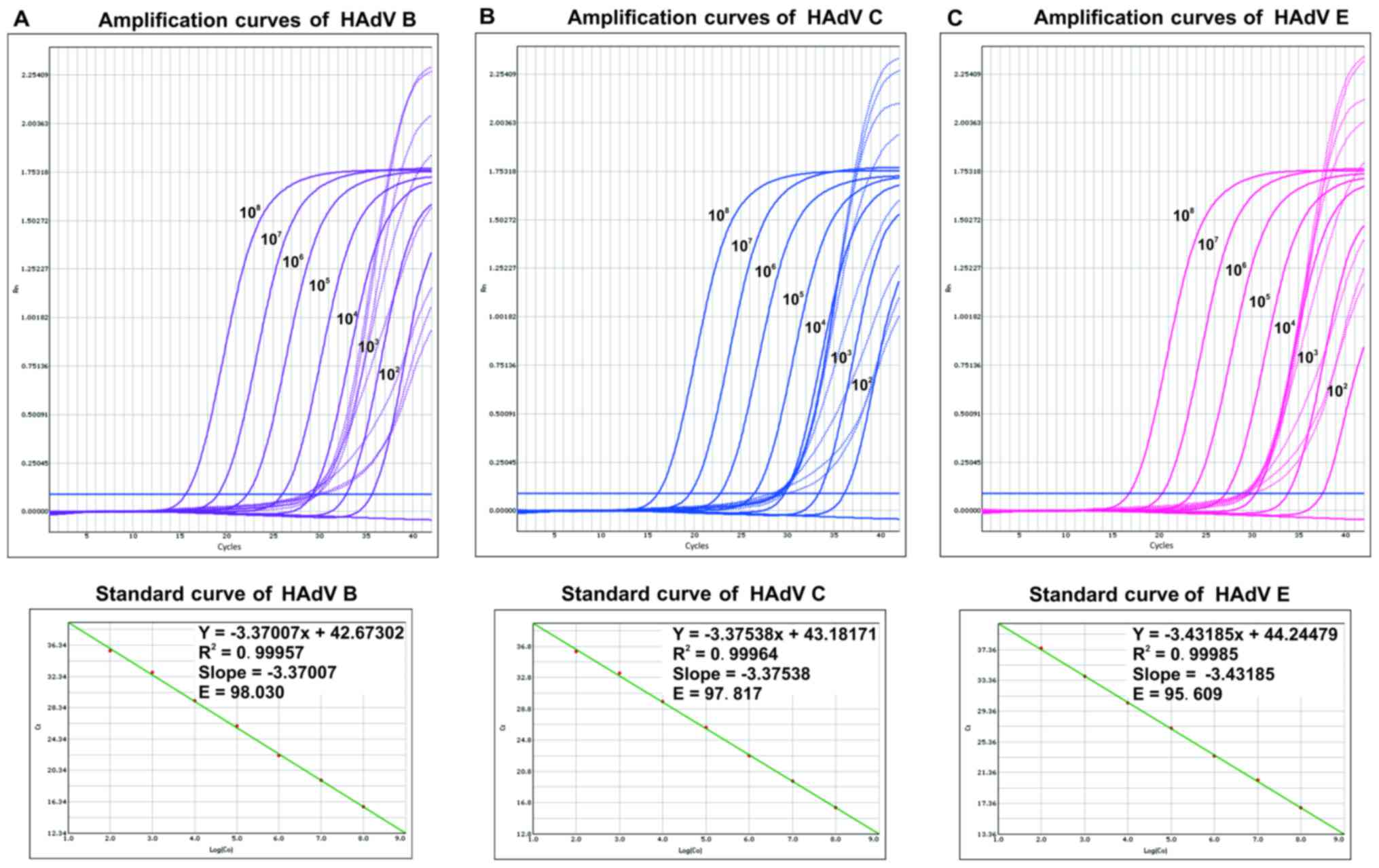
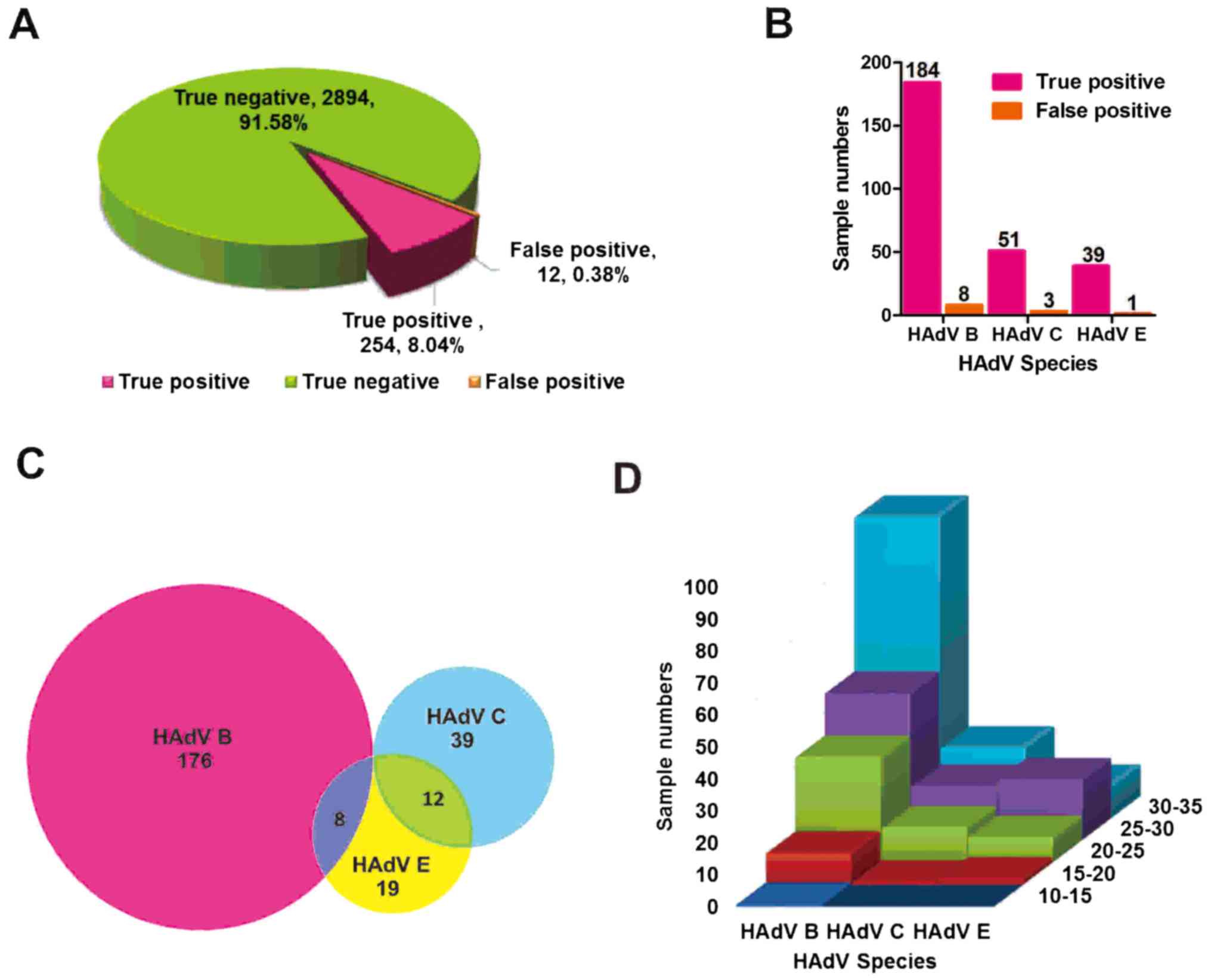
|
1
|
Sibanda T and Okoh AI: Assessment of the
incidence of enteric adenovirus species and serotypes in surface
waters in the eastern cape province of South Africa: Tyume River as
a case study. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012:9492162012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jones MS II, Harrach B, Ganac RD, Gozum
MM, Dela Cruz WP, Riedel B, Pan C, Delwart EL and Schnurr DP: New
adenovirus species found in a patient presenting with
gastroenteritis. J Virol. 81:5978–5984. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Walsh MP, Chintakuntlawar A, Robinson CM,
Madisch I, Harrach B, Hudson NR, Schnurr D, Heim A, Chodosh J, Seto
D and Jones MS: Evidence of molecular evolution driven by
recombination events influencing tropism in a novel human
adenovirus that causes epidemic keratoconjunctivitis. PLoS One.
4:e56352009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jeulin H, Salmon A, Bordigoni P and Venard
V: Comparison of in-house real-time quantitative PCR to the
Adenovirus R-Gene kit for determination of adenovirus load in
clinical samples. J Clin Microbiol. 48:3132–3137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang H, Zheng Y, Deng J, Chen X, Liu P and
Li X: Molecular epidemiology of respiratory adenovirus detection in
hospitalized children in Shenzhen, China. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:15011–15017. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Q, Jing S, Cheng Z, Yu Z, Dehghan S,
Shamsaddini A, Yan Y, Li M and Seto D: Comparative genomic analysis
of two emergent human adenovirus type 14 respiratory pathogen
isolates in China reveals similar yet divergent genomes. Emerg
Microbes Infect. 6:e922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kojaoghlanian T, Flomenberg P and Horwitz
MS: The impact of adenovirus infection on the immunocompromised
host. Rev Med Virol. 13:155–171. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stroparo E, Cruz CR, Mdo Debur C, Vidal
LR, Nogueira MB, Almeida SM, Pereira LA, Rotta I and Raboni SM:
Adenovirus respiratory infection: Significant increase in diagnosis
using PCR comparing with antigen detection and culture methods. Rev
Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 52:317–321. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen M, Zhu Z, Huang F, Liu D, Zhang T,
Ying D, Wu J and Xu W: Adenoviruses associated with acute
respiratory diseases reported in Beijing from 2011 to, 2013. PLoS
One. 10:e01213752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Echavarria M, Sanchez JL, Kolavic-Gray SA,
Polyak CS, Mitchell-Raymundo F, Innis BL, Vaughn D, Reynolds R and
Binn LN: Rapid detection of adenovirus in throat swab specimens by
PCR during respiratory disease outbreaks among military recruits. J
Clin Microbiol. 41:810–812. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu Z, Zhang Y, Xu S, Yu P, Tian X, Wang
L, Liu Z, Tang L, Mao N, Ji Y, et al: Outbreak of acute respiratory
disease in China caused by B2 species of adenovirus type 11. J Clin
Microbiol. 47:697–703. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pellet PE and Roizmann B: Field virology
(5th edition). 2007.
|
|
13
|
Shetty AK, Treynor E, Hill DW, Gutierrez
KM, Warford A and Baron EJ: Comparison of conventional viral
cultures with direct fluorescent antibody stains for diagnosis of
community-acquired respiratory virus infections in hospitalized
children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 22:789–794. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
De Vos N, Vankeerberghen A, Vaeyens F, Van
Vaerenbergh K, Boel A and De Beenhouwer H: Simultaneous detection
of human bocavirus and adenovirus by multiplex real-time PCR in a
Belgian paediatric population. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis.
28:1305–1310. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Blaschke AJ, Allison MA, Meyers L,
Rogatcheva M, Heyrend C, Mallin B, Carter M, Lafleur B, Barney T,
Poritz MA, et al: Non-invasive sample collection for respiratory
virus testing by multiplex PCR. J Clin Virol. 52:210–214. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dabisch-Ruthe M, Vollmer T, Adams O,
Knabbe C and Dreier J: Comparison of three multiplex PCR assays for
the detection of respiratory viral infections: Evaluation of xTAG
respiratory virus panel fast assay, RespiFinder 19 assay and
RespiFinder SMART 22 assay. BMC Infect Dis. 12:1632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Freymuth F, Vabret A, Cuvillon-Nimal D,
Simon S, Dina J, Legrand L, Gouarin S, Petitjean J, Eckart P and
Brouard J: Comparison of multiplex PCR assays and conventional
techniques for the diagnostic of respiratory virus infections in
children admitted to hospital with an acute respiratory illness. J
Med Virol. 78:1498–1504. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu L, Lin XY, Yang ZX, Yao XP, Li GL, Peng
SZ and Wang Y: A multiplex PCR for simultaneous detection of
classical swine fever virus, African swine fever virus, highly
pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus,
porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and
pseudorabies in swines. Pol J Vet Sci. 18:715–723. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang HS, Tsai CL, Chang J, Hsu TC, Lin S
and Lee CC: Multiplex PCR system for the rapid diagnosis of
respiratory virus infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Clin Microbiol Infect pii: S1198-743X. 30649–30653. 2017.
|
|
20
|
Tam Iroh PY, Zhang L and Cohen Z: Impact
of a transition from respiratory virus shell vial to multiplex PCR
on clinical outcomes and cost in hospitalized children. Children
(Basel). 4:pii: E3. 2017.
|
|
21
|
Liu JK, Wei CH, Yang XY, Dai AL and Li XH:
Multiplex PCR for the simultaneous detection of porcine
reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, classical swine fever
virus, and porcine circovirus in pigs. Mol Cell Probes. 27:149–152.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mahony J, Chong S, Merante F, Yaghoubian
S, Sinha T, Lisle C and Janeczko R: Development of a respiratory
virus panel test for detection of twenty human respiratory viruses
by use of multiplex PCR and a fluid microbead-based assay. J Clin
Microbiol. 45:2965–2970. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mahony JB, Blackhouse G, Babwah J, Smieja
M, Buracond S, Chong S, Ciccotelli W, O'Shea T, Alnakhli D,
Griffiths-Turner M and Goeree R: Cost analysis of multiplex PCR
testing for diagnosing respiratory virus infections. J Clin
Microbiol. 47:2812–2817. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Piewbang C, Rungsipipat A, Poovorawan Y
and Techangamsuwan S: Development and application of multiplex PCR
assays for detection of virus-induced respiratory disease complex
in dogs. J Vet Med Sci. 78:1847–1854. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yue F, Cui S, Zhang C and Yoon KJ: A
multiplex PCR for rapid and simultaneous detection of porcine
circovirus type 2, porcine parvovirus, porcine pseudorabies virus,
and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in clinical
specimens. Virus Genes. 38:392–397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boivin G, Côté S, Déry P, De Serres G and
Bergeron MG: Multiplex real-time PCR assay for detection of
influenza and human respiratory syncytial viruses. J Clin
Microbiol. 42:45–51. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang TG, Li AH, Lyu M, Chen M, Huang F
and Wu J: Detection of respiratory viral and bacterial pathogens
causing pediatric community-acquired pneumonia in Beijing using
real-time PCR. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 1:110–116. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Metzgar D, Gibbins C, Hudson NR and Jones
MS: Evaluation of multiplex type-specific real-time PCR assays
using the LightCycler and joint biological agent identification and
diagnostic system platforms for detection and quantitation of adult
human respiratory adenoviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 48:1397–1403.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lu X, Trujillo-Lopez E, Lott L and Erdman
DD: Quantitative real-time PCR assay panel for detection and
type-specific identification of epidemic respiratory human
adenoviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 51:1089–1093. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Washington C, Metzgar D, Hazbón MH, Binn
L, Lyons A, Coward C and Kuschner R: Multiplexed Luminex xMAP assay
for detection and identification of five adenovirus serotypes
associated with epidemics of respiratory disease in adults. J Clin
Microbiol. 48:2217–2222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Broeders S, Huber I, Grohmann L, Berben G,
Taverniers I, Mazzara M, Roosens N and Morisset D: Guidelines for
validation of qualitative real-time PCR methods. Trends Food Sci
Tech. 37:115–126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Fujimoto T, Okafuji T, Okafuji T, Ito M,
Nukuzuma S, Chikahira M and Nishio O: Evaluation of a bedside
immunochromatographic test for detection of adenovirus in
respiratory samples, by comparison to virus isolation, PCR, and
real-time PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 42:5489–5492. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Laamiri N, Fällgren P, Zohari S, Ben Ali
J, Ghram A, Leijon M and Hmila I: Accurate detection of avian
respiratory viruses by use of multiplex PCR-Based Luminex
suspension microarray assay. J Clin Microbiol. 54:2716–2725. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pierce VM, Elkan M, Leet M, McGowan KL and
Hodinka RL: Comparison of the Idaho Technology FilmArray system to
real-time PCR for detection of respiratory pathogens in children. J
Clin Microbiol. 50:364–371. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Popowitch EB, O'Neill SS and Miller MB:
Comparison of the Biofire FilmArray RP, Genmark eSensor RVP,
Luminex xTAG RVPv1, and Luminex xTAG RVP fast multiplex assays for
detection of respiratory viruses. J Clin Microbiol. 51:1528–1533.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Loeffelholz MJ, Pong DL, Pyles RB, Xiong
Y, Miller AL, Bufton KK and Chonmaitree T: Comparison of the
FilmArray respiratory panel and prodesse real-time PCR assays for
detection of respiratory pathogens. J Clin Microbiol. 49:4083–4088.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xu W, McDonough MC and Erdman DD:
Species-specific identification of human adenoviruses by a
multiplex PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol. 38:4114–4120.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Metzgar D, Osuna M, Yingst S, Rakha M,
Earhart K, Elyan D, Esmat H, Saad MD, Kajon A, Wu J, et al: PCR
analysis of egyptian respiratory adenovirus isolates, including
identification of species, serotypes, and coinfections. J Clin
Microbiol. 43:5743–5752. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rand KH, Rampersaud H and Houck HJ:
Comparison of two multiplex methods for detection of respiratory
viruses: FilmArray RP and xTAG RVP. J Clin Microbiol. 49:2449–2453.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Poritz MA, Blaschke AJ, Byington CL,
Meyers L, Nilsson K, Jones DE, Thatcher SA, Robbins T, Lingenfelter
B, Amiott E, et al: FilmArray, an automated nested multiplex PCR
system for multi-pathogen detection: Development and application to
respiratory tract infection. PLoS One. 6:e260472011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wada K, Kubota N, Ito Y, Yagasaki H, Kato
K, Yoshikawa T, Ono Y, Ando H, Fujimoto Y, Kiuchi T, et al:
Simultaneous quantification of Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus,
and human herpesvirus 6 DNA in samples from transplant recipients
by multiplex real-time PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol. 45:1426–1432.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gunson RN, Collins TC and Carman WF:
Practical experience of high throughput real time PCR in the
routine diagnostic virology setting. J Clin Virol. 35:355–367.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ratcliff RM, Chang G, Kok T and Sloots TP:
Molecular diagnosis of medical viruses. Curr Issues Mol Biol.
9:87–102. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wittwer CT, Herrmann MG, Gundry CN and
Elenitoba-Johnson KS: Real-time multiplex PCR assays. Methods.
25:430–442. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gunson RN, Bennett S, Maclean A and Carman
WF: Using multiplex real time PCR in order to streamline a routine
diagnostic service. J Clin Virol. 43:372–375. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Heim A, Ebnet C, Harste G and
Pring-Åkerblom P: Rapid and quantitative detection of human
adenovirus DNA by real-time PCR. J Med Virol. 70:228–239. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|