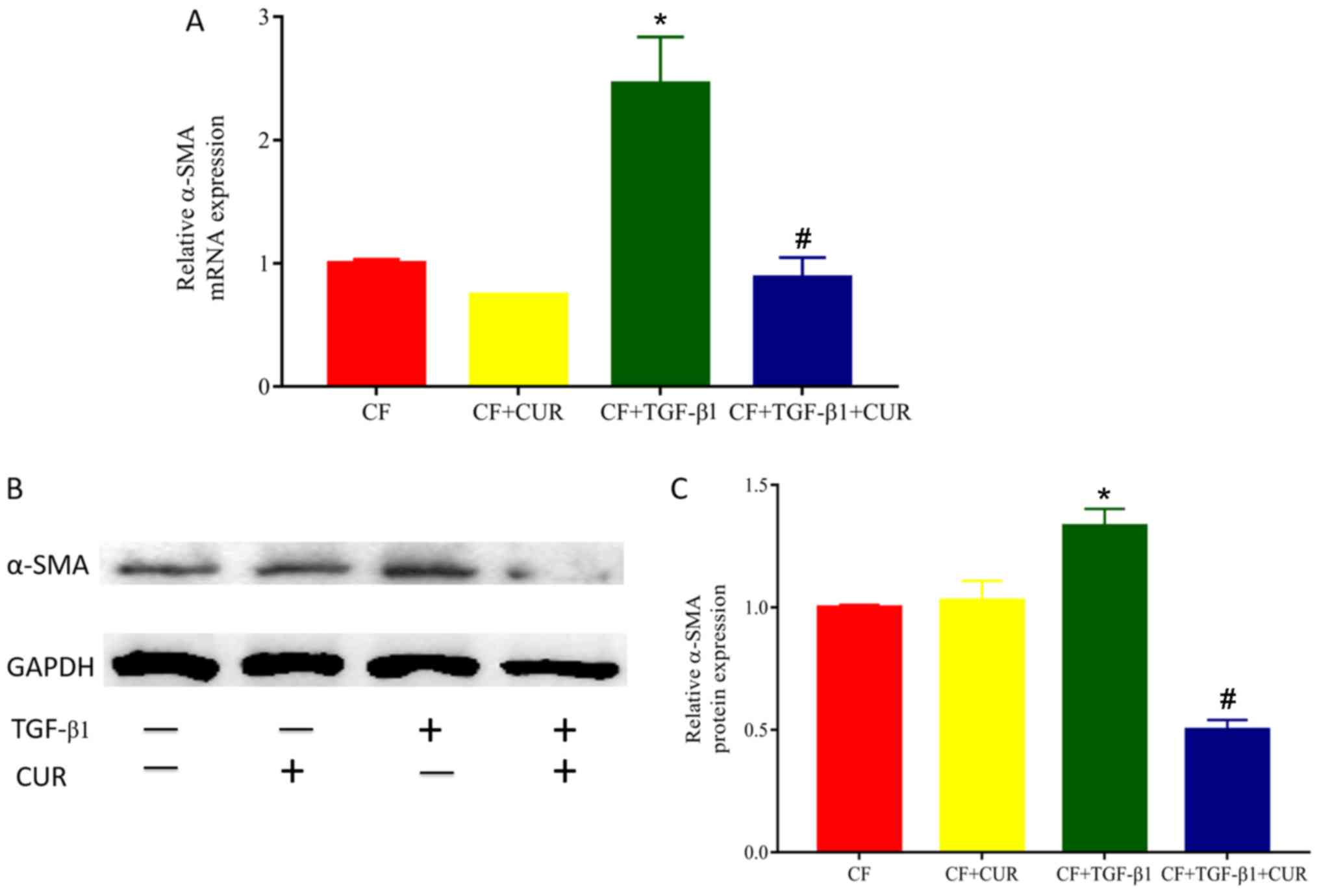
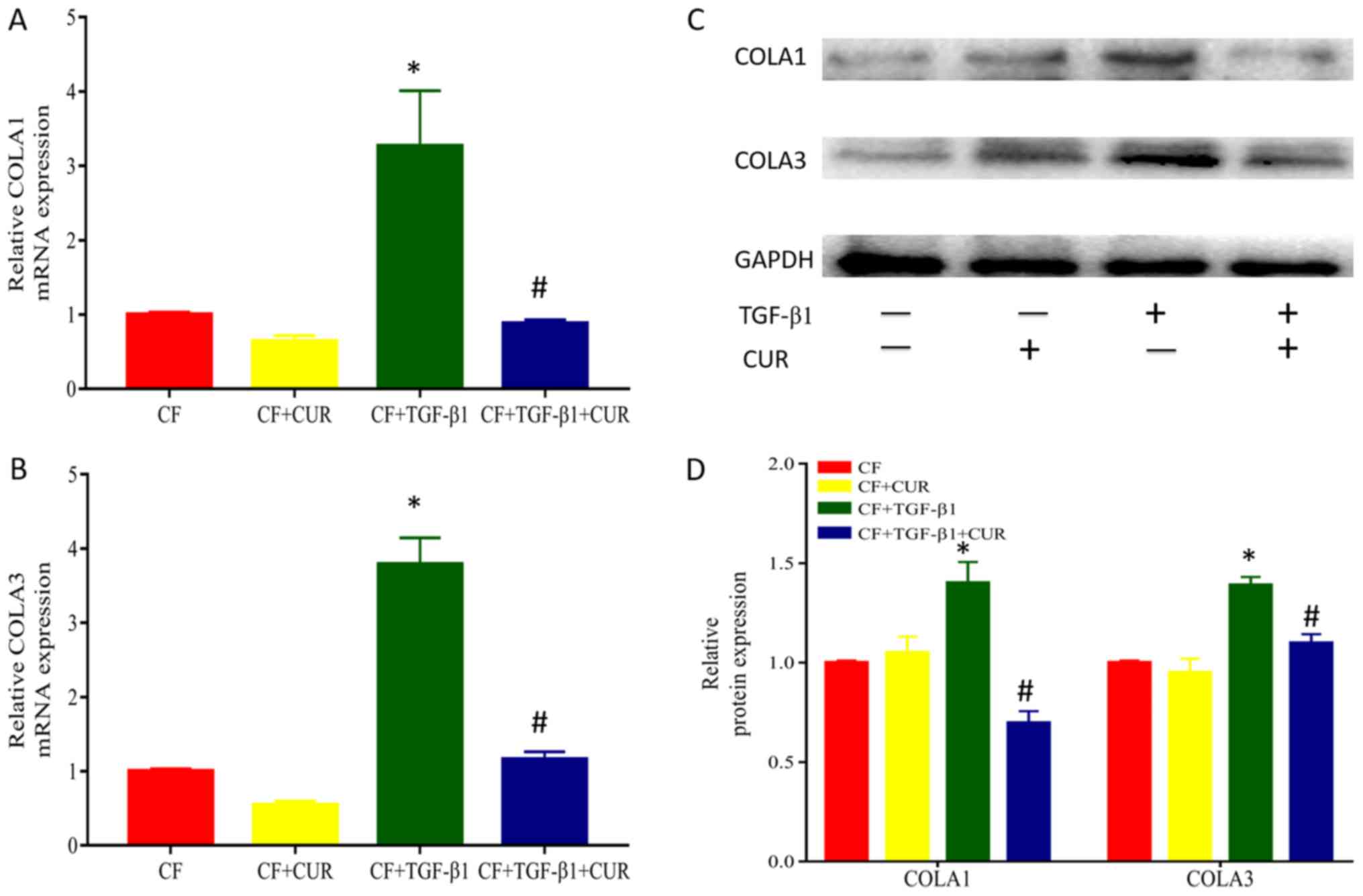
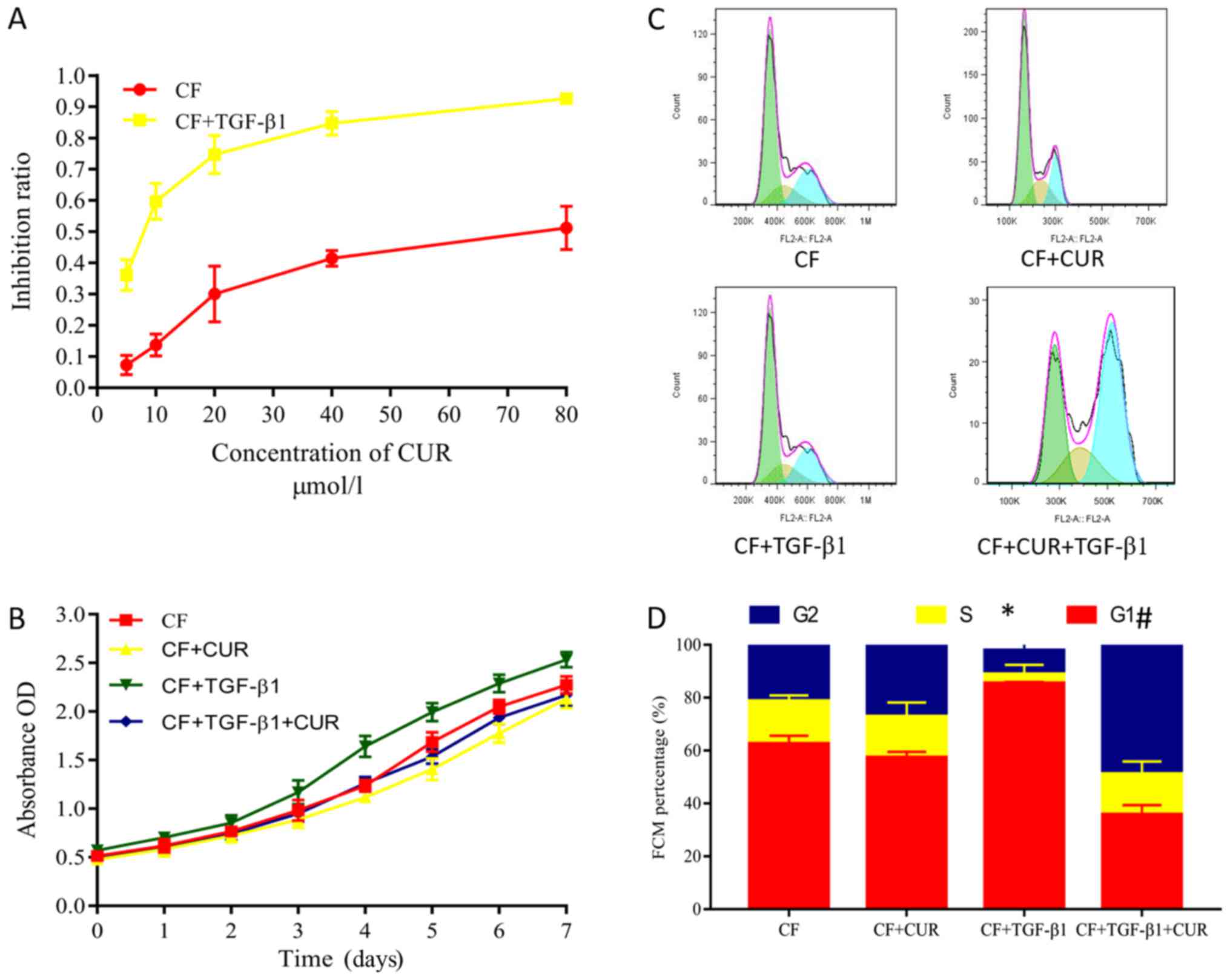
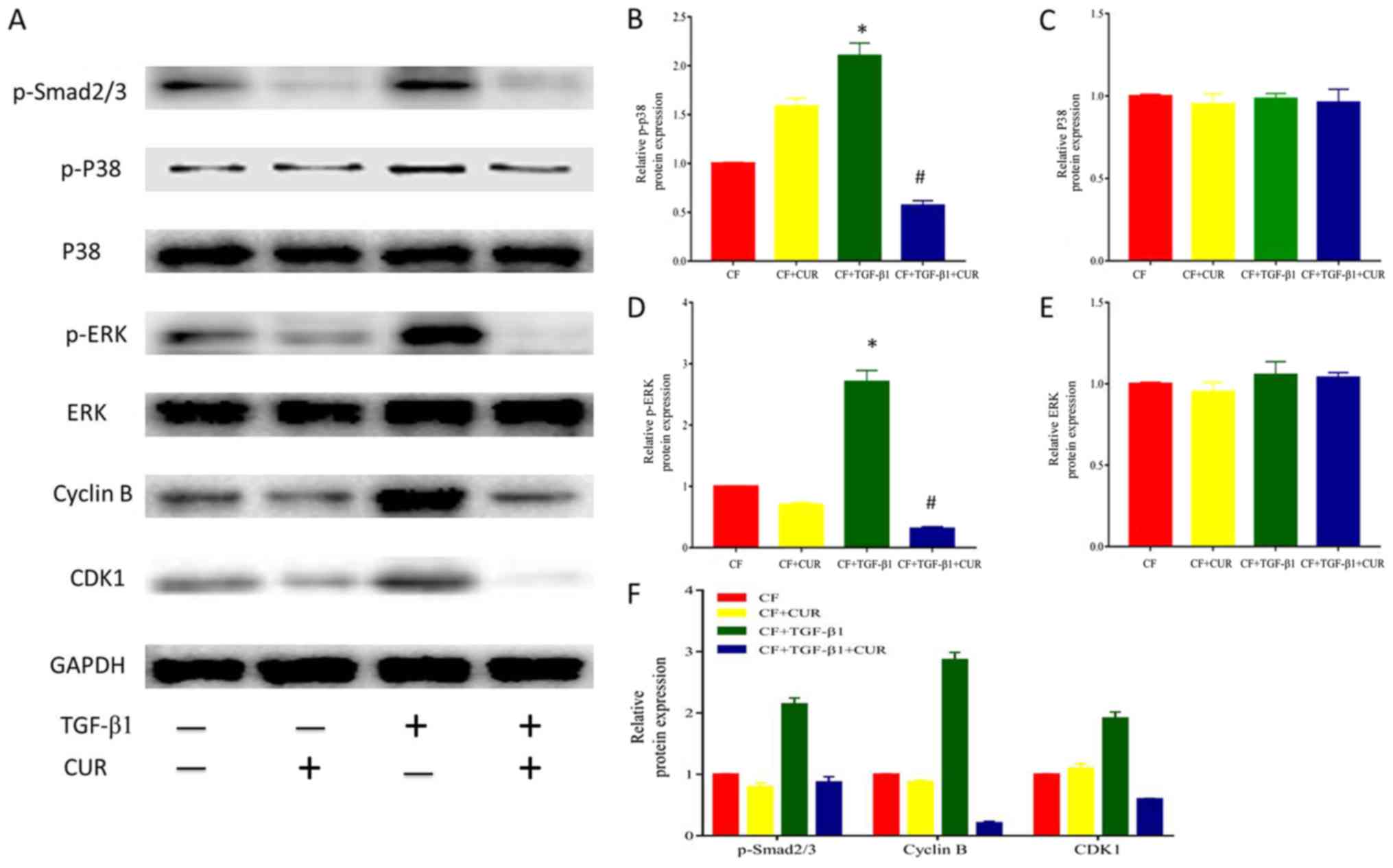
|
1
|
Schelbert EB, Piehler KM, Zareba KM, Moon
JC, Ugander M, Messroghli DR, Valeti US, Chang CC, Shroff SG, Diez
J, et al: Myocardial fibrosis quantified by extracellular volume is
associated with subsequent hospitalization for heart failure,
death, or both across the spectrum of ejection fraction and heart
failure stage. J Am Heart Assoc. 4:pii: e002613. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kong P, Christia P and Frangogiannis N:
The pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis. Cell Mol Life Sci.
71:549–574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Krenning G, Zeisberg E and Kalluri R: The
origin of fibroblasts and mechanism of cardiac fibrosis. J Cell
Physiol. 225:631–637. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khan R and Sheppard R: Fibrosis in heart
disease: Understanding the role of transforming growth factor-beta
in cardiomyopathy, valvular disease and arrhythmia. Immunology.
118:10–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ivey MJ and Tallquist MD: Defining the
cardiac fibroblast. Circ J. 80:2269–2276. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hewlings SJ and Kalman DS: Curcumin: A
review of its' effects on human health. Foods. 6:pii: E92. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hazarey VK, Sakrikar AR and Ganvir SM:
Efficacy of curcumin in the treatment for oral submucous fibrosis-A
randomized clinical trial. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 19:145–152.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen YN, Hsu SL, Liao MY, Liu YT, Lai CH,
Chen JF, Nguyen MT, Su YH, Chen ST and Wu LC: Ameliorative effect
of curcumin-encapsulated hyaluronic acid-PLA nanoparticles on
thioacetamide-induced murine hepatic fibrosis. Int J Environ Res
Public Health. 14:pii: E11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tyagi N, Dash D and Singh R: Curcumin
inhibits paraquat induced lung inflammation and fibrosis by
extracellular matrix modifications in mouse model.
Inflammopharmacology. 24:335–345. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu Y, Mou L, Yang F, Tu H and Lin W:
Curcumin attenuates cyclosporine A-induced renal fibrosis by
inhibiting hypermethylation of the klotho promoter. Mol Med Rep.
14:3229–3236. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu W, Wu J, Cai F, Xiang J, Zha W, Fan D,
Guo S, Ming Z and Liu C: Curcumin alleviates diabetic
cardiomyopathy in experimental diabetic rats. PLoS One.
7:e520132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang NP, Wang ZF, Tootle S, Philip T and
Zhao ZQ: Curcumin promotes cardiac repair and ameliorates cardiac
dysfunction following myocardial infarction. Br J Pharmacol.
167:1550–1562. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Meng Z, Yu XH, Chen J, Li L and Li S:
Curcumin attenuates cardiac fibrosis in spontaneously hypertensive
rats through PPAR-γ activation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:1247–1256.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chung CC, Kao YH, Liou JP and Chen YJ:
Curcumin suppress cardiac fibroblasts activities by regulating
proliferation, migration, and the extracellular matrix. Acta
Cardiol Sin. 30:474–482. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Porter KE and Turner NA: Cardiac
fibroblasts: At the heart of myocardial remodeling. Pharmacol Ther.
123:255–278. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
van den Borne SW, Diez J, Blankesteijn WM,
Verjans J, Hofstra L and Narula J: Myocardial remodeling after
infarction: The role of myofibroblasts. Nat Rev Cardiol. 7:30–37.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
de Haas HJ, Arbustini E, Fuster V, Kramer
CM and Narula J: Molecular imaging of the cardiac extracellular
matrix. Circ Res. 114:903–915. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li HL, Liu C, de Couto G, Ouzounian M, Sun
M, Wang AB, Huang Y, He CW, Shi Y, Chen X, et al: Curcumin prevents
and reverses murine cardiac hypertrophy. J Clin Invest.
118:879–893. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Canaud G and Bonventre JV: Cell cycle
arrest and the evolution of chronic kidney disease from acute
kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 30:575–583. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Derynck R and Zhang YE: Smad-dependent and
Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature.
425:577–584. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma J, Ma S and Ding CH: Curcumin reduces
cardiac fibrosis by inhibiting myofibroblast differentiation and
decreasing transforming growth factor β1 and matrix
metalloproteinase 9/tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1. Chin J
Integr Med. 23:362–369. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Voloshenyuk TG, Landesman ES, Khoutorova
E, Hart AD and Gardner JD: Induction of cardiac fibroblast lysyl
oxidase by TGF-β1 requires PI3 K/Akt, Smad3, and MAPK signaling.
Cytokine. 55:90–97. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang D, Liu X, Chen X, Gu J, Li F, Zhang
W and Zheng Y: Role of the MAPKs/TGF-β1/TRAF6 signaling pathway in
atrial fibrosis of patients with chronic atrial fibrillation and
rheumatic mitral valve disease. Cardiology. 129:216–223. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|