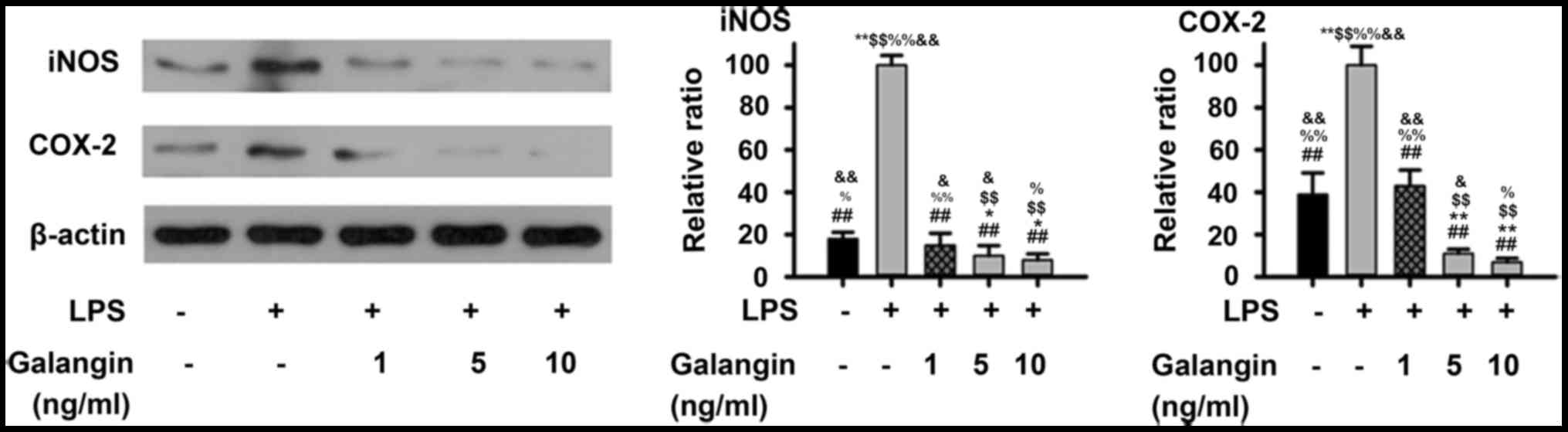
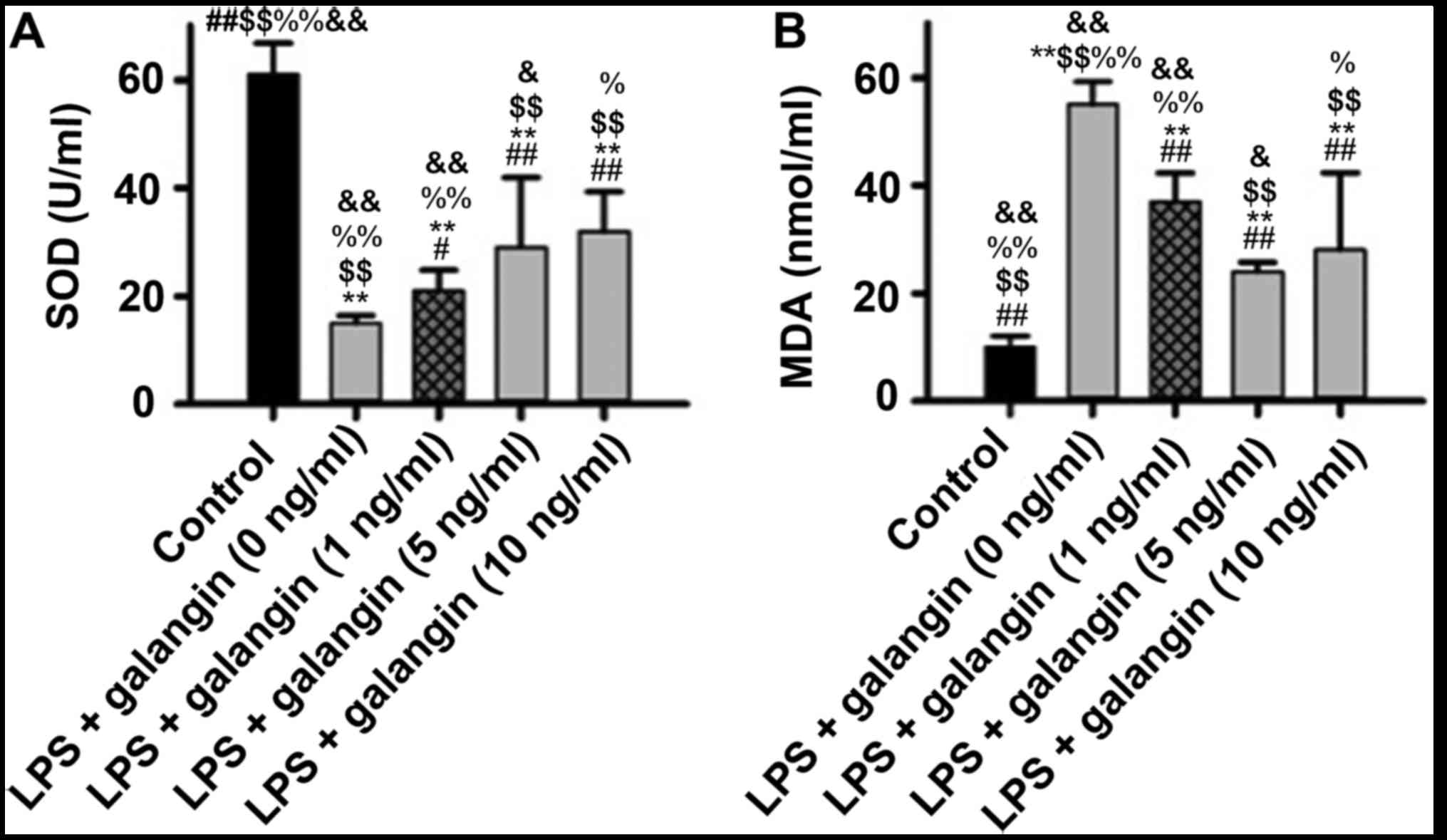
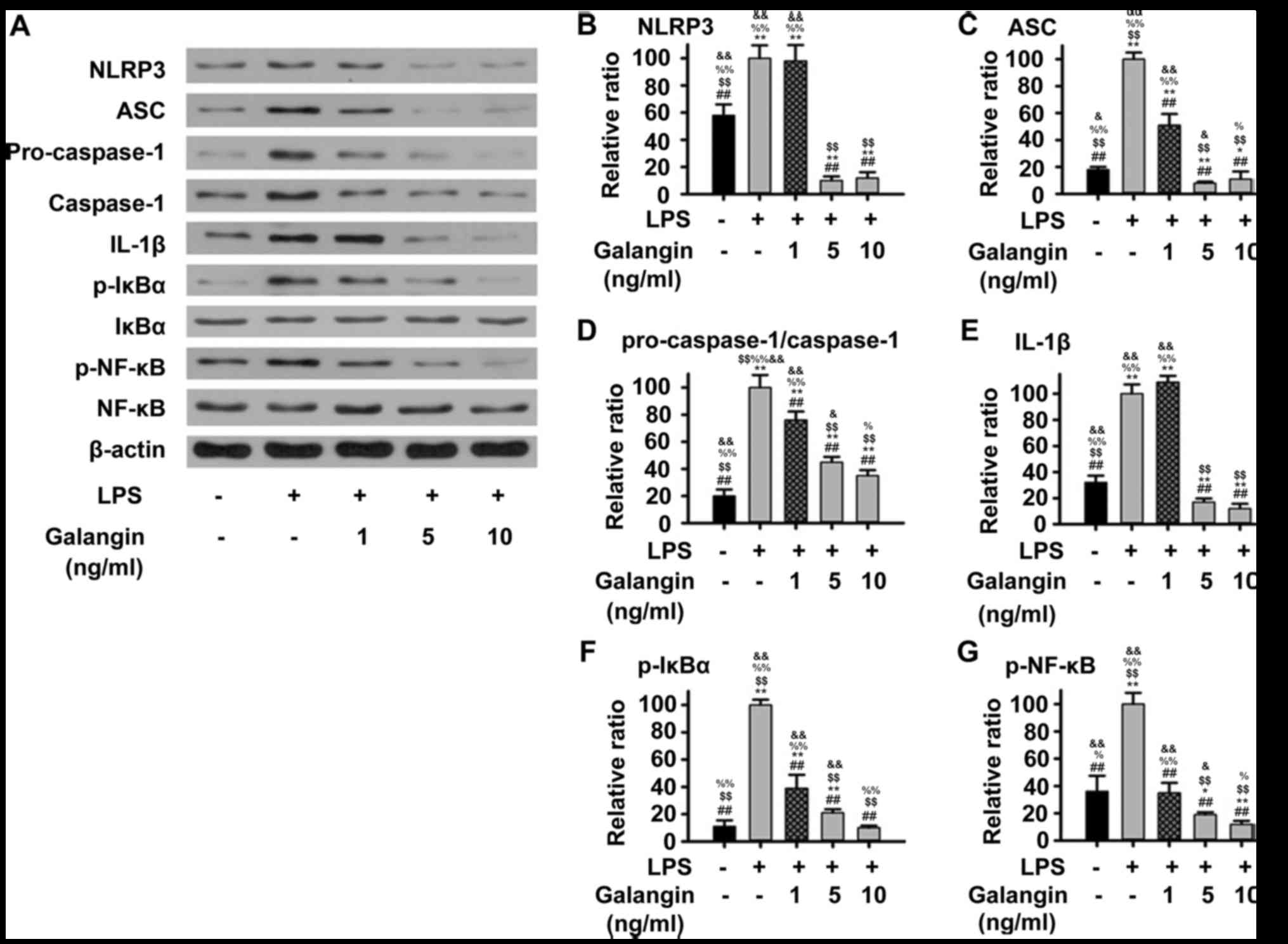
|
1
|
Chang X, He H, Zhu L, Gao J, Wei T, Ma Z
and Yan T: Protective effect of apigenin on Freund's complete
adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats via inhibiting P2×7/NF-κB
pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 236:41–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Majithia V and Geraci SA: Rheumatoid
arthritis: Diagnosis and management. Am J Med. 120:936–939. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S,
Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, et
al: Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20
age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global
burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 380:2095–2128. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Saag KG, Teng GG, Patkar NM, Anuntiyo J,
Finney C, Curtis JR, Paulus HE, Mudano A, Pisu M, Elkins-Melton M,
et al: American college of rheumatology 2008 recommendations for
the use of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic
drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 59:762–784. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartok B and Firestein GS: Fibroblast-like
synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol
Rev. 233:233–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
de Sousa EB, Casado PL, Moura Neto V,
Duarte ME and Aguiar DP: Synovial fluid and synovial membrane
mesenchymal stem cells: Latest discoveries and therapeutic
perspectives. Stem Cell Res Ther. 5:1122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chang SK, Gu Z and Brenner MB:
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes in inflammatory arthritis pathology:
The emerging role of cadherin-11. Immunol Rev. 233:256–266. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Firestein GS: Evolving concepts of
rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 423:356–361. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Simmonds RE and Foxwell BM: Signalling,
inflammation and arthritis: NF-kappaB and its relevance to
arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford). 47:584–590.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baldwin AS Jr: The NF-kappa B and I kappa
B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol.
14:649–683. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tak PP and Firestein GS: NF-kappaB: A key
role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 107:7–11. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yamamoto Y and Gaynor RB: Therapeutic
potential of inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway in the treatment
of inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest. 107:135–142. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
van Vuuren SF: Antimicrobial activity of
South African medicinal plants. J Ethnopharmacol. 119:462–472.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bestwick CS and Milne L: Influence of
galangin on HL-60 cell proliferation and survival. Cancer Lett.
243:80–89. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sivakumar AS and Anuradha CV: Effect of
galangin supplementation on oxidative damage and inflammatory
changes in fructose-fed rat liver. Chem Biol Interact. 193:141–148.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim HH, Bae Y and Kim SH: Galangin
attenuates mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation. Food Chem
Toxicol. 57:209–216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zha WJ, Qian Y, Shen Y, Du Q, Chen FF, Wu
ZZ, Li X and Huang M: Galangin abrogates ovalbumin-induced airway
inflammation via negative regulation of NF-kappaB. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:7676892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huh JE, Jung IT, Choi J, Baek YH, Lee JD,
Park DS and Choi DY: The natural flavonoid galangin inhibits
osteoclastic bone destruction and osteoclastogenesis by suppressing
NF-κB in collagen-induced arthritis and bone marrow-derived
macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 698:57–66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen S: Natural products triggering
biological targets-a review of the anti-inflammatory phytochemicals
targeting the arachidonic acid pathway in allergy asthma and
rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Drug Targets. 12:288–301. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wasserman AM: Diagnosis and management of
rheumatoid arthritis. Am Fam Physician. 84:1245–1252.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kapoor S, Fitzpatrick M, Clay E, Bayley R,
Wallace GR and Young SP: Metabolomics in the analysis of
inflammatory diseases. Roessner U: Metabolomics. Rijeka (HR):
InTech. Chapter 112012.
|
|
22
|
Yoshino S and Ohsawa M: The role of
lipopolysaccharide injected systemically in the reactivation of
collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 129:1309–1314.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Feldmann M, Brennan FM and Maini RN: Role
of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 14:397–440.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gracie JA, Forsey RJ, Chan WL, Gilmour A,
Leung BP, Greer MR, Kennedy K, Carter R, Wei XQ, Xu D, et al: A
proinflammatory role for IL-18 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin
Invest. 104:1393–1401. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Grabowski PS, Wright PK, Van't Hof RJ,
Helfrich MH, Ohshima H and Ralston SH: Immunolocalization of
inducible nitric oxide synthase in synovium and cartilage in
rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Br J Rheumatol.
36:651–655. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schleimer RP: Inflammation: Basic
principles and clinical correlates edited by John Gallin, Ira
Goldstein and Ralph Snyderman, Raven Press, $219.00 (xvii + 995
pages) ISBN 0 88167 344 7. Immunol Today. 9:327, 19871988.
|
|
27
|
Anderson GD, Hauser SD, McGarity KL,
Bremer ME, Isakson PC and Gregory SA: Selective inhibition of
cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 reverses inflammation and expression of
COX-2 and interleukin 6 in rat adjuvant arthritis. J Clin Invest.
97:2672–2679. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hadjigogos K: The role of free radicals in
the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Panminerva Med. 45:7–13.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mansour RB, Lassoued S, Gargouri B, El
Gaïd A, Attia H and Fakhfakh F: Increased levels of autoantibodies
against catalase and superoxide dismutase associated with oxidative
stress in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus
erythematosus. Scand J Rheumatol. 37:103–108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|