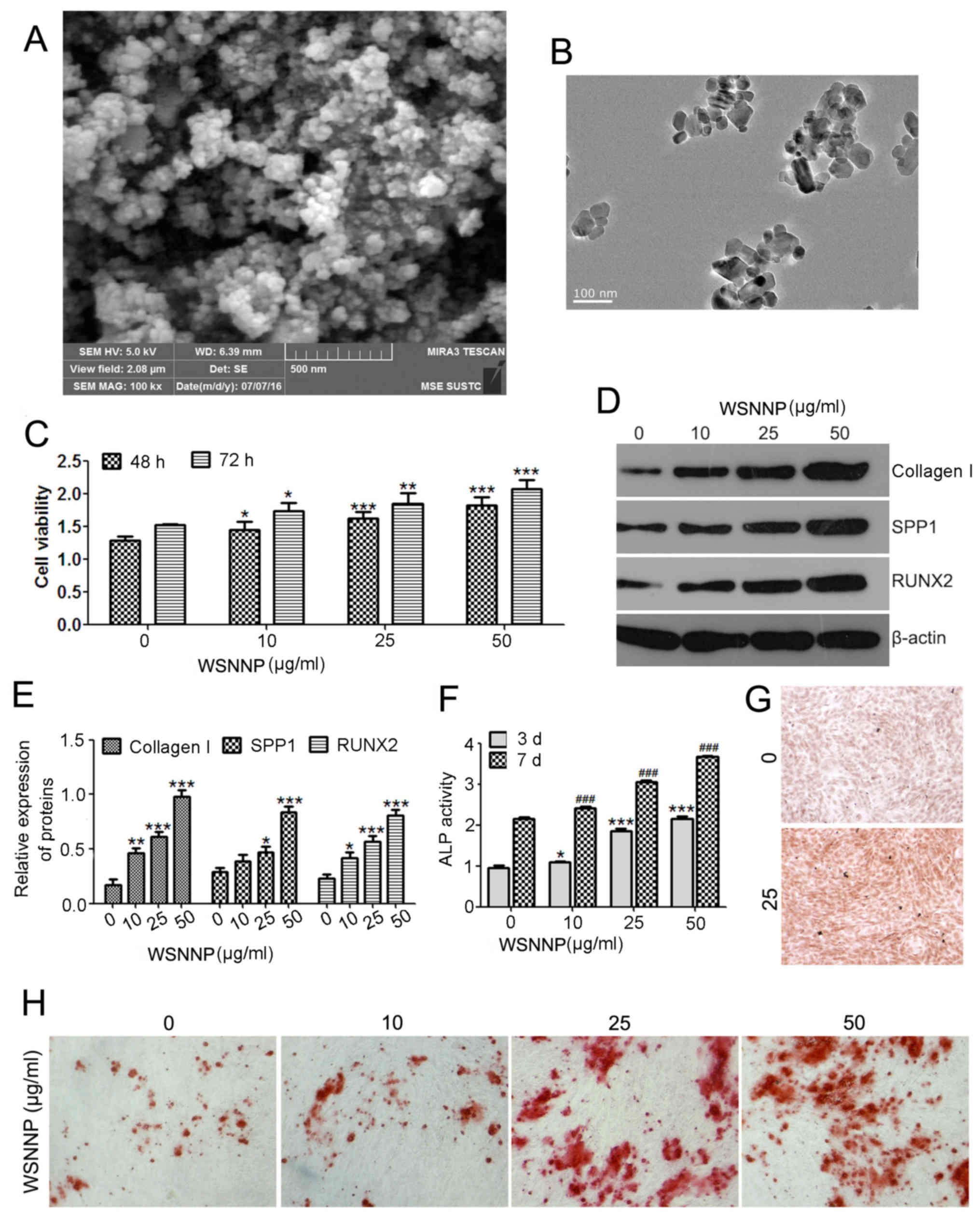
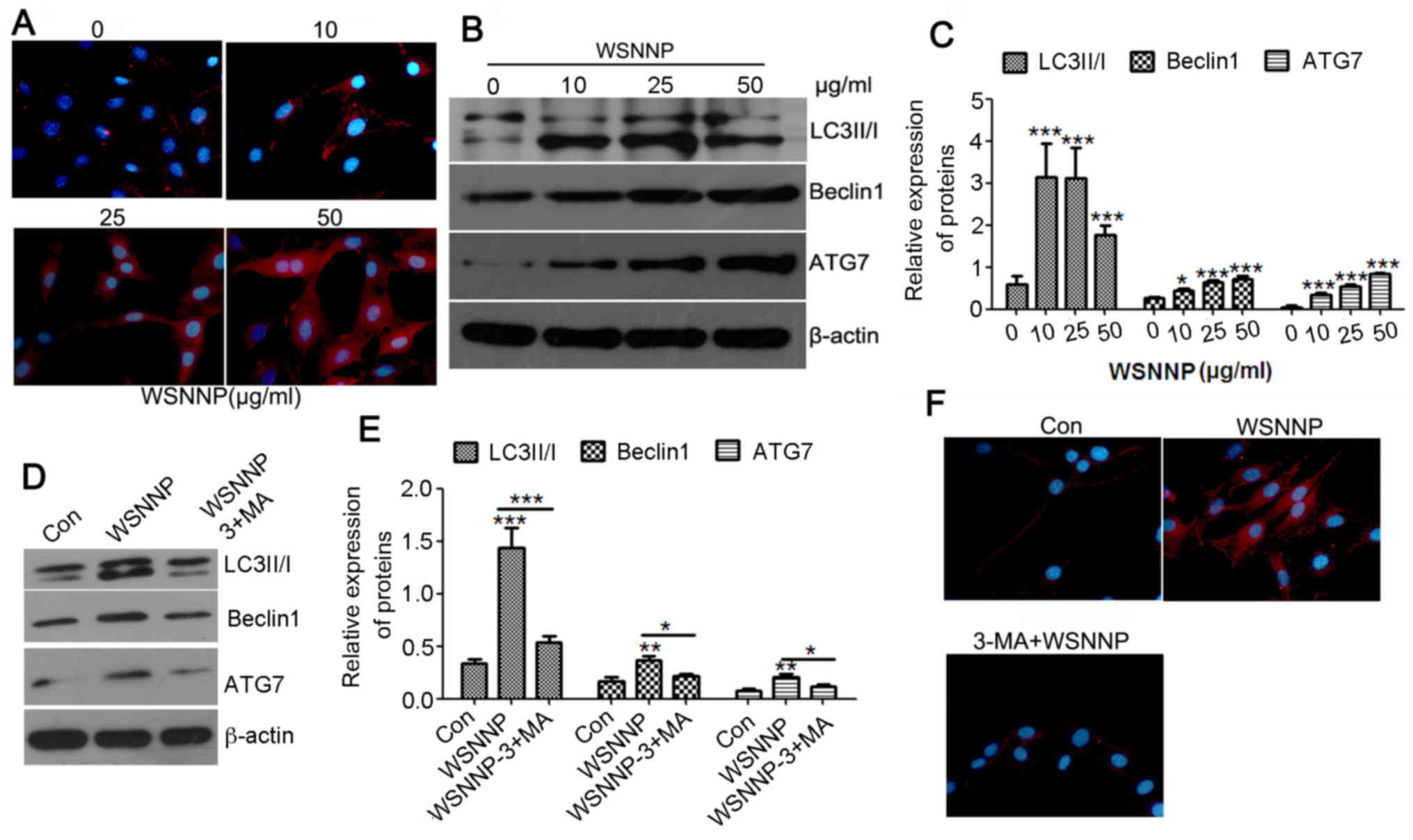
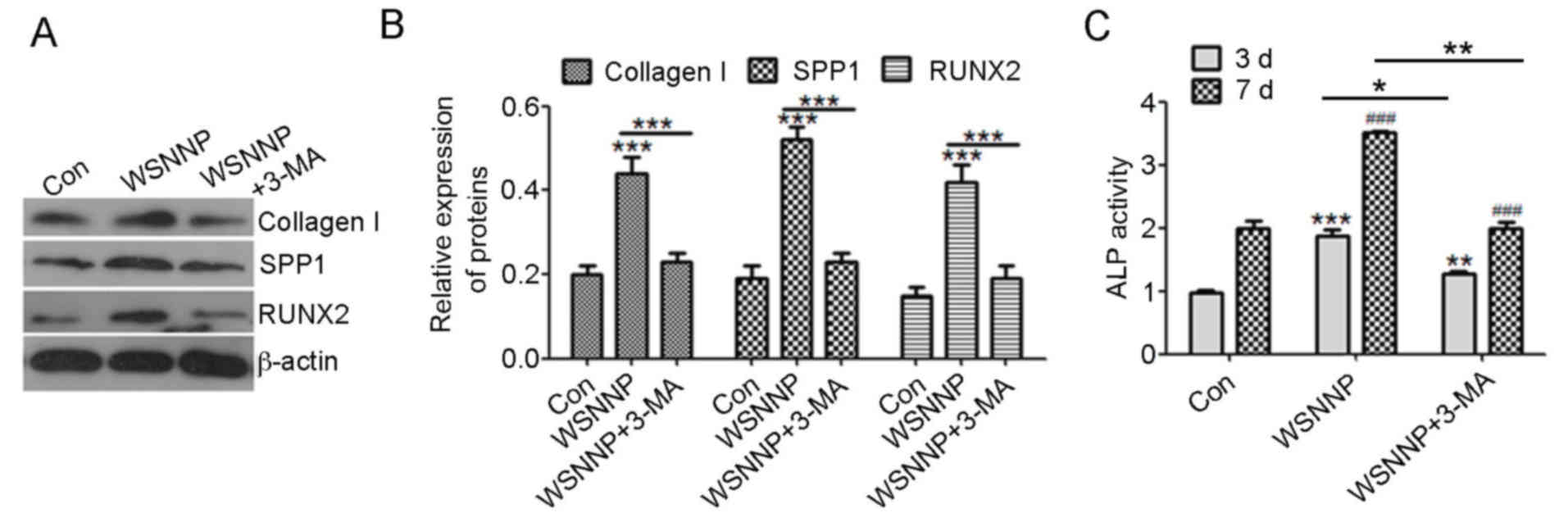
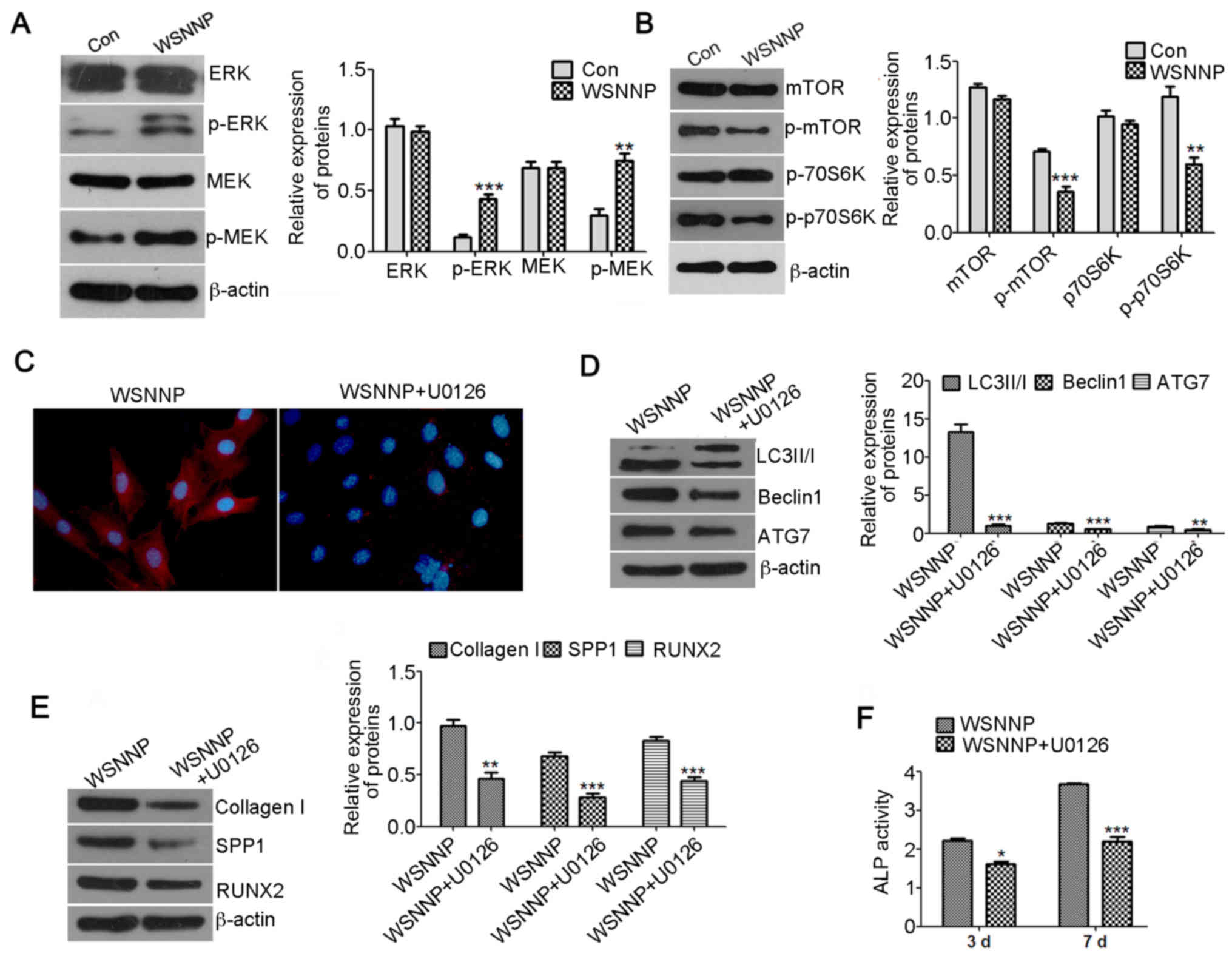
|
1
|
Maruotti N, Corrado A and Cantatore FP:
Osteoblast role in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol.
232:2957–2963. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Terrier Saint-Pastou C and Gasque P: Bone
responses in health and infectious diseases: A focus on
osteoblasts. J Infect. 75:281–292. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dallas SL, Prideaux M and Bonewald LF: The
osteocyte: An endocrine cell … and more. Endocr Rev. 34:658–690.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Insua A, Monje A, Wang HL and Miron RJ:
Basis of bone metabolism around dental implants during
osseointegration and peri-implant bone loss. J Biomed Mater Res A.
105:2075–2089. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jazayeri HE, Tahriri M, Razavi M, Khoshroo
K, Fahimipour F, Dashtimoghadam E, Almeida L and Tayebi L: A
current overview of materials and strategies for potential use in
maxillofacial tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.
70:913–929. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Uzeda MJ, de Brito Resende RF, Sartoretto
SC, Alves ATNN, Granjeiro JM and Calasans-Maia MD: Randomized
clinical trial for the biological evaluation of two nanostructured
biphasic calcium phosphate biomaterials as a bone substitute. Clin
Implant Dent Relat Res. 19:802–811. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Flausse A, Henrionnet C, Dossot M, Dumas
D, Hupont S, Pinzano A, Mainard D, Galois L, Magdalou J, Lopez E,
et al: Osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cells in hydrogel containing nacre powder. J Biomed Mater Res
A. 101:3211–3218. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pilliar RM, Filiaggi MJ, Wells JD, Grynpas
MD and Kandel RA: Porous calcium polyphosphate scaffolds for bone
substitute applications-in vitro characterization. Biomaterials.
22:963–972. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lopez E, Le Faou A, Borzeix S and Berland
S: Stimulation of rat cutaneous fibroblasts and their synthetic
activity by implants of powdered nacre (mother of pearl). Tissue
Cell. 32:95–101. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shen Y, Zhu J, Zhang H and Zhao F: In
vitro osteogenetic activity of pearl. Biomaterials. 27:281–287.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mouries LP, Almeida MJ, Milet C, Berland S
and Lopez E: Bioactivity of nacre water-soluble organic matrix from
the bivalve mollusk Pinctada maxima in three mammalian cell types:
Fibroblasts, bone marrow stromal cells and osteoblasts. Comp
Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 132:217–229. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lamghari M, Almeida MJ, Berland S, Huet H,
Laurent A, Milet C and Lopez E: Stimulation of bone marrow cells
and bone formation by nacre: In vivo and in vitro studies. Bone. 25
2 Suppl:91S–94S. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Asvanund P, Chunhabundit P and
Suddhasthira T: Potential induction of bone regeneration by nacre:
An in vitro study. Implant Dent. 20:32–39. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chaturvedi R, Singha PK and Dey S: Water
soluble bioactives of nacre mediate antioxidant activity and
osteoblast differentiation. PLoS One. 8:e845842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hesse E, Hefferan TE, Tarara JE, Haasper
C, Meller R, Krettek C, Lu L and Yaszemski MJ: Collagen type I
hydrogel allows migration, proliferation, and osteogenic
differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells. J Biomed Mater
Res A. 94:442–449. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leboy PS: Regulating bone growth and
development with bone morphogenetic proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1068:14–18. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang J, Whiteman MW, Lian H, Wang G, Singh
A, Huang D and Denmark T: A non-canonical MEK/ERK signaling pathway
regulates autophagy via regulating Beclin 1. J Biol Chem.
284:21412–21424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cagnol S and Chambard JC: ERK and cell
death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death-apoptosis, autophagy
and senescence. FEBS J. 277:2–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang X, Liu S, Xie L, Zhang R and Wang Z:
Pinctada fucata mantle gene 3 (PFMG3) promotes differentiation in
mouse osteoblasts (MC3T3-E1). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol
Biol. 158:173–180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Y, Huang Q and Feng Q: 3D scaffold of
PLLA/pearl and PLLA/nacre powder for bone regeneration. Biomed
Mater. 8:650012013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Almeida MJ, Milet C, Peduzzi J, Pereira L,
Haigle J, Barthelemy M and Lopez E: Effect of water-soluble matrix
fraction extracted from the nacre of Pinctada maxima on the
alkaline phosphatase activity of cultured fibroblasts. J Exp Zool.
288:327–334. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bedouet L, Marie A, Dubost L, Péduzzi J,
Duplat D, Berland S, Puisségur M, Boulzaguet H, Rousseau M, Milet C
and Lopez E: Proteomics analysis of the nacre soluble and insoluble
proteins from the oyster Pinctada margaritifera. Mar Biotechnol
(NY). 9:638–649. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bédouet L, Rusconi F, Rousseau M, Duplat
D, Marie A, Dubost L, Le Ny K, Berland S, Péduzzi J and Lopez E:
Identification of low molecular weight molecules as new components
of the nacre organic matrix. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol
Biol. 144:532–543. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bedouet L, Duplat D, Marie A, Dubost L,
Berland S, Rousseau M, Milet C and Lopez E: Heterogeneity of
proteinase inhibitors in the water-soluble organic matrix from the
oyster nacre. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 9:437–449. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oliveira DV, Silva TS, Cordeiro OD, Cavaco
SI and Simes DC: Identification of proteins with potential
osteogenic activity present in the water-soluble matrix proteins
from Crassostrea gigas nacre using a proteomic approach.
ScientificWorldJournal. 2012:7659092012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Duplat D, Gallet M, Berland S, Marie A,
Dubost L, Rousseau M, Kamel S, Milet C, Brazier M, Lopez E and
Bédouet L: The effect of molecules in mother-of-pearl on the
decrease in bone resorption through the inhibition of osteoclast
cathepsin K. Biomaterials. 28:4769–4778. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rousseau M, Boulzaguet H, Biagianti J,
Duplat D, Milet C, Lopez E and Bédouet L: Low molecular weight
molecules of oyster nacre induce mineralization of the MC3T3-E1
cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 85:487–497. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Laothumthut T, Jantarat J, Paemanee A,
Roytrakul S and Chunhabundit P: Shotgun proteomics analysis of
proliferating STRO-1-positive human dental pulp cell after exposure
to nacreous water-soluble matrix. Clin Oral Investig. 19:261–270.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
De Nunzio C, Giglio S, Stoppacciaro A,
Gacci M, Cirombella R, Luciani E, Tubaro A and Vecchione A:
Autophagy deactivation is associated with severe prostatic
inflammation in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms and
benign prostatic hyperplasia. Oncotarget. 8:50904–50910. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Takashi O and Matsu A: Autophagy. Arerugi.
66:1018–1019. 2017.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shetty R, Sharma A, Pahuja N, Chevour P,
Padmajan N, Dhamodaran K, Jayadev C, M M A, Nuijts R, Ghosh A and
Nallathambi J: Oxidative stress induces dysregulated autophagy in
corneal epithelium of keratoconus patients. PLoS One.
12:e1846282017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Piemontese M, Onal M, Xiong J, Han L,
Thostenson JD, Almeida M and O'Brien CA: Low bone mass and changes
in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the
osteoblast lineage. Sci Rep. 6:242622016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu W, Dai N, Wang Y, Xu C, Zhao H, Xia P,
Gu J, Liu X, Bian J, Yuan Y, et al: Role of autophagy in
cadmium-induced apoptosis of primary rat osteoblasts. Sci Rep.
6:204042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nollet M, Santucci-Darmanin S, Breuil V,
Al-Sahlanee R, Cros C, Topi M, Momier D, Samson M, Pagnotta S,
Cailleteau L, et al: Autophagy in osteoblasts is involved in
mineralization and bone homeostasis. Autophagy. 10:1965–1977. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xi G, Rosen CJ and Clemmons DR: IGF-I and
IGFBP-2 stimulate AMPK activation and autophagy, which are required
for osteoblast differentiation. Endocrinology. 157:268–281. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cinque L, Forrester A, Bartolomeo R,
Svelto M, Venditti R, Montefusco S, Polishchuk E, Nusco E, Rossi A,
Medina DL, et al: FGF signalling regulates bone growth through
autophagy. Nature. 528:272–275. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cheng Y, Qiu F, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: ERK and JNK mediate TNFalpha-induced p53 activation in
apoptotic and autophagic L929 cell death. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 376:483–488. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu P, Zhang Z, Wang Q, Guo R and Mei W:
Lithium chloride facilitates autophagy following spinal cord injury
via ERK-dependent pathway. Neurotox Res. 32:535–543. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang A, Zhang H, Liang Z, Xu K, Qiu W,
Tian Y, Guo H, Jia J, Xing E, Chen R, et al: U0126 attenuates
ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis and autophagy in myocardium
through MEK/ERK/EGR-1 pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 788:280–285. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|