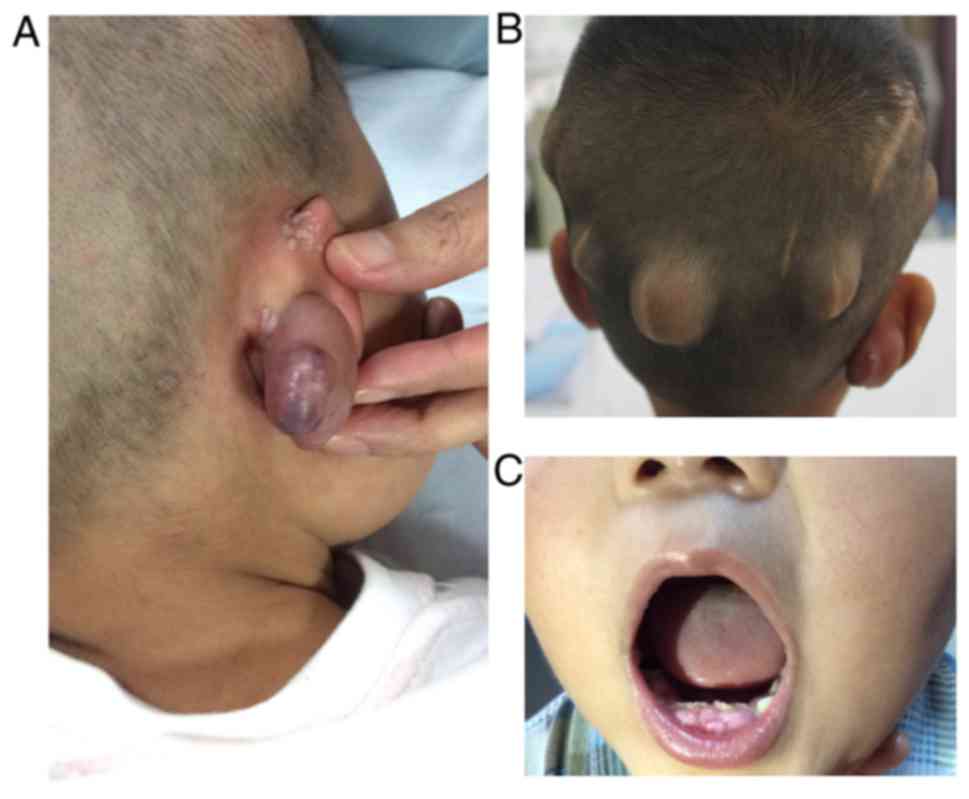
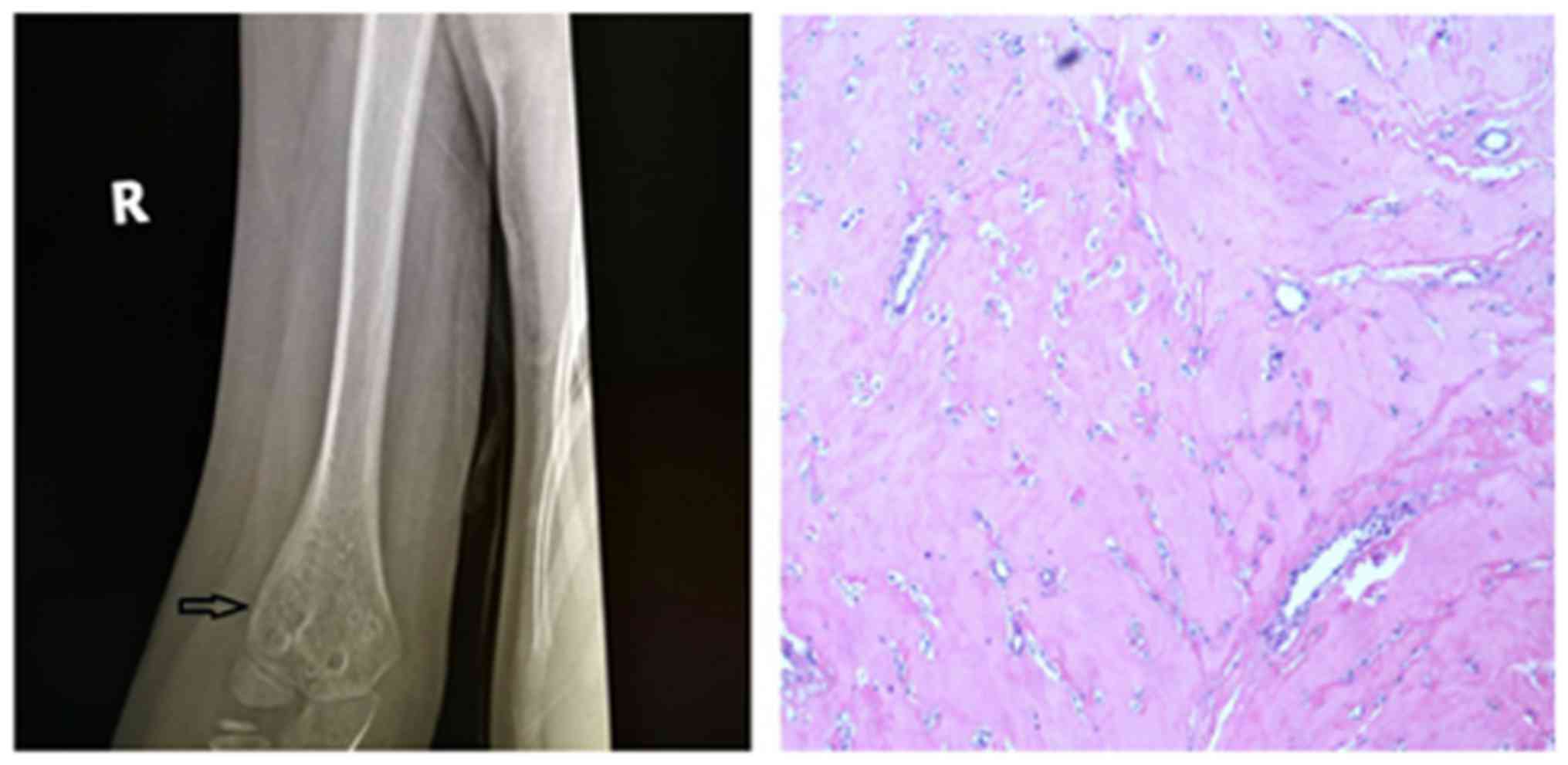
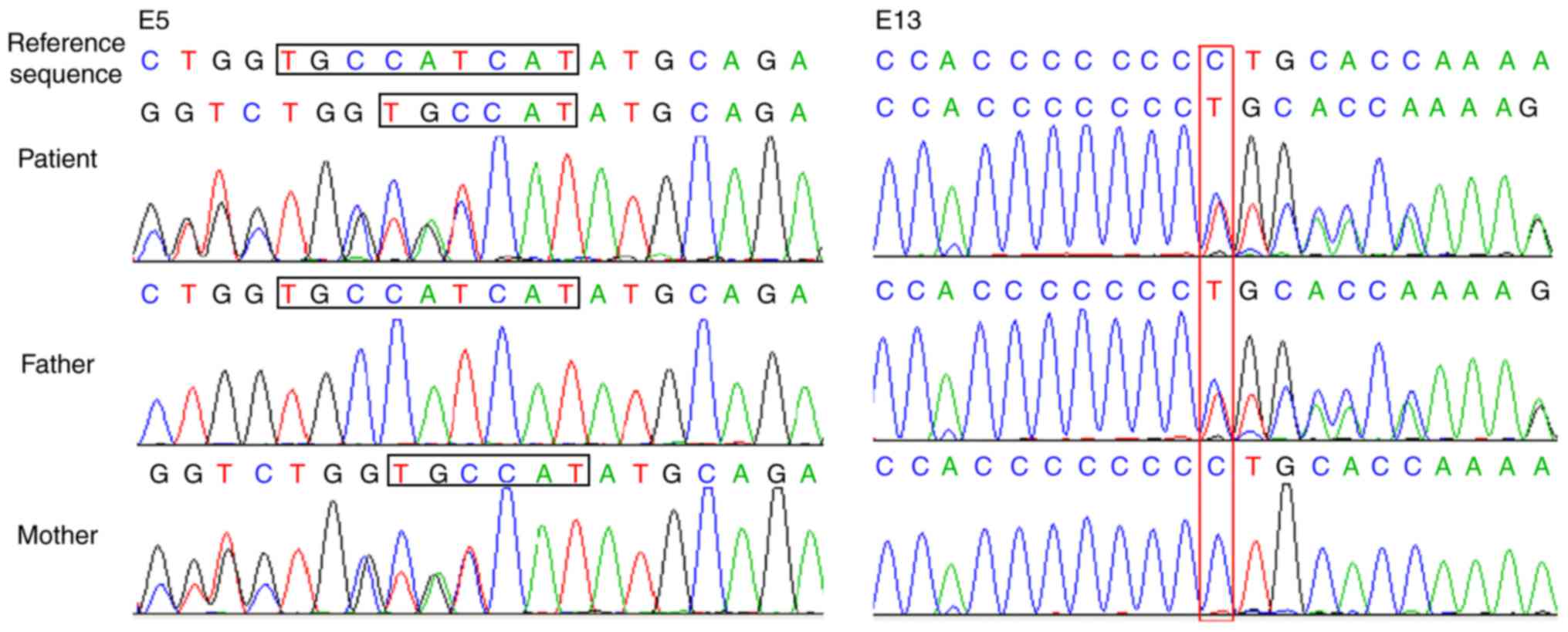
|
1
|
Denadai R, Raposo-Amaral CE, Bertola D,
Kim C, Alonso N, Hart T, Han S, Stelini RF, Buzzo CL, Raposo-Amaral
CA and Hart PS: Identification of 2 novel ANTXR2 mutations in
patients with hyaline fibromatosis syndrome and proposal of a
modified grading system. Am J Med Genet A. 158:732–742. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Nofal A, Sanad M, Assaf M, Nofal E, Nassar
A, Almokadem S, Attwa E and Elmosalamy K: Juvenile hyaline
fibromatosis and infantile systemic hyalinosis: A unifying term and
a proposed grading system. J Am Acad Dermatol. 61:695–700. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rahvar M, Teng J and Kim J: Systemic
hyalinosis with heterozygous CMG2 mutations: A case report and
review of literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 38:e60–e63. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Deuquet J, Lausch E, Guex N, Abrami L,
Salvi S, Lakkaraju A, Ramirez MC, Martignetti JA, Rokicki D, Bonafe
L, et al: Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome inducing mutations in the
ectodomain of anthrax toxin receptor 2 can be rescued by proteasome
inhibitors. EMBO Mol Med. 3:208–221. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Deuquet J, Lausch E, Superti-Furga A and
van der Goot FG: The dark sides of capillary morphogenesis gene 2.
EMBO J. 31:3–13. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jacquez P, Avila G, Boone K, Altiyev A,
Puschhof J, Sauter R, Arigi E, Ruiz B, Peng X, Almeida I, et al:
The disulfide bond Cys255-Cys279 in the immunoglobulin-like domain
of anthrax toxin receptor 2 is required for membrane insertion of
anthrax protective antigen pore. PLoS One. 10:e01308322015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hanks S, Adams S, Douglas J, Arbour L,
Atherton DJ, Balci S, Bode H, Campbell ME, Feingold M, Keser G, et
al: Mutations in the gene encoding capillary morphogenesis protein
2 cause juvenile hyaline fibromatosis and infantile systemic
hyalinosis. Am J Hum Genet. 73:791–800. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Abrami L, Leppla SH and van der Goot FG:
Receptor palmitoylation and ubiquitination regulate anthrax toxin
endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 172:309–320. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Abrami L, Kunz B and van der Goot FG:
Anthrax toxin triggers the activation of src-like kinases to
mediate its own uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:pp. 1420–1424.
2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
El-Maaytah M, Jerjes W, Shah P, Upile T,
Murphy C and Ayliffe P: Gingival hyperplasia associated with
juvenile hyaline fibromatosis: A case report and review of the
literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 68:2604–2608. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Muniz ML, Lobo AZ, Machado MC, Valente NY,
Kim CA, Lourenço SV and Nico MM: Exuberant juvenile hyaline
fibromatosis in two patients. Pediatr Dermatol. 23:458–464. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Faga A, Nicoletti G, Gregotti C, Finotti
V, Nitto A and Gioglio L: Effects of thermal water on skin
regeneration. Int J Mol Med. 29:732–740. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu JF, Li Y, Li K, Zhang X, Yang YN, Zhao
G and Liu ZR: Neuro-Sweet disease with positive modified acid-fast
staining of the cerebrospinal fluid: A case report. Exp Ther Med.
11:1239–1242. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Murray J: On three peculiar cases of
molluscum fibrosum in children. Med Chir Trans. 56:235–254. 1873.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gilaberte Y, González-Mediero I, López
Barrantes V and Zambrano A: Juvenile hyaline fibromatosis with
skull-encephalic anomalies: A case report and review of the
literature. Dermatology. 187:144–148. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Landing BH and Nadorra R: Infantile
systemic hyalinosis: Report of four cases of a disease, fatal in
infancy, apparently different from juvenile systemic hyalinosis.
Pediatr Pathol. 6:55–79. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Haidar Z, Temanni R, Chouery E, Jitesh P,
Liu W, Al-Ali R, Wang E, Marincola FM, Jalkh N, Haddad S, et al:
Diagnosis implications of the whole genome sequencing in a large
Lebanese family with hyaline fibromatosis syndrome. BMC Genet.
18:32017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jaouad IC, Guaoua S, Hajjioui A and
Sefiani A: Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome with mutation c.1074delT
of the CMG2 gene: A case report. J Med Case Rep. 8:2912014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dowling O, Difeo A, Ramirez MC, Tukel T,
Narla G, Bonafe L, Kayserili H, Yuksel-Apak M, Paller AS, Norton K,
et al: Mutations in capillary morphogenesis gene-2 result in the
allelic disorders juvenile hyaline fibromatosis and infantile
systemic hyalinosis. Am J Hum Genet. 73:957–966. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Narayanan DL and Phadke SR: Infantile
systemic hyalinosis with mutation in ANTXR2. Indian J Pediatr.
83:1356–1357. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee JY, Tsai YM, Chao SC and Tu YF:
Capillary morphogenesis gene-2 mutation in infantile systemic
hyalinosis: Ultrastructural study and mutation analysis in a
Taiwanese infant. Clin Exp Dermatol. 30:176–179. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hatamochi A, Sasaki T, Kawaguchi T, Suzuki
H and Yamazaki S: A novel point mutation in the gene encoding
capillary morphogenesis protein 2 in a Japanese patient with
juvenile hyaline fibromatosis. Br J Dermatol. 157:1037–1039. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Youssefian L, Vahidnezhad H, Aghighi Y,
Ziaee V, Zeinali S, Abiri M and Uitto J: Hyaline fibromatosis
syndrome: A novel mutation and recurrent founder mutation in the
CMG2/ANTXR2 gene. Acta Derm Venereol. 97:108–109. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shieh JT, Swidler P, Martignetti JA,
Ramirez MC, Balboni I, Kaplan J, Kennedy J, Abdul-Rahman O, Enns
GM, Sandborg C, et al: Systemic hyalinosis: A distinctive early
childhood-onset disorder characterized by mutations in the anthrax
toxin receptor 2 gene (ANTRX2). Pediatrics. 118:e1485–e1492. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sugiura K, Ohno A, Kono M, Kitoh H, Itomi
K and Akiyama M: Hyperpigmentation over the metacarpophalangeal
joints and the malleoli in a case of hyaline fibromatosis syndrome
with ANTXR2 mutations. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 30:e44–e46.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vahidnezhad H, Ziaee V, Youssefian L, Li
Q, Sotoudeh S and Uitto J: Infantile systemic hyalinosis in an
Iranian family with a mutation in the CMG2/ANTXR2 gene. Clin Exp
Dermatol. 40:636–639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
El-Kamah GY, Fong K, El-Ruby M, Afifi HH,
Clements SE, Lai-Cheong JE, Amr K, El-Darouti M and McGrath JA:
Spectrum of mutations in the ANTXR2 (CMG2) gene in infantile
systemic hyalinosis and juvenile hyaline fibromatosis. Br J
Dermatol. 163:213–215. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang Y, Li R, Li Y and Liao C:
Identification of novel compound heterozygous mutations in the
ANTXR2 gene in a Chinese patient with juvenile hyaline
fibromatosis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 34:866–869.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kurosaki T and Maquat L: Nonsense mediated
mRNA decay in humans at a glance. J Cell Sci. 129:461–467. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hug N, Longman D and Cáceres JF: Mechanism
and regulation of the nonsense-mediated decay pathway. Nucleic
Acids Res. 44:1483–1495. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wigelsworth DJ, Krantz BA, Christensen KA,
Lacy DB, Juris SJ and Collier RJ: Binding stoichiometry and
kinetics of the interaction of a human anthrax toxin receptor,
CMG2, with protective antigen. J Biol Chem. 279:23349–23356. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|