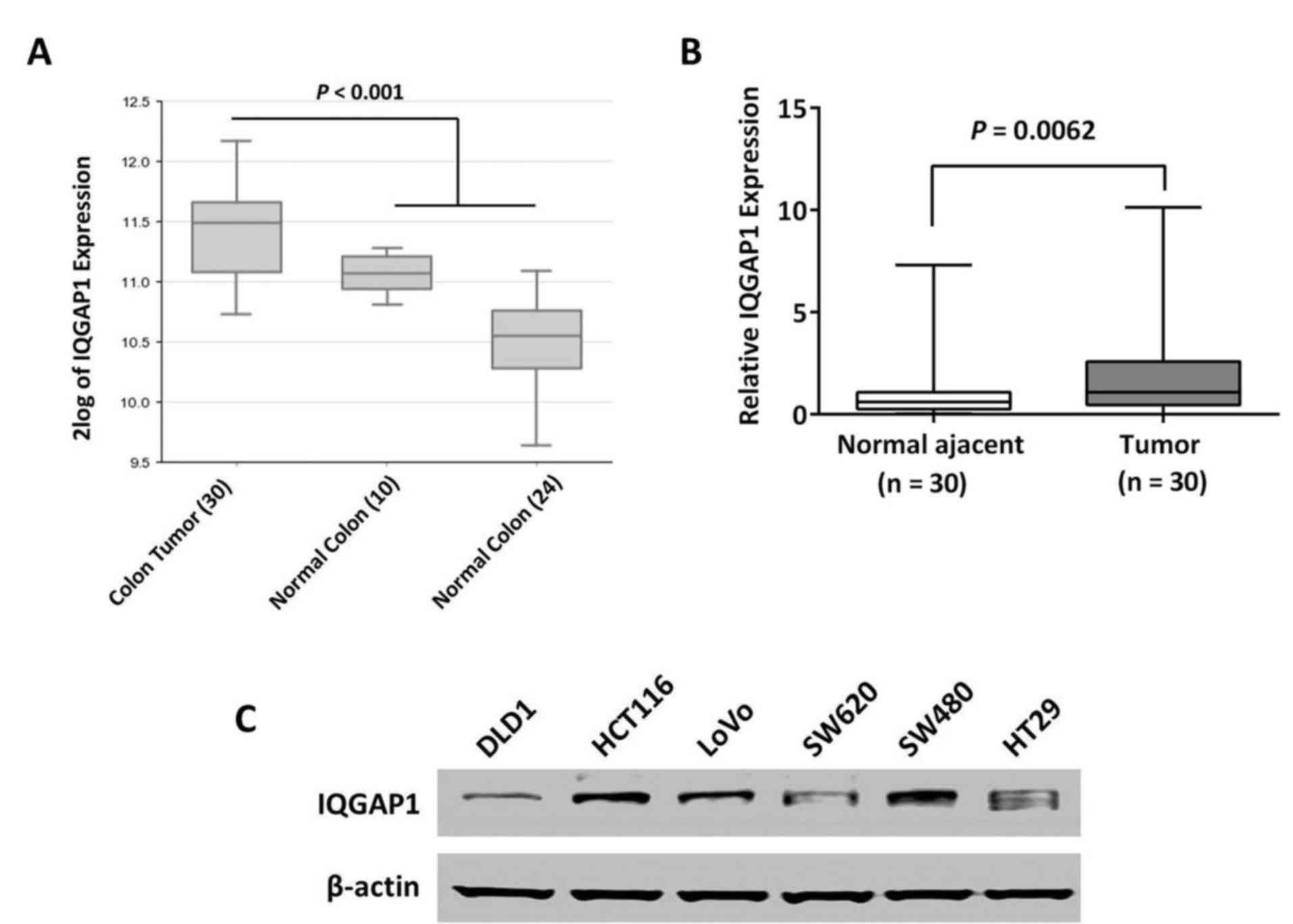
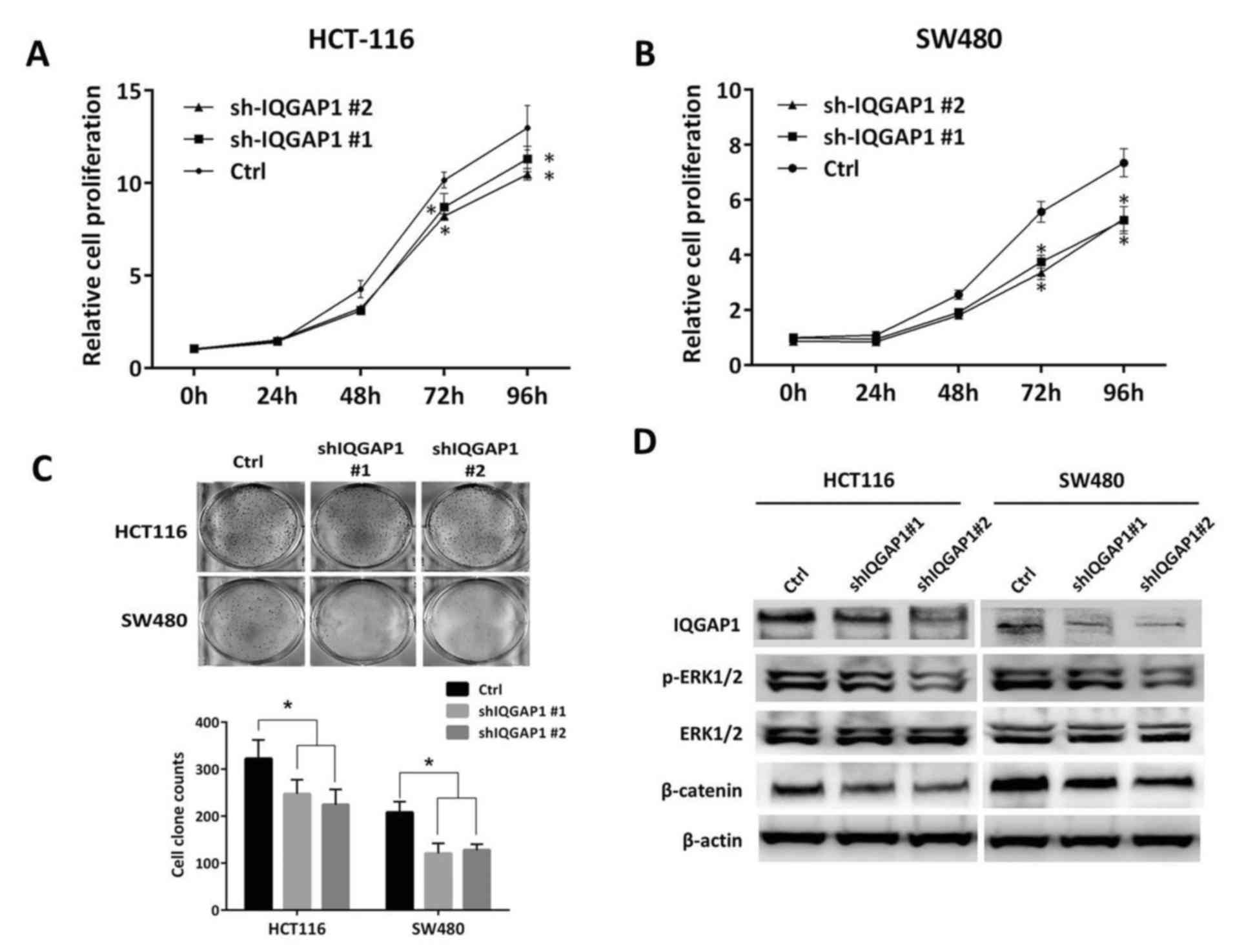
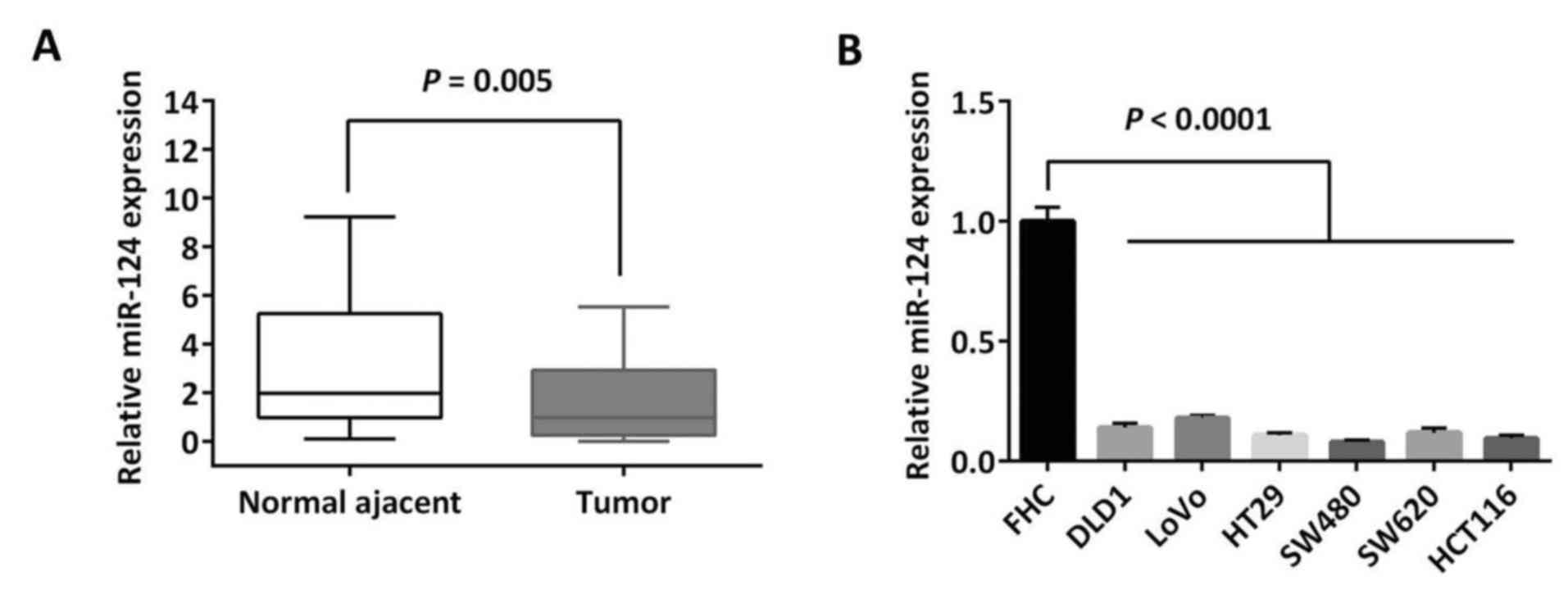
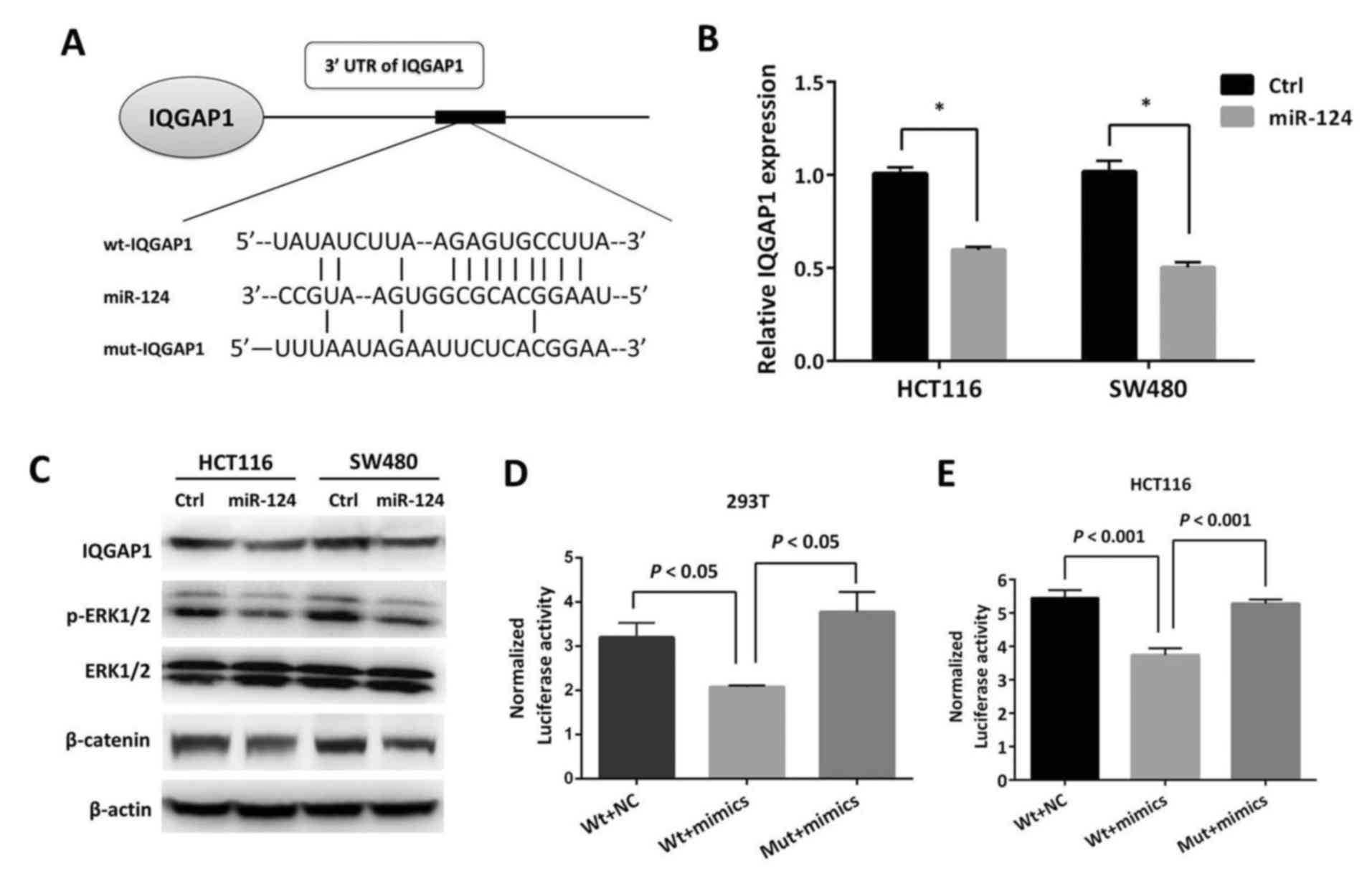
|
1
|
Esquela-Kerschera A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Furuta M, Kozaki KI, Tanaka S, Arii S,
Imoto I and Inazawa J: miR-124 and miR-203 are epigenetically
silenced tumor suppressive microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 31:766–776. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liang YJ, Wang QY, Zhou CX, Yin QQ, He M,
Yu XT, Cao DX, Chen GQ, He JR and Zhao Q: MiR-124 targets Slug to
regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:713–722. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wan HY, Li QQ, Zhang Y, Tian W, Li YN, Liu
M, Li X and Tang H: MiR-124 represses vasculogenic mimicry and cell
motility by targeting amotL1 in cervical cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
355:148–158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peng XH, Huang HR, Lu J, Liu X, Zhao FP,
Zhang B, Lin SX, Wang L, Chen HH, Xu X, et al: MiR-124 suppresses
tumor growth and metastasis by targeting Foxq1 in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 13:1862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y, Li H, Han J and Zhang Y:
Down-regulation of microRNA-124 is correlated with tumor metastasis
and poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:1967–1972. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Murray-Stewart T, Sierra JC, Piazuelo MB,
Mera RM, Chaturvedi R, Bravo LE, Correa P, Schneider BG, Wilson KT
and Casero RA: Epigenetic silencing of miR-124 prevents spermine
oxidase regulation: Implications for Helicobacter pylori-induced
gastric cancer. Oncogene. 35:5480–5488. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pronina IV, Loginov VI, Burdennyy AM,
Fridman MV, Senchenko VN, Kazubskaya TP, Kushlinskii NE, Dmitriev
AA and Braga EA: DNA methylation contributes to deregulation of 12
cancer-associated microRNAs and breast cancer progression. Gene.
604:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang H, Zhang TT, Jin S, Liu H, Zhang X,
Ruan CG, Wu DP, Han Y and Wang XQ: Pyrosequencing quantified
methylation level of miR-124 predicts shorter survival for patients
with myelodysplastic syndrome. Clin Epigenetics. 9:912017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zheng F, Liao YJ, Cai MY, Liu YH, Liu TH,
Chen SP, Bian XW, Guan XY, Lin MC, Zeng YX, et al: The putative
tumour suppressor microRNA-124 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma
cell aggressiveness by repressing ROCK2 and EZH2. Gut. 61:278–289.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cheng Y, Li Y, Nian Y, Liu D, Dai F and
Zhang J: STAT3 is involved in miR-124-mediated suppressive effects
on esophageal cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 15:3062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang MJ, Li Y, Wang R, Wang C, Yu YY, Yang
L, Zhang Y, Zhou B, Zhou ZG and Sun XF: Downregulation of
microRNA-124 is an independent prognostic factor in patients with
colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 28:183–189. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jinushi T, Shibayama Y, Kinoshita I,
Oizumi S, Jinushi M, Aota T, Takahashi T, Horita S, Dosaka-Akita H
and Iseki K: Low expression levels of microRNA-124-5p correlated
with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer via targeting of SMC4.
Cancer Med. 3:1544–1552. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Taniguchi K, Sugito N, Kumazaki M,
Shinohara H, Yamada N, Nakagawa Y, Ito Y, Otsuki Y, Uno B, Uchiyama
K and Akao Y: MicroRNA-124 inhibits cancer cell growth through
PTB1/PKM1/PKM2 feedback cascade incolorectal cancer. Cancer Lett.
363:17–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Z, Liu S, Tian L, Wu M, Ai F, Tang W,
Zhao L, Ding J, Zhang L and Tang A: miR-124 and miR-506 inhibit
colorectal cancer progression by targeting DNMT3B and DNMT1.
Oncotarget. 6:38139–38150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou L, Xu Z, Ren X, Chen K and Xin S:
MicroRNA-124 (MiR-124) inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis and
invasion in colorectal cancerby downregulating rho-associated
protein kinase 1(ROCK1). Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:1785–1795. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang Y, Zheng L, Huang J, Gao F, Lin X,
He L, Li D, Li Z, Ding Y and Chen L: MiR-124 Radiosensitizes human
colorectal cancer cells by targeting PRRX1. PLoS One. 9:e939172014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bai J, Li Y, Shao T, Zhao Z, Wang Y, Wu A,
Chen H, Li S, Jiang C, Xu J and Li X: Integrating analysis reveals
microRNA-mediated pathway crosstalk among Crohn's disease,
ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer. Mol Biosyst.
10:2317–2328. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roy M, Li Z and Sacks DB: IQGAP1 is a
scaffold for mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling. Mol Cell
Biol. 25:7940–7952. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roy M, Li Z and Sacks DB: IQGAP1 binds
ERK2 and modulates its activity. J Biol Chem. 279:17329–17337.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bourguignon LY, Gilad E, Rothman K and
Peyrollier K: Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction with IQGAP1 promotes
Cdc42 and ERK signaling, leading to actin binding, Elk-1/Estrogen
Receptor transcriptional activation, and ovarian cancer
progression. J Biol Chem. 280:11961–11972. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Briggs MW, Li Z and Sacks DB:
IQGAP1-mediated stimulation of transcriptional co-activation by
beta-catenin is modulated by calmodulin. J Biol Chem.
277:7453–7465. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Y, Wang A, Wang F, Wang M, Zhu M, Ma
Y and Wu R: IQGAP1 activates Tcf signal independent of Rac1 and
Cdc42 in injury and repair of bronchial epithelial cells. Exp Mol
Pathol. 85:122–128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schmidt VA, Chiariello CS, Capilla E,
Miller F and Bahou WF: Development of hepatocellular carcinoma in
Iqgap2-deficient mice is IQGAP1 dependent. Mol Cell Biol.
28:1489–1502. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nabeshima K, Shimao Y, Inoue T and Koono
M: Immunohistochemical analysis of IQGAP1 expression in human
colorectal carcinomas: Its overexpression in carcinomas and
association with invasion fronts. Cancer Lett. 176:101–109. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hayashi H, Nabeshima K, Aoki M, Hamasaki
M, Enatsu S, Yamauchi Y, Yamashita Y and Iwasaki H: Overexpression
of IQGAP1 in advanced colorectal cancer correlates with poor
prognosis-critical role in tumor invasion. Int J Cancer.
126:2563–2574. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Skrzypczak M, Goryca K, Rubel T, Paziewska
A, Mikula M, Jarosz D, Pachlewski J, Oledzki J and Ostrowski J:
Modeling oncogenic signaling in colon tumors by multidirectional
analyses of microarray data directed for maximization of analytical
reliability. PLoS One. 5:e130912010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression using real time PCR and the 2 (-Delta
Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Abel AM, Schuldt KM, Rajasekaran K, Hwang
D, Riese MJ, Rao S, Thakar MS and Malarkannan S: IQGAP1: Insights
into the function of a molecular puppeteer. Mol Immunol.
65:336–349. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dong P, Nabeshima K, Nishimura N, Kawakami
T, Hachisuga T, Kawarabayashi T and Iwasaki H: Overexpression and
diffuse expression pattern of IQGAP1 at invasion fronts are
independent prognostic parameters in ovarian carcinomas. Cancer
Lett. 243:120–127. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen F, Zhu HH, Zhou LF, Wu SS, Wang J and
Chen Z: IQGAP1 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and
promotes cell proliferation by Akt activation. Exp Mol Med.
42:477–483. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang XX, Li XZ, Zhai LQ, Liu ZR, Chen XJ
and Pei Y: Overexpression of IQGAP1 in human pancreatic cancer.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 12:540–545. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Smith JM, Hedman AC and Sacks DB: IQGAPs
choreograph cellular signaling from the membrane to the nucleus.
Trends Cell Biol. 25:171–184. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
White CD, Brown MD and Sacks DB: IQGAPs in
Cancer: A family of scaffold proteins underlying tumorigenesis.
FEBS Lett. 583:1817–1824. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jameson KL, Mazur PK, Zehnder AM, Zhang J,
Zarnegar B, Sage J and Khavari PA: IQGAP1 scaffold-kinase
interaction blockade selectively targets RAS-MAP kinase-driven
tumors. Nat Med. 19:626–630. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pi F, Binzel DW, Lee TJ, Li Z, Sun M,
Rychahou P, Li H, Haque F, Wang S, Croce CM, et al: Nanoparticle
orientation to control RNA loading and ligand display on
extracellular vesicles for cancer regression. Nat Nanotechnol.
13:82–89. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao CY, Cheng R, Yang Z and Tian ZM:
Nanotechnology for cancer therapy based on chemotherapy. Molecules.
23:E8262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Awasthi R, Roseblade A, Hansbro PM,
Rathbone MJ, Dua K and Bebawy M: Nanoparticles in cancer treatment:
Opportunities and obstacles. Curr Drug Targets. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rychahou P, Bae Y, Reichel D, Zaytseva YY,
Lee EY, Napier D, Weiss HL, Roller N, Frohman H, Le AT and Mark
Evers B: Colorectal cancer lung metastasis treatment with
polymer-drug nanoparticles. J Control Release. 275:85–91. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Marquez J, Fernandez-Piñeiro I,
Araúzo-Bravo MJ, Poschmann G, Stühler K, Khatib AM, Sanchez A, Unda
F, Ibarretxe G, Bernales I and Badiola I: Targeting liver
sinusoidal endothelial cells with miR-20a-loaded nanoparticles
reduces murine coloncancer metastasis to the liver. Int J Cancer.
143:709–719. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li Y, Duo Y, Bi J, Zeng X, Mei L, Bao S,
He L, Shan A, Zhang Y and Yu X: Targeted delivery of anti-miR-155
by functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for colorectal
cancer therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 13:1241–1256. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|