|
1
|
Yu HY, Li XY, Cai ZF, Li L, Shi XZ, Song
HX and Liu XJ: Eosinophil cationic protein mRNA expression in
children with bronchial asthma. Genet Mol Res. 14:14279–14285.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sussan TE, Gajghate S, Chatterjee S,
Mandke P, McCormick S, Sudini K, Kumar S, Breysse PN, Diette GB,
Sidhaye VK and Biswal S: Nrf2 reduces allergic asthma in mice
through enhanced airway epithelial cytoprotective function. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 309:L27–L36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Erokhina IL, Voronchikhin PA, Okovityi SV
and Emel'ianova OI: Reaction of population of pulmonary mast cells
in rat bronchial asthma under the effect of beta-adrenoreceptor
antagonists. Tsitologiia. 55:472–474. 2013.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ciepiela O, Ostafin M and Demkow U:
Neutrophils in asthma-a review. Respir Physiol Neurobiol.
209:13–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bang BR, Kwon HS, Kim SH, Yoon SY, Choi
JD, Hong GH, Park S, Kim TB, Moon HB and Cho YS: Interleukin-32γ
suppresses allergic airway inflammation in mouse models of asthma.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 50:1021–1030. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Adamek-Guzik T, Czerniawska-Mysik G and
Guzik T: Bronchial asthma-a chronic inflammatory disorder. Przegl
Lek. 53:12–19. 1996.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zakharyan R and Boyajyan A: Inflammatory
cytokine network in schizophrenia. World J Biol Psychiatry.
15:174–187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nakagome K and Nagata M: Pathogenesis of
airway inflammation in bronchial asthma. Auris Nasus Larynx.
38:555–563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Messler S, Kropp S, Episkopou V, Felici A,
Würthner J, Lemke R, Jerabek-Willemsen M, Willecke R, Scheu S,
Pfeffer K and Wurthner JU: The TGF-β signaling modulators
TRAP1/TGFBRAP1 and VPS39/Vam6/TLP are essential for early embryonic
development. Immunobiology. 216:343–350. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Travis MA and Sheppard D: TGF-β activation
and function in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 32:51–82. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu ML, Wang H, Wang ZR, Zhang YF, Chen
YQ, Zhu FH, Zhang YQ, Ma J and Li Z: TGF-β1 regulation of estrogen
production in mature rat Leydig cells. PLoS one. 8:e601972013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou F, Drabsch Y, Dekker TJ, de Vinuesa
AG, Li Y, Hawinkels LJ, Sheppard KA, Goumans MJ, Luwor RB, de Vries
CJ, et al: Nuclear receptor NR4A1 promotes breast cancer invasion
and metastasis by activating TGF-β signalling. Nat Commun.
5:33882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Syed V: TGF-β signaling in cancer. J Cell
Biochem. 117:1279–1287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Al-Alawi M, Hassan T and Chotirmall SH:
Transforming growth factor β and severe asthma: A perfect storm.
Respir Med. 108:1409–1423. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Massagué J, Seoane J and Wotton D: Smad
transcription factors. Genes Dev. 19:2783–2810. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Heldin CH and Moustakas A: Role of Smads
in TGFβ signaling. Cell Tissue Res. 347:21–36. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takagaki A, Otani S and Nanjo F:
Antioxidative activity of microbial metabolites of
(−)-epigallocatechin gallate produced in rat intestines. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 75:582–585. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Johnson MK and Loo G: Effects of
epigallocatechin gallate and quercetin on oxidative damage to
cellular DNA. Mutat Res. 459:211–218. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao Z, Han Y, Hu Y, Wu X, Wang Y, Zhang X,
Fu J, Zou X, Zhang J, Chen X, et al: Targeting HO-1 by
epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces contrast-induced renal injury
via anti-oxidative stress and anti-inflammation pathways. PLoS One.
11:e01490322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ohno A, Kataoka S, Ishii Y, Terasaki T,
Kiso M, Okubo M, Yamaguchi K and Tateda K: Evaluation of Camellia
sinensis catechins as a swine antimicrobial feed additive that does
not cause antibiotic resistance. Microbes Environ. 28:81–86. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Min KJ and Kwon TK: Anticancer effects and
molecular mechanisms of epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Integr Med Res.
3:16–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bitzer ZT, Elias RJ, Vijay-Kumar M and
Lambert JD: (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate decreases colonic
inflammation and permeability in a mouse model of colitis, but
reduces macronutrient digestion and exacerbates weight loss. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 60:2267–2274. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu D, Wang J, Pae M and Meydani SN: Green
tea EGCG, T cells and T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases. Mol
Aspects Med. 33:107–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Haque A, Rahman MA, Chen ZG, Saba NF,
Khuri FR, Shin DM and Amin Ruhul AR: Combination of erlotinib and
EGCG induces apoptosis of head and neck cancers through
posttranscriptional regulation of Bim and Bcl-2. Apoptosis.
20:986–995. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Funston W and Higgins B: Improving the
management of asthma in adults in primary care. Practitioner.
258:15–19. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chakrawarti L, Agrawal R, Dang S, Gupta S
and Gabrani R: Therapeutic effects of EGCG: A patent review. Expert
Opin Ther Pat. 26:907–916. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Intra J and Kuo SM: Physiological levels
of tea catechins increase cellular lipid antioxidant activity of
vitamin C and vitamin E in human intestinal caco-2 cells. Chem Biol
Interact. 169:91–99. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yamagata K, Tanaka N and Suzuki K:
Epigallocatechin 3-gallate inhibits 7-ketocholesterol-induced
monocyte-endothelial cell adhesion. Microvasc Res. 88:25–31. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Inoue T, Suzuki Y and Ra C:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces cytokine production in mast
cells by stimulating an extracellular superoxide-mediated calcium
influx. Biochem Pharmacol. 82:1930–1939. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shi J, Deng H, Pan H, Xu Y and Zhang M:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates microcystin-LR induced
oxidative stress and inflammation in human umbilical vein
endothelial cells. Chemosphere. 168:25–31. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu NH, Pei H, Huang YP and Li YF:
(−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits arsenic-induced
inflammation and apoptosis through suppression of oxidative stress
in mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 41:1788–1800. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bakr SI, Mahran MZ and Soliman DA: Role of
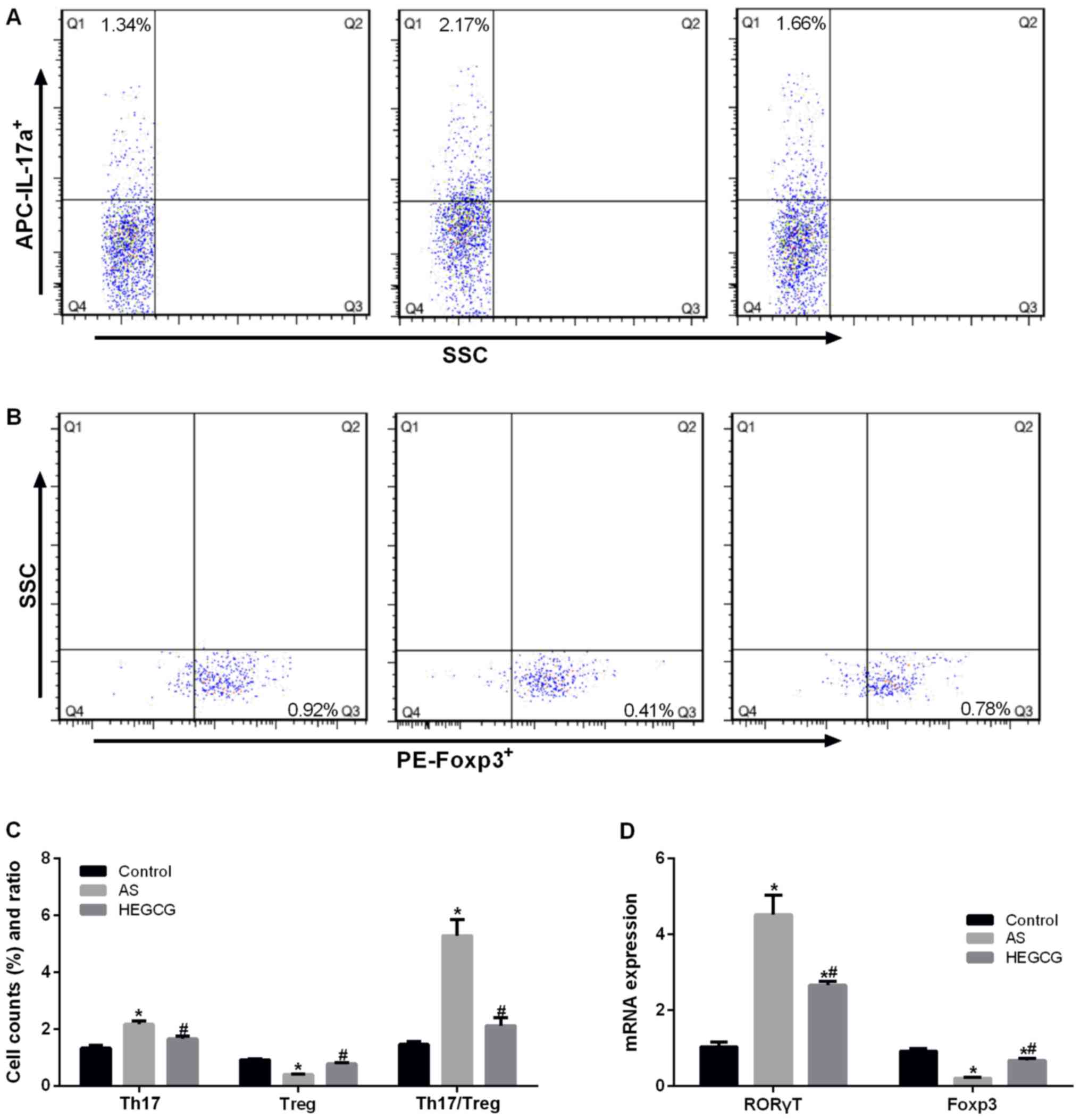
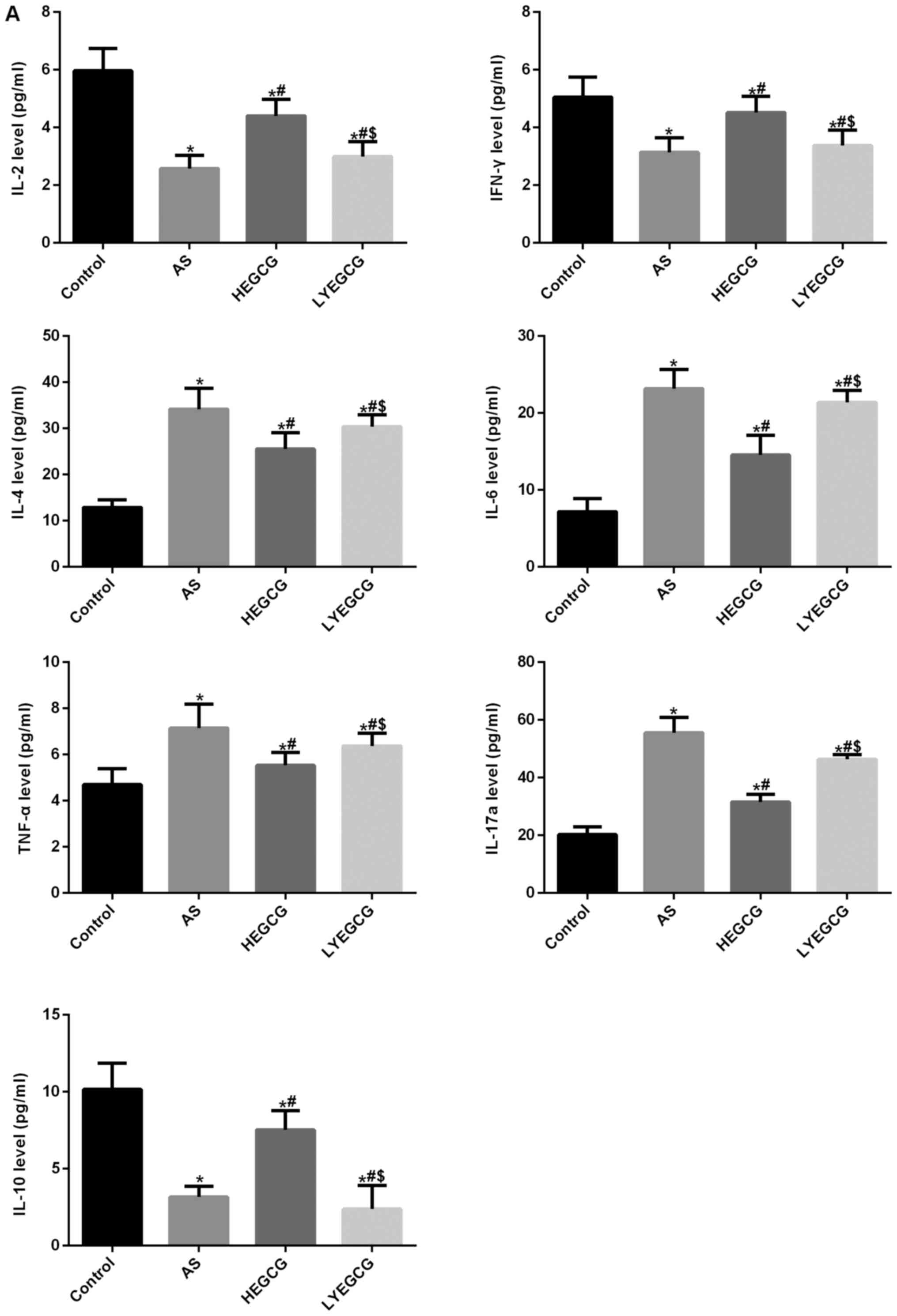
regulatory CD4+CD25+ Foxp3 T cells in
bronchial asthma in Egyptian children. Egypt J Immunol. 20:29–38.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Corrigan CJ and Kay AB: Asthma. Role of
T-lymphocytes and lymphokines. Br Med Bull. 48:72–84. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Maddur MS, Miossec P, Kaveri SV and Bayry
J: Th17 cells: Biology, pathogenesis of autoimmune and inflammatory
diseases and therapeutic strategies. Am J Pathol. 181:8–18. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Palomares O: The role of regulatory T
cells in IgE-mediated food allergy. J Investig Allergol Clin
Immunol. 23:371–382. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ierodiakonou D, Postma DS, Koppelman GH,
Gerritsen J, ten Hacken NH, Timens W, Boezen HM and Vonk JM: TGF-β1
polymorphisms and asthma severity, airway inflammation, and
remodeling. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 131:582–585. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Halwani R, Al-Muhsen S, Al-Jahdali H and
Hamid Q: Role of transforming growth factor-β in airway remodeling
in asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 44:127–133. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kamato D, Burch ML, Piva TJ, Rezaei HB,
Rostam MA, Xu S, Zheng W, Little PJ and Osman N: Transforming
growth factor-beta signalling: Role and consequences of Smad linker
region phosphorylation. Cell Signal. 25:2017–2024. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu X, Yang Y, Zhang X, Xu S, He S, Huang
W and Roberts MS: Compound Astragalus and Salvia
miltiorrhiza extract inhibits cell invasion by modulating
transforming growth factor-beta/Smad in HepG2 cell. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 25:420–426. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
McMillan SJ, Xanthou G and Lloyd CM:
Manipulation of allergen-induced airway remodeling by treatment
with anti-TGF-beta antibody: Effect on the Smad signaling pathway.
J Immunol. 174:5774–5780. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|