Introduction
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is a type of brain
injury within newborns, in which cerebral ischemia and reperfusion
lead to neuronal damage and neurological disability (1,2).
Increasing evidence has suggested that neuronal injury induces the
proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells/progenitor
cells (NSCs/NSPs) and adult neurogenesis (3–5).
NSPs possess a notable ability to self-renew and differentiate into
glia and functional neurons (6,7).
Animal and clinical studies (8)
have suggested that NSPs are a powerful potential treatment for
numerous diseases of the central nervous system (9–11).
Specifically, it has been reported that NSPs are involved in the
regeneration of neurons and glia during perinatal hypoxia/ischemia
(H/I) (12).
Numerous signaling pathways are involved in the
regulation of NSCs (13–16). N-Myc, which is mainly distributed
in the developing nervous system, is predominantly expressed in
NSCs and neuroectodermal progenitors under normal conditions
(17,18). In addition, N-Myc is required for
the development of the nervous system; loss of N-Myc function
results in the failure of neural progenitor cell expansion
(19). Notch signaling has been
associated with the regulation of NSCs; the Notch signaling pathway
promotes the survival and proliferation of normal and tumor-derived
NSCs, and prevents their differentiation (20–22).
Binding of the ligands Delta or Jagged to Notch receptors induces
the intramembranous proteolytic cleavage of the Notch receptor,
yielding an activated Notch intracellular domain (NICD), which is
necessary for the regulation of the transcription of several target
genes, such as fibroblast growth factor 5 (23).
By using mass spectrometry, E3 ubiquitin protein
ligase (Huwe1), containing a HECT domain, was purified from H1299
cells transfected with a plasmid expressing HA-ARF-Flag (24). Huwe1 has numerous substrates,
including N-Myc, p53 and cell division cycle 6 (25–29).
It has been demonstrated that Huwe1 is important for the transition
from NSCs/NSPs to differentiated neurons (27). Loss of Huwe1 severely disrupts
neurogenesis and the laminar organization in the cortex and,
interestingly, the N-Myc-Delta-like 3 (DLL3)-Notch1 signaling
cascade has been reported to be involved in this process (27,30).
In vitro and in vivo research has indicated that
Huwe1 is a key factor for neurogenesis; however, the exact
biological function and underlying mechanism of Huwe1 remains
controversial: Huwe1 affects the accumulation of many substrates,
including N-Myc, c-Myc and Mcl1, which are involved in
carcinogenesis. However, Huwe1 also promotes the accumulation of
p53 protein, which inhibits the growth and development of multiple
cancer types.
We previously generated neural progenitor L2.3 cells
from a rat E14.5 cortex with the ability to differentiate into
neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and other neuronal cell types
(31,32). In the present study, radial glial
L2.3 cells were used to investigate the role of Huwe1 and the
downstream N-Myc-DLL3-Notch1 signaling pathway during
oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) and the restoration of normal
conditions.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
The culturing conditions of L2.3 cells were
described previously (32).
Briefly, L2.3 cells were cultured as neurospheres for 3 to 4 days
in culture medium: Dulbecco's modified Eagles medium/F12
(Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA)
supplemented with 25 mM glucose (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA,
Darmstadt, Germany), 2 mM glutamine, 100 units/ml penicillin and
0.1 mg/ml streptomycin (both Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.), 10 ng/ml fibroblastic growth factor 2 (FGF2; BD Biosciences,
San Jose, CA, USA), 2 µg/ml heparin (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) and
1X B27 (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). Cells were
propagated as neurospheres and passaged by mild trypsinization
(0.025% for 5 min at 37°C with 5% CO2) every 3 days.
Cells (1×104) were cultured on laminin-coated coverslips
in 10 ng/ml FGF2-containing serum-free culture medium (DMEM/F12
with 25 mM glucose, 2 mM glutamine, 100 units/ml penicillin, 0.1
mg/ml streptomycin, 10 ng/ml FGF2, 2 µg/ml heparin and 1X B27) for
2 days at 37°C prior to transduction with a lentiviral vector
(described below). For differentiation, cells were cultured on
laminin-coated coverslips in 10 ng/ml FGF2-containing serum-free
medium for 1 day, then the medium was replaced with FGF2-free
culture medium with fetal bovine serum (1%) (Gibco; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.) for 5 days. The cells were then fixed and stained
with specific antibodies as described below.
Establishment of the OGD-injured L2.3
cell model
OGD was conducted to induce H/I in vitro.
Cells (~1×104) were washed three times with glucose-free
culture medium (DMEM/F12 with 2 mM glutamine, 100 units/ml
penicillin and 0.1 mg/ml streptomycin, 10 ng/ml FGF2, 2 µg/ml
heparin and 1X B27) prior to oxygen deprivation and placed in an
anaerobic chamber, then perfused with N2 (95%) and
CO2 (5%) at 37°C for 6 h. Following OGD, the cells were
transferred to the aforementioned culture medium and cultured with
CO2 (5%) at 37°C for the normalization of oxygen and
glucose levels for 8, 16 and 24 h. Cells cultured under normoxic
conditions were considered the control group.
Lentiviral constructs and
transduction
GIPZ lentiviral microRNA-adapted short hairpin
(sh)RNA vectors (sequences unavailable; expressing control
non-silencing shRNA, rat Huwe1 shRNA and N-Myc shRNA, respectively)
were obtained from Open Biosystems, Inc. (Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.). In accordance with the Trans-Lentiviral packaging system
(Open Biosystems, Inc.; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), lentiviral
packaging was conducted using 5.0×105 TLA-293T cells
(Open Biosystems; GE Healthcare Dharmacon, Inc., Lafayette, CO,
USA). The DMEM/F12 medium containing the packaging plasmids was
aspirated and replaced with complete medium (DMEM/F12 containing
20% FBS) 12 h following transfection. The cell supernatant,
containing the lentivirus was collected after 72 h, centrifuged at
12,000 × g and 4°C for 20 min and stored at −80°C. To determine the
titers of lentiviral particles in the isolated supernatants,
TLA-293T cells were transduced with serial dilutions (5X, 10X, 20X)
of the lentiviral supernatants (500 × g at 4°C for 10 min) for 48 h
and were identified by green fluorescent protein fluorescence and
sorted on a BD FACS Aria II (BD Biosciences). As determined by
trypan blue staining technique, the viability of cells after cell
sorting was higher than 95%. (33)
(×4 magnification, 488 nm excitation). L2.3 cells were transduced
with lentiviral particles (Huwe1 shRNA or Huwe1 shRNA and N-Myc
shRNA) diluted (2X, 5X) in serum free medium containing 10 µg/ml of
Polybrene® (Merck KGaA) at a multiplicity of infection
(MOI) of 10, all carrying green fluorescent protein (GFP). After 6
h, an equal amount (1 ml) of culture medium was added to each well.
The transduction cocktail was removed and replaced with complete
medium containing puromycin (2 µg/ml) the following day, and
western blot analysis for Huwe1 and N-Myc expression in cell
lysates was performed to select for Huwe1 shRNA-transfected cells
or Huwe1 and N-Myc shRNA-transfected cells. Control
shRNA-transfected cells and untransfected cells were used as the
controls.
Cell viability assay
A Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Molecular
Technologies, Inc., Kumamoto, Japan) was used to assess cell
viability: 100 µl of the L2.3 cell suspension (in PBS) was seeded
in 96-well plates (50,000 cells/well). Untransfected cells were
used as the control. The kit was utilized according to the
manufacturer's protocols; the absorbance at 450 nm was measured
with a microplate reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA,
USA). Cell viability was calculated by setting the absorbance of
the normoxic control to 100%.
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release
assay
LDH release in the culture medium was measured using
an LDH diagnostic kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute,
Nanjing, China), according to the manufacturer's protocols. LDH
activity was calculated in 96-well plates (5×104
cells/well) by measuring the absorbance at 490 nm with a microplate
reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.).
5-bromo-2′deoxyurine (BrdU) assay
Cells were treated with 10 µM BrdU (Roche
Diagnostics, Sussex, UK) for 24 h. Spheres were dissociated with 10
mg/ml collagenase for 10 min at room temperature and
~2×104 cells were fixed with a formalin solution for 15
min at 37°C on a Matrigel-coated coverslip (incubated overnight
with Matrigel at 37°C). Following permeabilization with PBS
containing Triton X-100 (0.1%) at room temperature for 30 min, DNA
denaturation was performed with 2N HCl for 10 min at room
temperature, followed by neutralization with 0.1 M sodium
tetra-borate for 10 min at room temperature. The subsequent steps
conducted were described below in ‘Immunocytochemistry’.
Genome-integrated BrdU was detected using an anti-BrdU antibody
(1:200; cat. no 555627; BD Biosciences) and a Cy3 conjugated
anti-mouse secondary antibody (1:1,000; cat. no. 115-165-003;
Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, Inc., West Grove, PA, USA).
The proportion of BrdU positive cells relative to the total number
of cells was estimated using a fluorescent microscope (×10
magnification, 550 nm excitation). Three fields of view were
analyzed.
Immunocytochemistry
L2.3 cells underwent expansion for 5 days under
normal conditions or following OGD. Cells (2×104) were
fixed in paraformaldehyde (4%) at room temperature for 15 min. The
primary antibodies employed were: Mouse anti-nestin (1:200; cat.
no. MAB5326; Merck KGaA) or rabbit anti-microtubule-associated
protein 2 (MAP2; 1:100; cat. no. M3696; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA).
Following incubation at 4°C overnight, the cells were washed and
incubated with the appropriate secondary antibodies at 37°C for 1
h, including fluorescein isothiocyanate goat anti-mouse secondary
antibody (cat. no. ab6785; 1:1,000; Abcam, Cambridge, USA), Cy3
goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (cat. no. BA1032; 1:500; Wuhan
Boster Biological Technology, Ltd., Wuhan, China). Cell nuclei were
counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI,
Sigma-Aldrich, 1:10,000, USA, cat. no. D9564) at 37°C for 30 min,
using a fluorescent microscope (×100 magnification, 359 nm
excitation). Three fields of view were analyzed using a fluorescent
microscope (Nikon Tie).
Western blot analysis
Cells were lysed with SDS lysis buffer [50 mM Tris
(pH 8.1), 1% SDS, 2 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 25 mM
β-glycerophosphate, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM Na3VO4
and 0.5 µg/ml leupeptin] and heat-denatured at 95°C for 5 min.
Protein concentration was measured with a bicinchoninic acid
protein assay. Cellular proteins (20 µg/lane) were separated via
SDS-PAGE (10%) and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride
membranes. The membranes were blocked for 1 h with blocking buffer
at room temperature (1X PBS with 0.1% Tween 20 and 5% non-fat dry
milk) and then incubated with primary antibodies against Huwe1
(1:500; cat. no. ab701612; Abcam), Notch1 (1:200; cat. no. sc6014;
Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas TX, USA), NICD (1:1,000;
cat. no. AB8925; Cell Signaling Technology, USA), DLL3 (1:200,
Abcam, USA, cat. no. ab103102), N-Myc (1:200; cat. no. ab24193) at
4°C overnight, and then with anti-rabbit horseradish
peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (1:1,000; cat. no. ab6721;
Abcam) at 37°C for 1 h. The blots were developed using an enhanced
chemiluminescence detection system (Merck KGaA). An anti-GAPDH
antibody (mouse IgG; cat. no. ab70699; 1:1,000; Abcam) was used to
detect GAPDH and normalize the sample loading. The western blot
image was analyzed by Bio-Rad Image Lab 4.1 (Bio-Rad Laboratories,
Inc.). Experiments were performed three times.
Statistical analysis
For comparisons among multiple groups, one-way
analysis of variance followed by Fisher's Least Significant
Difference method was performed to determine the statistical
differences between groups by using the SPSS 15.0 software. All
data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation of three
experiments. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically
significant difference.
Results
Huwe1 knockdown decreases cell
viability after 6 h
We previously reported that, upon the onset of OGD,
the viability of L2.3 cells progressively decreased; the cell
number was significantly lower after 6 h (P<0.001, n=3)
(34). Accordingly, in the present
study, 6 h was selected as the duration of OGD. To investigate
whether Huwe1 serves a key role in OGD, the expression levels of
Huwe1 in L2.3 cells exposed to OGD for 6 h were determined,
followed by the restoration of normal conditions at 8, 16 and 24 h
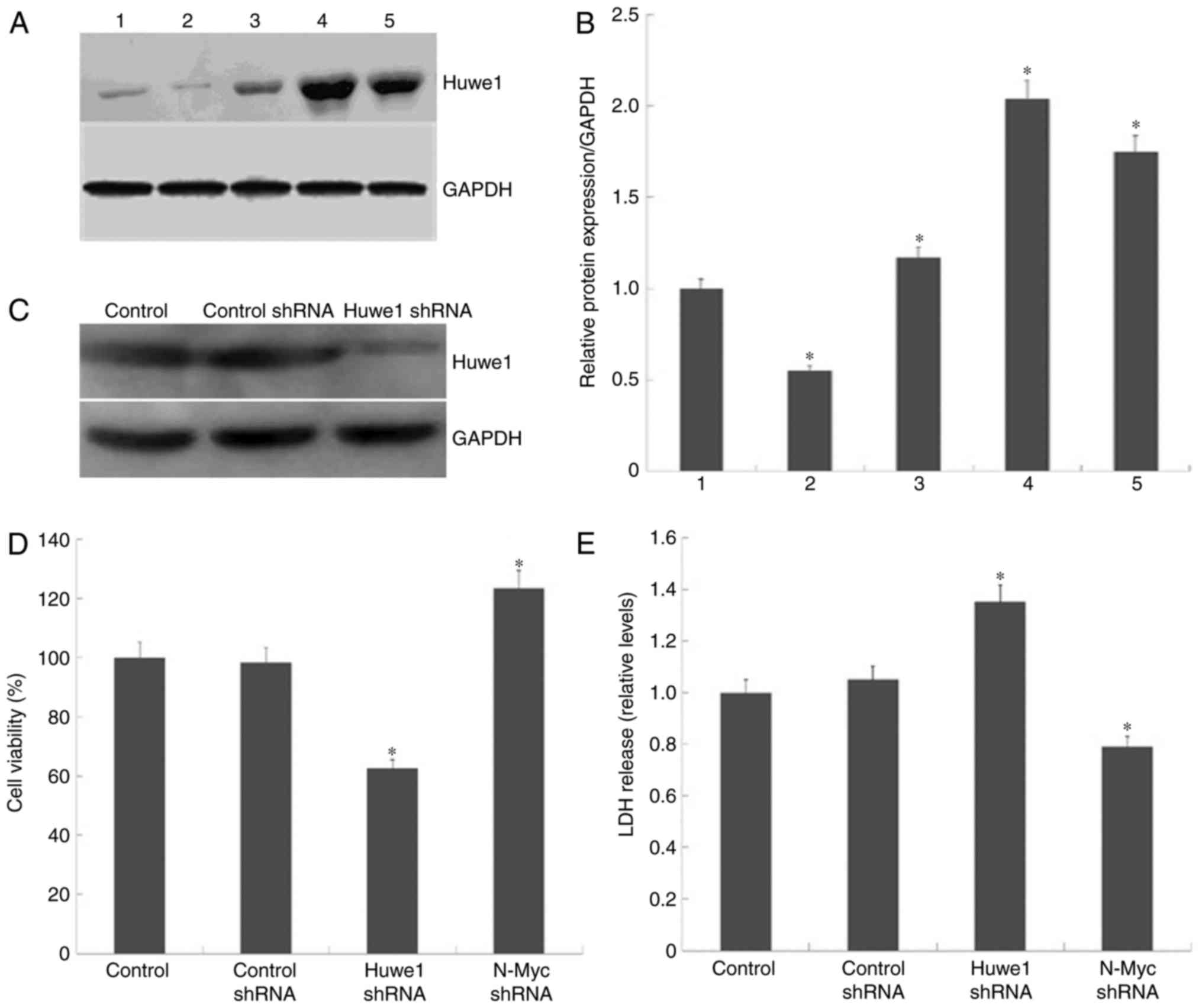
(Fig. 1A). Quantification of Huwe1
protein expression levels were normalized to GAPDH (Fig. 1B). The results revealed that the
expression levels of Huwe1 were significantly increased in
OGD-treated L2.3 cells compared with cells unexposed to OGD.
To evaluate the role of Huwe1 in L2.3 cells, GIPZ
shRNA lentiviral vectors were employed to knockdown Huwe1
expression in L2.3 cells (Fig. 1C)
as aforementioned. Accordingly, knockdown of Huwe1 expression was
associated with significant reductions in the viability of L2.3
cells exposed to OGD (Fig. 1D);
LDH release was significantly elevated compared with in OGD control
and OGD control shRNA cells (Fig.
1E). The data indicated that Huwe1 may be required to maintain
L2.3 cell viability following the onset of OGD. To further evaluate
whether N-Myc is involved in Huwe1-mediated survival of L2.3 cells
during OGD, the cell viability and LDH release in N-Myc-silenced
L2.3 cells were determined. The results revealed that the
downregulation of N-Myc expression reduced LDH release and
increased cell viability compared with in the normal control and
OGD control shRNA groups (Fig. 1D and
E).
Huwe1 knockdown induces nestin
expression and the proliferation of L2.3 cells
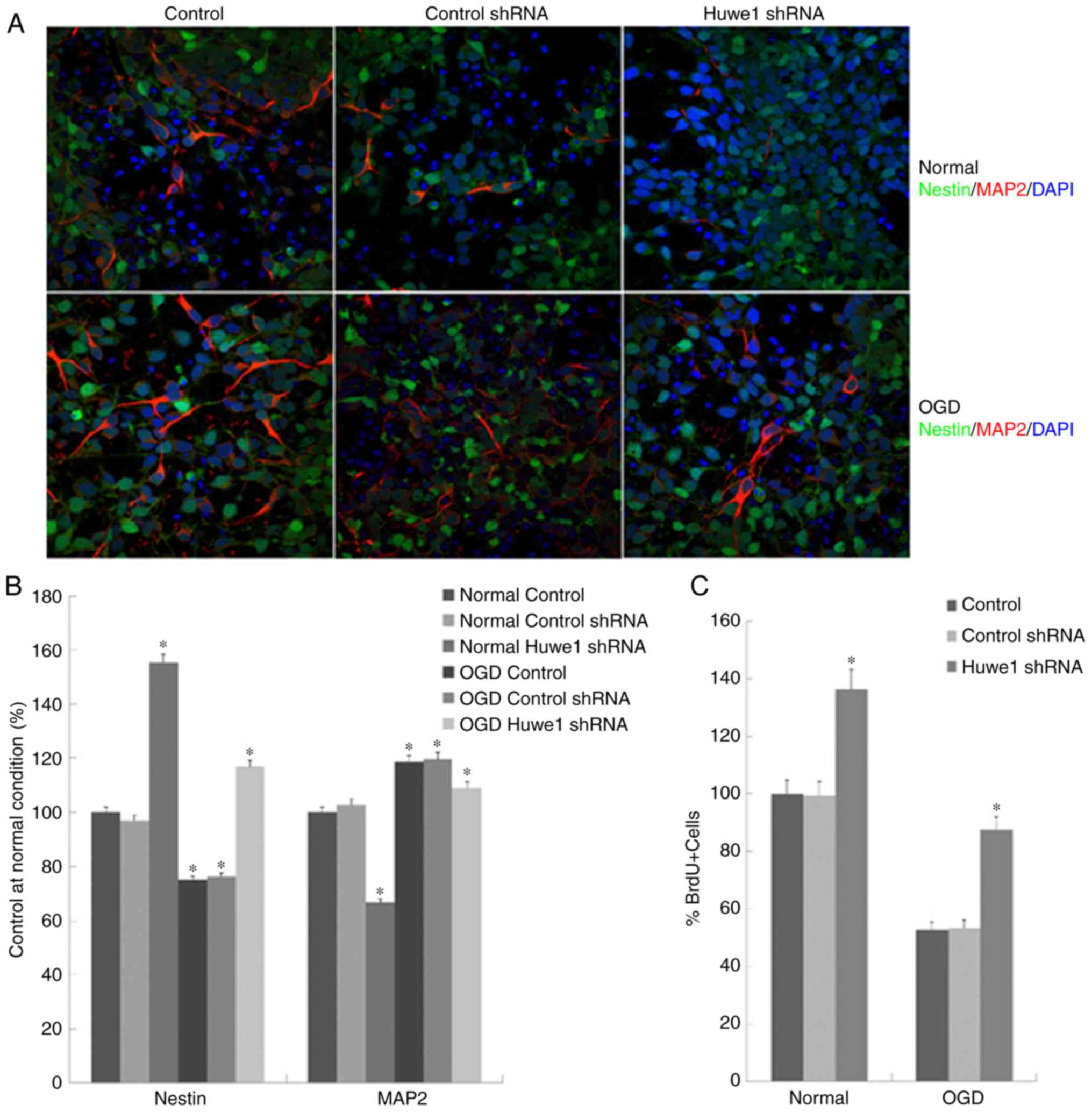
The present study analyzed the expression of nestin
and MAP2 in L2.3 cells to determine whether cell proliferation led
to cell differentiation. L2.3 cells underwent expansion for 5 days
under normal condition or following OGD, and were stained with
neural precursor cell marker nestin (green), neuronal marker MAP2
(red) and DAPI (blue). As presented in Fig. 2A and B, a significant increase in
the number of MAP2+ cells was detected following OGD
exposure compared with in the normal control conditions. Knockdown
of Huwe1 expression induced a significant increase in the
percentage of nestin+ cells and a decrease in
MAP2+ precursor cells (35) under normal and OGD conditions.
To determine whether the reduced viability of
Huwe1-silenced L2.3 cells was due to the inhibition of
proliferation, BrdU incorporation assays were conducted. The
results of the present study revealed that BrdU+ cells
were more abundant in the control than under the OGD condition;
notably fewer BrdU+. A significantly greater number of
Huwe1-silenced cells were observed in OGD condition compared with
in normal conditions (Fig. 2C).
This indicated that, under normal conditions, a higher percentage
of actively dividing cells may be detected. The results were
consistent with the onset of cell proliferation, suggesting that
Huwe1 may inhibit the proliferation in L2.3 cells.
OGD/restoration (OGD/R) inhibits
N-Myc-DLL3-Notch signaling in L2.3 cells
The potential mechanisms underlying the effects of
Huwe1 in the neuronal differentiation of L2.3 cells were
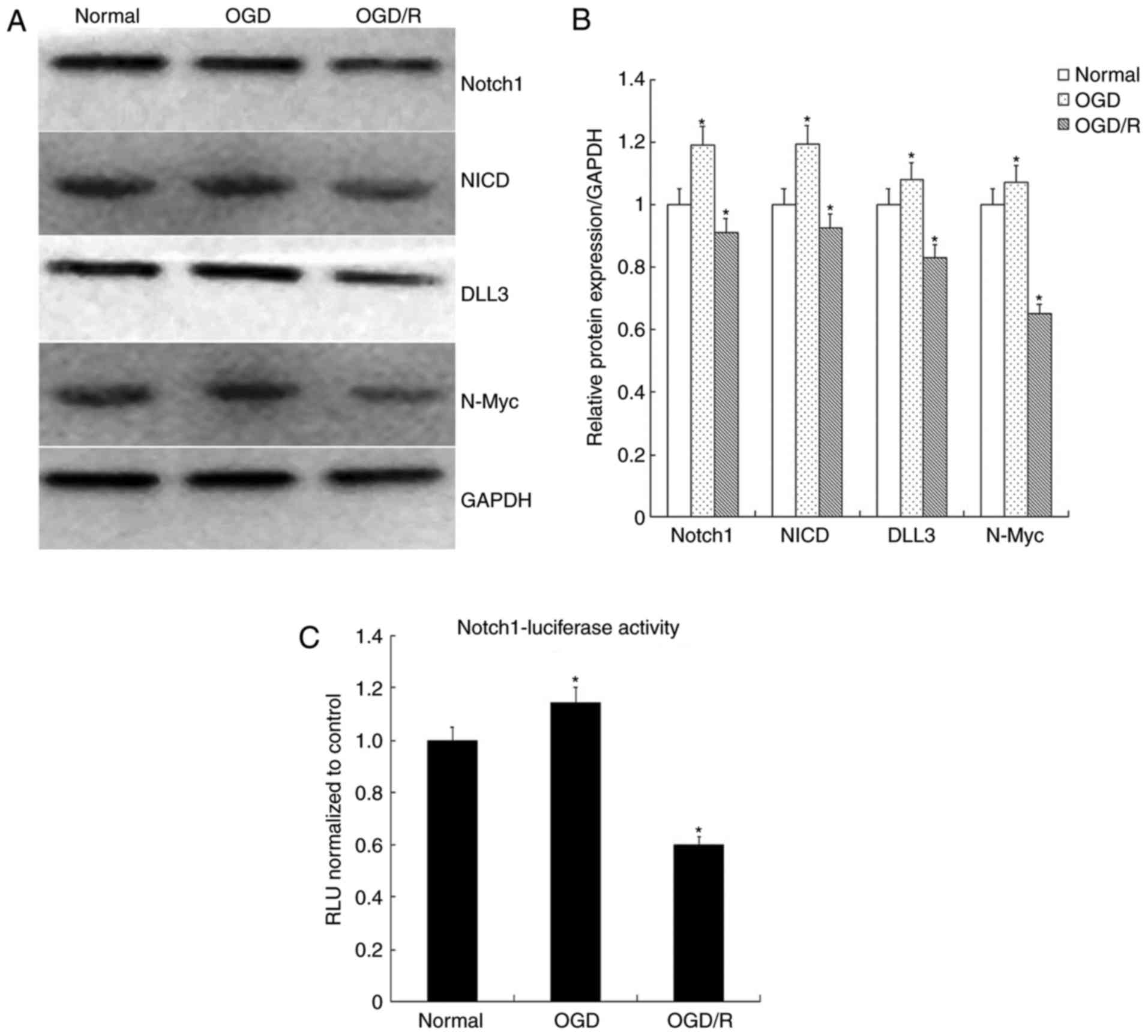
investigated in the present study. As presented in Fig. 1A, the expression levels of Huwe1
began to increase significantly after 16 h following the
restoration of normal conditions. Therefore, 16 h was selected as
the duration of restoration for the normal culture conditions. The
results demonstrated that the expression levels of Notch1, NICD,
DLL3 and N-Myc were significantly increased following exposure to
OGD for 6 h and decreased after restoration for 16 h (OGD/R)
compared with in the normal control (Fig. 3A and B). The results suggested that
OGD/R may inhibit Notch signaling.
Additionally, Notch1-transcriptional activity was
analyzed via a luciferase reporter assay, which revealed a
significant decrease in Notch1 activation when L2.3 cells were
exposed to OGD/R compared with in the normal control (Fig. 3C). These results further indicated
that Notch signaling may be associated with cell fate.
Huwe1 mediates the survival of L2.3
cells via the N-Myc-Notch1 signaling pathway during OGD and
restoration
To evaluate whether Huwe1 affects the Notch1
signaling pathway, Huwe1 was downregulated in L2.3 cells, which
were exposed to OGD for 6 h and restoration for 16 h. The results
demonstrated that N-Myc and the components of the Notch1 signaling
pathway, including Notch1, NICD and DLL3 were significantly
upregulated following the knockdown of Huwe1 compared with in the
control groups (Fig. 4A and B).
Additionally, knockdown of N-Myc expression in L2.3 cells was
conducted (Fig. 4C), which
revealed that the expression levels of the Notch1 signaling pathway
components were not altered following knockdown of both Huwe1 and
N-Myc expression (Fig. 4D and E).
These results indicated that Huwe1 may require N-Myc to suppress
the activation of the Notch1 signaling in L2.3 cells during OGD and
the restoration of normal conditions.
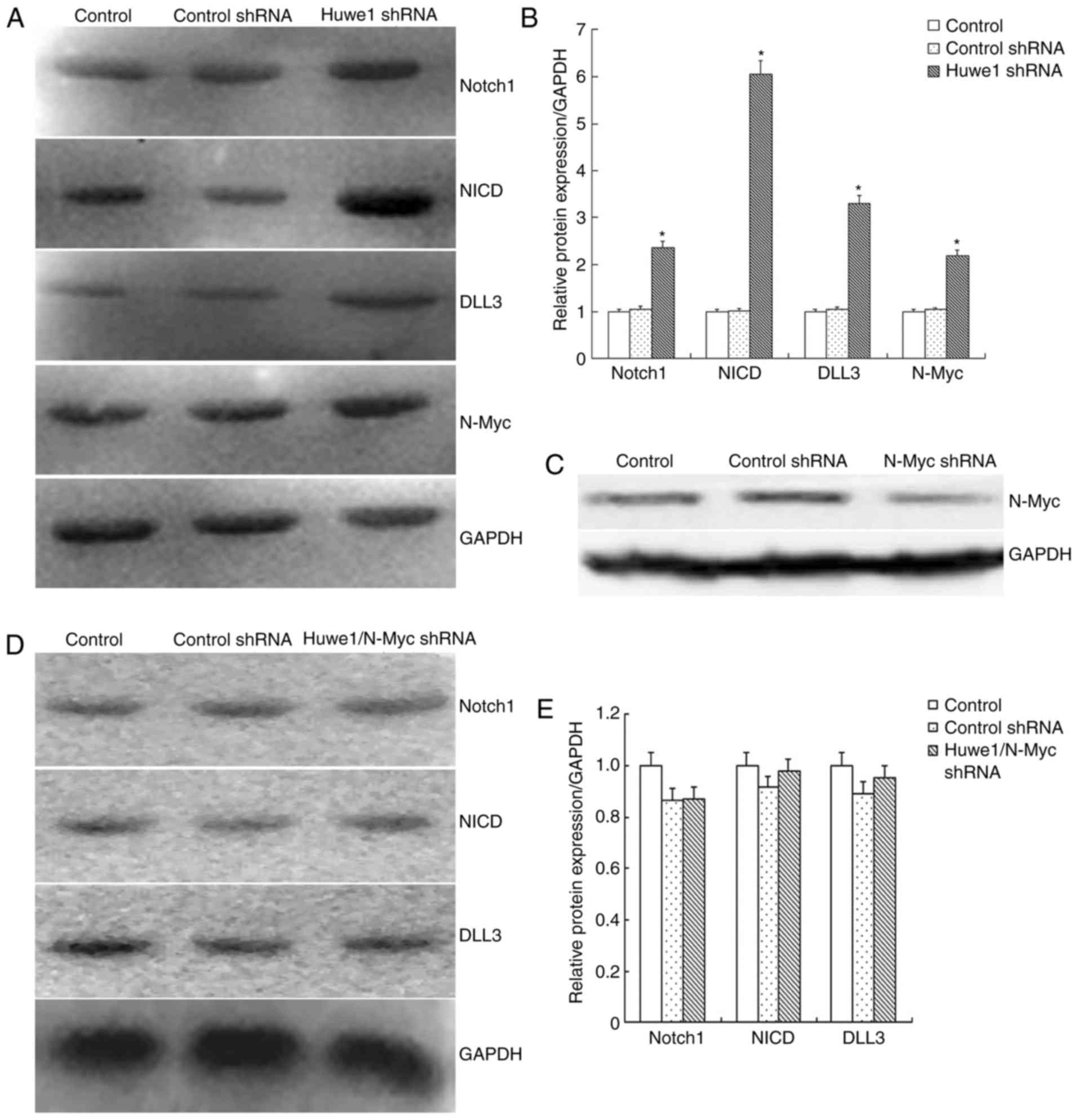 | Figure 4.Huwe1 mediates the survival of L2.3
cells via the N-Myc-Notch1 signaling pathway during oxygen-glucose
deprivation and restoration. (A) Representative western blot
analysis for the expression of Notch1, NICD, DLL3, N-Myc and GAPDH
in L2.3 cells transduced with viral particles overexpressing Huwe1
shRNA. (B) Quantification of western blot analysis presented in
(A); expression levels were normalized to that of GAPDH. Three
independent experiments were performed in triplicate. *P<0.05
vs. the control and control shRNA groups. (C) N-Myc protein levels
measured in control L2.3 cells and L2.3 cells transduced with viral
particles overexpressing control shRNA or N-Myc shRNA. (D)
Representative western blotting for the expression of Notch1, NICD,
DLL3, and GAPDH of L2.3 cells transduced with viral particles
overexpressing Huwe1 shRNA and N-Myc shRNA. (E) Quantification of
western blot analysis presented in (D); expression levels were
normalized to that of GAPDH. Data are presented as the mean ±
standard error. Three independent experiments were performed in
triplicate. *P<0.05 vs. the control and control shRNA groups.
DLL3, Delta-like 3; NICD, Notch intracellular domain Huwe1, E3
ubiquitin protein ligase; NICD, Notch intracellular domain; shRNA,
short hairpin RNA. |
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, the present study is
the first to report the protective role of Huwe1 in L2.3 cells
under the OGD condition. Specifically, Huwe1 was observed to rescue
L2.3 cells from OGD-induced injury by inhibiting proliferation and
inducing neuronal differentiation. Subsequently, its effects on the
downstream N-Myc-Delta-like 3-Notch1 signaling pathway were
investigated to explore the underlying mechanisms. Mechanistically,
it was demonstrated that Huwe1 mediated the survival of L2.3 cells
via inhibition of the N-Myc-Notch1 signaling axis in the present
study. Thus, in response to OGD and the restoration of normal
conditions, Huwe1 was proposed to inhibit the N-Myc-Notch1
signaling axis and induce the differentiation of L2.3 cells in the
present study. In addition, the effects of Huwe1 on Notch1
signaling were notably abolished via the knockdown of N-Myc.
Therefore, the findings of the present study indicated that the
Huwe1-N-Myc-Notch1 axis may be a novel neuroprotective pathway
associated with ischemic stroke.
Huwe1 is important for neurogenesis (30); however, the biological function of
Huwe1 in neurological diseases remains unknown (36). The present study reported that
Huwe1 served a role in the survival of L2.3 cells under the OGD
condition, which suggests Huwe1 as a potential target in the
treatment of ischemic stroke. Consistent with the role of Huwe1 on
the transition from NSCs to differentiated neurons, Huwe1 may
improve the neurobehavioral outcomes following ischemic brain
injury by enhancing neuronal differentiation and rescuing cells
from OGD-induced insults. Previous studies have reported that Huwe1
acts via the N-Myc-DLL3-Notch1 signaling pathway during neural
development (27,30). Huwe1 was reported to suppress the
N-Myc-DLL3 cascade associated with the initiation of neurogenesis
in the developing brain, and negatively regulated the expression of
DLL3 in an N-Myc-dependent manner, and the activation Notch1, a
transmembrane receptor on the surface of neural progenitors, was
proposed to be involved in NSC maintenance (37,38).
When activated by the ligands of neighboring cells, NICD
translocates to the nucleus and activates transcription (39). In the developing brain, activated
Notch signaling maintains the state of NSCs by promoting the
proliferation of neural progenitors and inhibiting the
differentiation progenitor cells into neurons (40). In support of this, a study
indicated that attenuation of Notch signaling promoted the
differentiation of neural progenitors in the subacute phase
following ischemia (41). In
conclusion, Huwe1 may protect neural progenitors L2.3 cells from
injury associated with OGD and the restoration of normal
conditions; however, further investigation is required to evaluate
the pathological mechanism underlying the protective effects of
Huwe1 in the acute phase of stroke.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the National
Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 81401238, 81330016
and 81630038), the Ministry of Education of China (grant nos.
313037 and 20110181130002), the State Commission of Science
Technology of China (grant no. 2012BAI04B04), the Science and
Technology Bureau of Sichuan Province (grant nos. 2012SZ0010,
2014SZ0149 and 2016JY0028), and the Clinical Discipline Program
(Neonatology) of the Ministry of Health of China (grant no.
1311200003303).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
XJ, JY and WX performed the experiments and analyzed
the data. HL and YQ conducted the cell culture and molecular
pathway experiments. HY and YT analyzed the resulting data and
drafted the manuscript. All authors were responsible for drafting
the manuscript, and read and approved the final version.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Zhou L, Li F, Xu HB, Luo CX, Wu HY, Zhu
MM, Lu W, Ji X, Zhou QG and Zhu DY: Treatment of cerebral ischemia
by disrupting ischemia-induced interaction of nNOS with PSD-95. Nat
Med. 16:1439–1443. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miclescu A, Sharma HS, Martijn C and
Wiklund L: Methylene blue protects the cortical blood-brain barrier
against ischemia/reperfusion-induced disruptions. Crit Care Med.
38:2199–2206. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu P, Woodruff G, Wang Y, Graham L, Hunt
M, Wu D, Boehle E, Ahmad R, Poplawski G, Brock J, et al:
Long-distance axonal growth from human induced pluripotent stem
cells after spinal cord injury. Neuron. 83:789–796. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kärkkäinen V, Pomeshchik Y, Savchenko E,
Dhungana H, Kurronen A, Lehtonen S, Naumenko N, Tavi P, Levonen AL,
Yamamoto M, et al: Nrf2 regulates neurogenesis and protects neural
progenitor cells against Aβ toxicity. Stem Cells. 32:1904–1916.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sabelström H, Stenudd M, Réu P, Dias DO,
Elfineh M, Zdunek S, Damberg P, Göritz C and Frisén J: Resident
neural stem cells restrict tissue damage and neuronal loss after
spinal cord injury in mice. Science. 342:637–640. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Klempin F, Marr RA and Peterson DA:
Modification of pax6 and olig2 expression in adult hippocampal
neurogenesis selectively induces stem cell fate and alters both
neuronal and glial populations. Stem Cells. 30:500–509. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Covey MV, Streb JW, Spektor R and Ballas
N: REST regulates the pool size of the different neural lineages by
restricting the generation of neurons and oligodendrocytes from
neural stem/progenitor cells. Development. 139:2878–2890. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Burns AJ, Goldstein AM, Newgreen DF, Stamp
L, Schäfer KH, Metzger M, Hotta R, Young HM, Andrews PW, Thapar N,
et al: White paper on guidelines concerning enteric nervous system
stem cell therapy for enteric neuropathies. Dev Biol. 417:229–251.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Goldman S: Stem and progenitor cell-based
therapy of the human central nervous system. Nat Biotechnol.
23:862–871. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rafalski VA, Ho PP, Brett JO, Ucar D,
Dugas JC, Pollina EA, Chow LM, Ibrahim A, Baker SJ, Barres BA, et
al: Expansion of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells following SIRT1
inactivation in the adult brain. Nat Cell Biol. 15:614–624. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bonnamain V, Neveu I and Naveilhan P:
Neural stem/progenitor cells as a promising candidate for
regenerative therapy of the central nervous system. Front Cell
Neurosci. 6:172012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Felling RJ, Snyder MJ, Romanko MJ,
Rothstein RP, Ziegler AN, Yang Z, Givogri MI, Bongarzone ER and
Levison SW: Neural stem/progenitor cells participate in the
regenerative response to perinatal hypoxia/ischemia. J Neurosci.
26:4359–4369. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zelentsova K, Talmi Z, Abboud-Jarrous G,
Sapir T, Capucha T, Nassar M and Burstyn-Cohen T: Protein S
regulates neural stem cell quiescence and neurogenesis. Stem Cells.
35:679–693. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu M, Guan Z, Shen Q, Flinter F,
Domínguez L, Ahn JW, Collier DA, O'Brien T and Shen S: Ulk4
regulates neural stem cell pool. Stem Cells. 34:2318–2331. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Venkatesh K, Reddy LVK, Abbas S, Mullick
M, Moghal ETB, Balakrishna JP and Sen D: NOTCH signaling is
essential for maturation, self-renewal, and tri-differentiation of
in vitro derived human neural stem cells. Cell Reprogram.
19:372–383. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Georges P, Boissart C, Poulet A,
Peschanski M and Benchoua A: Protein kinase-A inhibition is
sufficient to support human neural stem cells self-renewal. Stem
Cells. 33:3666–3672. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Swartling FJ, Savov V, Persson AI, Chen J,
Hackett CS, Northcott PA, Grimmer MR, Lau J, Chesler L, Perry A, et
al: Distinct neural stem cell populations give rise to disparate
brain tumors in response to N-MYC. Cancer Cell. 21:601–613. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zinin N, Adameyko I, Wilhelm M, Fritz N,
Uhlén P, Ernfors P and Henriksson MA: MYC proteins promote neuronal
differentiation by controlling the mode of progenitor cell
division. EMBO Rep. 15:383–391. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Knoepfler PS, Cheng PF and Eisenman RN:
N-myc is essential during neurogenesis for the rapid expansion of
progenitor cell populations and the inhibition of neuronal
differentiation. Genes Dev. 16:2699–2712. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Androutsellis-Theotokis A, Leker RR,
Soldner F, Hoeppner DJ, Ravin R, Poser SW, Rueger MA, Bae SK,
Kittappa R and McKay RD: Notch signalling regulates stem cell
numbers in vitro and in vivo. Nature. 442:823–826. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mizutani K, Yoon K, Dang L, Tokunaga A and
Gaiano N: Differential Notch signalling distinguishes neural stem
cells from intermediate progenitors. Nature. 449:351–355. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aguirre A, Rubio ME and Gallo V: Notch and
EGFR pathway interaction regulates neural stem cell number and
self-renewal. Nature. 467:323–327. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ramasamy SK and Lenka N: Notch exhibits
ligand bias and maneuvers stage-specific steering of neural
differentiation in embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol.
30:1946–1957. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhong Q, Gao W, Du F and Wang X:
Mule/ARF-BP1, a BH3-only E3 ubiquitin ligase, catalyzes the
polyubiquitination of Mcl-1 and regulates apoptosis. Cell.
121:1085–1095. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen D, Kon N, Li M, Zhang W, Qin J and Gu
W: ARF-BP1/Mule is a critical mediator of the ARF tumor suppressor.
Cell. 121:1071–1083. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bernassola F, Karin M, Ciechanover A and
Melino G: The HECT family of E3 ubiquitin ligases: Multiple players
in cancer development. Cancer Cell. 14:10–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao X, Heng JI, Guardavaccaro D, Jiang R,
Pagano M, Guillemot F, Iavarone A and Lasorella A: The HECT-domain
ubiquitin ligase Huwe1 controls neural differentiation and
proliferation by destabilizing the N-Myc oncoprotein. Nat Cell
Biol. 10:643–653. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Leboucher GP, Tsai YC, Yang M, Shaw KC,
Zhou M, Veenstra TD, Glickman MH and Weissman AM: Stress-induced
phosphorylation and proteasomal degradation of mitofusin 2
facilitates mitochondrial fragmentation and apoptosis. Mol Cell.
47:547–557. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hao Z, Duncan GS, Su YW, Li WY, Silvester
J, Hong C, You H, Brenner D, Gorrini C, Haight J, et al: The E3
ubiquitin ligase Mule acts through the ATM-p53 axis to maintain B
lymphocyte homeostasis. J Exp Med. 209:173–186. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao X, D' Arca D, Lim WK, Brahmachary M,
Carro MS, Ludwig T, Cardo CC, Guillemot F, Aldape K, Califano A, et
al: The N-Myc-DLL3 cascade is suppressed by the ubiquitin ligase
Huwe1 to inhibit proliferation and promote neurogenesis in the
developing brain. Dev Cell. 17:210–221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li H, Babiarz J, Woodbury J,
Kane-Goldsmith N and Grumet M: Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of CNS
radial glial cells and their transition to restricted precursors.
Dev Biol. 271:225–238. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li H, Han YR, Bi C, Davila J, Goff LA,
Thompson K, Swerdel M, Camarillo C, Ricupero CL, Hart RP, et al:
Functional differentiation of a clone resembling embryonic cortical
interneuron progenitors. Dev Neurobiol. 68:1549–1564. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schroers R, Davis CM, Wagner HJ and Chen
SY: Lentiviral transduction of human T-lymphocytes with a RANTES
intrakine inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection.
Gene Ther. 9:889–897. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zeng W, Tong Y, Li H, Luo R and Mao M:
P2×7 receptor modulation of the viability of radial glial clone
L2.3 cells during hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Mol Med Rep.
5:1357–1361. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Maddodi N, Bhat KM, Devi S, Zhang SC and
Setaluri V: Oncogenic BRAFV600E induces expression of neuronal
differentiation marker MAP2 in melanoma cells by promoter
demethylation and down-regulation of transcription repressor HES1.
J Biol Chem. 285:242–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou J, Liu Q, Mao M and Tong Y: Huwe1 as
a therapeutic target for neural injury. Genet Mol Res.
13:4320–4325. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Benner EJ, Luciano D, Jo R, Abdi K,
Paez-Gonzalez P, Sheng H, Warner DS, Liu C, Eroglu C and Kuo CT:
Protective astrogenesis from the SVZ niche after injury is
controlled by Notch modulator Thbs4. Nature. 497:369–373. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mizeracka K, DeMaso CR and Cepko CL:
Notch1 is required in newly postmitotic cells to inhibit the rod
photoreceptor fate. Development. 140:3188–3197. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Altmann C, Vasic V, Hardt S, Heidler J,
Häussler A, Wittig I, Schmidt MH and Tegeder I: Progranulin
promotes peripheral nerve regeneration and reinnervation: Role of
notch signaling. Mol Neurodegener. 11:692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Giachino C, Basak O, Lugert S, Knuckles P,
Obernier K, Fiorelli R, Frank S, Raineteau O, Alvarez-Buylla A and
Taylor V: Molecular diversity subdivides the adult forebrain neural
stem cell population. Stem Cells. 32:70–84. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Oya S, Yoshikawa G, Takai K, Tanaka JI,
Higashiyama S, Saito N, Kirino T and Kawahara N: Attenuation of
Notch signaling promotes the differentiation of neural progenitors
into neurons in the hippocampal CA1 region after ischemic injury.
Neuroscience. 158:683–692. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|