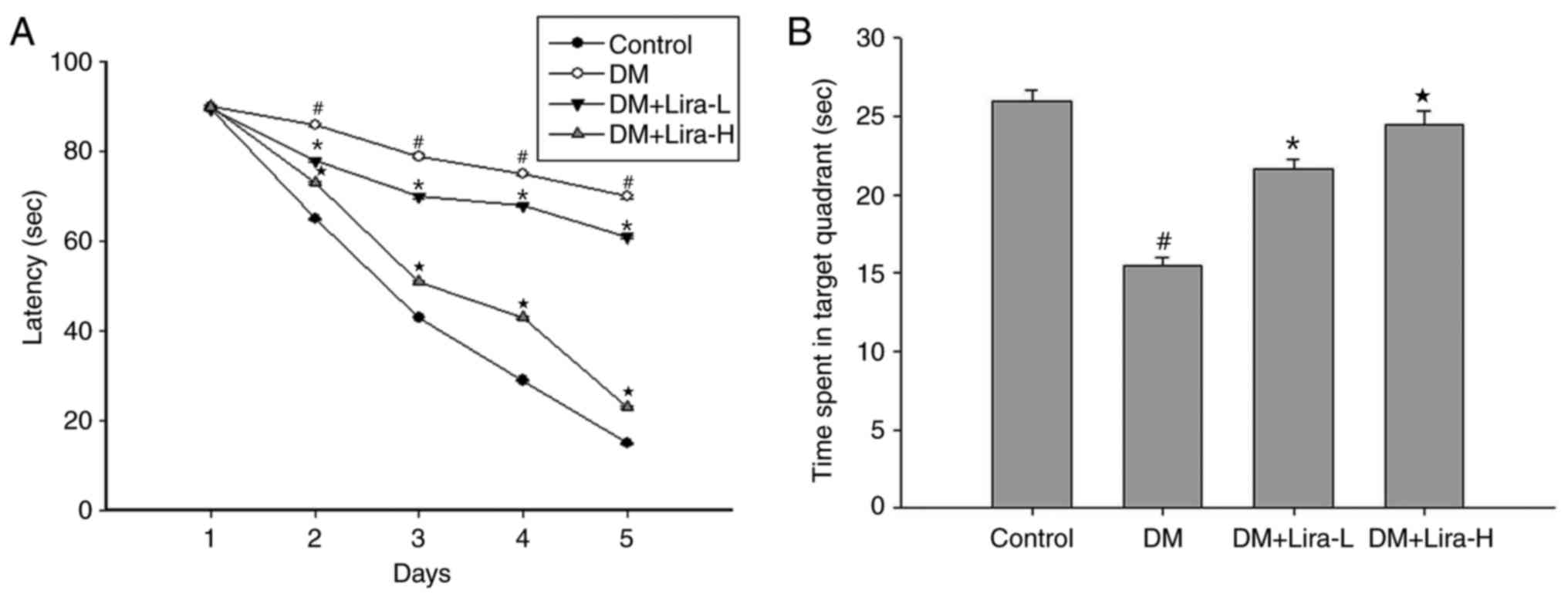
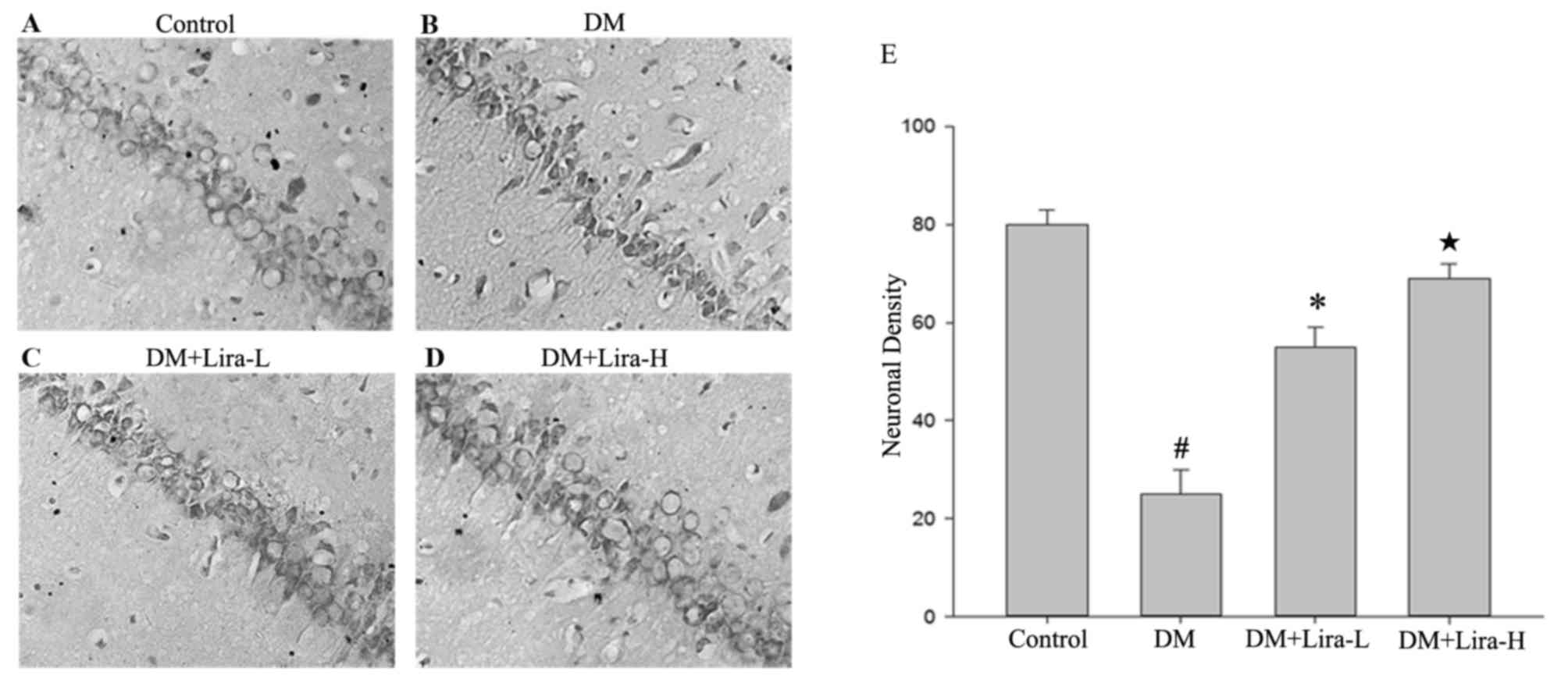
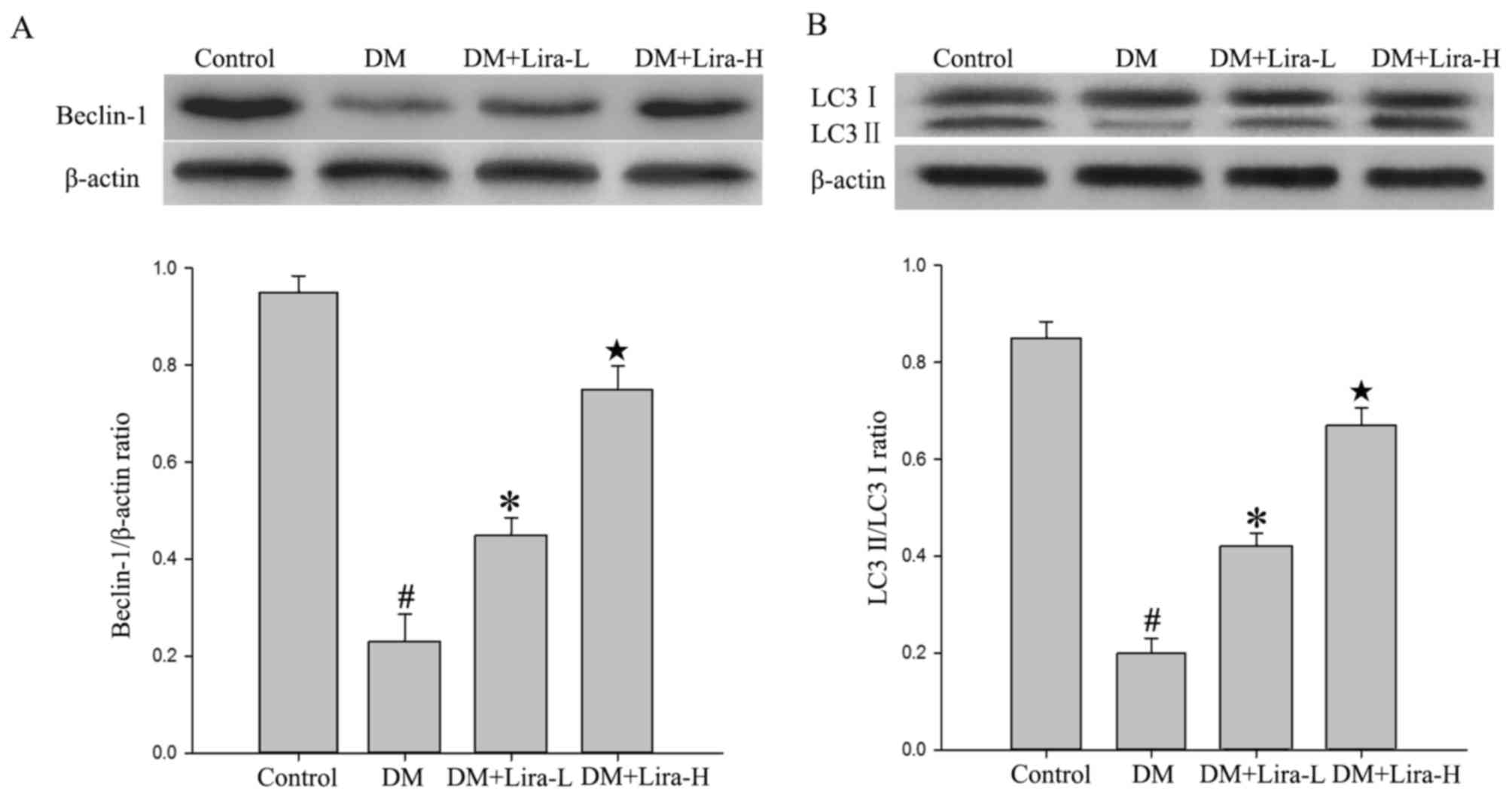
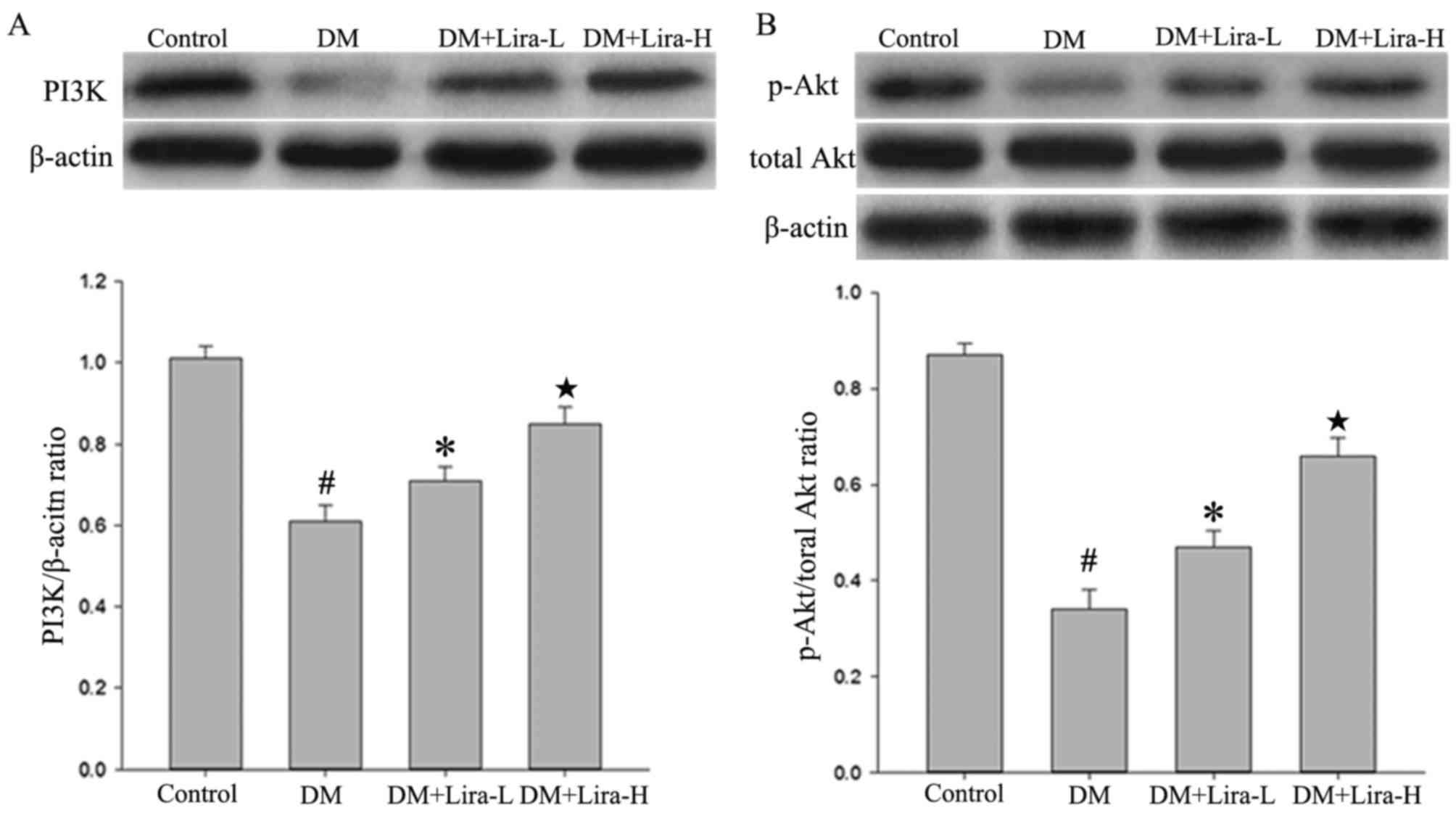
|
1
|
Dobretsov M, Romanovsky D and Stimers JR:
Early diabetic neuropathy: Triggers and mechanisms. World J
Gastroenterol. 13:175–191. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McCrimmon RJ, Ryan CM and Frier BM:
Diabetes and cognitive dysfunction. Lancet. 379:2291–2299. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mijnhout GS, Scheltens P, Diamant M,
Biessels GJ, Wessels AM, Simsek S, Snoek FJ and Heine RJ: Diabetic
encephalopathy: A concept in need of a definition. Diabetologia.
49:1447–1448. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Carvalho C, Santos MS, Oliveira CR and
Moreira PI: Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes-related
alterations in brain mitochondria, autophagy and synaptic markers.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:1665–1675. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Feinkohl I, Price JF, Strachan MW and
Frier BM: The impact of diabetes on cognitive decline: Potential
vascular, metabolic and psychosocial risk factors. Alzheimers Res
Ther. 7:462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vagelatos NT and Eslick GD: Type 2
diabetes as a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease: The confounders,
interactions and neuropathology associated with this relationship.
Epidemiol Rev. 35:152–160. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Muriach M, Flores-Bellver M, Romero FJ and
Barcia JM: Diabetes and the brain: Oxidative stress, inflammation
and autophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:1021582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guan ZF, Tao YH, Zhang XM, Guo QL, Liu YC,
Zhang Y, Wang YM, Ji G, Wu GF, Wang NN, et al: G-CSF and cognitive
dysfunction in elderly diabetic mice with cerebral small vessel
disease: Preventive intervention effects and underlying mechanisms.
CNS Neurosci Ther. 23:462–474. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kong FJ, Ma LL, Guo JJ, Xu LH, Li Y and Qu
S: Endoplasmic reticulum stress/autophagy pathway is involved in
diabetes-induced neuronal apoptosis and cognitive decline in mice.
Clin Sci. 132:111–125. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qian M, Fang X and Wang X: Autophagy and
inflammation. Clin Transl Med. 6:242017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guan ZF, Zhou XL, Zhang XM, Zhang Y, Wang
YM, Guo QL, Ji G, Wu GF, Wang NN, Yang H, et al: Beclin-1-mediated
autophagy may be involved in the elderly cognitive and affective
disorders in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Transl
Neurodegener. 5:222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Palleria C, Leporini C, Maida F, Succurro
E, De Sarro G, Arturi F and Russo E: Potential effects of current
drug therapies on cognitive impairment in patients with type 2
diabetes. Front Neuroendocrinol. 42:76–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Goto H, Nomiyama T, Mita T, Yasunari E,
Azuma K, Komiya K, Arakawa M, Jin WL, Kanazawa A, Kawamori R, et
al: Exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, reduces
intimal thickening after vascular injury. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 405:79–84. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen S, Liu AR, An FM, Yao WB and Gao XD:
Amelioration of neurodegenerative changes in cellular and rat
models of diabetes-related Alzheimer's disease by exendin-4. Age.
34:1211–1224. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Solmaz V, Çınar BP, Yiğittürk G, Çavuşoğlu
T, Taşkıran D and Erbaş O: Exenatide reduces TNF-α expression and
improves hippocampal neuron numbers and memory in streptozotocin
treated rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 765:482–487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zheng T, Qin L, Chen B, Hu X, Zhang X, Liu
Y, Liu H, Qin S, Li G and Li Q: Association of plasma DPP4 activity
with mild cognitive impairment in elderly patients with type 2
diabetes: Results from the GDMD study in China. Diabetes Care.
39:1594–1601. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen B, Zheng T, Qin L, Hu X, Zhang X, Liu
Y, Liu H, Qin S, Li G and Li Q: Strong association between plasma
dipeptidyl peptidase-4 activity and impaired cognitive function in
elderly population with normal glucose tolerance. Fron Aging
Neurosci. 9:2472017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zheng T, Liu H, Qin L, Chen B, Zhang X, Hu
X, Xiao L and Qin S: Oxidative stress-mediated influence of plasma
DPP4 activity to BDNF ratio on mild cognitive impairment in elderly
type 2 diabetic patients: Results from the GDMD study in China.
Metabolism. March 21–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Jacobsen LV, Hindsberger C, Robson R and
Zdravkovic M: Effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of
the GLP-1 analogue liraglutide. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 68:898–905.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McClean PL and Hölscher C: Liraglutide can
reverse memory impairment, synaptic loss and reduce plaque load in
aged APP/PS1 mice, a model of Alzheimer's disease.
Neuropharmacology. 76:57–67. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hansen HH, Fabricius K, Barkholt P,
Niehoff ML, Morley JE, Jelsing J, Pyke C, Knudsen LB, Farr SA and
Vrang N: The GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide improves memory
function and increases hippocampal CA1 neuronal numbers in a
senescence-accelerated mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J
Alzheimers Dis. 46:877–888. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miao X, Gu Z, Liu Y, Jin M, Lu Y, Gong Y,
Li L and Li C: The glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue liraglutide
promotes autophagy through the modulation of 5′-AMP-activated
protein kinase in INS-1 β-cells under high glucose conditions.
Peptides. 100:127–139. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Candeias E, Sebastião I, Cardoso S,
Carvalho C, Santos MS, Oliveira CR, Moreira PI and Duarte AI: Brain
GLP-1/IGF-1 signaling and autophagy mediate exendin-4 protection
against apoptosis in type 2 diabetic rats. Mol Neurobiol.
55:4030–4050. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
National Research Council (US), .
Institute for Laboratory Animal Research: Guide for the care and
use of laboratory animals. The National Academies Press;
Washington, DC: 1996
|
|
25
|
Ryan CM, van Duinkerken E and Rosano C:
Neurocognitive consequences of diabetes. Am Psychol. 71:563–576.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stranahan AM: Models and mechanisms for
hippocampal dysfunction in obesity and diabetes. Neuroscience.
309:125–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yates KF, Sweat V, Yau PL, Turchiano MM
and Convit A: Impact of metabolic syndrome on cognition and brain:
A selected review of the literature. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
32:2060–2067. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
de Faria JM, Duarte DA, Montemurro C,
Papadimitriou A, Consonni SR and de Faria Lopes JB: Defective
autophagy in diabetic retinopathy defective autophagy. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57:4356–4366. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ma LY, Lv YL, Huo K, Liu J, Shang SH, Fei
YL, Li YB, Zhao BY, Wei M, Deng YN and Qu QM: Autophagy-lysosome
dysfunction is involved in Aβ deposition in STZ-induced diabetic
rats. Behav Brain Res. 320:484–493. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guan ZF, Zhou XL, Zhang XM, Zhang Y, Wang
YM, Guo QL, Ji G, Wu GF, Wang NN, Yang H, et al: Beclin-1-mediated
autophagy may be involved in the elderly cognitive and affective
disorders in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Transl
Neurodegener. 5:222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li XH, Xin X, Wang Y, Wu JZ, Jin ZD, Ma
LN, Nie CJ, Xiao X, Hu Y and Jin MW: Pentamethylquercetin protects
against diabetes-related cognitive deficits in diabetic
Goto-Kakizaki rats. J Alzheimers Dis. 34:755–767. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xue H, Ji Y, Wei S, Yu Y, Yan X, Liu S,
Zhang M, Yao F, Lan X and Chen L: HGSD attenuates neuronal
apoptosis through enhancing neuronal autophagy in the brain of
diabetic mice: The role of AMP-activated protein kinase. Life Sci.
153:23–34. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Qin L, Wang Z, Tao L and Wang Y: ER stress
negatively regulates AKT/TSC/mTOR pathway to enhance autophagy.
Autophagy. 6:239–247. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yan J, Feng Z and Liu J, Shen W, Wang Y,
Wertz K, Weber P, Long J and Liu J: Enhanced autophagy plays a
cardinal role in mitochondrial dysfunction in type 2 diabetic
Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rats: Ameliorating effects of
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. J Nutr Biochem. 23:716–724. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Holz GG IV, Kiihtreiber WM and Habener JF:
Pancreatic beta-cells are rendered glucose-competent by the
insulinotropic hormone glucagon-like peptide-1(7–37). Nature.
36:362–365. 1993. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Palleria C, Leo A, Andreozzi F, Citaro R,
Lannone M, Spiga R, Sesti G, Constanti A, De Sarri G, Arturi F and
Russo E: Liraglutide prevents cognitive decline in a rat model of
streptozotocin-induced diabetes independently from its peripheral
metabolic effects. Behav Brain Res. 321:157–169. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Porter WD, Flatt PR, Hölscher C and Gault
VA: Liraglutide improves hippocampal synaptic plasticity associated
with increased expression of Mash1 in ob/ob mice. Int J Obes
(Lond). 37:678–684. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu XM, Ou QY, Zhao W, Liu J and Zhang H:
The GLP-1 analogue liraglutide protects cardiomyocytes from high
glucose-induced apoptosis by activating the Epac-1/Akt pathway. Exp
Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 122:608–614. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Badawi GA, Abd El Fattah MA, Zaki HF and
Sayed EI MI: Sitagliptin and liraglutide reversed nigrostriatal
degeneration of rodent brain in rotenone-induced Parkinson's
disease. Inflammopharmacology. 25:369–382. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Abbas NAT and Kabil SL: Liraglutide
ameliorates cardiotoxicity induced by doxorubicin in rats through
the Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway (J). Archiv Für Exp Pathol Und
Pharmakol. 1–9. 2017.
|
|
41
|
Zhu H, Zhang Y, Shi Z, Lu D, Li T, Ding Y,
Ruan Y and Xu A: The neuroprotection of liraglutide against
ischaemia-induced apoptosis through the activation of the PI3K/AKT
and MAPK Pathways. Sci Rep. 6:268592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|