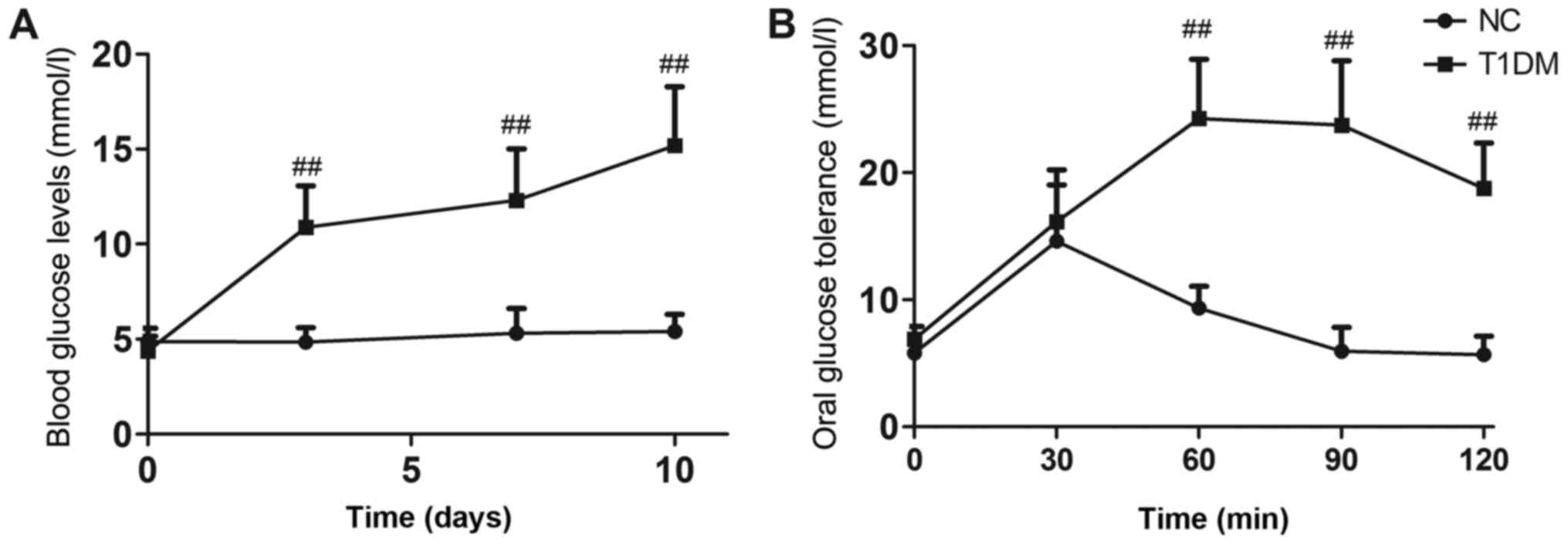
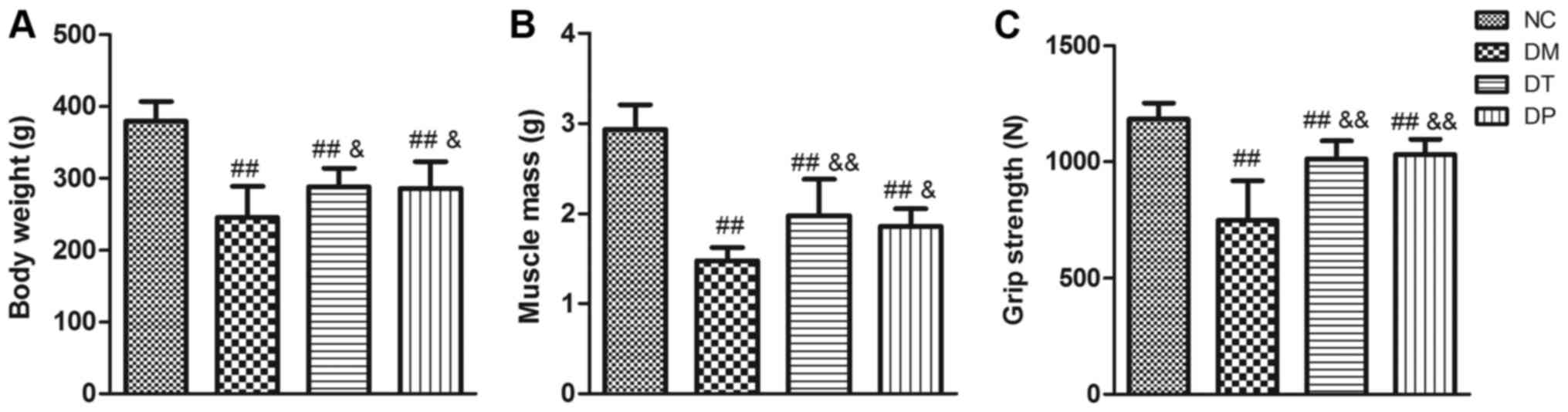
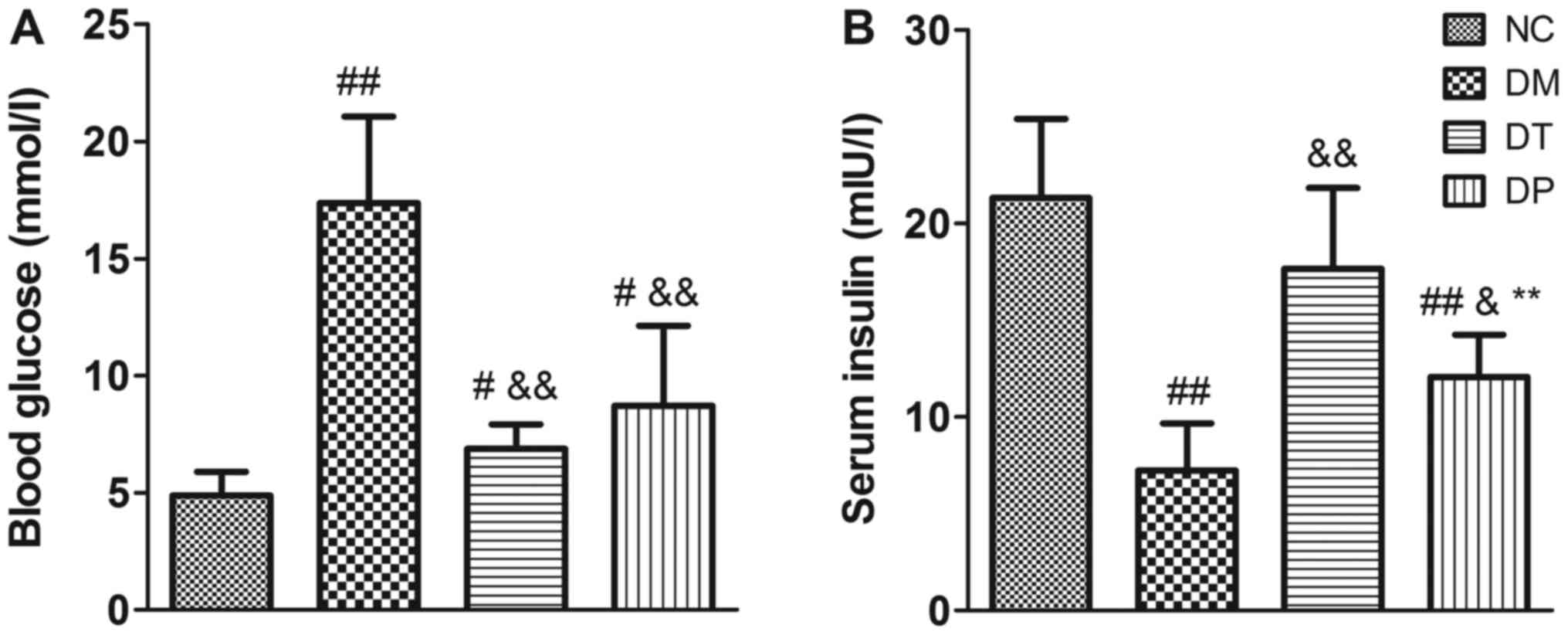
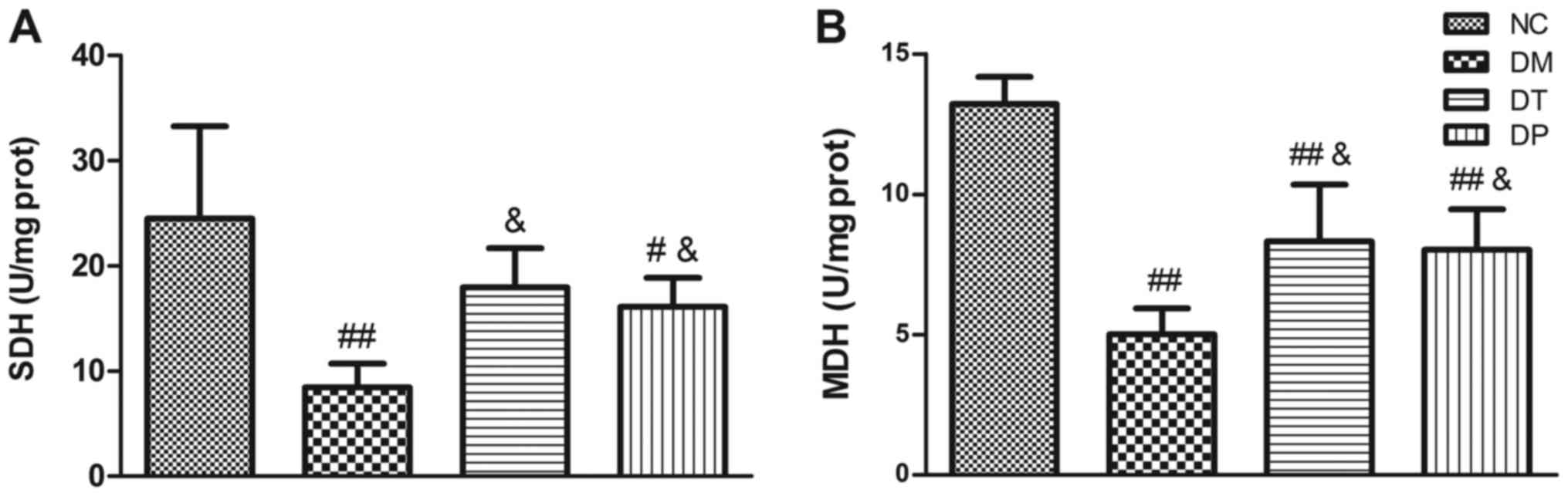
|
1
|
Atkinson MA and Eisenbarth GS: Type 1
diabetes: New perspectives on disease pathogenesis and treatment.
Lancet. 358:221–229. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Andersen H, Gjerstad MD and Jakobsen J:
Atrophy of foot muscles: A measure of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes
Care. 27:2382–2385. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fritzsche K, Blüher M, Schering S,
Buchwalow IB, Kern M, Linke A, Oberbach A, Adams V and Punkt K:
Metabolic profile and nitric oxide synthase expression of skeletal
muscle fibers are altered in patients with type 1 diabetes. Exp
Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 116:606–613. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Krause MP, Riddell MC, Gordon CS, Imam SA,
Cafarelli E and Hawke TJ: Diabetic myopathy differs between
Ins2Akita+/- and streptozotocin-induced Type 1 diabetic models. J
Appl Physiol (1985). 106:1650–1659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jakobsen J and Reske-Nielsen E: Diffuse
muscle fiber atrophy in newly diagnosed diabetes. Clin Neuropathol.
5:73–77. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Riddell MC and Iscoe KE: Physical
activity, sport, and pediatric diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 7:60–70.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hulmi JJ, Silvennoinen M, Lehti M, Kivelä
R and Kainulainen H: Altered REDD1, myostatin, and
Akt/mTOR/FoxO/MAPK signaling in streptozotocin-induced diabetic
muscle atrophy. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 302:E307–E315. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang L, Liu CT, Wang XD, Luo K, Zhang DD,
Chi AP, Zhang J and Sun LJ: A prepared anti-MSTN polyclonal
antibody reverses insulin resistance of diet-induced obese rats via
regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR&FoxO1 signal pathways. Biotechnol
Lett. 36:2417–2423. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McPherron AC, Lawler AM and Lee SJ:
Regulation of skeletal muscle mass in mice by a new TGF-beta
superfamily member. Nature. 387:83–90. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Glass DJ: PI3 kinase regulation of
skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy. Curr Top Microbiol
Immunol. 346:267–278. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chang CW and Lien IN: Tardy effect of
neurogenic muscular atrophy by magnetic stimulation. Am J Phys Med
Rehabil. 73:275–279. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livingstone SJ, Levin D, Looker HC,
Lindsay RS, Wild SH, Joss N, Leese G, Leslie P, McCrimmon RJ,
Metcalfe W, et al: Estimated life expectancy in a Scottish cohort
with type 1 diabetes, 2008–2010. JAMA. 313:37–44. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu H, Zhang J, Lei Y, Han Z, Rong D, Yu Q,
Zhao M and Tian J: Low frequency pulsed electromagnetic field
promotes C2C12 myoblasts proliferation via activation of MAPK/ERK
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 479:97–102. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu M, Lee C, Laron D, Zhang N, Waldorff
EI, Ryaby JT, Feeley B and Liu X: Role of pulsed electromagnetic
fields (PEMF) on tenocytes and myoblasts-potential application for
treating rotator cuff tears. J Orthop Res. 35:956–964. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tucker JJ, Cirone JM, Morris TR, Nuss CA,
Huegel J, Waldorff EI, Zhang N, Ryaby JT and Soslowsky LJ: Pulsed
electromagnetic field therapy improves tendon-to-bone healing in a
rat rotator cuff repair model. J Orthop Res. 35:902–909. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fricke O, Seewi O, Semler O, Tutlewski B,
Stabrey A and Schoenau E: The influence of auxology and long-term
glycemic control on muscle function in children and adolescents
with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact.
8:188–195. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Junod A, Lambert AE, Stauffacher W and
Renold AE: Diabetogenic action of streptozotocin: Relationship of
dose to metabolic response. J Clin Invest. 48:2129–2139. 1969.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li RJ, Qiu SD, Tian H and Zhou SW:
Diabetes induced by multiple low doses of STZ can be spontaneously
recovered in adult mice. Dongwuxue Yanjiu. 34:238–243. 2013.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tsai CC, Chan P, Chen LJ, Chang CK, Liu Z
and Lin JW: Merit of ginseng in the treatment of heart failure in
type 1-like diabetic rats. Biomed Res Int. 2014:4841612014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lewis MI, Fournier M, Wang H, Storer TW,
Casaburi R and Kopple JD: Effect of endurance and/or strength
training on muscle fiber size, oxidative capacity, and capillarity
in hemodialysis patients. J Appl Physiol (1985). 119:865–871. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Eprintsev AT, Falaleeva MI, Lyashchenko
MS, Gataullinaa MO and Kompantseva EI: Isoformes of malate
dehydrogenase from rhodovulum steppense A-20s grown
chemotrophically under aerobic condtions. Prikl Biokhim Mikrobiol.
52:168–173. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen V and Ianuzzo CD: Metabolic
alterations in skeletal muscle of chronically
streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 217:131–138.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ianuzzo CD and Armstrong RB:
Phosphofructokinase and succinate dehydrogenase activities of
normal and diabetic rat skeletal muscle. Horm Metab Res. 8:244–245.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cai F: Studies of enzyme histochemistry
and ultrastructure of the myocardium in rats with
streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 69276–278.
(20)1989.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jia Q, Ma S, Liu X, Li S, Wang Y, Gao Q
and Yang R: Effects of hydrogen sulfide on contraction capacity of
diaphragm from type 1 diabetic rats. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi
Xue Ban. 41:496–501. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee SJ: Sprinting without myostatin: A
genetic determinant of athletic prowess. Trends Genet. 23:475–477.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rebbapragada A, Benchabane H, Wrana JL,
Celeste AJ and Attisano L: Myostatin signals through a transforming
growth factor beta-like signaling pathway to block adipogenesis.
Mol Cell Biol. 23:7230–7242. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee SJ: Regulation of muscle mass by
myostatin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 20:61–86. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jeong J, Conboy MJ and Conboy IM:
Pharmacological inhibition of myostatin/TGF-β receptor/pSmad3
signaling rescues muscle regenerative responses in mouse model of
type 1 diabetes. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 34:1052–1060. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sriram S, Subramanian S, Juvvuna PK,
McFarlane C, Salerno MS, Kambadur R and Sharma M: Myostatin induces
DNA damage in skeletal muscle of streptozotocin-induced type 1
diabetic mice. J Biol Chem. 289:5784–5798. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Glass DJ: Skeletal muscle hypertrophy and
atrophy signaling pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 37:1974–1984.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Leger B, Cartoni R, Praz M, Lamon S,
Dériaz O, Crettenand A, Gobelet C, Rohmer P, Konzelmann M, Luthi F
and Russell AP: Akt signalling through GSK-3beta, mTOR and Foxo1 is
involved in human skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy. J
Physiol. 576:923–933. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dang K, Li YZ, Gong LC, Xue W, Wang HP,
Goswami N and Gao YF: Stable atrogin-1 (Fbxo32) and MuRF1 (Trim63)
gene expression is involved in the protective mechanism in soleus
muscle of hibernating Daurian ground squirrels (Spermophilus
dauricus). Biol Open. 5:62–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bodine SC, Stitt TN, Gonzalez M, Kline WO,
Stover GL, Bauerlein R, Zlotchenko E, Scrimgeour A, Lawrence JC,
Glass DJ and Yancopoulos GD: Akt/mTOR pathway is a crucial
regulator of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and can prevent muscle
atrophy in vivo. Nat Cell Biol. 3:1014–1019. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hoffman EP and Nader GA: Balancing muscle
hypertrophy and atrophy. Nat Med. 10:584–585. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rodriguez J, Vernus B, Chelh I,
Cassar-Malek I, Gabillard JC, Sassi Hadj A, Seiliez I, Picard B and
Bonnieu A: Myostatin and the skeletal muscle atrophy and
hypertrophy signaling pathways. Cell Mol Life Sci. 71:4361–4371.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kamei Y, Miura S, Suzuki M, Kai Y,
Mizukami J, Taniguchi T, Mochida K, Hata T, Matsuda J, Aburatani H,
et al: Skeletal muscle FOXO1 (FKHR) transgenic mice have less
skeletal muscle mass, down-regulated Type I (slow twitch/red
muscle) fiber genes, and impaired glycemic control. J Biol Chem.
279:41114–41123. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bonaldo P and Sandri M: Cellular and
molecular mechanisms of muscle atrophy. Dis Model Mech. 6:25–39.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang J, Zhuang P, Wang Y, Song L, Zhang
M, Lu Z, Zhang L, Wang J, Alemu PN, Zhang Y, et al: Reversal of
muscle atrophy by Zhimu-Huangbai herb-pair via Akt/mTOR/FoxO3
signal pathway in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. PLoS One.
9:e1009182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Patterson TE, Sakai Y, Grabiner MD,
Ibiwoye M, Midura RJ, Zborowski M and Wolfman A: Exposure of murine
cells to pulsed electromagnetic fields rapidly activates the mTOR
signaling pathway. Bioelectromagnetics. 27:535–544. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|