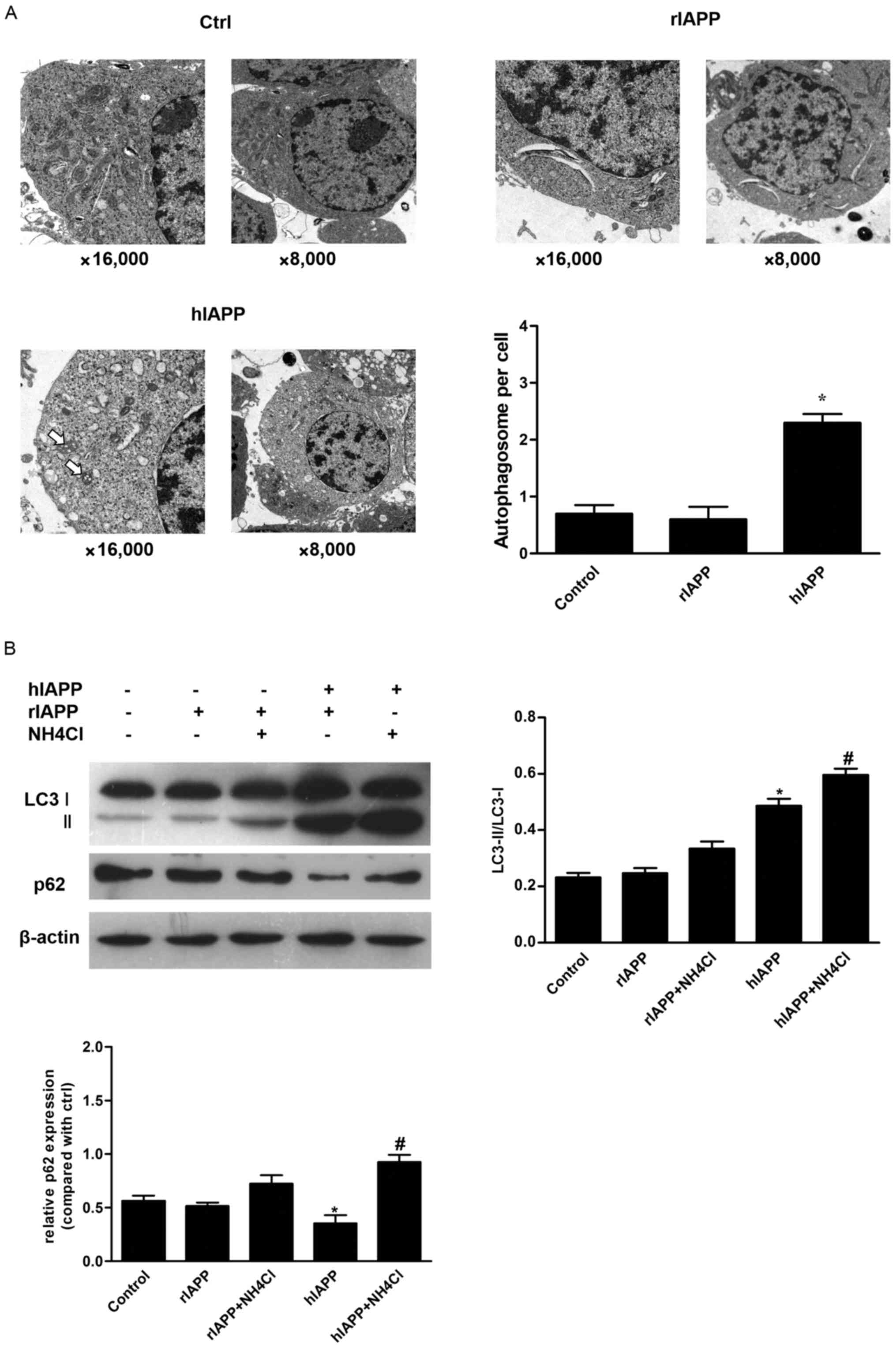
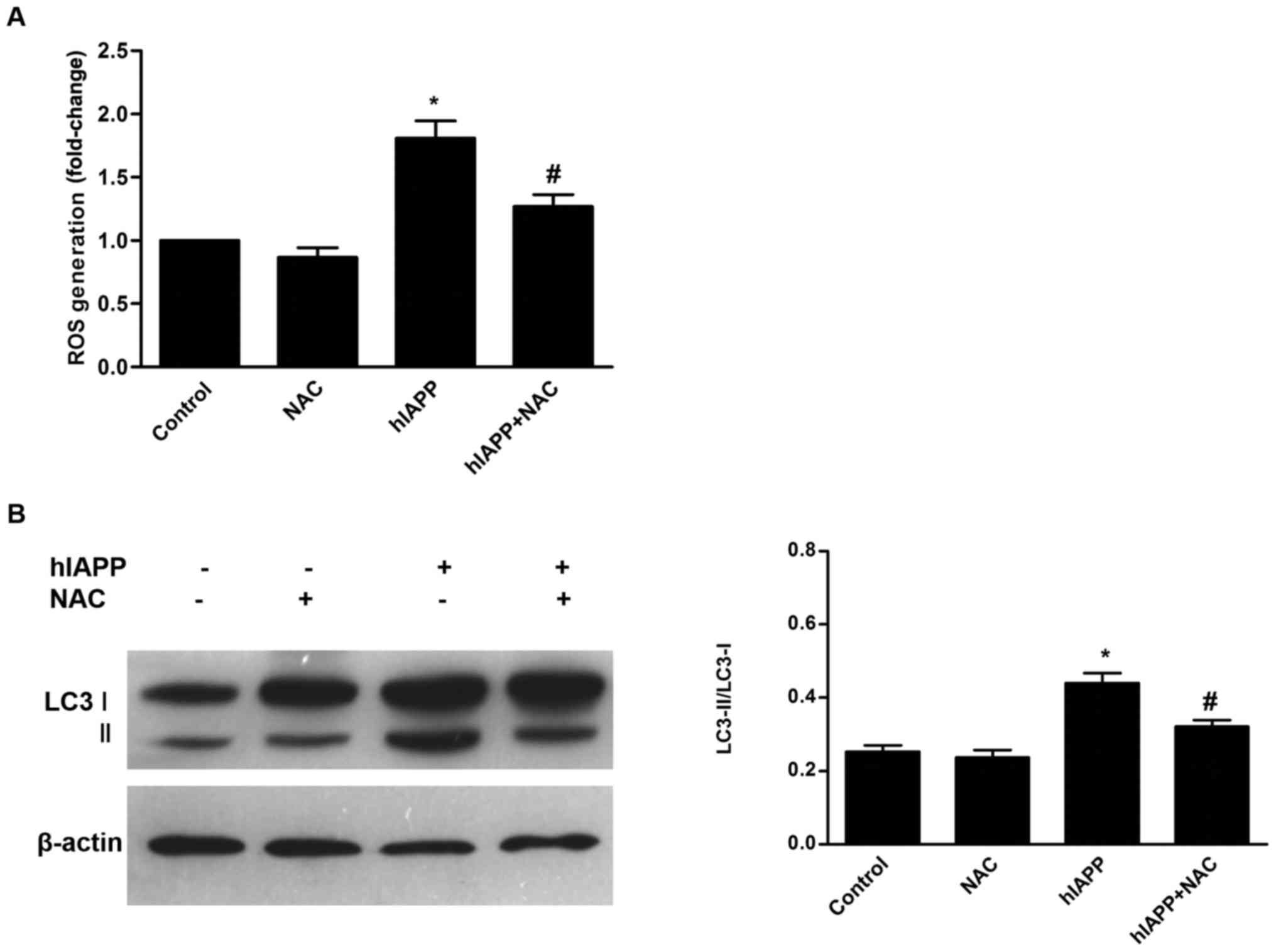
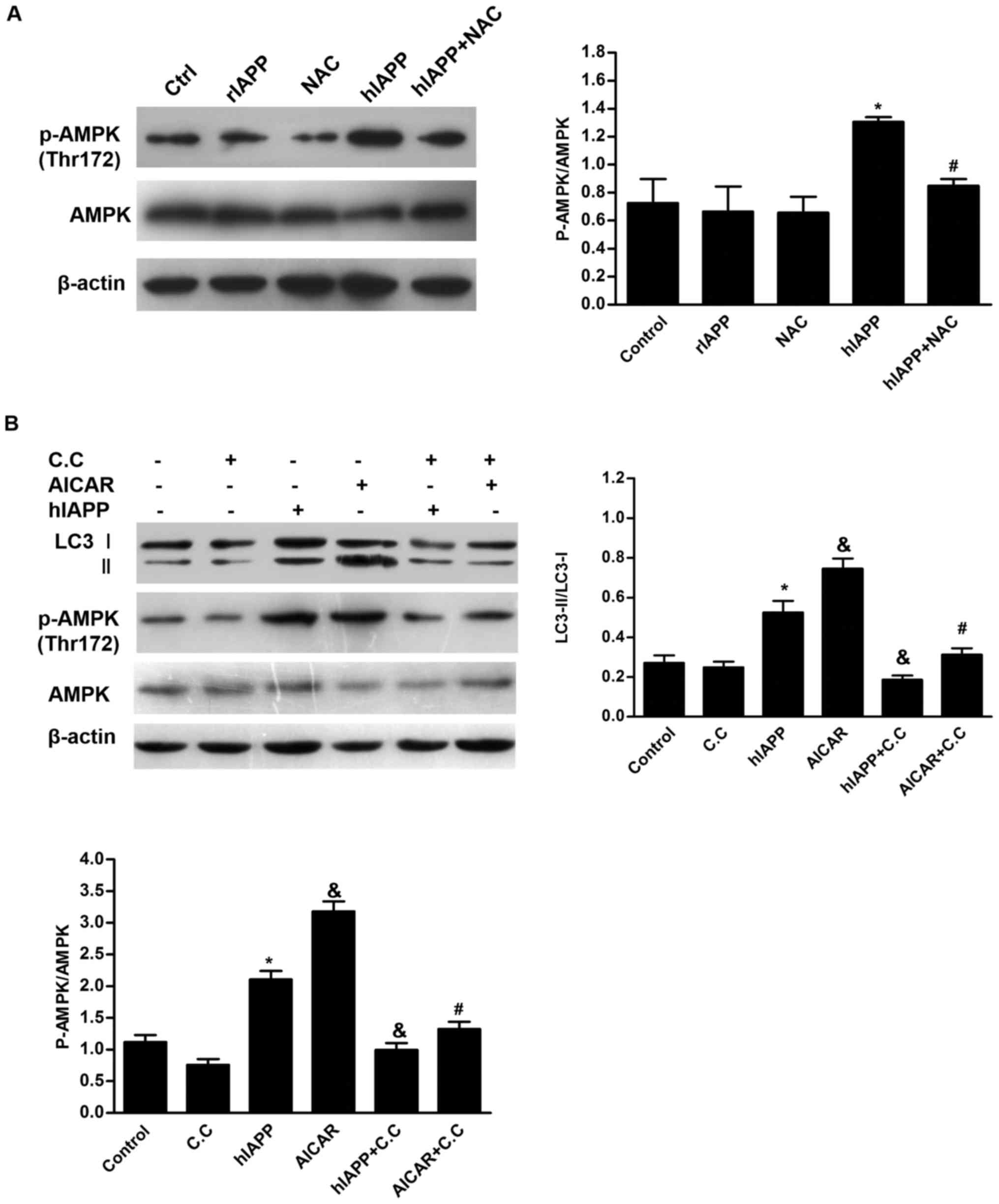
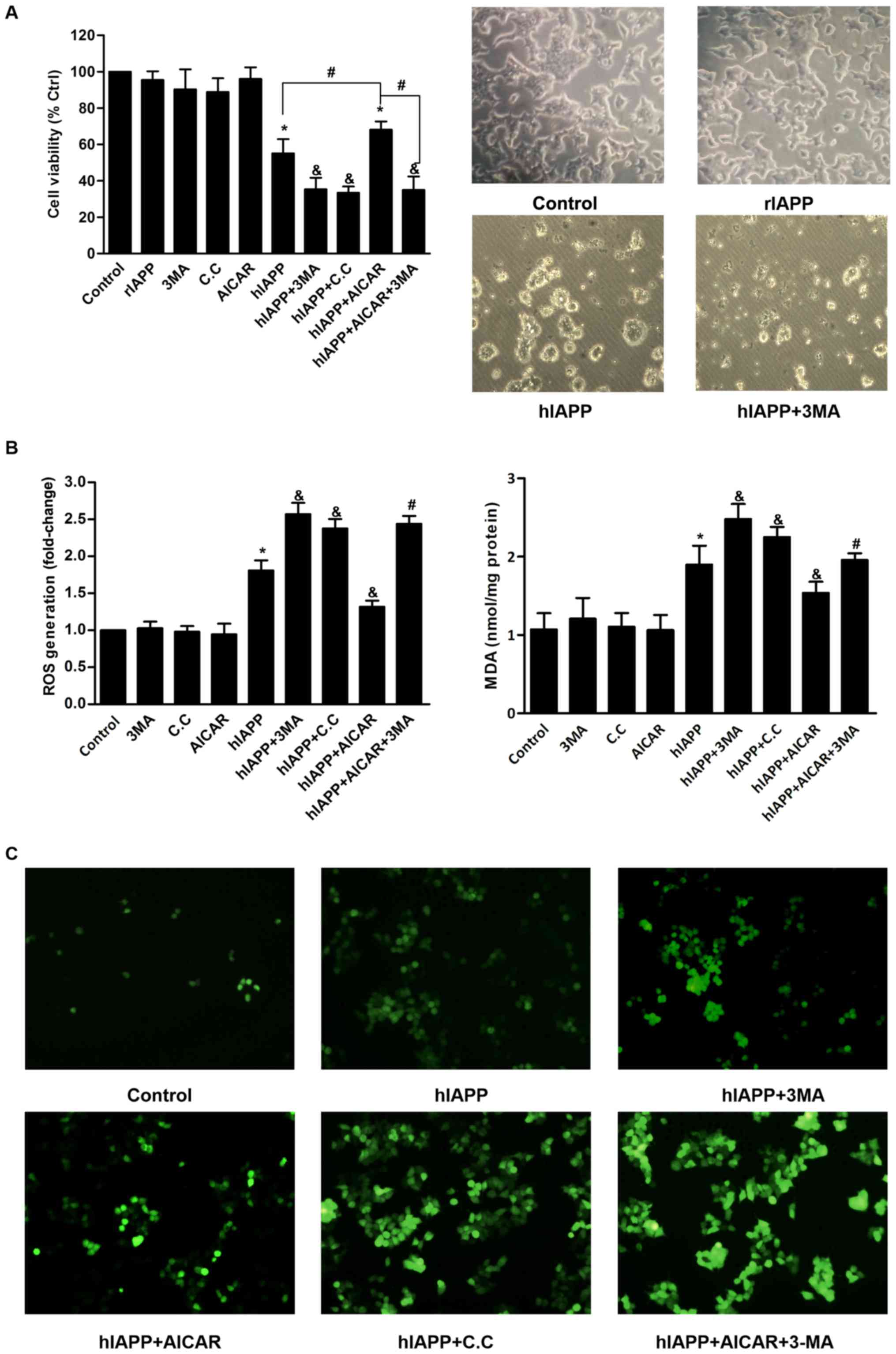
|
1
|
Cooper GJ, Willis AC, Clark A, Turner RC,
Sim RB and Reid KB: Purification and characterization of a peptide
from amyloid-rich pancreases of type 2 diabetic patients. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 84:8628–8632. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kahn SE, D'Alessio DA, Schwartz MW,
Fujimoto WY, Ensinck JW, Taborsky GJ Jr and Porte D Jr: Evidence of
cosecretion of islet amyloid polypeptide and insulin by beta-cells.
Diabetes. 39:634–638. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lukinius A, Wilander E, Westermark GT,
Engström U and Westermark P: Co-localization of islet amyloid
polypeptide and insulin in the B cell secretory granules of the
human pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 32:240–244. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
O'Brien TD, Butler PC, Westermark P and
Johnson KH: Islet amyloid polypeptide: A review of its biology and
potential roles in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Vet
Pathol. 30:317–332. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Westermark P, Andersson A and Westermark
GT: Islet amyloid polypeptide, islet amyloid, and diabetes
mellitus. Physiol Rev. 91:795–826. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kloppel G, Löhr M, Habich K, Oberholzer M
and Heitz PU: Islet pathology and the pathogenesis of type 1 and
type 2 diabetes mellitus revisited. Surv Synth Pathol Res.
4:110–125. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Costes S, Langen R, Gurlo T, Matveyenko AV
and Butler PC: β-Cell failure in type 2 diabetes: A case of asking
too much of too few? Diabetes. 62:327–335. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lorenzo A, Razzaboni B, Weir GC and
Yankner BA: Pancreatic islet cell toxicity of amylin associated
with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Nature. 368:756–760. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gurlo T, Ryazantsev S, Huang CJ, Yeh MW,
Reber HA, Hines OJ, O'Brien TD, Glabe CG and Butler PC: Evidence
for proteotoxicity in beta cells in type 2 diabetes: Toxic islet
amyloid polypeptide oligomers form intracellularly in the secretory
pathway. Am J Pathol. 176:861–869. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Westermark GT and Westermark P: Importance
of aggregated islet amyloid polypeptide for the progressive
beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes and in transplanted human
islets. Exp Diabetes Res. 2008:5283542008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Czarna M and Jarmuszkiewicz W: Role of
mitochondria in reactive oxygen species generation and removal;
relevance to signaling and programmed cell death. Postepy Biochem.
52:145–156. 2006.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xin A, Mizukami H, Inaba W, Yoshida T,
Takeuchi YK and Yagihashi S: Pancreas atrophy and islet amyloid
deposition in patients with elderly-onset type 2 diabetes. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 102:3162–3171. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li XL, Xu G, Chen T, Wong YS, Zhao HL, Fan
RR, Gu XM, Tong PC and Chan JC: Phycocyanin protects INS-1E
pancreatic beta cells against human islet amyloid
polypeptide-induced apoptosis through attenuating oxidative stress
and modulating JNK and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:1526–1535. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Konarkowska B, Aitken JF, Kistler J, Zhang
S and Cooper GJ: Thiol reducing compounds prevent human
amylin-evoked cytotoxicity. FEBS J. 272:4949–4959. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Scherz-Shouval R and Elazar Z: Regulation
of autophagy by ROS: Physiology and pathology. Trends Biochem Sci.
36:30–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang YP, Liang ZQ, Gu ZL and Qin ZH:
Molecular mechanism and regulation of autophagy. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 26:1421–1434. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wen X, Wu J, Wang F, Liu B, Huang C and
Wei Y: Deconvoluting the role of reactive oxygen species and
autophagy in human diseases. Free Radic Biol Med. 65:402–410. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hull RL, Westermark GT, Westermark P and
Kahn SE: Islet amyloid: A critical entity in the pathogenesis of
type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 89:3629–3643. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Morita S, Sakagashira S, Shimajiri Y,
Eberhardt NL, Kondo T, Kondo T and Sanke T: Autophagy protects
against human islet amyloid polypeptide-associated apoptosis. J
Diabetes Investig. 2:48–55. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ebato C, Uchida T, Arakawa M, Komatsu M,
Ueno T, Komiya K, Azuma K, Hirose T, Tanaka K, Kominami E, et al:
Autophagy is important in islet homeostasis and compensatory
increase of beta cell mass in response to high-fat diet. Cell
Metab. 8:325–332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Las G, Serada SB, Wikstrom JD, Twig G and
Shirihai OS: Fatty acids suppress autophagic turnover in β-cells. J
Biol Chem. 286:42534–42544. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rubinsztein DC, DiFiglia M, Heintz N,
Nixon RA, Qin ZH, Ravikumar B, Stefanis L and Tolkovsky A:
Autophagy and its possible roles in nervous system diseases, damage
and repair. Autophagy. 1:11–22. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oh SH, Kim YS, Lim SC, Hou YF, Chang IY
and You HJ: Dihydrocapsaicin (DHC), a saturated structural analog
of capsaicin, induces autophagy in human cancer cells in a
catalase-regulated manner. Autophagy. 4:1009–1019. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu L, Wan F, Dutta S, Welsh S, Liu Z,
Freundt E, Baehrecke EH and Lenardo M: Autophagic programmed cell
death by selective catalase degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:4952–4957. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shigihara N, Fukunaka A, Hara A, Komiya K,
Honda A, Uchida T, Abe H, Toyofuku Y, Tamaki M, Ogihara T, et al:
Human IAPP-induced pancreatic β cell toxicity and its regulation by
autophagy. J Clin Invest. 124:3634–3644. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A,
Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, a
mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pant K, Saraya A and Venugopal SK:
Oxidative stress plays a key role in butyrate-mediated autophagy
via Akt/mTOR pathway in hepatoma cells. Chem Biol Interact.
273:99–106. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Smuder AJ, Sollanek KJ, Nelson WB, Min K,
Talbert EE, Kavazis AN, Hudson MB, Sandri M, Szeto HH and Powers
SK: Crosstalk between autophagy and oxidative stress regulates
proteolysis in the diaphragm during mechanical ventilation. Free
Radic Biol Med. 115:179–190. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu S, Sun Y and Li Z: Resveratrol
protects Leydig cells from nicotine-induced oxidative damage
through enhanced autophagy. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. Nov
22–2017.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
32
|
She C, Zhu LQ, Zhen YF, Wang XD and Dong
QR: Activation of AMPK protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced
osteoblast apoptosis through autophagy induction and NADPH
maintenance: New implications for osteonecrosis treatment? Cell
Signal. 26:1–8. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Egan DF, Shackelford DB, Mihaylova MM,
Gelino S, Kohnz RA, Mair W, Vasquez DS, Joshi A, Gwinn DM, Taylor
R, et al: Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein
kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy. Science. 331:456–461.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zraika S, Hull RL, Udayasankar J,
Aston-Mourney K, Subramanian SL, Kisilevsky R, Szarek WA and Kahn
SE: Oxidative stress is induced by islet amyloid formation and
time-dependently mediates amyloid-induced beta cell apoptosis.
Diabetologia. 52:626–635. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gorowara S, Sapru S and Ganguly NK: Role
of intracellular second messengers and reactive oxygen species in
the pathophysiology of V. cholera O139 treated rabbit ileum.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1407:21–30. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li X, Ma L, Zheng W and Chen T: Inhibition
of islet amyloid polypeptide fibril formation by
selenium-containing phycocyanin and prevention of beta cell
apoptosis. Biomaterials. 35:8596–8604. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schimmack G, Defronzo RA and Musi N:
AMP-activated protein kinase: Role in metabolism and therapeutic
implications. Diabetes Obes Metab. 8:591–602. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Feng Z, Zhang H, Levine AJ and Jin S: The
coordinate regulation of the p53 and mTOR pathways in cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:8204–8209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wu J, Wu JJ, Yang LJ, Wei LX and Zou DJ:
Rosiglitazone protects against palmitate-induced pancreatic
beta-cell death by activation of autophagy via 5′-AMP-activated
protein kinase modulation. Endocrine. 44:87–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Han D, Yang B, Olson LK, Greenstein A,
Baek SH, Claycombe KJ, Goudreau JL, Yu SW and bKim EK: Activation
of autophagy through modulation of 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase
protects pancreatic beta-cells from high glucose. Biochem J.
425:541–551. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jia Z and Misra HP: Reactive oxygen
species in in vitro pesticide-induced neuronal cell (SH-SY5Y)
cytotoxicity: Role of NFkappaB and caspase-3. Free Radic Biol Med.
42:288–298. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Robertson RP: Chronic oxidative stress as
a central mechanism for glucose toxicity in pancreatic islet beta
cells in diabetes. J Biol Chem. 279:42351–42354. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X,
Fenyk-Melody J, Wu M, Ventre J, Doebber T, Fujii N, et al: Role of
AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J
Clin Invest. 108:1167–1174. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Osman I, Fairaq A and Segar L:
Pioglitazone attenuates injury-induced neointima formation in mouse
femoral artery partially through the activation of AMP-activated
protein kinase. Pharmacology. 100:64–73. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|