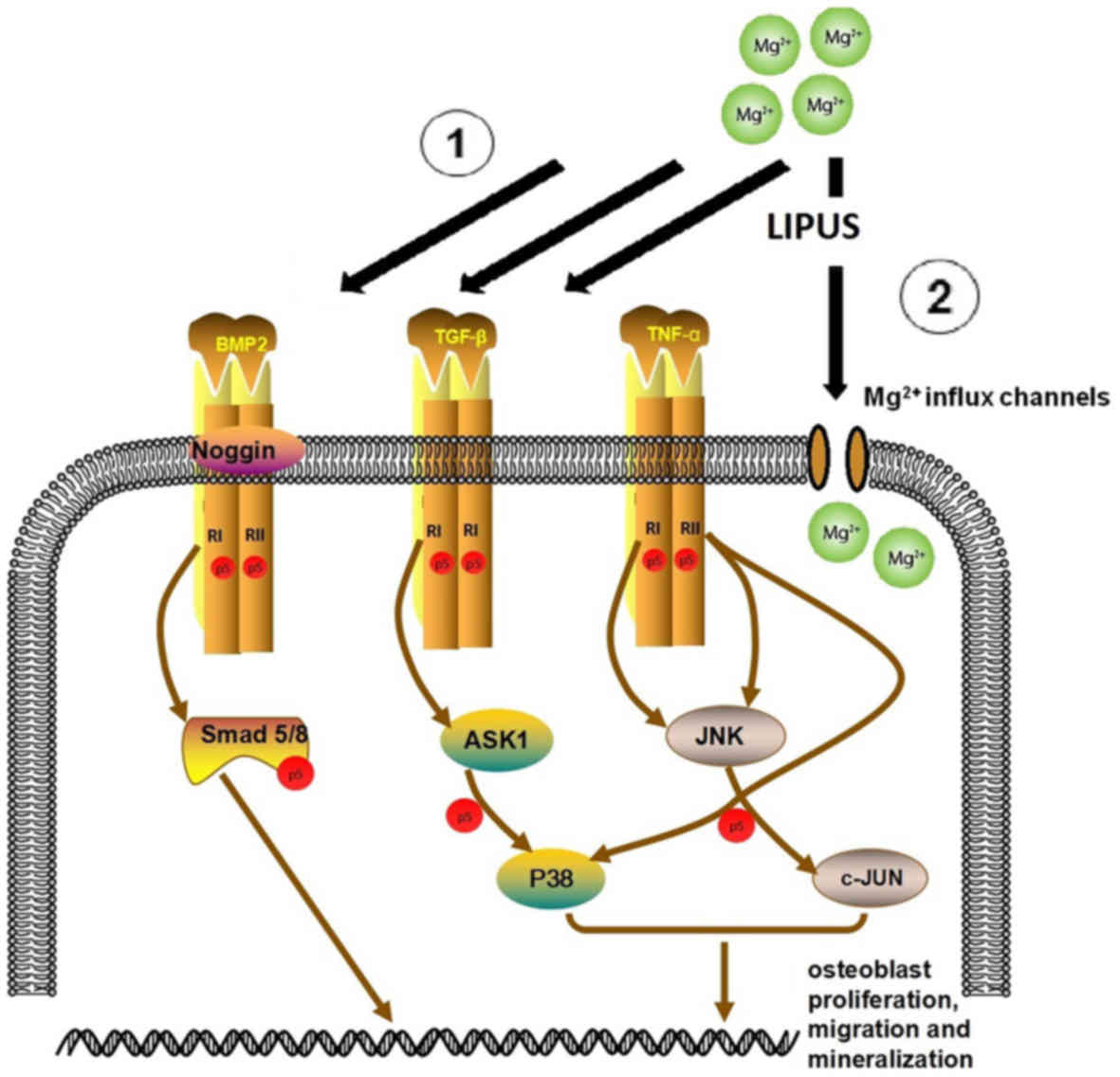
|
1
|
Payr E: Beitrage zur technik der
blutgefass- und nervennaht nebst mittheilungen über die verwendung
eines resorbirbaren metalles in der chirurgie. Arch Klin Chir.
62:67–93. 1900.(In German).
|
|
2
|
Zhao D, Witte F, Lu F, Wang J, Li J and
Qin L: Current status on clinical applications of magnesium-based
orthopaedic implants: A review from clinical translational
perspective. Biomaterials. 112:287–302. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao D, Huang S, Lu F, Wang B, Yang L, Qin
L, Yang K, Li Y, Li W, Wang W, et al: Vascularized bone grafting
fixed by biodegradable magnesium screw for treating osteonecrosis
of the femoral head. Biomaterials. 81:84–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Swaminathan R: Magnesium metabolism and
its disorders. Clin Biochem Rev. 24:47–66. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pasternak K, Kocot J and Horecka A:
Biochemistry of magnesium. J Elementol. 15:601–616. 2010.
|
|
6
|
Jahnen-Dechent W and Ketteler M: Magnesium
basics. Clin Kidney J. 5 Suppl 1:i3–i14. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Abed E and Moreau R: Importance of
melastatin-like transient receptor potential 7 and magnesium in the
stimulation of osteoblast proliferation and migration by
platelet-derived growth factor. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
297:C360–C368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ding S, Zhang J, Tian Y, Huang B, Yuan Y
and Liu C: Magnesium modification up-regulates the bioactivity of
bone morphogenetic protein-2 upon calcium phosphate cement via
enhanced BMP receptor recognition and Smad signaling pathway.
Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 145:140–151. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rude RK, Gruber HE, Wei LY and Frausto A:
Immunolocalization of RANKL is increased and OPG decreased during
dietary magnesium deficiency in the rat. Nutr Metab (Lond).
2:242005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang J, Ma XY, Feng YF, Ma ZS, Ma TC,
Zhang Y, Li X, Wang L and Lei W: Magnesium ions promote the
biological behaviour of rat calvarial osteoblasts by activating the
PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res. 179:284–293.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gray J and Luan B: Protective coatings on
magnesium and its alloys-a critical review. J Alloys Compd.
336:88–113. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yamamoto A, Watanabe A, Sugahara K,
Tsubakino H and Fukumoto S: Improvement of corrosion resistance of
magnesium alloys by vapor deposition. Scr Mater. 44:1039–1042.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Saris NE, Mervaala E, Karppanen H, Khawaja
JA and Lewenstam A: Magnesium. An update on physiological, clinical
and analytical aspects. Clin Chim Acta. 294:1–26. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zberg B, Uggowitzer PJ and Löffler JF:
MgZnCa glasses without clinically observable hydrogen evolution for
biodegradable implants. Nat Mater. 8:887–891. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang B, Zhao L, Zhu W, Fang L and Ren F:
Mussel-inspired nano-multilayered coating on magnesium alloys for
enhanced corrosion resistance and antibacterial property. Colloids
Surf B Biointerfaces. 157:432–439. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang Y, Wang B, Jia Z, Lu X, Fang L, Wang
K and Ren F: Polydopamine mediated assembly of hydroxyapatite
nanoparticles and bone morphogenetic protein-2 on magnesium alloys
for enhanced corrosion resistance and bone regeneration. J Biomed
Mater Res A. 105:2750–2761. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Z, Shizhao S, Chen M, Fahlman BD, Debao
Liu and Bi H: In vitro and in vivo corrosion, mechanical properties
and biocompatibility evaluation of MgF2-coated Mg-Zn-Zr
alloy as cancellous screws. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.
75:1268–1280. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Padilla F, Puts R, Vico L, Guignandon A
and Raum K: Stimulation of bone repair with ultrasound. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 880:385–427. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Poolman RW, Agoritsas T, Siemieniuk RA,
Harris IA, Schipper IB, Mollon B, Smith M, Albin A, Nador S, Sasges
W, et al: Low intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) for bone healing:
A clinical practice guideline. BMJ. 356:j5762017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Alvarenga EC, Rodrigues R, Caricati-Neto
A, Silva-Filho FC, Paredes-Gamero EJ and Ferreira AT: Low-intensity
pulsed ultrasound-dependent osteoblast proliferation occurs by via
activation of the P2Y receptor: Role of the P2Y1 receptor. Bone.
46:355–362. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Miyasaka M, Nakata H, Hao J, Kim YK,
Kasugai S and Kuroda S: Low-Intensity pulsed ultrasound stimulation
enhances Heat-shock protein 90 and mineralized nodule formation in
mouse calvaria-derived osteoblasts. Tissue Eng Part A.
21:2829–2839. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saini V, Yadav S and McCormick S:
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound modulates shear stress induced
PGHS-2 expression and PGE2 synthesis in MLO-Y4 osteocyte-like
cells. Ann Biomed Eng. 39:378–393. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang FS, Kuo YR, Wang CJ, Yang KD, Chang
PR, Huang YT, Huang HC, Sun YC, Yang YJ and Chen YJ: Nitric oxide
mediates ultrasound-induced hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha
activation and vascular endothelial growth factor-A expression in
human osteoblasts. Bone. 35:114–123. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang Z, Ren L, Deng F, Wang Z and Song J:
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound induces osteogenic differentiation
of human periodontal ligament cells through activation of bone
morphogenetic protein-smad signaling. J Ultrasound Med. 33:865–873.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kinami Y, Noda T and Ozaki T: Efficacy of
low-intensity pulsed ultrasound treatment for surgically managed
fresh diaphyseal fractures of the lower extremity: Multi-center
retrospective cohort study. J Orthop Sci. 18:410–418. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nolte P, Anderson R, Strauss E, Wang Z, Hu
L, Xu Z and Steen RG: Heal rate of metatarsal fractures: A
propensity-matching study of patients treated with low-intensity
pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) vs. surgical and other treatments.
Injury. 47:2584–2590. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Salem KH and Schmelz A: Low-intensity
pulsed ultrasound shortens the treatment time in tibial distraction
osteogenesis. Int Orthop. 38:1477–1482. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Seger EW, Jauregui JJ, Horton SA, Davalos
G, Kuehn E and Stracher MA: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for
nonoperative treatment of scaphoid nonunions: A meta-analysis. Hand
(N Y). Apr 1–2017.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou X, Castro NJ, Zhu W, Cui H,
Aliabouzar M, Sarkar K and Zhang LG: Improved human bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis in 3D bioprinted tissue
scaffolds with low intensity pulsed ultrasound stimulation. Sci
Rep. 6:328762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nagasaki R, Mukudai Y, Yoshizawa Y,
Nagasaki M, Shiogama S, Suzuki M, Kondo S, Shintani S and Shirota
T: A combination of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound and
nanohydroxyapatite concordantly enhances osteogenesis of
adipose-derived stem cells from buccal fat pad. Cell Med.
7:123–131. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kubanek J, Shi J, Marsh J, Chen D, Deng C
and Cui J: Ultrasound modulates ion channel currents. Sci Rep.
6:241702016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Franz-Odendaal TA, Hall BK and Witten PE:
Buried alive: How osteoblasts become osteocytes. Dev Dyn.
235:176–190. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hallab NJ, Vermes C, Messina C, Roebuck
KA, Glant TT and Jacobs JJ: Concentration- and
composition-dependent effects of metal ions on human MG-63
osteoblasts. J Biomed Mater Res. 60:420–433. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang J, Witte F, Xi T, Zheng Y, Yang K,
Yang Y, Zhao D, Meng J, Li Y, Li W, et al: Recommendation for
modifying current cytotoxicity testing standards for biodegradable
magnesium-based materials. Acta Biomater. 21:237–249. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He LY, Zhang XM, Liu B, Tian Y and Ma WH:
Effect of magnesium ion on human osteoblast activity. Braz J Med
Biol Res. 49:pii. 2016.doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20165257. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Suzuki A, Takayama T, Suzuki N, Sato M,
Fukuda T and Ito K: Daily low-intensity pulsed ultrasound-mediated
osteogenic differentiation in rat osteoblasts. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 41:108–115. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu S, Kawahara Y, Manabe T, Ogawa K,
Matsumoto M, Sasaki A and Yuge L: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound
accelerates osteoblast differentiation and promotes bone formation
in an osteoporosis rat model. Pathobiology. 76:99–107. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Man J, Shelton RM, Cooper PR, Landini G
and Scheven BA: Low intensity ultrasound stimulates osteoblast
migration at different frequencies. J Bone Miner Metab. 30:602–607.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rahman MS, Akhtar N, Jamil HM, Banik RS
and Asaduzzaman SM: TGF-β/BMP signaling and other molecular events:
Regulation of osteoblastogenesis and bone formation. Bone Res.
3:150052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Huang C, Jacobson K and Schaller MD: MAP
kinases and cell migration. J Cell Sci. 117:4619–4628. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gdalyahu A, Ghosh I, Levy T, Sapir T,
Sapoznik S, Fishler Y, Azoulai D and Reiner O: DCX, a new mediator
of the JNK pathway. EMBO J. 23:823–832. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang C, Rajfur Z, Borchers C, Schaller MD
and Jacobson K: JNK phosphorylates paxillin and regulates cell
migration. Nature. 424:219–223. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Javelaud D, Laboureau J, Gabison E,
Verrecchia F and Mauviel A: Disruption of basal JNK activity
differentially affects key fibroblast functions important for wound
healing. J Biol Chem. 278:24624–24628. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hannigan MO, Zhan L, Ai Y, Kotlyarov A,
Gaestel M and Huang CK: Abnormal migration phenotype of
mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2-/-
neutrophils in Zigmond chambers containing
formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine gradients. J Immunol.
167:3953–3961. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
McLaughlin MM, Kumar S, McDonnell PC, Van
Horn S, Lee JC, Livi GP and Young PR: Identification of
mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase-activated protein kinase-3,
a novel substrate of CSBP p38 MAP kinase. J Biol Chem.
271:8488–8492. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rodriguez-Carballo E, Gámez B and Ventura
F: p38 MAPK signaling in osteoblast differentiation. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 4:402016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mehrotra M, Krane SM, Walters K and
Pilbeam C: Differential regulation of platelet-derived growth
factor stimulated migration and proliferation in osteoblastic
cells. J Cell Biochem. 93:741–752. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Osta B, Benedetti G and Miossec P:
Classical and paradoxical effects of TNF-α on bone homeostasis.
Front Immunol. 5:482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Glass GE, Chan JK, Freidin A, Feldmann M,
Horwood NJ and Nanchahal J: TNF-alpha promotes fracture repair by
augmenting the recruitment and differentiation of muscle-derived
stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:1585–1590. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mountziaris PM, Lehman Dennis E,
Mountziaris I, Sing DC, Kasper FK and Mikos AG: Effect of
temporally patterned TNF-α delivery on in vitro osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells cultured on
biodegradablepolymer scaffolds. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.
24:1794–1813. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hess K, Ushmorov A, Fiedler J, Brenner RE
and Wirth T: TNF-alpha promotes osteogenic differentiation of human
mesenchymal stem cells by triggering the NF-kappaB signaling
pathway. Bone. 45:367–376. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gröber U, Schmidt J and Kisters K:
Magnesium in prevention and therapy. Nutrients. 7:8199–8226. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|