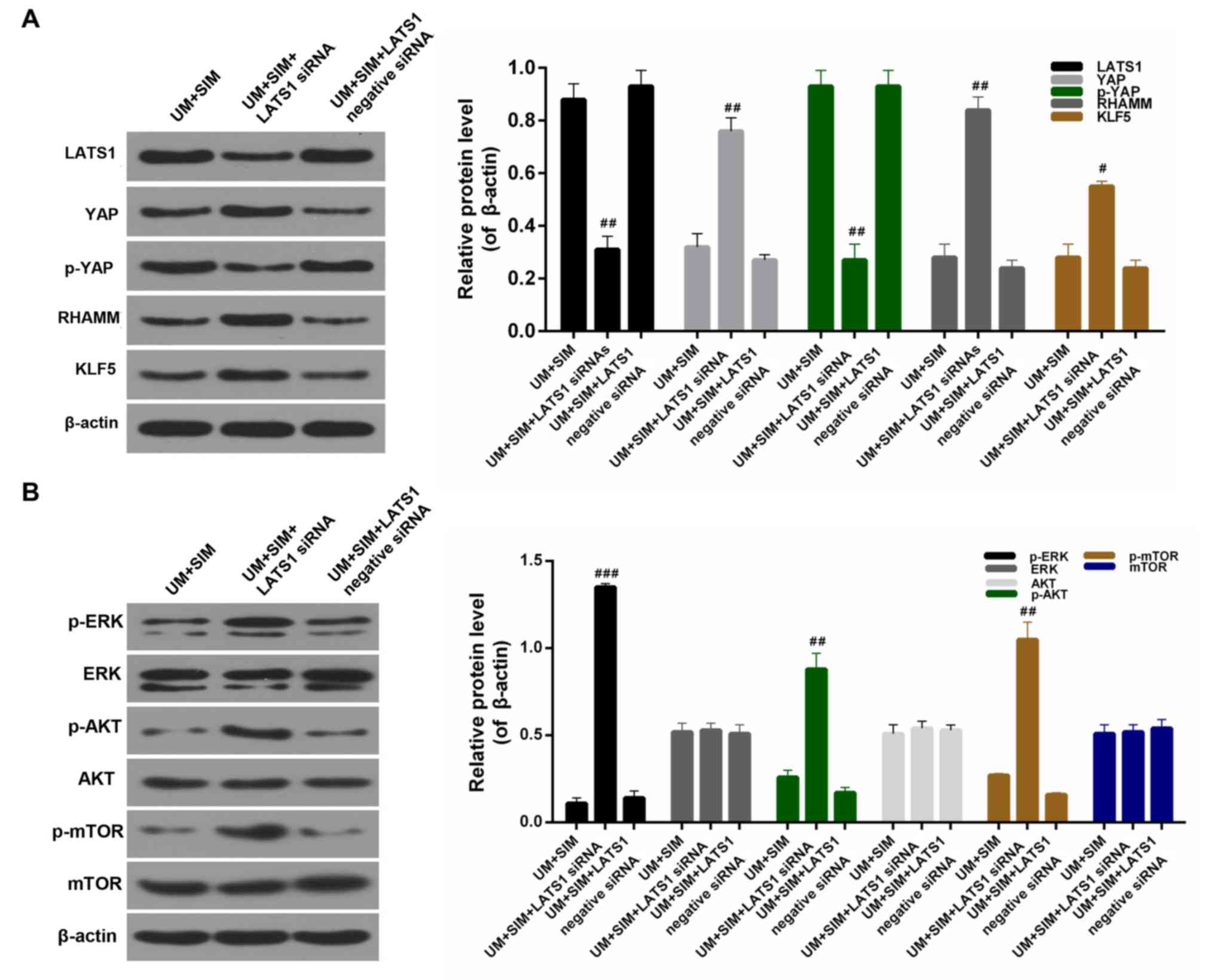
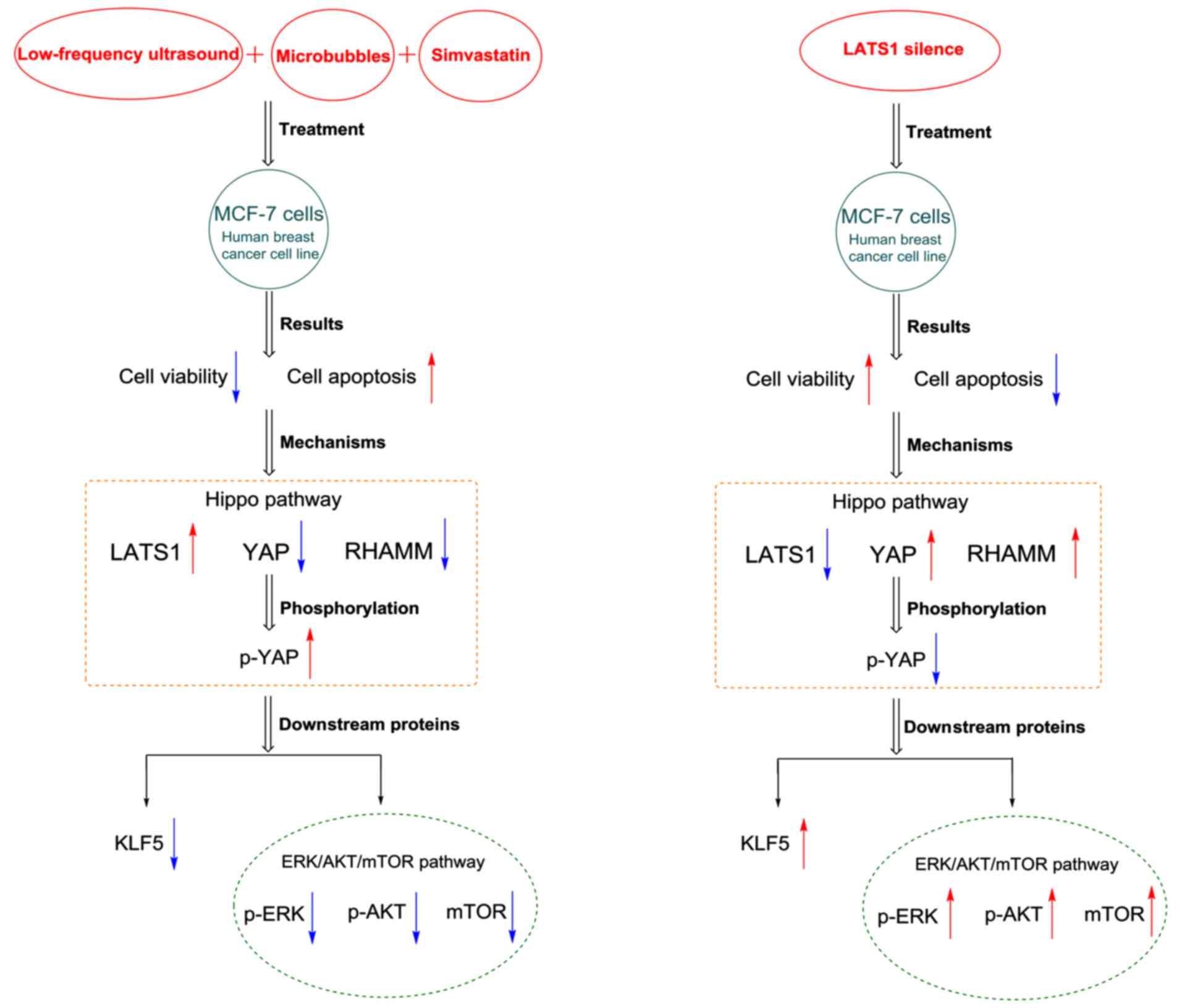
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Parkin DM and Steliarova-Foucher
E: Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008.
Eur J Cancer. 46:765–781. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber
RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thurlimann B and Senn HJ: Panel members:
Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer:
Highlights of the St gallen international expert consensus on the
primary therapy of early breast cancer 2013. Ann Oncol.
24:2206–2223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:52–62. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB,
Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:271–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Enderle L and McNeill H: Hippo gains
weight: Added insights and complexity to pathway control. Sci
Signal. 6:re72013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Halder G and Johnson RL: Hippo signaling:
Growth control and beyond. Development. 138:9–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Staley BK and Irvine KD: Hippo signaling
in Drosophila: Recent advances and insights. Dev Dyn. 241:3–15.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Svobodová J, Šmerdová L, Procházková J,
Topinka J, Líbalová H, Machala M and Vondráček J: Induction of
apoptosis in undifferentiated liver progenitor cells following
down-regulation of YAP1/TAZ and exposure to toxic AhR ligand.
Toxicol Lett. 280:S132–S133. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ferraiuolo M, Verduci L, Blandino G and
Strano S: Mutant p53 Protein and the Hippo Transducers YAP and TAZ:
A critical oncogenic node in human cancers. Int J Mol Sci.
18:9612017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Hao Y, Chun A, Cheung K, Rashidi B and
Yang X: Tumor suppressor LATS1 is a negative regulator of oncogene
YAP. J Biol Chem. 283:5496–5509. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Harvey K and Tapon N: The
Salvador-Warts-Hippo pathway-an emerging tumour-suppressor network.
Nat Rev Cancer. 7:182–191. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pan D: The hippo signaling pathway in
development and cancer. Dev Cell. 19:491–505. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Varelas X: The Hippo pathway effectors TAZ
and YAP in development, homeostasis and disease. Development.
141:1614–1626. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Z, Wu Y, Wang H, Zhang Y, Mei L, Fang
X, Zhang X, Zhang F, Chen H, Liu Y, et al: Interplay of mevalonate
and Hippo pathways regulates RHAMM transcription via YAP to
modulate breast cancer cell motility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:E89–E98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kilili GK and Kyriakis JM: Mammalian
Ste20-like kinase (Mst2) indirectly supports Raf-1/ERK pathway
activity via maintenance of protein phosphatase-2A catalytic
subunit levels and consequent suppression of inhibitory Raf-1
phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 285:15076–15087. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang C, Thor AD, Moore DH III, Zhao Y,
Kerschmann R, Stern R, Watson PH and Turley EA: The overexpression
of RHAMM, a hyaluronan-binding protein that regulates ras
signaling, correlates with overexpression of mitogen-activated
protein kinase and is a significant parameter in breast cancer
progression. Clin Cancer Res. 4:567–576. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang J, Ji JY, Yu M, Overholtzer M,
Smolen GA, Wang R, Brugge JS, Dyson NJ and Haber DA: YAP-dependent
induction of amphiregulin identifies a non-cell-autonomous
component of the Hippo pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 11:1444–1450. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Boudreau DM, Yu O and Johnson J: Statin
use and cancer risk: A comprehensive review. Expert Opin Drug Saf.
9:603–621. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gopalan A, Yu W, Sanders BG and Kline K:
Simvastatin inhibition of mevalonate pathway induces apoptosis in
human breast cancer cells via activation of JNK/CHOP/DR5 signaling
pathway. Cancer Lett. 329:9–16. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qi XF, Zheng L, Lee KJ, Kim DH, Kim CS,
Cai DQ, Wu Z, Qin JW, Yu YH and Kim SK: HMG-CoA reductase
inhibitors induce apoptosis of lymphoma cells by promoting ROS
generation and regulating Akt, Erk and p38 signals via suppression
of mevalonate pathway. Cell Death Dis. 4:e5182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pelaia G, Gallelli L, Renda T, Fratto D,
Falcone D, Caraglia M, Busceti MT, Terracciano R, Vatrella A,
Maselli R and Savino R: Effects of statins and farnesyl transferase
inhibitors on ERK phosphorylation, apoptosis and cell viability in
non-small lung cancer cells. Cell Prolif. 45:557–565. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Clendenen TV, Koenig KL, Arslan AA,
Lukanova A, Berrino F, Gu Y, Hallmans G, Idahl A, Krogh V, Lokshin
AE, et al: Factors associated with inflammation markers, a
cross-sectional analysis. Cytokine. 56:769–778. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fang Z, Tang Y, Fang J, Zhou Z, Xing Z,
Guo Z, Guo X, Wang W, Jiao W, Xu Z and Liu Z: Simvastatin inhibits
renal cancer cell growth and metastasis via AKT/mTOR, ERK and
JAK2/STAT3 pathway. PLoS One. 8:e628232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kochuparambil ST, Al-Husein B, Goc A,
Soliman S and Somanath PR: Anticancer efficacy of simvastatin on
prostate cancer cells and tumor xenografts is associated with
inhibition of Akt and reduced prostate-specific antigen expression.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 336:496–505. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ashush H, Rozenszajn LA, Blass M,
Barda-Saad M, Azimov D, Radnay J, Zipori D and Rosenschein U:
Apoptosis induction of human myeloid leukemic cells by ultrasound
exposure. Cancer Res. 60:1014–1020. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rosenthal I, Sostaric JZ and Riesz P:
Sonodynamic therapy-a review of the synergistic effects of drugs
and ultrasound. Ultrason Sonochem. 11:349–363. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Korosoglou G, Hardt SE, Bekeredjian R,
Jenne J, Konstantin M, Hagenmueller M, Katus HA and Kuecherer H:
Ultrasound exposure can increase the membrane permeability of human
neutrophil granulocytes containing microbubbles without causing
complete cell destruction. Ultrasound Med Biol. 32:297–303. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Korosoglou G, Behrens S, Bekeredjian R,
Hardt S, Hagenmueller M, Dinjus E, Bohm KJ, Unger E, Katus HA and
Kuecherer H: The potential of a new stable ultrasound contrast
agent for site-specific targeting. An in vitro experiment.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 32:1473–1478. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nie F, Xu HX, Lu MD, Wang Y and Tang Q:
Anti-angiogenic gene therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma mediated
by microbubble-enhanced ultrasound exposure: An in vivo
experimental study. J Drug Target. 16:389–395. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang Y, Hu B, Diao X and Zhang J:
Antitumor effect of microbubbles enhanced by low frequency
ultrasound cavitation on prostate carcinoma xenografts in nude
mice. Exp Ther Med. 3:187–191. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xing W, Gang WZ, Yong Z, Yi ZY, Shan XC
and Tao RH: Treatment of xenografted ovarian carcinoma using
paclitaxel-loaded ultrasound microbubbles. Acad Radiol.
15:1574–1579. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu HL, Fan CH, Ting CY and Yeh CK:
Combining microbubbles and ultrasound for drug delivery to brain
tumors: current progress and overview. Theranostics. 4:432–444.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Unger E, Porter T, Lindner J and Grayburn
P: Cardiovascular drug delivery with ultrasound and microbubbles.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 72:110–126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Junhua A, Yun J, Zhenzhou W, Ling Y and
Ding L: Treatment of malignant liver tumors by radiofrequency
ablation combined with low-frequency ultrasound radiation with
microbubbles. PLoS One. 8:e533512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu WP, Shen E, Bai WK, Wang Y and Hu B:
Enhanced antitumor effects of low-frequency ultrasound and
microbubbles in combination with simvastatin by downregulating
caveolin-1 in prostatic DU145 cells. Oncol Lett. 7:2142–2148. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yoon YI, Yoon TJ and Lee HJ: Optimization
of ultrasound parameters for microbubble-nanoliposome
complex-mediated delivery. Ultrasonography. 34:297–303. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lweesy K, Fraiwan L, Al-Bataineh O, Hamdi
N and Dickhaus H: Optimization of ultrasound array designs for high
intensity focused treatment of prostate cancer and benign prostatic
hyperplasia. Med Biol Eng Comput. 47:635–640. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Feng Y, Tian Z and Wan M: Bioeffects of
low-intensity ultrasound in vitro: Apoptosis, protein profile
alteration and potential molecular mechanism. J Ultrasound Med.
29:963–974. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang Z, Chen J, Chen L, Yang X, Zhong H,
Qi X, Bi Y and Xu K: Low frequency and intensity ultrasound induces
apoptosis of brain glioma in rats mediated by caspase-3, Bcl-2 and
survivin. Brain Res. 1473:25–34. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Alberts AW: Lovastatin and
simvastatin-inhibitors of HMG CoA reductase and cholesterol
biosynthesis. Cardiology. 77 Suppl 4:S14–S21. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kamigaki M, Sasaki T, Serikawa M, Inoue M,
Kobayashi K, Itsuki H, Minami T, Yukutake M, Okazaki A, Ishigaki T,
et al: Statins induce apoptosis and inhibit proliferation in
cholangiocarcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 39:561–568. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Toepfer N, Childress C, Parikh A,
Rukstalis D and Yang W: Atorvastatin induces autophagy in prostate
cancer PC3 cells through activation of LC3 transcription. Cancer
Biol Ther. 12:691–699. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Seeger H, Wallwiener D and Mueck AO:
Statins can inhibit proliferation of human breast cancer cells in
vitro. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 111:47–48. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Relja B, Meder F, Wilhelm K, Henrich D,
Marzi I and Lehnert M: Simvastatin inhibits cell growth and induces
apoptosis and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in hepatic cancer cells. Int
J Mol Med. 26:735–741. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cho SJ, Kim JS, Kim JM, Lee JY, Jung HC
and Song IS: Simvastatin induces apoptosis in human colon cancer
cells and in tumor xenografts and attenuates colitis-associated
colon cancer in mice. Int J Cancer. 123:951–957. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Koyuturk M, Ersoz M and Altiok N:
Simvastatin induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells: p53 and
estrogen receptor independent pathway requiring signalling through
JNK. Cancer Lett. 250:220–228. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen K and Wang D: Lats1 is the Key
Component of Hippo Signaling Pathway: A New Tumor Molecular
Biomarker and A Potential Therapeutic Target. Chinese J Cell Biol.
37:256–262. 2015.
|
|
48
|
Jansson L and Larsson J: Normal
hematopoietic stem cell function in mice with enforced expression
of the Hippo signaling effector YAP1. PLoS One. 7:e320132012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhi X, Zhao D, Zhou Z, Liu R and Chen C:
YAP promotes breast cell proliferation and survival partially
through stabilizing the KLF5 transcription factor. Am J Pathol.
180:2452–2461. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shin SY and Nguyen Lan LK: Unveiling
hidden dynamics of hippo signalling: A systems analysis. Genes
Bacfl. 7:E442016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Castelnovo LF, Bonalume V, Melif S,
Ballabio M, Colleoni D and Magnaghi V: Schwann cell development,
maturation and regeneration: A focus on classic and emerging
intracellular signaling pathways. Neural Regen Res. 12:1013–1023.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lai D, Ho KC, Hao Y and Yang X: Taxol
resistance in breast cancer cells is mediated by the hippo pathway
component TAZ and its downstream transcriptional targets Cyr61 and
CTGF. Cancer Res. 71:2728–2738. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mi W, Lin Q, Childress C, Sudol M,
Robishaw J, Berlot CH, Shabahang M and Yang W: Geranylgeranylation
signals to the Hippo pathway for breast cancer cell proliferation
and migration. Oncogene. 34:3095–3106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|