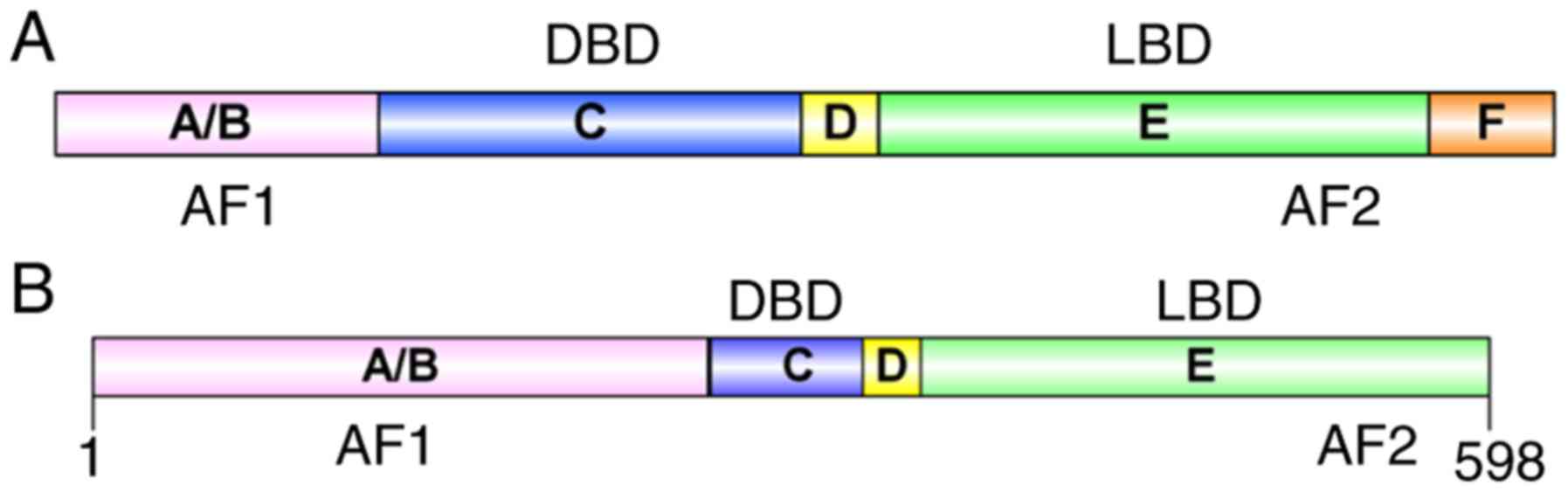
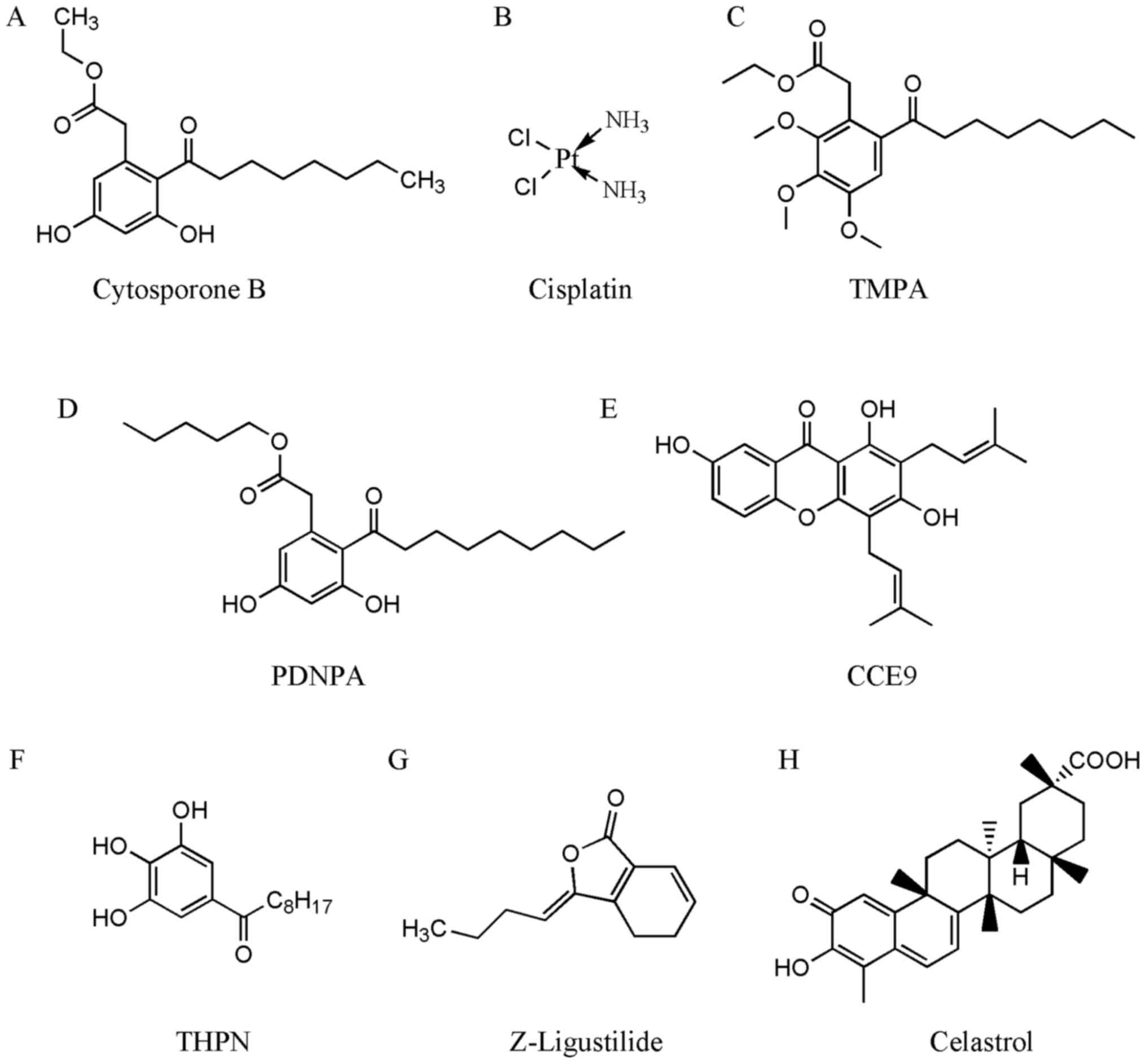
|
1
|
Mangelsdorf DJ, Thummel C, Beato M,
Herrlich P, Schütz G, Umesono K, Blumberg B, Kastner P, Mark M,
Chambon P and Evans RM: The nuclear receptor superfamily: The
second decade. Cell. 83:835–839. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Margolis RN and Christakos S: The nuclear
receptor superfamily of steroid hormones and vitamin D gene
regulation. An update. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1192:208–214. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Robinson-Rechavi M, Garcia Escriva H and
Laudet V: The nuclear receptor superfamily. J Cell Sci.
116:585–586. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Giguere V: Structure and function of the
nuclear receptor superfamily for steroid, thyroid hormone and
retinoic acid. Genet Eng (N Y). 12:183–200. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brelivet Y, Rochel N and Moras D:
Structural analysis of nuclear receptors: From isolated domains to
integral proteins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 348:466–473. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McEwan IJ: The Nuclear receptor
superfamily at thirty. Methods Mol Biol. 1443:3–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Germain P, Staels B, Dacquet C, Spedding M
and Laudet V: Overview of nomenclature of nuclear receptors.
Pharmacol Rev. 58:685–704. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rastinejad F, Huang P, Chandra V and
Khorasanizadeh S: Understanding nuclear receptor form and function
using structural biology. J Mol Endocrinol. 51:T1–T21. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chandra V, Huang P, Hamuro Y, Raghuram S,
Wang Y, Burris TP and Rastinejad F: Structure of the intact
PPAR-gamma-RXR-nuclear receptor complex on DNA. Nature.
456:350–356. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Olefsky JM: Nuclear receptor minireview
series. J Biol Chem. 276:36863–36864. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen T: Nuclear receptor drug discovery.
Curr Opin Chem Biol. 12:418–426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen T: Overcoming drug resistance by
regulating nuclear receptors. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 62:1257–1264.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hazel TG, Nathans D and Lau LF: A gene
inducible by serum growth factors encodes a member of the steroid
and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
85:8444–8448. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Watson MA and Milbrandt J: The NGFI-B
gene, a transcriptionally inducible member of the steroid receptor
gene superfamily: Genomic structure and expression in rat brain
after seizure induction. Mol Cell Biol. 9:4213–4219. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chang C, Kokontis J, Liao SS and Chang Y:
Isolation and characterization of human TR3 receptor: A member of
steroid receptor superfamily. J Steroid Biochem. 34:391–395. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hwang DS, Lee BY, Kim HS, Lee MC, Kyung
DH, Om AS, Rhee JS and Lee JS: Genome-wide identification of
nuclear receptor (NR) superfamily genes in the copepod Tigriopus
japonicus. BMC Genomics. 15:9932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sharma Y, Chilamakuri CS, Bakke M and
Lenhard B: Computational characterization of modes of
transcriptional regulation of nuclear receptor genes. PLoS One.
9:e888802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kurakula K, Koenis DS, van Tiel CM and de
Vries CJ: NR4A nuclear receptors are orphans but not lonesome.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:2543–2555. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rehman SU, Sarwar T, Husain MA, Ishqi HM
and Tabish M: Identification of two novel isoforms of mouse NUR77
lacking N-terminal domains. IUBMB Life. 69:106–114. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wilson TE, Fahrner TJ and Milbrandt J: The
orphan receptors NGFI-B and steroidogenic factor 1 establish
monomer binding as a third paradigm of nuclear receptor-DNA
interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 13:5794–5804. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maira M, Martens C, Philips A and Drouin
J: Heterodimerization between members of the Nur subfamily of
orphan nuclear receptors as a novel mechanism for gene activation.
Mol Cell Biol. 19:7549–7557. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Forman BM, Goode E, Chen J, Oro AE,
Bradley DJ, Perlmann T, Noonan DJ, Burka LT, McMorris T, Lamph WW,
et al: Identification of a nuclear receptor that is activated by
farnesol metabolites. Cell. 81:687–693. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Perlmann T and Jansson L: A novel pathway
for vitamin A signaling mediated by RXR heterodimerization with
NGFI-B and NURR1. Genes Dev. 9:769–782. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Flaig R, Greschik H, Peluso-Iltis C and
Moras D: Structural basis for the cell-specific activities of the
NGFI-B and the Nurr1 ligand-binding domain. J Biol Chem.
280:19250–19258. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Michiels P, Atkins K, Ludwig C, Whittaker
S, van Dongen M and Günther U: Assignment of the orphan nuclear
receptor Nurr1 by NMR. Biomol NMR Assign. 4:101–105. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wansa KD, Harris JM and Muscat GE: The
activation function-1 domain of Nur77/NR4A1 mediates
trans-activation, cell specificity, and coactivator recruitment. J
Biol Chem. 277:33001–33011. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lanig H, Reisen F, Whitley D, Schneider G,
Banting L and Clark T: In silico adoption of an orphan nuclear
receptor NR4A1. PLoS One. 10:e01352462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moore TW, Mayne CG and Katzenellenbogen
JA: Minireview: Not picking pockets: Nuclear receptor
alternate-site modulators (NRAMs). Mol Endocrinol. 24:683–695.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chang LF, Lin PC, Ho LI, Liu PY, Wu WC,
Chiang IP, Chang HW, Lin SZ, Harn YC, Harn HJ and Chiou TW:
Overexpression of the orphan receptor Nur77 and its translocation
induced by PCH4 may inhibit malignant glioma cell growth and induce
cell apoptosis. J Surg Oncol. 103:442–450. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Holmes WF, Soprano DR and Soprano KJ:
Early events in the induction of apoptosis in ovarian carcinoma
cells by CD437: Activation of the p38 MAP kinase signal pathway.
Oncogene. 22:6377–6386. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Niu G, Lu L, Gan J, Zhang D, Liu J and
Huang G: Dual roles of orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77/NGFI-B in
mediating cell survival and apoptosis. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol.
313:219–258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou F, Drabsch Y, Dekker TJ, de Vinuesa
AG, Li Y, Hawinkels LJ, Sheppard KA, Goumans MJ, Luwor RB, de Vries
CJ, et al: Nuclear receptor NR4A1 promotes breast cancer invasion
and metastasis by activating TGF-β signalling. Nat Commun.
5:33882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hedrick E and Safe S: Transforming growth
factor β/NR4A1-inducible breast cancer cell migration and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is p38α (Mitogen-Activated
Protein Kinase 14) dependent. Mol Cell Biol. 37:pii: e00306. –17.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Delgado E, Boisen MM, Laskey R, Chen R,
Song C, Sallit J, Yochum ZA, Andersen CL, Sikora MJ, Wagner J, et
al: High expression of orphan nuclear receptor NR4A1 in a subset of
ovarian tumors with worse outcome. Gynecol Oncol. 141:348–356.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang X, Yan G, Diao Z, Sun H and Hu Y:
NUR77 inhibits the expression of TIMP2 and increases the migration
and invasion of HTR-8/SVneo cells induced by CYR61. Placenta.
33:561–567. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lin B, Kolluri SK, Lin F, Liu W, Han YH,
Cao X, Dawson MI, Reed JC and Zhang XK: Conversion of Bcl-2 from
protector to killer by interaction with nuclear orphan receptor
Nur77/TR3. Cell. 116:527–540. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cao X, Liu W, Lin F, Li H, Kolluri SK, Lin
B, Han YH, Dawson MI and Zhang XK: Retinoid X receptor regulates
Nur77/TR3-dependent apoptosis [corrected] by modulating its nuclear
export and mitochondrial targeting. Mol Cell Biol. 24:9705–9725.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang XK: Targeting Nur77 translocation.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 11:69–79. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Han YH, Cao X, Lin B, Lin F, Kolluri SK,
Stebbins J, Reed JC, Dawson MI and Zhang XK: Regulation of Nur77
nuclear export by c-Jun N-terminal kinase and Akt. Oncogene.
25:2974–2986. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen HZ, Zhao BX, Zhao WX, Li L, Zhang B
and Wu Q: Akt phosphorylates the TR3 orphan receptor and blocks its
targeting to the mitochondria. Carcinogenesis. 29:2078–2088. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
No H, Bang Y, Lim J, Kim SS, Choi HS and
Choi HJ: Involvement of induction and mitochondrial targeting of
orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 in 6-OHDA-induced SH-SY5Y cell death.
Neurochem Int. 56:620–626. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Debernard Boldingh KA, Mathisen GH and
Paulsen RE: Differences in NGFI-B, Nurr1, and NOR-1 expression and
nucleocytoplasmic translocation in glutamate-treated neurons.
Neurochem Int. 61:79–88. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Renaud J, Chiasson K, Bournival J,
Rouillard C and Martinoli MG: 17β-estradiol delays 6-OHDA-induced
apoptosis by acting on Nur77 translocation from the nucleus to the
cytoplasm. Neurotox Res. 25:124–134. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Agostini-Dreyer A, Jetzt AE, Stires H and
Cohick WS: Endogenous IGFBP-3 mediates intrinsic apoptosis through
modulation of Nur77 phosphorylation and nuclear export.
Endocrinology. 156:4141–4151. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hu Y, Chau T, Liu HX, Liao D, Keane R, Nie
Y, Yang H and Wan YJ: Bile acids regulate nuclear receptor (Nur77)
expression and intracellular location to control proliferation and
apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res. 13:281–292. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Drouin J, Maira M and Philips A: Novel
mechanism of action for Nur77 and antagonism by glucocorticoids: A
convergent mechanism for CRH activation and glucocorticoid
repression of POMC gene transcription. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
65:59–63. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Maira M, Martens C, Batsché E, Gauthier Y
and Drouin J: Dimer-specific potentiation of NGFI-B (Nur77)
transcriptional activity by the protein kinase A pathway and
AF-1-dependent coactivator recruitment. Mol Cell Biol. 23:763–776.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Rambaud J, Desroches J, Balsalobre A and
Drouin J: TIF1beta/KAP-1 is a coactivator of the orphan nuclear
receptor NGFI-B/Nur77. J Biol Chem. 284:14147–14156. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lee SO, Abdelrahim M, Yoon K,
Chintharlapalli S, Papineni S, Kim K, Wang H and Safe S:
Inactivation of the orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 inhibits
pancreatic cancer cell and tumor growth. Cancer Res. 70:6824–6836.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hedrick E, Lee SO, Doddapaneni R, Singh M
and Safe S: NR4A1 antagonists inhibit β1-integrin-dependent breast
cancer cell migration. Mol Cell Biol. 36:1383–1394. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hedrick E, Li X and Safe S: Penfluridol
represses integrin expression in breast cancer through induction of
reactive oxygen species and downregulation of Sp transcription
factors. Mol Cancer Ther. 16:205–216. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lacey A, Rodrigues-Hoffman A and Safe S:
PAX3-FOXO1A expression in rhabdomyosarcoma is driven by the
targetable nuclear receptor NR4A1. Cancer Res. 77:732–741. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chao LC, Zhang Z, Pei L, Saito T, Tontonoz
P and Pilch PF: Nur77 coordinately regulates expression of genes
linked to glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle. Mol Endocrinol.
21:2152–2163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kanzleiter T, Preston E, Wilks D, Ho B,
Benrick A, Reznick J, Heilbronn LK, Turner N and Cooney GJ:
Overexpression of the orphan receptor Nur77 alters glucose
metabolism in rat muscle cells and rat muscle in vivo.
Diabetologia. 53:1174–1183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Pei L, Waki H, Vaitheesvaran B, Wilpitz
DC, Kurland IJ and Tontonoz P: NR4A orphan nuclear receptors are
transcriptional regulators of hepatic glucose metabolism. Nat Med.
12:1048–1055. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Pols TW, Ottenhoff R, Vos M, Levels JH,
Quax PH, Meijers JC, Pannekoek H, Groen AK and de Vries CJ: Nur77
modulates hepatic lipid metabolism through suppression of SREBP1c
activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 366:910–916. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhao Y and Bruemmer D: NR4A orphan nuclear
receptors: Transcriptional regulators of gene expression in
metabolism and vascular biology. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
30:1535–1541. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhao Y, Liu Y and Zheng D: Alpha
1-antichymotrypsin/SerpinA3 is a novel target of orphan nuclear
receptor Nur77. FEBS J. 275:1025–1038. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lee BH, Indran IR, Tan HM, Li Y, Zhang Z,
Li J and Yong EL: A dietary medium-chain fatty acid, decanoic acid,
inhibits recruitment of Nur77 to the HSD3B2 promoter in vitro and
reverses endocrine and metabolic abnormalities in a rat model of
polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocrinology. 157:382–394. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kolluri SK, Zhu X, Zhou X, Lin B, Chen Y,
Sun K, Tian X, Town J, Cao X, Lin F, et al: A short Nur77-derived
peptide converts Bcl-2 from a protector to a killer. Cancer Cell.
14:285–298. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu J, Wang GH, Duan YH, Dai Y, Bao Y, Hu
M, Zhou YQ, Li M, Jiang F, Zhou H, et al: Modulation of the
Nur77-Bcl-2 apoptotic pathway by p38alpha MAPK. Oncotarget.
8:69731–69745. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhao BX, Chen HZ, Lei NZ, Li GD, Zhao WX,
Zhan YY, Liu B, Lin SC and Wu Q: p53 mediates the negative
regulation of MDM2 by orphan receptor TR3. EMBO J. 25:5703–5715.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li GD, Fang JX, Chen HZ, Luo J, Zheng ZH,
Shen YM and Wu Q: Negative regulation of transcription coactivator
p300 by orphan receptor TR3. Nucleic Acids Res. 35:7348–7359. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lei NZ, Zhang XY, Chen HZ, Wang Y, Zhan
YY, Zheng ZH, Shen YM and Wu Q: A feedback regulatory loop between
methyltransferase PRMT1 and orphan receptor TR3. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:832–848. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhan YY, Chen Y, Zhang Q, Zhuang JJ, Tian
M, Chen HZ, Zhang LR, Zhang HK, He JP, Wang WJ, et al: The orphan
nuclear receptor Nur77 regulates LKB1 localization and activates
AMPK. Nat Chem Biol. 8:897–904. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang RH, He JP, Su ML, Luo J, Xu M, Du XD,
Chen HZ, Wang WJ, Wang Y, Zhang N, et al: The orphan receptor TR3
participates in angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy by
controlling mTOR signalling. EMBO Mol Med. 5:137–148. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li L, Liu Y, Chen HZ, Li FW, Wu JF, Zhang
HK, He JP, Xing YZ, Chen Y, Wang WJ, et al: Impeding the
interaction between Nur77 and p38 reduces LPS-induced inflammation.
Nat Chem Biol. 11:339–346. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wang WJ, Wang Y, Hou PP, Li FW, Zhou B,
Chen HZ, Bian XL, Cai QX, Xing YZ, He JP, et al: Induction of
autophagic death in cancer cells by agonizing TR3 and attenuating
Akt2 activity. Chem Biol. 22:1040–1051. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
To SK, Zeng JZ and Wong AS: Nur77: A
potential therapeutic target in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
16:573–585. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zeng Y, Ye X, Liao D, Huang S, Mao H, Zhao
D and Zeng H: Orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 is a specific
therapeutic target for hepatic cancers. J Clin Exp Oncol. 6:pii:
184. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Brady SF, Wagenaar MM, Singh MP, Janso JE
and Clardy J: The cytosporones, new octaketide antibiotics isolated
from an endophytic fungus. Org Lett. 2:4043–4046. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhan Y, Du X, Chen H, Liu J, Zhao B, Huang
D, Li G, Xu Q, Zhang M, Weimer BC, et al: Cytosporone B is an
agonist for nuclear orphan receptor Nur77. Nat Chem Biol.
4:548–556. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Liu JJ, Zeng HN, Zhang LR, Zhan YY, Chen
Y, Wang Y, Wang J, Xiang SH, Liu WJ, Wang WJ, et al: A unique
pharmacophore for activation of the nuclear orphan receptor Nur77
in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Res. 70:3628–3637. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Yao LM, He JP, Chen HZ, Wang Y, Wang WJ,
Wu R, Yu CD and Wu Q: Orphan receptor TR3 participates in
cisplatin-induced apoptosis via Chk2 phosphorylation to repress
intestinal tumorigenesis. Carcinogenesis. 33:301–311. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Duan YH, Dai Y, Wang GH, Zhang X, Chen HF,
Chen JB, Yao XS and Zhang XK: Bioactive xanthones from the stems of
Cratoxylum formosum ssp. pruniflorum. J Nat Prod. 73:1283–1287.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wang WJ, Wang Y, Chen HZ, Xing YZ, Li FW,
Zhang Q, Zhou B, Zhang HK, Zhang J, Bian XL, et al: Orphan nuclear
receptor TR3 acts in autophagic cell death via mitochondrial
signaling pathway. Nat Chem Biol. 10:133–140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zeng Q, Jia YW, Xu PL, Xiao MW, Liu YM,
Peng SL and Liao X: Quick and selective extraction of Z-ligustilide
from Angelica sinensis using magnetic multiwalled carbon
nanotubes. J Sep Sci. 38:4269–4275. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kan WL, Cho CH, Rudd JA and Lin G: Study
of the anti-proliferative effects and synergy of phthalides from
Angelica sinensis on colon cancer cells. J Ethnopharmacol.
120:36–43. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Qi H, Jiang Z, Wang C, Yang Y, Li L, He H
and Yu Z: Sensitization of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells
by Z-ligustilide through inhibiting autophagy and accumulating DNA
damages. Oncotarget. 8:29300–29317. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Abedin MJ, Wang D, McDonnell MA, Lehmann U
and Kelekar A: Autophagy delays apoptotic death in breast cancer
cells following DNA damage. Cell Death Differ. 14:500–510. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Greenhill C: Celastrol identified as a
leptin sensitizer and potential novel treatment for obesity. Nat
Rev Endocrinol. 11:4442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Liu J, Lee J, Hernandez Salazar MA,
Mazitschek R and Ozcan U: Treatment of obesity with celastrol.
Cell. 161:999–1011. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Hu M, Luo Q, Alitongbieke G, Chong S, Xu
C, Xie L, Chen X, Zhang D, Zhou Y, Wang Z, et al: Celastrol-induced
Nur77 interaction with TRAF2 alleviates inflammation by promoting
mitochondrial ubiquitination and autophagy. Mol Cell. 66:141–153,
e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Andey T, Patel A, Jackson T, Safe S and
Singh M: 1,1-Bis (3′-indolyl)-1-(p-substitutedphenyl)methane
compounds inhibit lung cancer cell and tumor growth in a metastasis
model. Eur J Pharm Sci. 500:227–241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Yoon K, Lee SO, Cho SD, Kim K, Khan S and
Safe S: Activation of nuclear TR3 (NR4A1) by a diindolylmethane
analog induces apoptosis and proapoptotic genes in pancreatic
cancer cells and tumors. Carcinogenesis. 32:836–842. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Cho SD, Yoon K, Chintharlapalli S,
Abdelrahim M, Lei P, Hamilton S, Khan S, Ramaiah SK and Safe S:
Nur77 agonists induce proapoptotic genes and responses in colon
cancer cells through nuclear receptor-dependent and nuclear
receptor-independent pathways. Cancer Res. 67:674–683. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Lee SO, Li X, Hedrick E, Jin UH, Tjalkens
RB, Backos DS, Li L, Zhang Y, Wu Q and Safe S: Diindolylmethane
analogs bind NR4A1 and are NR4A1 antagonists in colon cancer cells.
Mol Endocrinol. 28:1729–1739. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Cho SD, Lee SO, Chintharlapalli S,
Abdelrahim M, Khan S, Yoon K, Kamat AM and Safe S: Activation of
nerve growth factor-induced B alpha by methylene-substituted
diindolylmethanes in bladder cancer cells induces apoptosis and
inhibits tumor growth. Mol Pharmacol. 77:396–404. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Hedrick E, Lee SO and Safe S: The nuclear
orphan receptor NR4A1 regulates β1-integrin expression in
pancreatic and colon cancer cells and can be targeted by NR4A1
antagonists. Mol Carcinog. 56:2066–2075. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Hedrick E, Lee SO, Doddapaneni R, Singh M
and Safe S: Nuclear receptor 4A1 as a drug target for breast cancer
chemotherapy. Endocr Relat Cancer. 22:831–840. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Lacey A, Hedrick E, Li X, Patel K,
Doddapaneni R, Singh M and Safe S: Nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) as
a drug target for treating rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS). Oncotarget.
7:31257–31269. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Hedrick E, Lee SO, Kim G, Abdelrahim M,
Jin UH, Safe S and Abudayyeh A: Nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) as a
drug target for renal cell adenocarcinoma. PLoS One.
10:e01283082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Wang JR, Gan WJ, Li XM, Zhao YY, Li Y, Lu
XX, Li JM and Wu H: Orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 promotes
colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by regulating MMP-9 and
E-cadherin. Carcinogenesis. 35:2474–2484. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
To SK, Zeng WJ, Zeng JZ and Wong AS:
Hypoxia triggers a Nur77-β-catenin feed-forward loop to promote the
invasive growth of colon cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 110:935–945.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wu J, Liu J, Jia R and Song H: Nur77
inhibits androgen-induced bladder cancer growth. Cancer Invest.
31:654–660. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Wohlkoenig C, Leithner K, Olschewski A,
Olschewski H and Hrzenjak A: TR3 is involved in hypoxia-induced
apoptosis resistance in lung cancer cells downstream of HIF-1α.
Lung Cancer. 111:15–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|