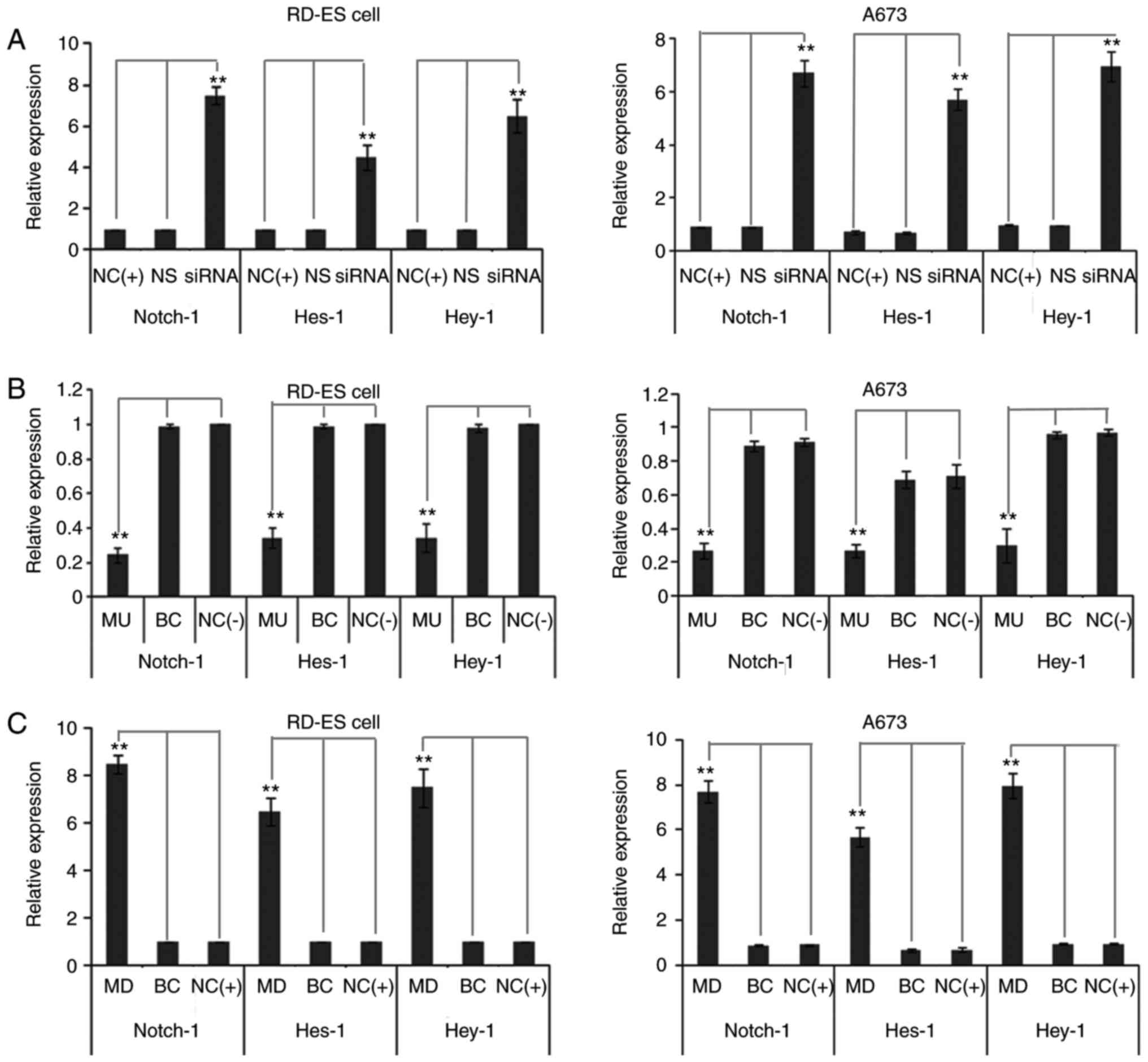
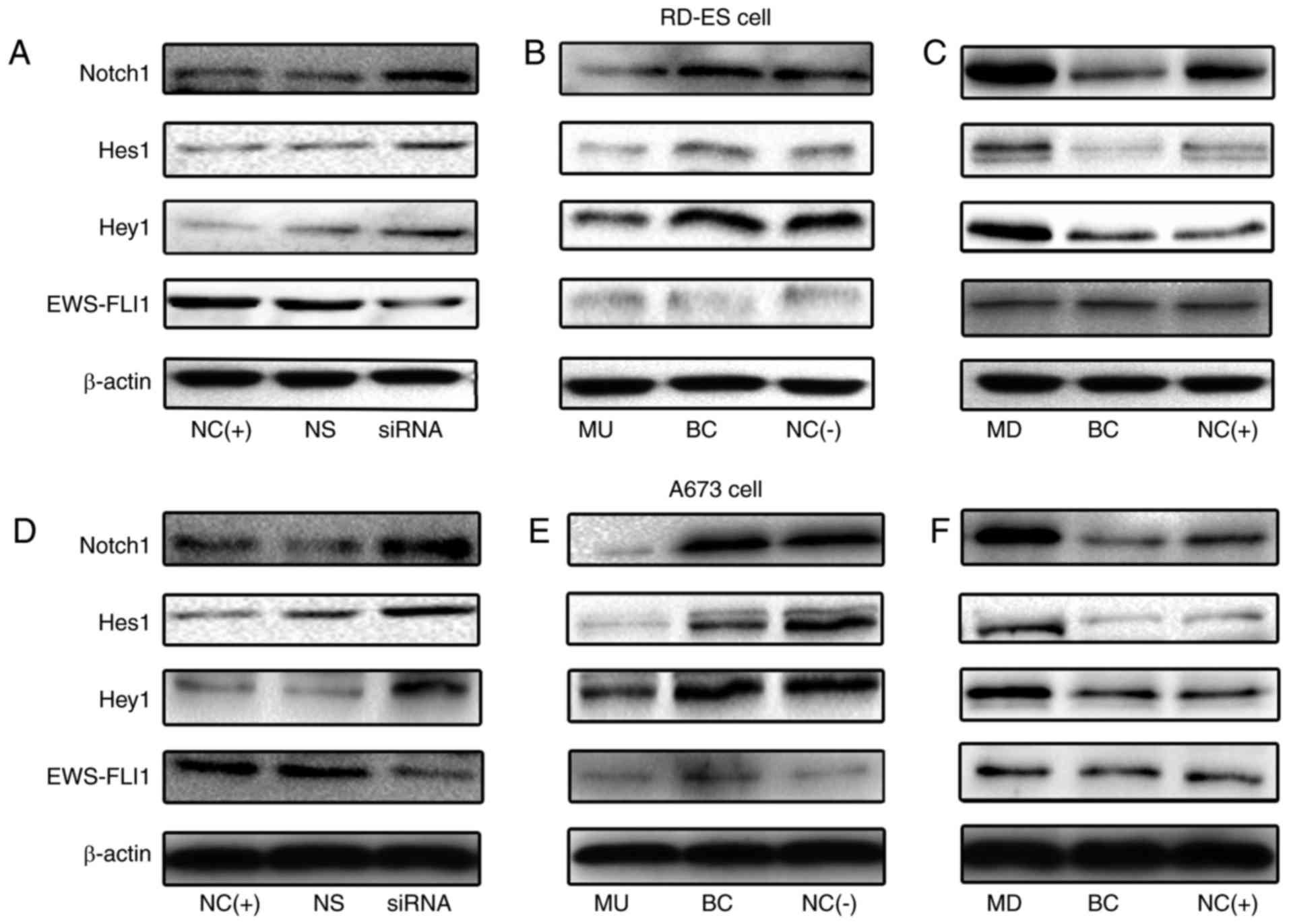
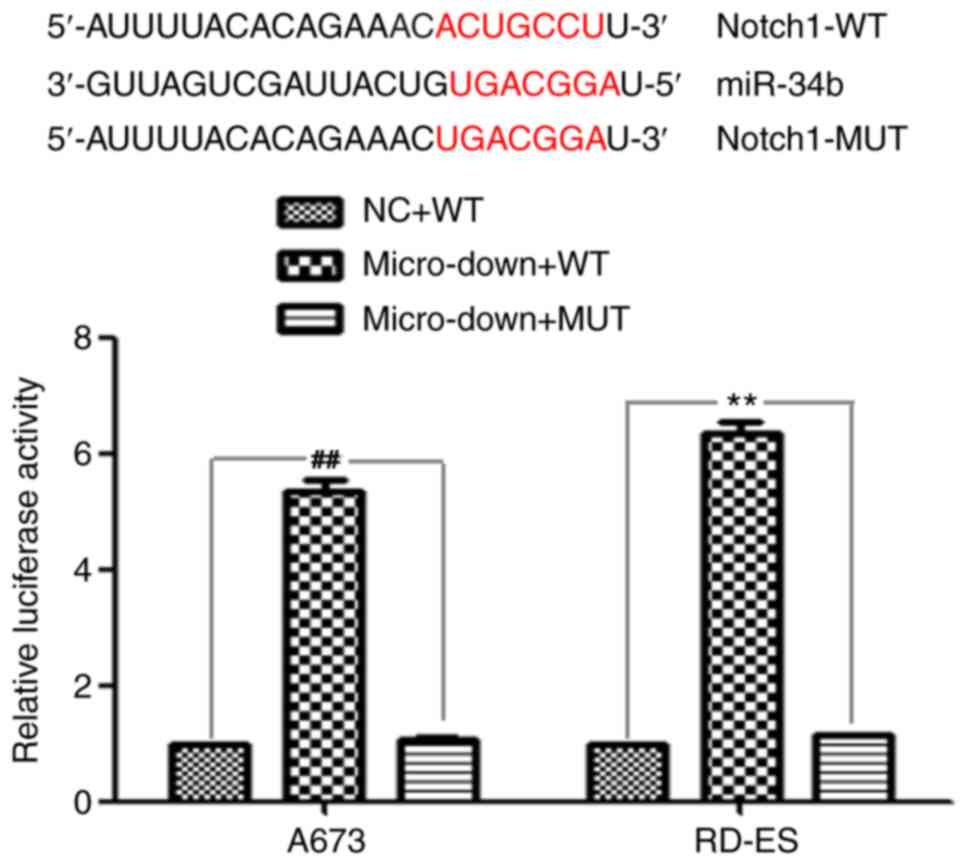
|
1
|
Riggi N and Stamenkovic I: The Biology of
Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Lett. 254:1–10. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bacci G, Forni C, Longhi A, Ferrari S,
Donati D, De Paolis M, Barbieri E, Pignotti E, Rosito P and Versari
M: Long-term outcome for patients with non-metastatic Ewing's
sarcoma treated with adjuvant and neoadjuvant chemotherapies. 402
patients treated at Rizzoli between 1972 and 1992. Eur J Cancer.
40:73–83. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grier HE, Krailo MD, Tarbell NJ, Link MP,
Fryer CJ, Pritchard DJ, Gebhardt MC, Dickman PS, Perlman EJ, Meyers
PA, et al: Addition of ifosfamide and etoposide to standard
chemotherapy for Ewing's sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal
tumor of bone. N Engl J Med. 348:694–701. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Esiashvili N, Goodman M and Marcus RB Jr:
Changes in incidence and survival of Ewing sarcoma patients over
the past 3 decades: Surveillance epidemiology and end results data.
J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 30:425–430. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Riggi N, Suva ML, Suva D, Cironi L,
Provero P, Tercier S, Joseph JM, Stehle JC, Baumer K, Kindler V and
Stamenkovic I: EWS-FLI-1 expression triggers a Ewing's sarcoma
initiation program in primary human mesenchymal stem cells. Cancer
Res. 68:2176–2185. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Riggi N, Cironi L, Provero P, Suva ML,
Kaloulis K, Garcia-Echeverria C, Hoffmann F, Trumpp A and
Stamenkovic I: Development of Ewing's sarcoma from primary bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells. Cancer Res.
65:11459–1168. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jedlicka P: Ewing Sarcoma, an enigmatic
malignancy of likely progenitor cell origin, driven by
transcription factor oncogenic fusions. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
3:338–347. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aryee DN, Niedan S, Kauer M, Schwentner R,
Bennani-Baiti IM, Ban J, Muehlbacher K, Kreppel M, Walker RL,
Meltzer P, et al: Hypoxia modulates EWS-FLI1 transcriptional
signature and enhances the malignant properties of Ewing's sarcoma
cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 70:4015–4023. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bachmaier R, Aryee DN, Jug G, Kauer M,
Kreppel M, Lee KA and Kovar H: O-GlcNAcylation is involved in the
transcriptional activity of EWS-FLI1 in Ewing's sarcoma. Oncogene.
28:1280–1284. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hancock JD and Lessnick SL: A
transcriptional profiling meta-analysis reveals a core EWS-FLI gene
expression signature. Cell Cycle. 7:250–256. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
De Vito C, Riggi N, Suva ML, Janiszewska
M, Horlbeck J, Baumer K, Provero P and Stamenkovic I: Let-7a is a
direct EWS-FLI-1 target implicated in Ewing's sarcoma development.
PLoS One. 6:e235922011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ban J, Jug G, Mestdagh P, Schwentner R,
Kauer M, Aryee DN, Schaefer KL, Nakatani F, Scotlandi K, Reiter M,
et al: Hsa-mir-145 is the top EWS-FLI1-repressed microRNA involved
in a positive feedback loop in Ewing's sarcoma. Oncogene.
30:2173–2180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Riggi N, Suva ML, De Vito C, Provero P,
Stehle JC, Baumer K, Cironi L, Janiszewska M, Petricevic T, Suvà D,
et al: EWS-FLI-1 modulates miRNA145 and SOX2 expression to initiate
mesenchymal stem cell reprogramming toward Ewing sarcoma cancer
stem cells. Genes Dev. 24:916–932. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Papagiannakopoulos T and Kosik KS:
MicroRNAs: Regulators of oncogenesis and stemness. BMC Med.
6:152008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sandberg R, Neilson JR, Sarma A, Sharp PA
and Burge CB: Proliferating cells express mRNAs with shortened 3′
untranslated regions and fewer microRNA target sites. Science.
320:1643–1647. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McKinsey EL, Parrish JK, Irwin AE,
Niemeyer BF, Kern HB, Birks DK and Jedlicka P: A novel oncogenic
mechanism in Ewing sarcoma involving IGF pathway targeting by
EWS/Fli1-regulated microRNAs. Oncogene. 30:4910–4920. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Robin TP, Smith A, McKinsey E, Reaves L,
Jedlicka P and Ford HL: EWS/FLI1 regulates EYA3 in Ewing sarcoma
via modulation of miRNA-708, resulting in increased cell survival
and chemoresistance. Mol Cancer Res. 10:1098–1108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dong F and Lou D: MicroRNA-34b/c
suppresses uveal melanoma cell proliferation and migration through
multiple targets. Mol Vis. 18:537–546. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, Shahryari V,
Arora S, Zaman MS, Chang I, Yamamura S, Tanaka Y, Chiyomaru T, et
al: miRNA-34b inhibits prostate cancer through demethylation,
active chromatin modifications, and AKT pathways. Clin Cancer Res.
19:73–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hermeking H: The miR-34 family in cancer
and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 17:193–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakatani F, Ferracin M, Manara MC, Ventura
S, Del Monaco V, Ferrari S, Alberghini M, Grilli A, Knuutila S,
Schaefer KL, et al: miR-34a predicts survival of Ewing's sarcoma
patients and directly influences cell chemo-sensitivity and
malignancy. J Pathol. 226:796–805. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zweidler-McKay PA: Notch signaling in
pediatric malignancies. Current Oncol Rep. 10:459–468. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M, Tang W, Yang M, Li
L, Xiang D, Desano JT, Bommer GT, Fan D, et al: MicroRNA miR-34
inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS One.
4:e68162009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weiler J, Hunziker J and Hall J:
Anti-miRNA oligonucleotides (AMOs): Ammunition to target miRNAs
implicated in human disease? Gene Ther. 13:496–502. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Delattre O, Zucman J, Melot T, Garau XS,
Zucker JM, Lenoir GM, Ambros PF, Sheer D, Turc-Carel C, Triche TJ,
et al: The Ewing family of tumors-a subgroup of small-round-cell
tumors defined by specific chimeric transcripts. N Engl J Med.
331:294–299. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tsugita M, Yamada N, Noguchi S, Yamada K,
Moritake H, Shimizu K, Akao Y and Ohno T: Ewing sarcoma cells
secrete EWS/Fli-1 fusion mRNA via microvesicles. PLoS One.
8:e774162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zucman J, Melot T, Desmaze C, Ghysdael J,
Plougastel B, Peter M, Zucker JM, Triche TJ, Sheer D, Turc-Carel C,
et al: Combinatorial generation of variable fusion proteins in the
Ewing family of tumours. EMBO J. 12:4481–4487. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Turc-Carel C, Aurias A, Mugneret F, Lizard
S, Sidaner I, Volk C, Thiery JP, Olschwang S, Philip I, Berger MP,
et al: Chromosomes in Ewing's sarcoma. I. An evaluation of 85 cases
of remarkable consistency of t(11;22)(q24;q12). Cancer Genet
Cytogenet. 32:229–238. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Delattre O, Zucman J, Plougastel B,
Desmaze C, Melot T, Peter M, Kovar H, Joubert I, de Jong P, Rouleau
G, et al: Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by
chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature. 359:162–165.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Douglass EC, Valentine M, Green AA, Hayes
FA and Thompson EI: t(11;22) and other chromosomal rearrangements
in Ewing's sarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 77:1211–1215.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
May WA, Gishizky ML, Lessnick SL, Lunsford
LB, Lewis BC, Delattre O, Zucman J, Thomas G and Denny CT: Ewing
sarcoma 11;22 translocation produces a chimeric transcription
factor that requires the DNA-binding domain encoded by FLI1 for
transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:pp. 5752–5756. 1993;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Im YH, Kim HT, Lee C, Poulin D, Welford S,
Sorensen PH, et al: EWS-FLI1, EWS-ERG, and EWS-ETV1 oncoproteins of
Ewing tumor family all suppress transcription of transforming
growth factor beta type II receptor gene. Cancer Res. 60:1536–1540.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mendell JT: miRiad roles for the miR-17-92
cluster in development and disease. Cell. 133:217–22. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hermeking H: p53 enters the microRNA
world. Cancer Cell. 12:414–418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yamazaki H, Chijiwa T, Inoue Y, Abe Y,
Suemizu H, Kawai K, Wakui M, Furukawa D, Mukai M, Kuwao S, et al:
Overexpression of the miR-34 family suppresses invasive growth of
malignant melanoma with the wild-type p53 gene. Exp Ther Med.
3:793–796. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Harata K, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, Kimura
M, Mitsui A, Ogawa R, Katada T, Tanaka T, Shiozaki M and Fujii Y:
MicroRNA-34b has an oncogenic role in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 1:685–689. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Giard DJ, Aaronson SA, Todaro GJ, Arnstein
P, Kersey JH, Dosik H and Parks WP: In vitro cultivation of human
tumors: Establishment of cell lines derived from a series of solid
tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 51:1417–1423. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lobry C, Oh P and Aifantis I: Oncogenic
and tumor suppressor functions of Notch in cancer: It's NOTCH what
you think. J Exp Med. 208:1931–1935. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Avila JL and Kissil JL: Notch signaling in
pancreatic cancer: Oncogene or tumor suppressor? Trends Mol Med.
19:320–327. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yap LF, Lee D, Khairuddin A, Pairan MF,
Puspita B, Siar CH and Paterson IC: The opposing roles of NOTCH
signalling in head and neck cancer: A mini review. Oral Dis.
21:850–857. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rampias T, Vgenopoulou P, Avgeris M,
Polyzos A, Stravodimos K, Valavanis C, Scorilas A and Klinakis A: A
new tumor suppressor role for the Notch pathway in bladder cancer.
Nat Med. 20:1199–1205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ban J, Bennani-Baiti IM, Kauer M, Schaefer
KL, Poremba C, Jug G, Schwentner R, Smrzka O, Muehlbacher K, Aryee
DN and Kovar H: EWS-FLI1 suppresses NOTCH-activated p53 in Ewing's
sarcoma. Cancer Res. 68:7100–7109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Schaefer KL, Eisenacher M, Braun Y,
Brachwitz K, Wai DH, Dirksen U, Lanvers-Kaminsky C, Juergens H,
Herrero D, Stegmaier S, et al: Microarray analysis of Ewing's
sarcoma family of tumours reveals characteristic gene expression
signatures associated with metastasis and resistance to
chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer. 44:699–709. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Baliko F, Bright T, Poon R, Cohen B, Egan
SE and Alman BA: Inhibition of notch signaling induces neural
differentiation in Ewing sarcoma. Am J Pathol. 170:1686–1694. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ji Q, Hao X, Meng Y, Zhang M, Desano J,
Fan D and Xu L: Restoration of tumor suppressor miR-34 inhibits
human p53-mutant gastric cancer tumorspheres. BMC Cancer.
8:2662008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tang Y, Tang Y and Cheng YS: miR-34a
inhibits pancreatic cancer progression through Snail1-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the Notch signaling pathway.
Sci Rep. 7:382322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bennani-Baiti IM, Aryee DN, Ban J, Machado
I, Kauer M, Muhlbacher K, Amann G, Llombart-Bosch A and Kovar H:
Notch signalling is off and is uncoupled from HES1 expression in
Ewing's sarcoma. J Pathol. 225:353–363. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sharma S, Kelly TK and Jones PA:
Epigenetics in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 31:27–36. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lee YS and Dutta A: MicroRNAs in cancer.
Annu Rev Pathol. 4:199–227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Groth C and Fortini ME: Therapeutic
approaches to modulating Notch signaling: Current challenges and
future prospects. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 23:465–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Vrba L, Munoz-Rodriguez JL, Stampfer MR
and Futscher BW: miRNA gene promoters are frequent targets of
aberrant DNA methylation in human breast cancer. PLoS One.
8:e543982013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang
CV and Mendell JT: c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1
expression. Nature. 435:839–843. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|