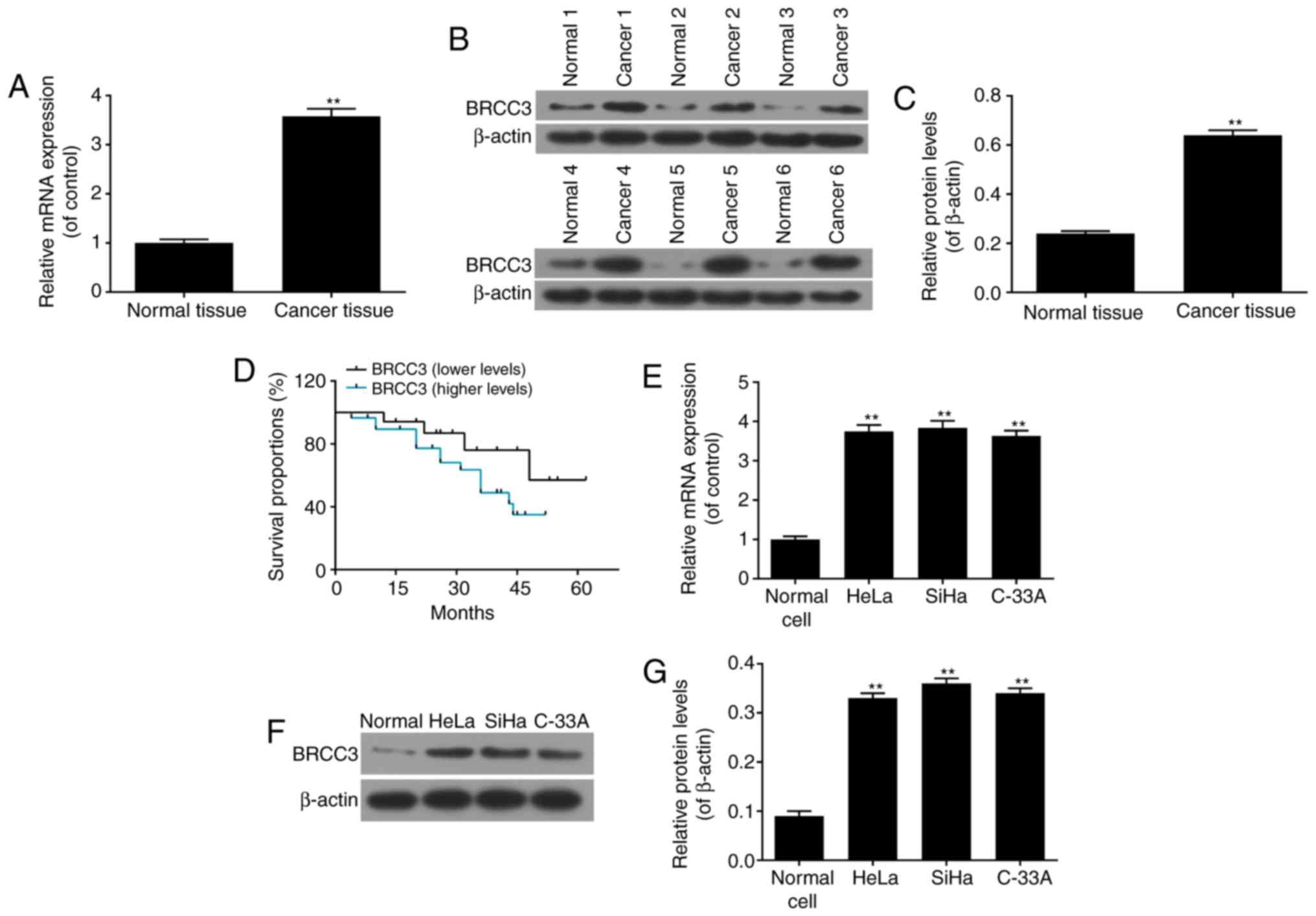
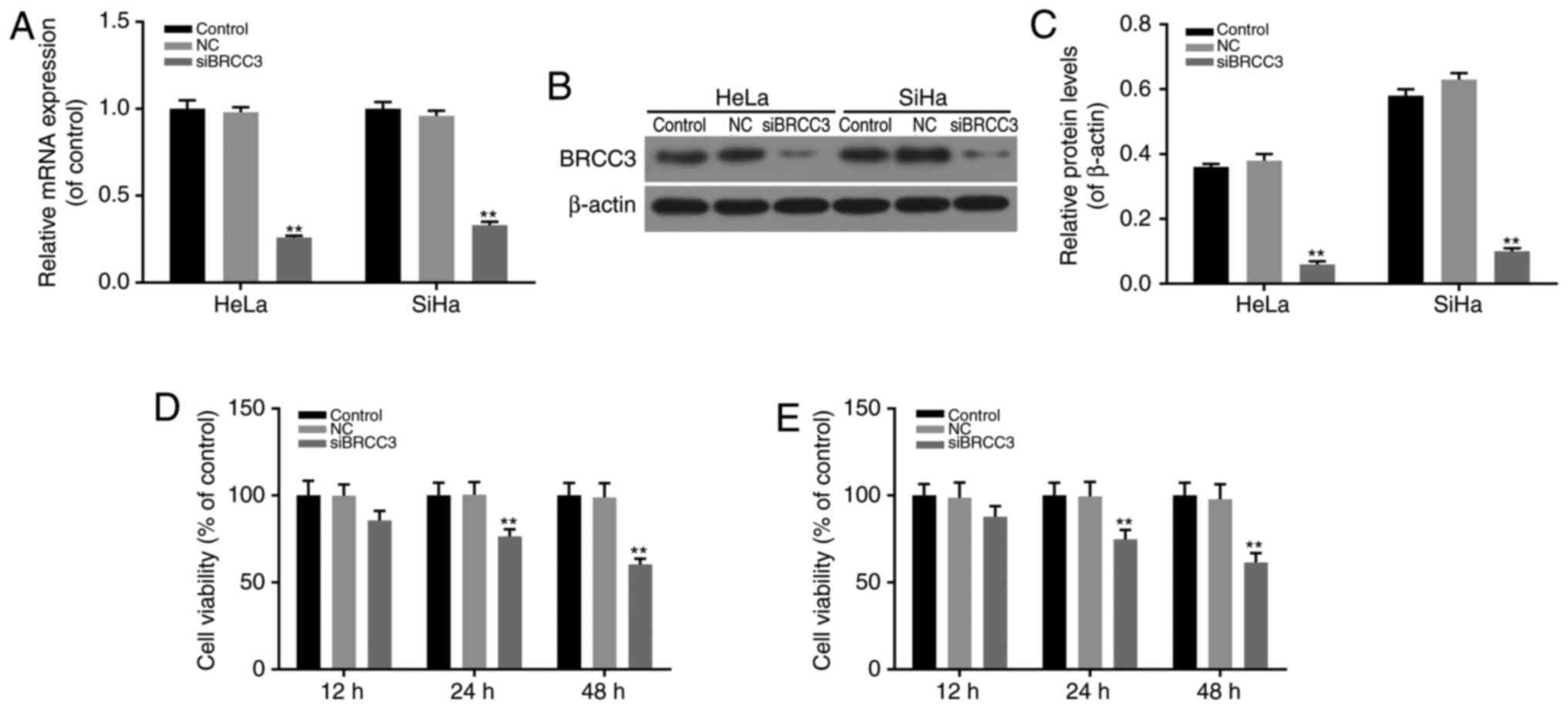
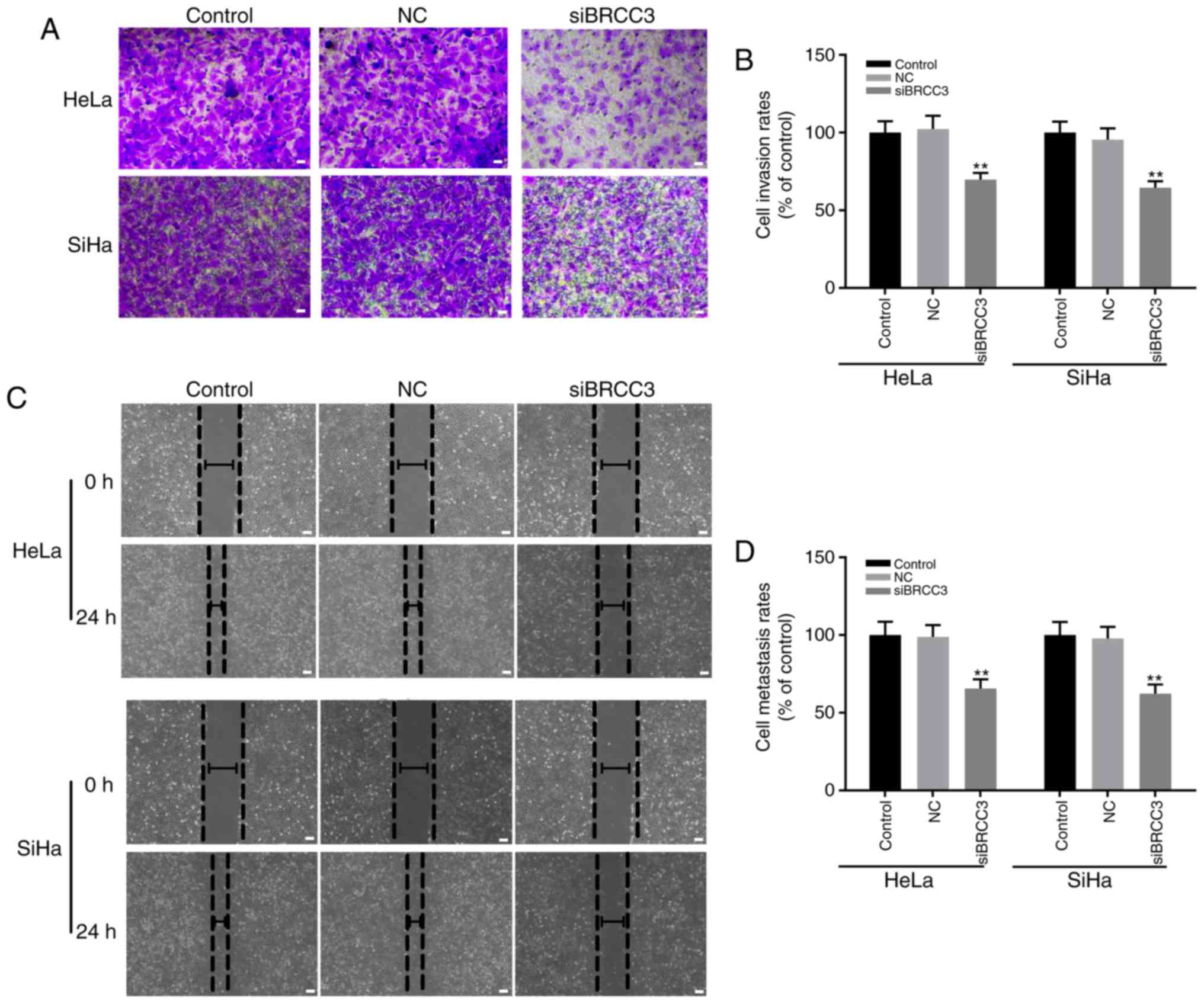
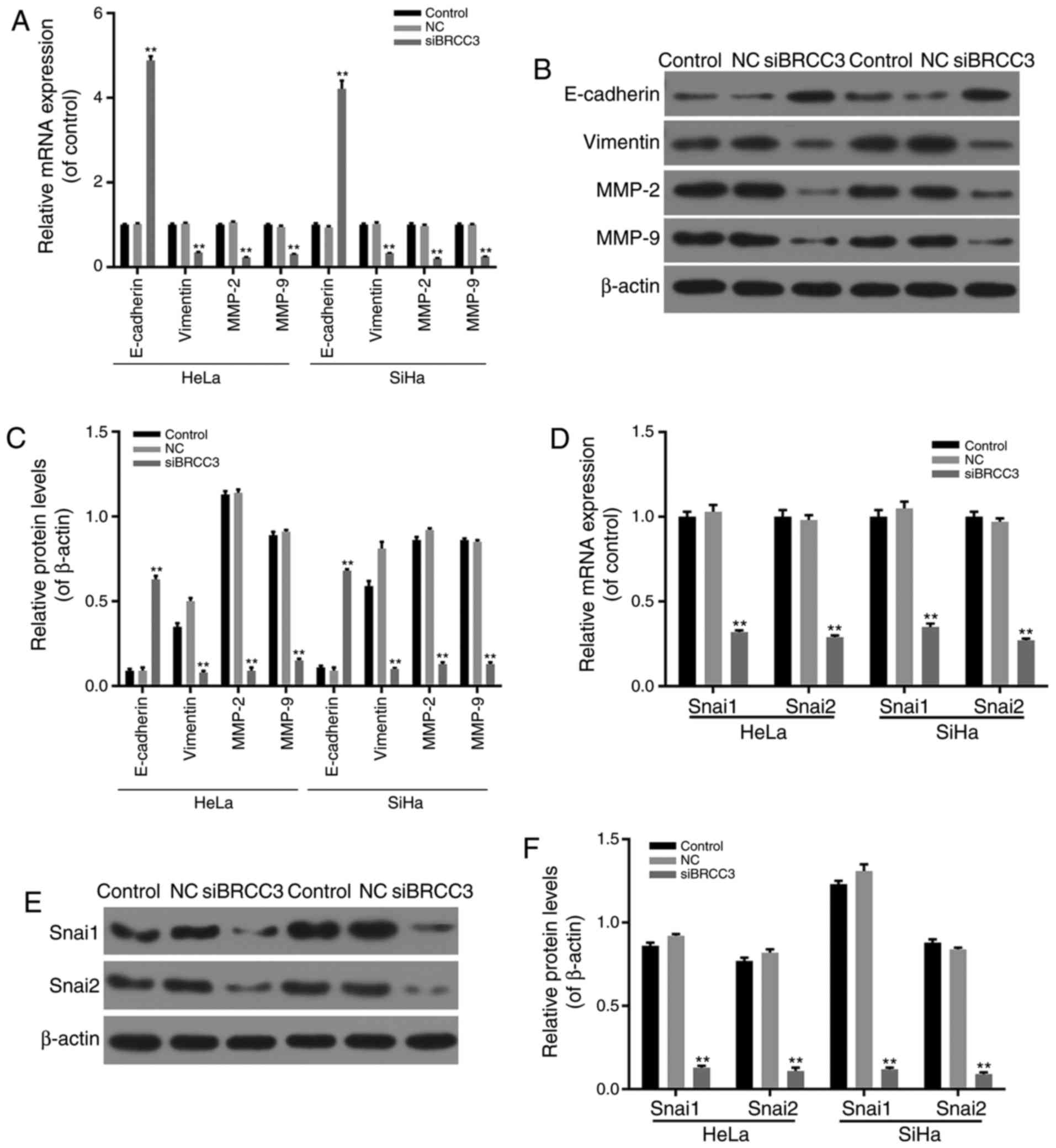
|
1
|
Furusawa Y, Yunoki T, Hirano T, Minagawa
S, Izumi H, Mori H, Hayashi A and Tabuchi Y: Identification of
genes and genetic networks associated with BAG3-dependent cell
proliferation and cell survival in human cervical cancer HeLa
cells. Mol Med Rep. Aug 10–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kan Y, Dong D, Zhang Y, Jiang W, Zhao N,
Han L, Fang M, Zang Y, Hu C, Tian J, et al: Radiomic signature as a
predictive factor for lymph node metastasis in early-stage cervical
cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging. Aug 13–2018.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Okuhara T, Ishikawa H, Goto E, Okada M,
Kato M and Kiuchi T: Processing fluency effect of a leaflet for
breast and cervical cancer screening: A randomized controlled study
in Japan. Psychol Health Med. 11:1–11. 2018.
|
|
4
|
Forouzanfar MH, Foreman KJ, Delossantos
AM, Lozano R, Lopez AD, Murray CJ and Naghavi M: Breast and
cervical cancer in 187 countries between 1980 and 2010: A
systematic analysis. Lancet. 378:1461–1484. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Krieger N, Bassett MT and Gomez SL: Breast
and cervical cancer in 187 countries between 1980 and 2010. Lancet.
379:1391–1392. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Eifel PJ, Winter K, Morris M, Levenback C,
Grigsby PW, Cooper J, Rotman M, Gershenson D and Mutch DG: Pelvic
irradiation with concurrent chemotherapy versus pelvic and
para-aortic irradiation for high-risk cervical cancer: An update of
radiation therapy oncology group trial (RTOG) 90–90. J Clin Oncol.
22:872–880. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Smith JS, Lindsay L, Hoots B, Keys J,
Franceschi S, Winer R and Clifford GM: Human papillomavirus type
distribution in invasive cervical cancer and high-grade cervical
lesions: A meta-analysis update. Int J Cancer. 121:621–632. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Borges BES, Brito EB, Fuzii HT, Baltazar
CS, Sá AB, Silva CIMD, Santos GFS and Pinheiro MDCN: Human
papillomavirus infection and cervical cancer precursor lesions in
women living by Amazon rivers: Investigation of relations with
markers of oxidative stress. Einstein (Sao Paulo).
16:eAO41902018.(In English; Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Budukh A, Palayekar V, Maheshwari A,
Deodhar K, Purwar P, Bagal S, Vadigoppula A, Lokhande M, Panse N,
Dikshit R, et al: Menstrual pad, a cervical cancer screening tool,
a population-based study in rural India. Eur J Cancer Prev. Jul
12–2017.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
10
|
Qureshi R, Arora H and Rizvi MA: EMT in
cervical cancer: Its role in tumour progression and response to
therapy. Cancer Lett. 356:321–331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Okusha Y, Eguchi T, Sogawa C, Okui T,
Nakano K, Okamoto K and Kozaki KI: The intranuclear PEX domain of
MMP involves proliferation, migration, and metastasis of aggressive
adenocarcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem. May 15–2018.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vences-Catalán F and Levy S: Immune
targeting of tetraspanins involved in cell invasion and metastasis.
Front Immunol. 9:12772018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schwickert G, Walenta S, Sundfør K,
Rofstad EK and Mueller-Klieser W: Correlation of high lactate
levels in human cervical cancer with incidence of metastasis.
Cancer Res. 55:4757–4759. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim HJ, Do IG, Jeon HK, Cho YJ, Park YA,
Choi JJ, Sung CO, Lee YY, Choi CH, Kim TJ, et al: Galectin 1
expression is associated with tumor invasion and metastasis in
stage IB to IIA cervical cancer. Hum Pathol. 44:62–68. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baquero Díaz A, Romero BR, Gomez-Izquierdo
L, Polo RA, Martin-Juan J and Rodriguez-Panadero F:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in malignant mesothelioma. Eur
Res J. 38:29502011.
|
|
16
|
Kahlert UD, Nikkhah G and Maciaczyk J:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal(-like) transition as a relevant molecular
event in malignant gliomas. Cancer Lett. 331:131–138. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chaw SY, Majeed Abdul A, Dalley AJ, Chan
A, Stein S and Farah CS: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)
biomarkers-E-cadherin, beta-catenin, APC and Vimentin-in oral
squamous cell carcinogenesis and transformation. Oral Oncol.
48:997–1006. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hao L, Ha JR, Kuzel P, Garcia E and Persad
S: Cadherin switch from E- to N-cadherin in melanoma progression is
regulated by the PI3K/PTEN pathway through Twist and Snail. Br J
Dermatol. 166:1184–1197. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo D, Xu X, Li J, Chen C, Chen W, Wang F,
Xie Y and Li F: The PDK1/cJun pathway activated by TGFβ induces EMT
and promotes proliferation and invasion in human glioblastoma. Int
J Oncol. Aug 14–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zuo Q, Wang J, Chen C, Zhang Y, Feng DX,
Zhao R and Chen T: ASCL2 expression contributes to gastric tumor
migration and invasion by downregulating miR223 and inducing EMT.
Mol Med Rep. Aug 8–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li J, Yu H, Xi M, Ma D and Lu X: The SNAI1
3′UTR functions as a sponge for multiple
migration-/invasion-related microRNAs. Tumor Biol. 36:1067–1072.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dong Y, Hakimi MA, Chen X, Kumaraswamy E,
Cooch NS, Godwin AK and Shiekhattar R: Regulation of BRCC, a
holoenzyme complex containing BRCA1 and BRCA2, by a
signalosome-like subunit and its role in DNA repair. Mol Cell.
12:1087–1099. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Py BF, Kim MS, Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg H
and Yuan J: Deubiquitination of NLRP3 by BRCC3 critically regulates
inflammasome activity. Mol Cell. 49:331–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Boudreau HE, Broustas CG, Gokhale PC,
Kumar D, Mewani RR, Rone JD, Haddad BR and Kasid U: Expression of
BRCC3, a novel cell cycle regulated molecule, is associated with
increased phospho-ERK and cell proliferation. Int J Mol Med.
19:29–39. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tu Z, Xu B, Qu C, Tao Y, Chen C, Hua W,
Feng G, Chang H, Liu Z, Li G, et al: BRCC3 acts as a prognostic
marker in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with
radiotherapy and mediates radiation resistance in vitro. Radiat
Oncol. 10:1232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rebbeck TR, Mitra N, Wan F, Sinilnikova
OM, Healey S, McGuffog L, Mazoyer S, Chenevix-Trench G, Easton DF,
Antoniou AC, et al: Association of type and location of BRCA1 and
BRCA2 mutations with risk of breast and ovarian cancer. JAMA.
313:1347–1361. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chai KM, Wang CY, Liaw HJ, Fang KM, Yang
CS and Tzeng SF: Downregulation of BRCA1-BRCA2-containing complex
subunit 3 sensitizes glioma cells to temozolomide. Oncotarget.
5:10901–10915. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Del Carmen MG, Pareja R, Melamed A,
Rodriguez J, Greer A, Clark RM and Rice LW: Isolated para-aortic
lymph node metastasis in FIGO stage IA2-IB2 carcinoma of the
cervix: Revisiting the role of surgical assessment. Gynecol Oncol.
150:406–411. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tomita N, Mizuno M, Makita C, Kondo S,
Mori M, Sakata J, Tsubouchi H, Hirata K, Tachibana H and Kodaira T:
Propensity score analysis of radical hysterectomy versus definitive
chemoradiation for FIGO stage IIB cervical cancer. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. Aug 7–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jiang C, Wang H, Zhou L, Jiang T, Xu Y and
Xia L: MicroRNA-212 inhibits the metastasis of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma by targeting SOX4. Oncol Rep. 38:82–88. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Cheng R, Liu S, Qu F, Yin
X, Wang Q, Xiao B and Ye Z: Radiomics analysis of apparent
diffusion coefficient in cervical cancer: A preliminary study on
histological grade evaluation. J Magn Reson Imaging. May
14–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wipperman J, Neil T and Williams T:
Cervical cancer: Evaluation and management. Am Fam Physician.
97:449–454. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kodama J, Shinyo Y, Hasengaowa, Kusumoto
T, Seki N, Nakamura K, Hongo A and Hiramatsu Y: Loss of basement
membrane heparan sulfate expression is associated with pelvic lymph
node metastasis in invasive cervical cancer. Oncol Rep. 14:89–92.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rhim AD, Mirek ET, Aiello NM, Maitra A,
Bailey JM, Mcallister F, Reichert M, Beatty GL, Rustgi AK,
Vonderheide RH, et al: EMT and dissemination precede pancreatic
tumor formation. Cell. 148:349–361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
De Craene B and Berx G: Regulatory
networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:97–110. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Frixen UH, Behrens J, Sachs M, Eberle G,
Voss B, Warda A, Löchner D and Birchmeier W: E-cadherin-mediated
cell-cell adhesion prevents invasiveness of human carcinoma cells.
J Cell Biol. 113:173–185. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I,
Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F and Nieto MA: The
transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kokkinos MI, Wafai R, Wong MK, Newgreen
DF, Thompson EW and Waltham M: Vimentin and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in human breast cancer - observations in vitro and in
vivo. Cells Tissues Organs. 185:191–203. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sheu BC, Lien HC, Ho HN, Lin HH, Chow SN,
Huang SC and Hsu SM: Increased expression and activation of
gelatinolytic matrix metalloproteinases is associated with the
progression and recurrence of human cervical cancer. Cancer Res.
63:6537–6542. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhai Y, Hotary KB, Nan B, Bosch FX, Muñoz
N, Weiss SJ and Cho KR: Expression of membrane type 1 matrix
metalloproteinase is associated with cervical carcinoma progression
and invasion. Cancer Res. 65:6543–6550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lizarraga F, Espinosa M, Ceballos-Cancino
G, Vazquez-Santillan K, Bahena-Ocampo I, Schwarz-Cruz Y, Celis A,
Vega-Gordillo M, Lopez Garcia P, Maldonado V and Melendez-Zajgla J:
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-4 (TIMP-4) regulates
stemness in cervical cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 55:1952–1961.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li XW, Tuergan M and Abulizi G: Expression
of MAPK1 in cervical cancer and effect of MAPK1 gene silencing on
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and metastasis. Asian
Pac J Trop Med. 8:937–943. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kahlert UD, Joseph JV and Kruyt FAE: EMT-
and MET-related processes in nonepithelial tumors: Importance for
disease progression, prognosis, and therapeutic opportunities. Mol
Oncol. 11:860–877. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Thaper D, Vahid S, Nip KM, Moskalev I,
Shan X, Frees S, Roberts ME, Ketola K, Harder KW, Gregory-Evans C,
et al: Targeting Lyn regulates Snail family shuttling and inhibits
metastasis. Oncogene. 36:3964–3975. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Qi J, Li T, Bian H, Li F, Ju Y, Gao S, Su
J, Ren W and Qin C: SNAI1 promotes the development of HCC through
the enhancement of proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis. FEBS
Open Bio. 6:326–337. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shields MA, Ebine K, Sahai V, Kumar K,
Siddiqui K, Hwang RF, Grippo PJ and Munshi HG: Snail cooperates
with KrasG12D to promote pancreatic fibrosis. Mol Cancer Res.
11:1078–1087. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kang AR, An HT, Ko J and Kang S: Ataxin-1
regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cervical cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 8:18248–18259. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lin CY, Tsai PH, Kandaswami CC, Lee PP,
Huang CJ, Hwang JJ and Lee MT: Matrix metalloproteinase-9
cooperates with transcription factor Snail to induce
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Sci. 102:815–827. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|