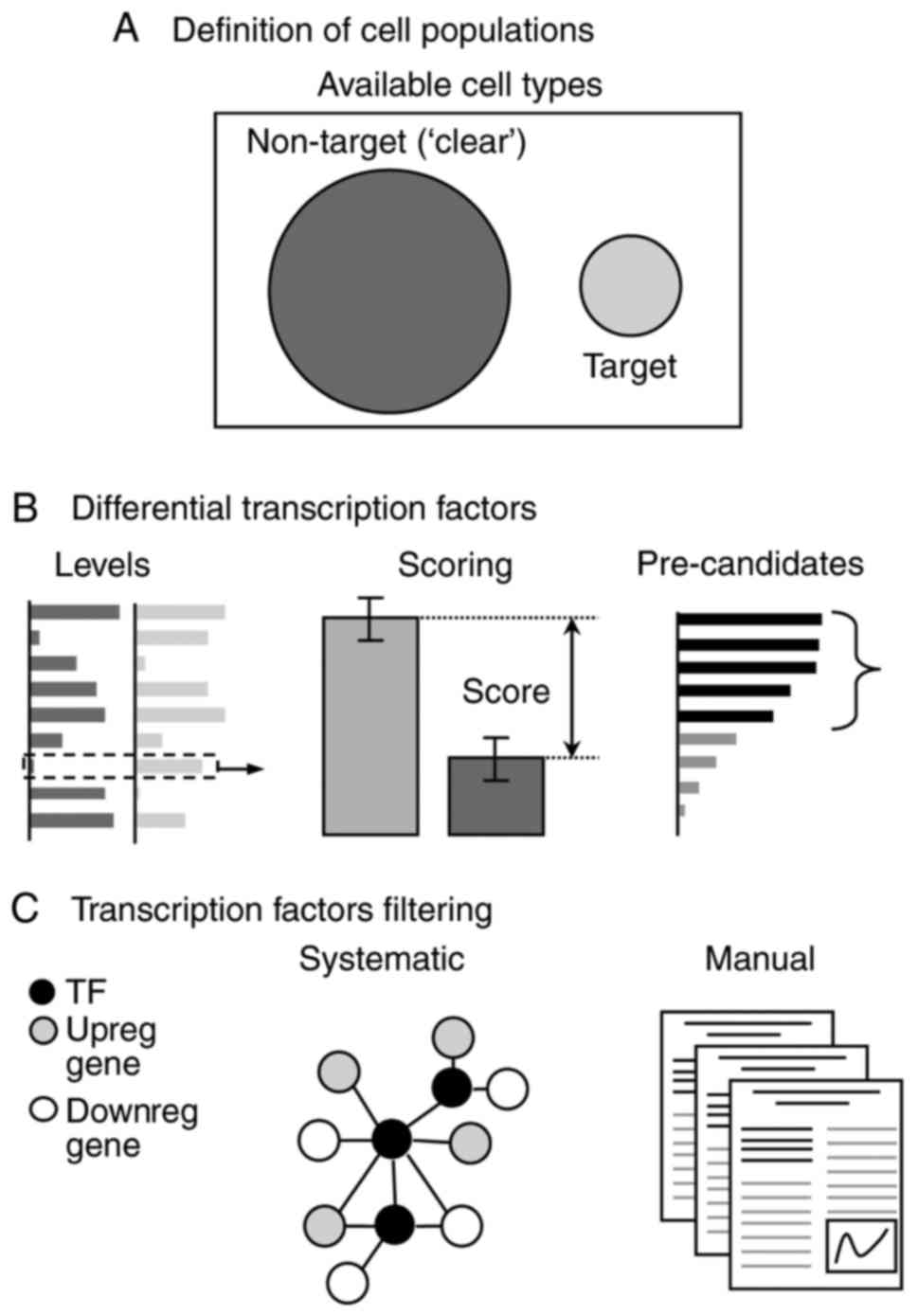
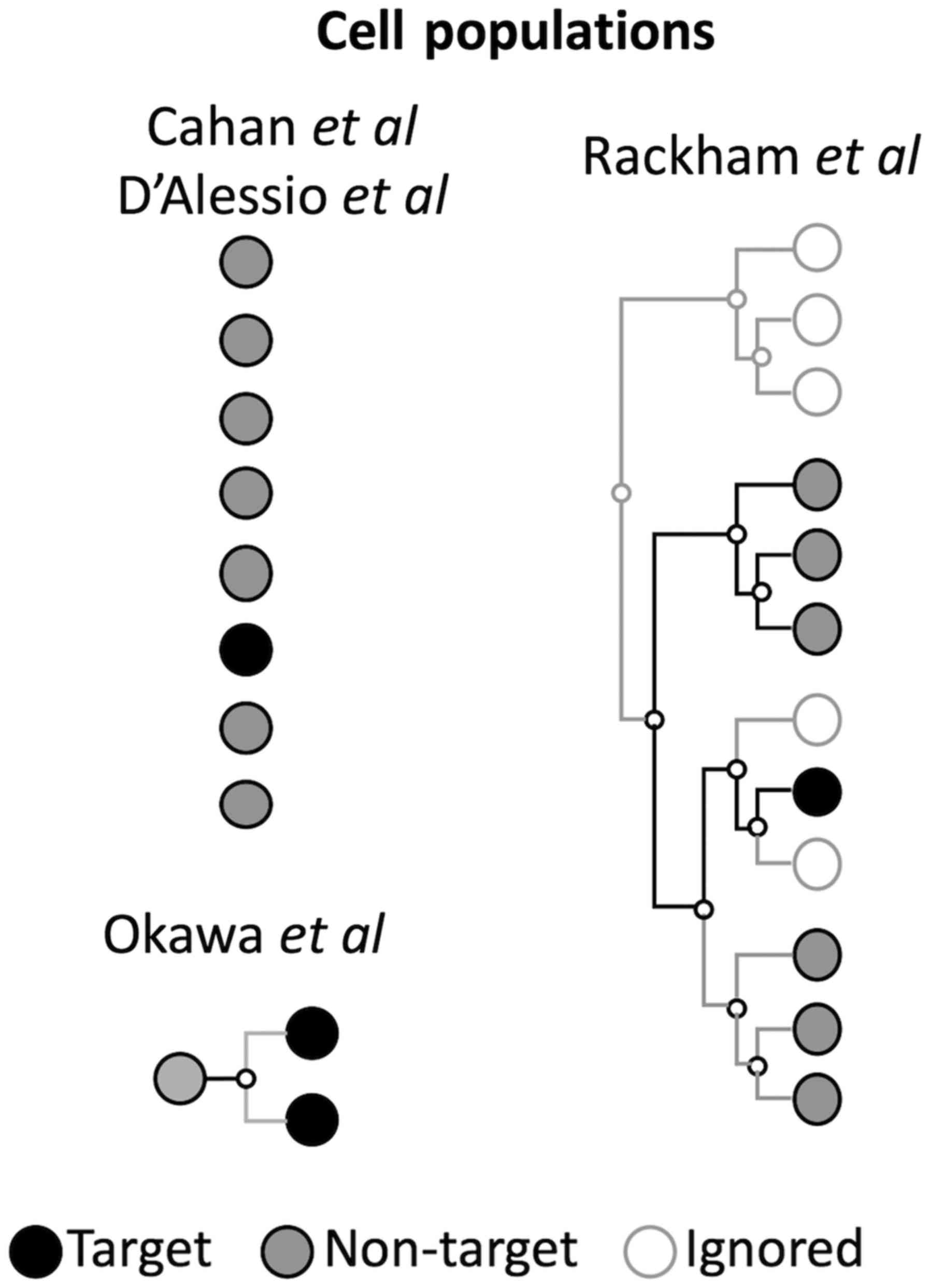
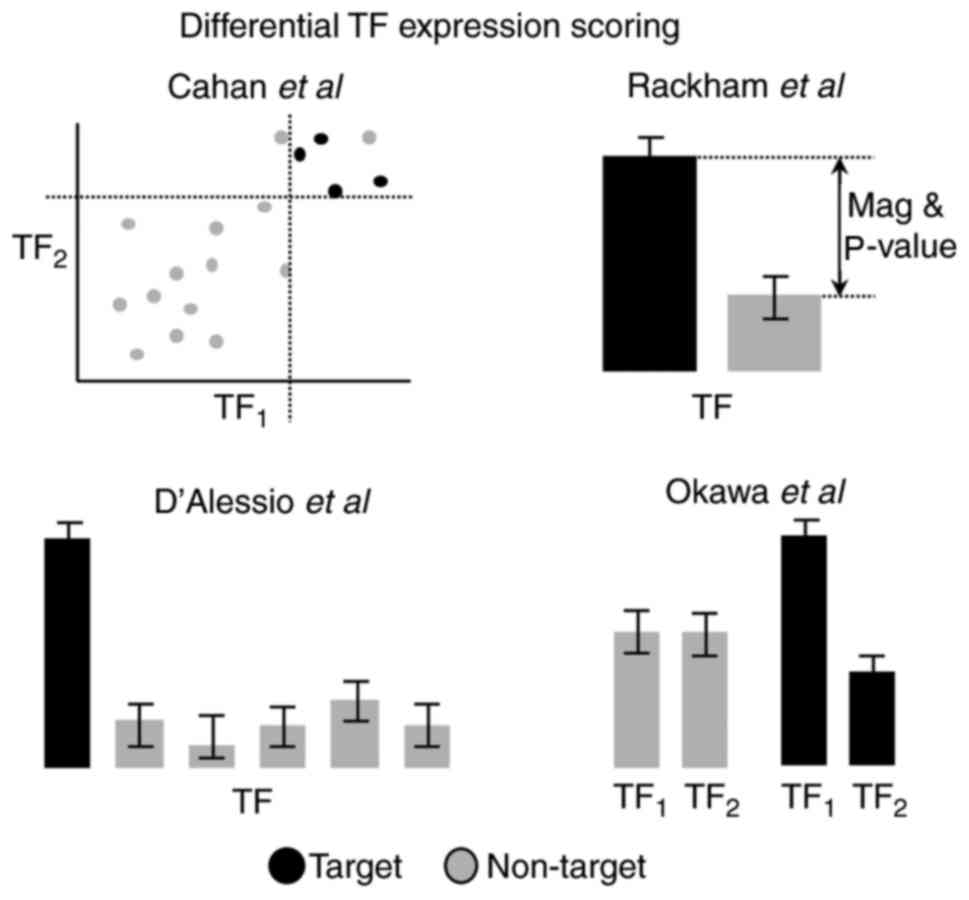
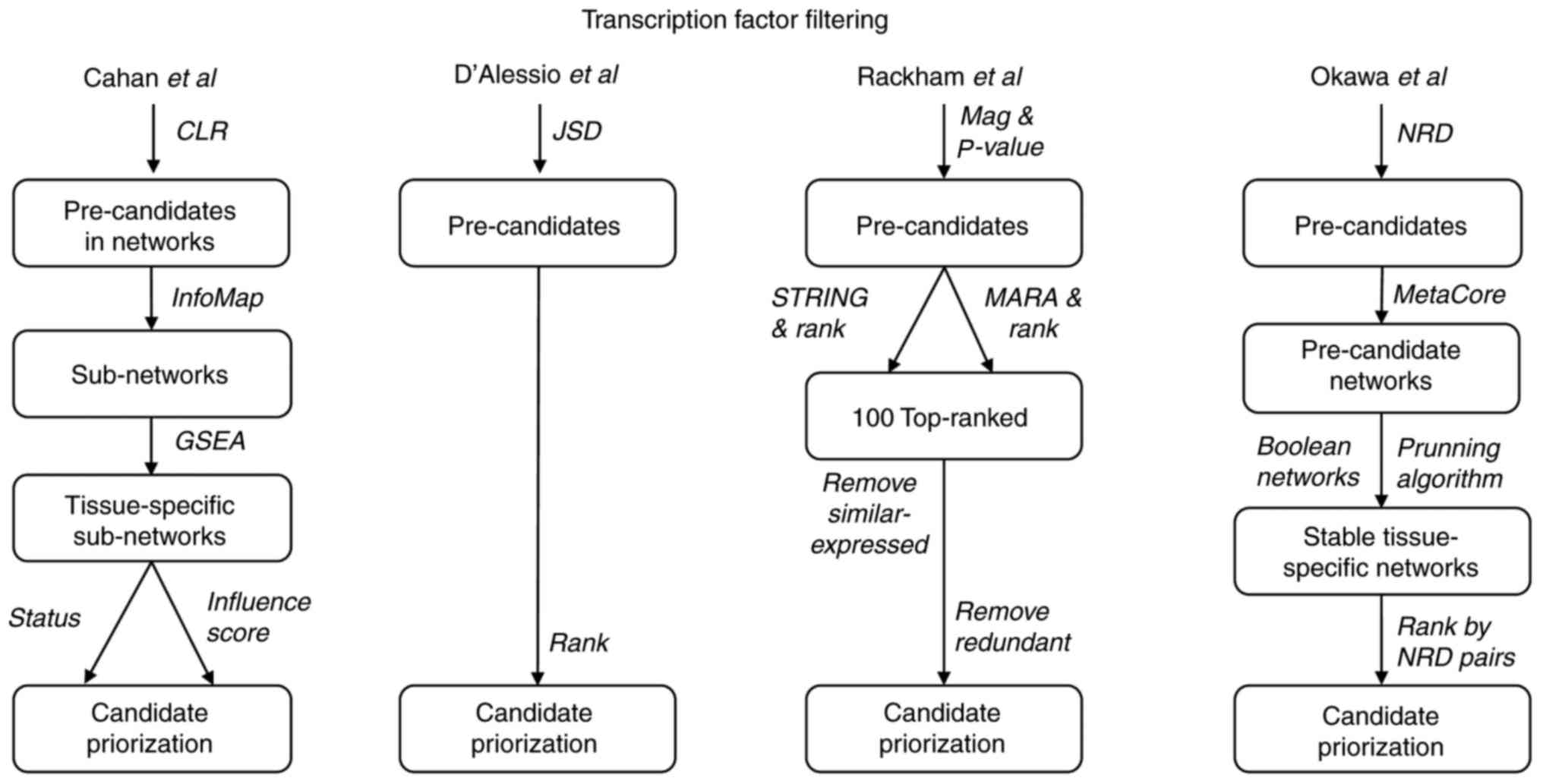
|
1
|
Meguid Abdel E, Ke Y, Ji J and El-Hashash
AHK: Stem cells applications in bone and tooth repair and
regeneration: New insights, tools and hopes. J Cell Physiol.
233:1825–1835. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tabar V and Studer L: Pluripotent stem
cells in regenerative medicine: Challenges and recent progress. Nat
Rev Genet. 15:82–92. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Valdez-Garcia JE, Zavala J and Trevino V:
Current state and future perspectives in corneal endothelium
differentiationFrontiers in Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine
Research. Atta-ur-Rahman and Anjum S: Bentham: 2017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mora C, Serzanti M, Consiglio A, Memo M
and Dell'Era P: Clinical potentials of human pluripotent stem
cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 33:351–360. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
López-González R and Velasco I:
Therapeutic potential of motor neurons differentiated from
embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. Arch Med
Res. 43:1–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lizio M, Harshbarger J, Shimoji H, Severin
J, Kasukawa T, Sahin S, Abugessaisa I, Fukuda S, Hori F,
Ishikawa-Kato S, et al: Gateways to the FANTOM5 promoter level
mammalian expression atlas. Genome Biol. 16:222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li M and Belmonte JC: Ground rules of the
pluripotency gene regulatory network. Nat Rev Genet. 18:180–191.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li M, Liu G and Belmonte Izpisua JC:
Navigating the epigenetic landscape of pluripotent stem cells. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:524–535. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moris N, Pina C and Arias AM: Transition
states and cell fate decisions in epigenetic landscapes. Nat Rev
Genet. 17:693–703. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vaquerizas JM, Kummerfeld SK, Teichmann SA
and Luscombe NM: A census of human transcription factors: Function,
expression and evolution. Nat Rev Genet. 10:252–263. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Frum T and Ralston A: Cell signaling and
transcription factors regulating cell fate during formation of the
mouse blastocyst. Trends Genet. 31:402–410. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Morris SA: Direct lineage reprogramming
via pioneer factors; a detour through developmental gene regulatory
networks. Development. 143:2696–2705. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Iwafuchi-Doi M and Zaret KS: Cell fate
control by pioneer transcription factors. Development.
143:1833–1837. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M,
Ichisaka T, Tomoda K and Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem
cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell.
131:861–872. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vierbuchen T, Ostermeier A, Pang ZP,
Kokubu Y, Südhof TC and Wernig M: Direct conversion of fibroblasts
to functional neurons by defined factors. Nature. 463:1035–1041.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ieda M, Fu JD, Delgado-Olguin P, Vedantham
V, Hayashi Y, Bruneau BG and Srivastava D: Direct reprogramming of
fibroblasts into functional cardiomyocytes by defined factors.
Cell. 142:375–386. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Protze S, Khattak S, Poulet C, Lindemann
D, Tanaka EM and Ravens U: A new approach to transcription factor
screening for reprogramming of fibroblasts to cardiomyocyte-like
cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 53:323–332. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bonilla-Porras AR, Velez-Pardo C and
Jimenez-Del-Rio M: Fast transdifferentiation of human Wharton's
jelly mesenchymal stem cells into neurospheres and nerve-like
cells. J Neurosci Methods. 282:52–60. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Abad M, Hashimoto H, Zhou H, Morales MG,
Chen B, Bassel-Duby R and Olson EN: Notch inhibition enhances
cardiac reprogramming by increasing MEF2C transcriptional activity.
Stem Cell Rep. 8:548–560. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Islas JF, Liu Y, Weng KC, Robertson MJ,
Zhang S, Prejusa A, Harger J, Tikhomirova D, Chopra M, Iyer D, et
al: Transcription factors ETS2 and MESP1 transdifferentiate human
dermal fibroblasts into cardiac progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 109:13016–13021. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Waddington CH: The strategy of the genes.
Routledge: 1957
|
|
23
|
Cahan P, Li H, Morris SA, Da Rocha
Lummertz E, Daley GQ and Collins JJ: CellNet: Network biology
applied to stem cell engineering. Cell. 158:903–915. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
D'Alessio AC, Fan ZP, Wert KJ, Baranov P,
Cohen MA, Saini JS, Cohick E, Charniga C, Dadon D, Hannett NM, et
al: A systematic approach to identify candidate transcription
factors that control cell identity. Stem Cell Reports. 5:763–775.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rackham OJL, Firas J, Fang H, Oates ME,
Holmes ML and Knaupp AS: FANTOM Consortium, Suzuki H, Nefzger CM,
Daub CO, et al: A predictive computational framework for
direct reprogramming between human cell types. Nat Genet.
48:331–335. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Okawa S, Nicklas S, Zickenrott S,
Schwamborn JC and Del Sol A: A generalized gene-regulatory network
model of stem cell differentiation for predicting lineage
specifiers. Stem Cell Rep. 7:307–315. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Barrett T, Suzek TO, Troup DB, Wilhite SE,
Ngau WC, Ledoux P, Rudnev D, Lash AE, Fujibuchi W and Edgar R: NCBI
GEO: Mining millions of expression profiles-database and tools.
Nucleic Acids Res. 33:(Database Issue). D562–D566. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:(Database Issue).
D991–D995. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Parkinson H, Kapushesky M, Shojatalab M,
Abeygunawardena N, Coulson R, Farne A, Holloway E, Kolesnykov N,
Lilja P, Lukk M, et al: ArrayExpress-a public database of
microarray experiments and gene expression profiles. Nucleic Acids
Res. 35:(Database Issue). D747–D750. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kolesnikov N, Hastings E, Keays M,
Melnichuk O, Tang YA, Williams E, Dylag M, Kurbatova N, Brandizi M,
Burdett T, et al: ArrayExpress update-simplifying data submissions.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43:(Database Issue). D1113–D1116. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rosenbloom KR, Sloan CA, Malladi VS,
Dreszer TR, Learned K, Kirkup VM, Wong MC, Maddren M, Fang R,
Heitner SG, et al: ENCODE Data in the UCSC genome browser: Year 5
update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:(Database Issue). D56–D63. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim SY, Lee JW and Sohn IS: Comparison of
various statistical methods for identifying differential gene
expression in replicated microarray data. Stat Methods Med Res.
15:3–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang HC, Niu Y and Qin LX: Differential
expression analysis for RNA-Seq: An overview of statistical methods
and computational software. Cancer Inform. 14 Suppl 1:S57–S67.
2015.
|
|
34
|
Seyednasrollah F, Laiho A and Elo LL:
Comparison of software packages for detecting differential
expression in RNA-seq studies. Brief Bioinform. 16:59–70. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sullivan GM and Feinn R: Using effect
size-or why the P value is not enough. J Grad Med Educ. 4:279–282.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang S, Guo YP, May G and Enver T:
Bifurcation dynamics in lineage-commitment in bipotent progenitor
cells. Dev Biol. 305:695–713. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jacob F and Monod J: Genetic regulatory
mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 3:318–356.
1961. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Roeder I and Glauche I: Towards an
understanding of lineage specification in hematopoietic stem cells:
A mathematical model for the interaction of transcription factors
GATA-1 and PU.1. J Theor Biol. 241:852–865. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Faith JJ, Hayete B, Thaden JT, Mogno I,
Wierzbowski J, Cottarel G, Kasif S, Collins JJ and Gardner TS:
Large-scale mapping and validation of escherichia coli
transcriptional regulation from a compendium of expression
profiles. PLoS Biol. 5:e82007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rosvall M and Bergstrom CT: Maps of random
walks on complex networks reveal community structure. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:1118–1123. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
FANTOM Consortium H, . Suzuki H, Forrest
AR, van Nimwegen E, Daub CO, Balwierz PJ, Irvine KM, Lassmann T,
Ravasi T, Hasegawa Y, et al: The transcriptional network that
controls growth arrest and differentiation in a human myeloid
leukemia cell line. Nat Genet. 41:553–562. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:(Database Issue). D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nikolsky Y, Ekins S, Nikolskaya T and
Bugrim A: A novel method for generation of signature networks as
biomarkers from complex high throughput data. Toxicol Lett.
158:20–29. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Crespo I and Del Sol A: A general strategy
for cellular reprogramming: The importance of transcription factor
cross-repression. Stem Cells. 31:2127–2135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kauffman SA: Homeostasis and
differentiation in random genetic control networks. Nature.
224:177–178. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang HM, Liu T, Liu CJ, Song S, Zhang X,
Liu W, Jia H, Xue Y and Guo AY: AnimalTFDB 2.0: A resource for
expression, prediction and functional study of animal transcription
factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:(Database Issue). D76–D81. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xiang FL, Guo M and Yutzey KE:
Overexpression of Tbx20 in adult cardiomyocytes promotes
proliferation and improves cardiac function after myocardial
infarction. Circulation. 133:1081–1092. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chakraborty S and Yutzey KE: Tbx20
regulation of cardiac cell proliferation and lineage specialization
during embryonic and fetal development in vivo. Dev Biol.
363:234–246. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Addis RC, Ifkovits JL, Pinto F, Kellam LD,
Esteso P, Rentschler S, Christoforou N, Epstein JA and Gearhart JD:
Optimization of direct fibroblast reprogramming to cardiomyocytes
using calcium activity as a functional measure of success. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 60:97–106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fu JD, Stone NR, Liu L, Spencer CI, Qian
L, Hayashi Y, Delgado-Olguin P, Ding S, Bruneau BG and Srivastava
D: Direct reprogramming of human fibroblasts toward a
cardiomyocyte-like state. Stem Cell Reports. 1:235–247. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chen O and Qian L: Direct cardiac
reprogramming: Advances in cardiac regeneration. Biomed Res Int.
2015:5804062015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ieda M, Tsuchihashi T, Ivey KN, Ross RS,
Hong TT, Shaw RM and Srivastava D: Cardiac fibroblasts regulate
myocardial proliferation through beta1 integrin signaling. Dev
Cell. 16:233–244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rastegar-Pouyani S, Khazaei N, Wee P,
Yaqubi M and Mohammadnia A: Meta-analysis of transcriptome
regulation during induction to cardiac myocyte fate from mouse and
human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 232:2053–2062. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kamaraj US, Gough J, Polo JM, Petretto E
and Rackham OJ: Computational methods for direct cell conversion.
Cell Cycle. 15:3343–3354. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ebrahimi B: Biological computational
approaches: New hopes to improve (re)programming robustness,
regenerative medicine and cancer therapeutics. Differentiation.
92:35–40. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Risebro CA, Searles RG, Melville AA, Ehler
E, Jina N, Shah S, Pallas J, Hubank M, Dillard M, Harvey NL, et al:
Prox1 maintains muscle structure and growth in the developing
heart. Development. 136:495–505. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu Q, Jiang C, Xu J, Zhao MT, Van Bortle
K, Cheng X, Wang G, Chang HY, Wu JC and Snyder MP: Genome-wide
temporal profiling of transcriptome and open chromatin of early
cardiomyocyte differentiation derived from hiPSCs and hESCs. Circ
Res. 121:376–391. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Shekhar A, Lin X, Liu FY, Zhang J, Mo H,
Bastarache L, Denny JC, Cox NJ, Delmar M, Roden DM, et al:
Transcription factor ETV1 is essential for rapid conduction in the
heart. J Clin Invest. 126:4444–4459. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Koizumi A, Sasano T, Kimura W, Miyamoto Y,
Aiba T, Ishikawa T, Nogami A, Fukamizu S, Sakurada H, Takahashi Y,
et al: Genetic defects in a His-Purkinje system transcription
factor, IRX3, cause lethal cardiac arrhythmias. Eur Heart J.
37:1469–1475. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Nam YS, Kim Y, Joung H, Kwon DH, Choe N,
Min HK, Kim YS, Kim HS, Kim DK, Cho YK, et al: Small heterodimer
partner blocks cardiac hypertrophy by interfering with GATA6
signaling. Circ Res. 115:493–503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Frausto RF, Wang C and Aldave AJ:
Transcriptome analysis of the human corneal endothelium. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 55:7821–7830. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Trevino V: Chi-Co-Express: A database of
human co-expression networks from global cell states. Manuscr Prep.
2017.
|
|
64
|
Li Q, Birkbak NJ, Gyorffy B, Szallasi Z
and Eklund AC: Jetset: Selecting the optimal microarray probe set
to represent a gene. BMC Bioinformatics. 12:4742011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Pressman CL, Chen H and Johnson RL: LMX1B,
a LIM homeodomain class transcription factor, is necessary for
normal development of multiple tissues in the anterior segment of
the murine eye. Genesis. 26:15–25. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Powell C, Cornblath E and Goldman D:
Zinc-binding domain-dependent, deaminase-independent actions of
apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide 2
(Apobec2), mediate its effect on zebrafish retina regeneration. J
Biol Chem. 289:28924–28941. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Chen L, Martino V, Dombkowski A, Williams
T, West-Mays J and Gage PJ: AP-2β is a downstream effector of PITX2
required to specify endothelium and establish angiogenic privilege
during corneal development. Invest Opthalmol Vis Sci. 57:1072–1081.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Bradley JL, Edwards CS and Fullard RJ:
Adaptation of impression cytology to enable conjunctival surface
cell transcriptome analysis. Curr Eye Res. 39:31–41. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Khor CC, Do T, Jia H, Nakano M, George R,
Abu-Amero K, Duvesh R, Chen LJ, Li Z, Nongpiur ME, et al:
Genome-wide association study identifies five new susceptibility
loci for primary angle closure glaucoma. Nat Genet. 48:556–562.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|