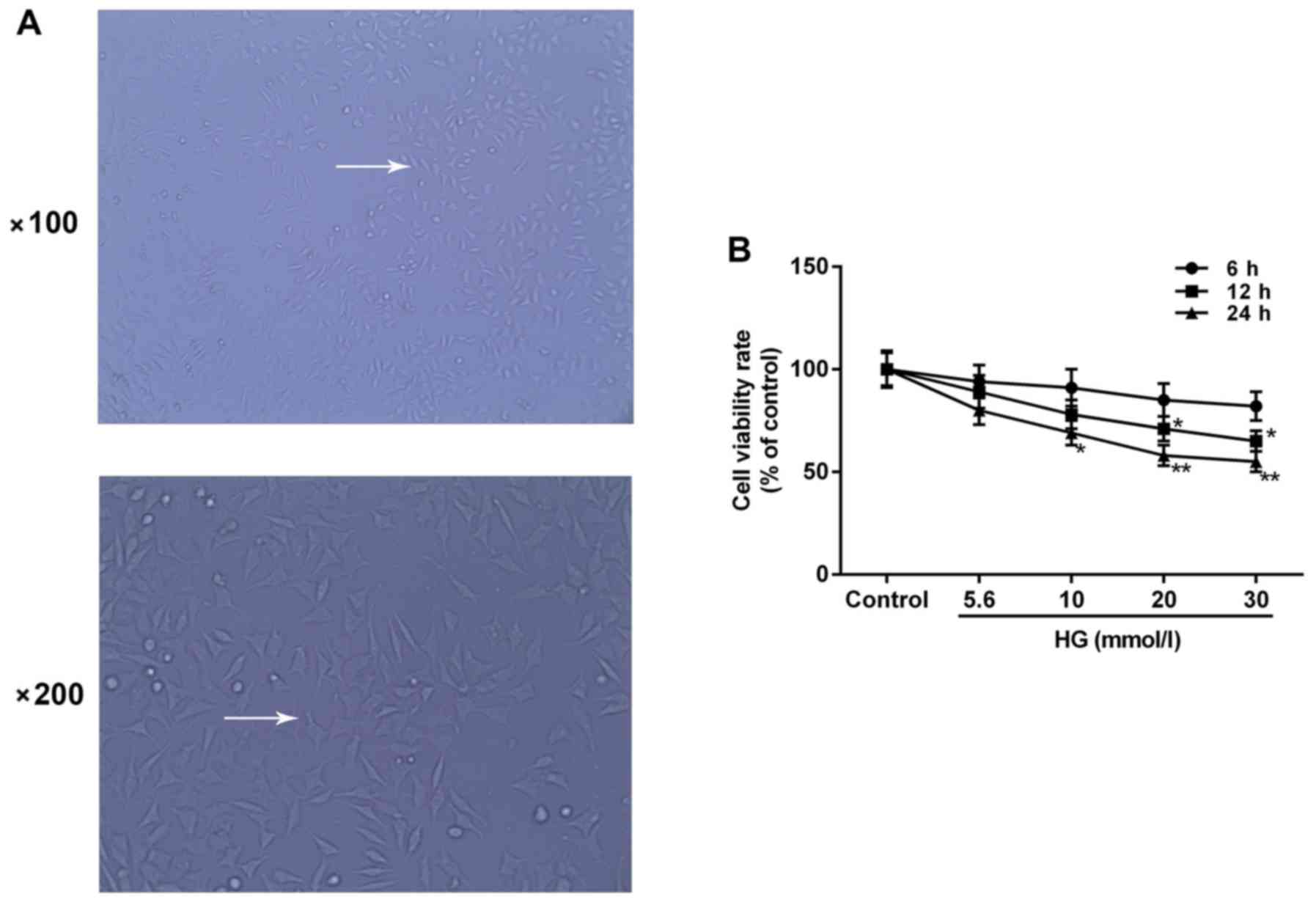
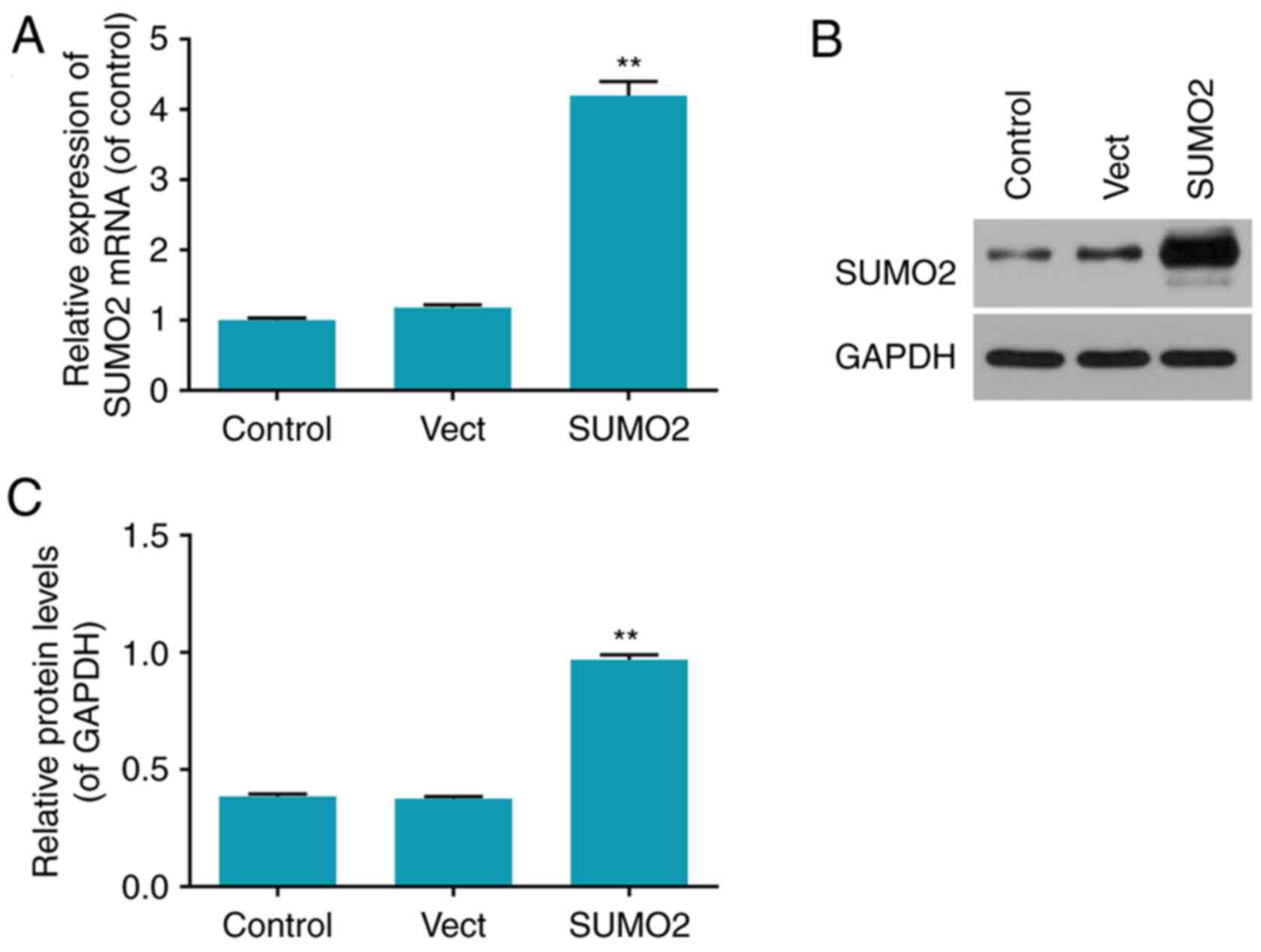
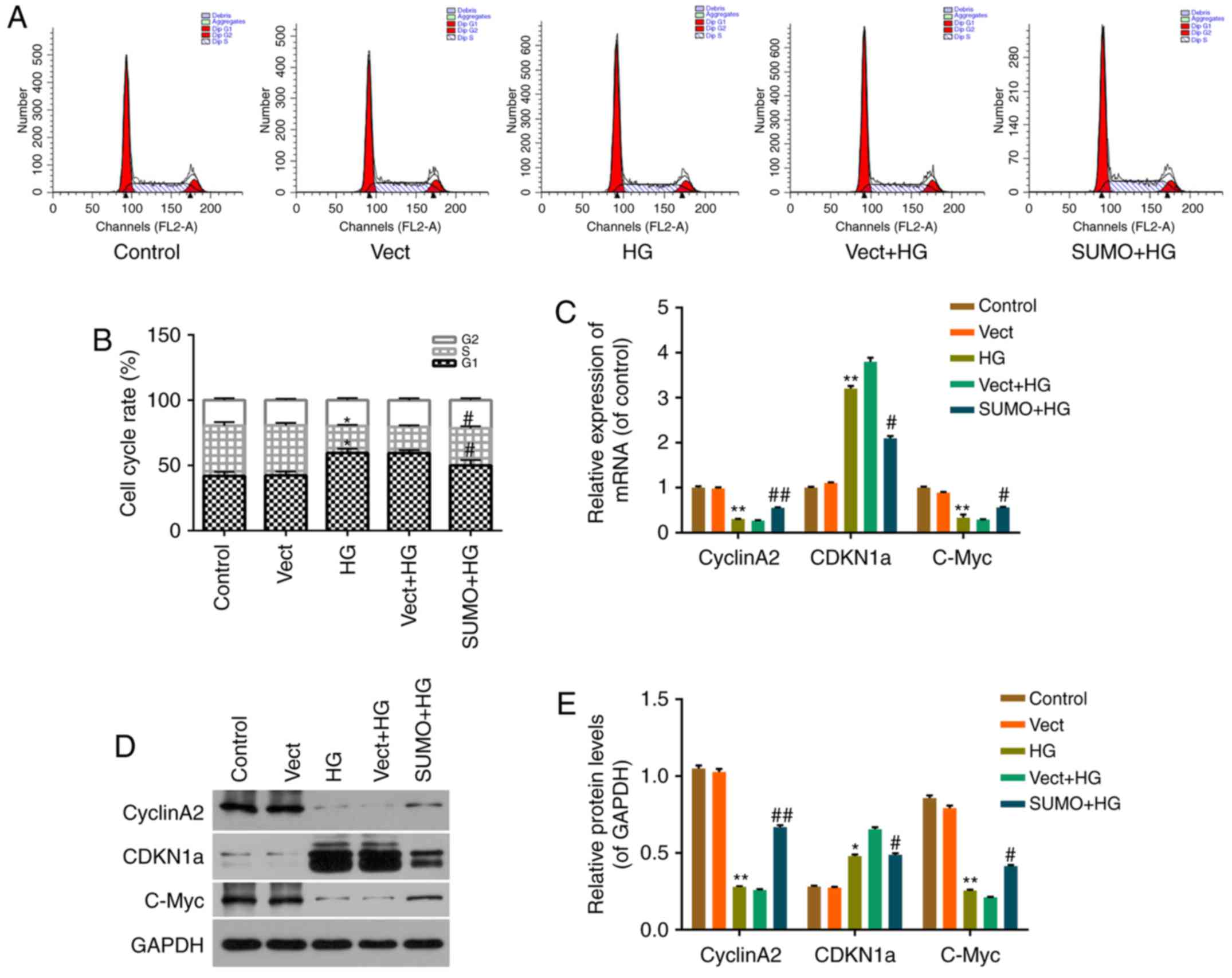
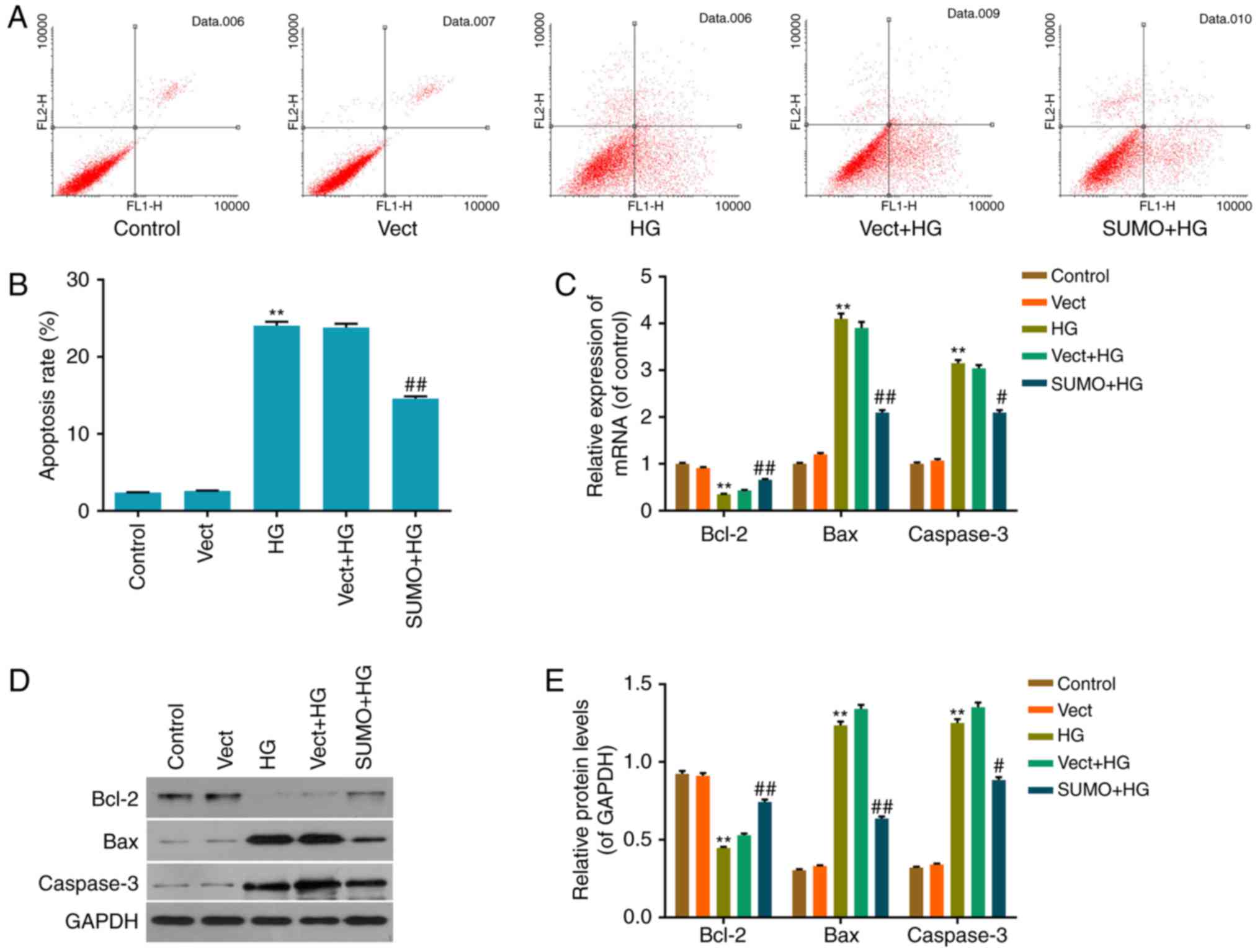
|
1
|
Manyari DE: Prognostic implications of
echocardiographically determined left ventricular mass in the
Framingham Heart Study. N Engl J Med. 323:1706–1707. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rohini A, Agrawal N, Koyani CN and Singh
R: Molecular targets and regulators of cardiac hypertrophy.
Pharmacol Res. 61:269–280. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tate M, Deo M, Cao AH, Hood SG, Huynh K,
Kiriazis H, Du XJ, Julius TL, Figtree GA, Dusting GJ, et al:
Insulin replacement limits progression of diabetic cardiomyopathy
in the low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Diab Vasc Dis
Res. 14:423–433. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu X, Bai T, Xu Z, Liu Q, Zheng Y and Cai
L: Pathophysiological fundamentals of diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Compr Physiol. 7:693–711. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mishra PK, Ying W, Nandi SS, Bandyopadhyay
GK, Patel KK and Mahata SK: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: An
immunometabolic perspective. Front endocrinol (Lausanne). 8:722017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Prakoso D, DeBlasio MJ, Qin C, Rosli S,
Kiriazis H, Qian H, Du XJ, Weeks KL, Gregorevic P, McMullen JR and
Ritchie RH: Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase (p110α) gene delivery limits
diabetes-induced cardiac NADPH oxidase and cardiomyopathy in a
mouse model with established diastolic dysfunction. Clin Sci
(Lond). 131:1345–1360. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bell DS: Diabetic cardiomyopathy. A unique
entity or a complication of coronary artery disease? Diabetes Care.
18:708–714. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ounzain S and Pedrazzini T: The promise of
enhancer-associated long noncoding RNAs in cardiac regeneration.
Trends Cardiovasc Med. 25:592–602. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dhiman M and Garg NJ: NADPH oxidase
inhibition ameliorates Trypanosoma cruzi-induced myocarditis during
Chagas disease. J Pathol. 225:583–596. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marushchak M, Lisnianska N, Krynytska
Capital IU and Chornomydz I: The mechanisms of apoptosis initiation
in rats with chronic enterocolitis combined with
streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Georgian Med News. 125–130.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hong YA, Lim JH, Kim MY, Kim Y, Park HS,
Kim HW, Choi BS, Chang YS, Kim HW, Kim TY, et al: Extracellular
superoxide dismutase attenuates renal oxidative stress through the
activation of AMPK in diabetic nephropathy. Antioxid Redox Signal.
Nov 14–2017.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7207.
|
|
12
|
Tabebi M, Khabou B, Boukadi H, Ben Hamad
M, Ben Rhouma B, Tounsi S, Maalej A, Kamoun H, Keskes-Ammar L, Abid
M, et al: Association study of apoptosis gene polymorphisms in
mitochondrial diabetes: A potential role in the pathogenicity of
MD. Gene. 639:18–26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bugyei-Twum A, Advani A, Advani SL, Zhang
Y, Thai K, Kelly DJ and Connelly KA: High glucose induces Smad
activation via the transcriptional coregulator p300 and contributes
to cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
13:892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wilkinson KA and Henley JM: Mechanisms,
regulation and consequences of protein SUMOylation. Biochem J.
428:133–145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Princz A and Tavernarakis N: The role of
SUMOylation in ageing and senescent decline. Mech Ageing Dev.
162:85–90. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hay RT: SUMO: A history of modification.
Mol Cell. 18:1–12. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li XC, Zeng Y, Sun RR, Liu M, Chen S and
Zhang PY: SUMOylation in cardiac disorders-a review. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 21:1583–1587. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo B, Yang SH, Witty J and Sharrocks AD:
Signalling pathways and the regulation of SUMO modification.
Biochem Soc Trans. 35:1414–1418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Geiss-Friedlander R and Melchior F:
Concepts in sumoylation: A decade on. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
8:947–956. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rosonina E, Akhter A, Dou Y, Babu J and
Theivakadadcham Sri VS: Regulation of transcription factors by
sumoylation. Transcription. 8:220–231. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bedford L, Lowe J, Dick LR, Mayer RJ and
Brownell JE: Ubiquitin-like protein conjugation and the
ubiquitin-proteasome system as drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
10:29–46. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Paddibhatla I, Lee MJ, Kalamarz ME,
Ferrarese R and Govind S: Role for sumoylation in systemic
inflammation and immune homeostasis in Drosophila larvae.
PLoS Pathog. 6:e10012342010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wilson VG: Viral interplay with the host
sumoylation system. Adv Exp Med Biol. 963:359–388. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chang E and Abe J: Kinase-SUMO networks in
diabetes-mediated cardiovascular disease. Metabolism Clin Exp.
65:623–633. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Shishido T, Woo CH, Ding B, McClain C,
Molina CA, Yan C, Yang J and Abe J: Effects of MEK5/ERK5
association on small ubiquitin-related modification of ERK5:
Implications for diabetic ventricular dysfunction after myocardial
infarction. Circ Res. 102:1416–1425. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang L, Mao Y, Pan J, Wang S, Chen L and
Xiang J: Bamboo leaf extract ameliorates cardiac fibrosis possibly
via alleviating inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis.
Biomed Pharmacother. 95:808–817. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu H, Sun F, Li X and Sun L:
Downregulation of miR-23a inhibits high glucose-induced EMT and
renal fibrogenesis by upregulation of SnoN. Hum Cell. 31:22–32.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kang JS, Saunier EF, Akhurst RJ and
Derynck R: The type I TGF-beta receptor is covalently modified and
regulated by sumoylation. Nat Cell Biol. 10:654–664. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin X, Liang M, Liang YY, Brunicardi FC
and Feng XH: SUMO-1/Ubc9 promotes nuclear accumulation and
metabolic stability of tumor suppressor Smad4. J Biol Chem.
278:31043–31048. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Haas AV and McDonnell ME: Pathogenesis of
cardiovascular disease in diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.
47:51–63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Singh RM, Waqar T, Howarth FC, Adeghate E,
Bidasee K and Singh J: Hyperglycemia-induced cardiac contractile
dysfunction in the diabetic heart. Heart Fail Rev. 23:37–54. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bernt A, Rangrez AY, Eden M, Jungmann A,
Katz S, Rohr C, Muller OJ, Katus HA, Sossalla ST, Williams T, et
al: Sumoylation-independent activation of
Calcineurin-NFAT-signaling via SUMO2 mediates cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy. Sci Rep. 6:357582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim EY, Zhang Y, Ye B, Segura AM, Beketaev
I, Xi Y, Yu W, Chang J, Li F and Wang J: Involvement of activated
SUMO-2 conjugation in cardiomyopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1852:1388–1399. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Valle-Casuso JC, Allouch A, David A, Lenzi
GM, Studdard L, Barre-Sinoussi F, Muller-Trutwin M, Kim B, Pancino
G and Saez-Cirion A: p21 restricts HIV-1 in monocyte-derived
dendritic cells through the reduction of dNTP biosynthesis and
regulation of SAMHD1 antiviral activity. J Virol. 91:e013242017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Brooks G, Poolman RA and Li JM: Arresting
developments in the cardiac myocyte cell cycle: Role of
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Cardiovasc Res. 39:301–311.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hauck L, Harms C, Grothe D, An J, Gertz K,
Kronenberg G, Dietz R, Endres M and von Harsdorf R: Critical role
for FoxO3a-dependent regulation of p21CIP1/WAF1 in response to
statin signaling in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 100:50–60. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Koga K, Kenessey A and Ojamaa K:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor antagonizes pressure
overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 304:H282–H293. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kaplan A, Abidi E, Ghali R, Booz GW,
Kobeissy F and Zouein FA: Functional, cellular and molecular
remodeling of the heart under influence of oxidative cigarette
tobacco smoke. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:37591862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang D, Li Y, Heims-Waldron D, Bezzerides
V, Guatimosim S, Guo Y, Gu F, Zhou P, Lin Z, Ma Q, et al:
Mitochondrial cardiomyopathy caused by elevated reactive oxygen
species and impaired cardiomyocyte proliferation. Circ Res.
122:74–87. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Deng H, Cheng Y, Guo Z, Zhang F, Lu X,
Feng L, Wang X and Xu Z: Overexpression of cyclinA2 ameliorates
hypoxia-impaired proliferation of cardiomyocytes. Exp Ther Med.
8:1513–1517. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fu XJ, Li HX, Yang K, Chen D and Tang H:
The important tumor suppressor role of PER1 in regulating the
cyclin-CDK-CKI network in SCC15 human oral squamous cell carcinoma
cells. Onco Targets Ther. 9:2237–2245. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang XH, Tang F, Shin J and Cunningham JM:
Incorporating genomic, transcriptomic and clinical data: a
prognostic and stem cell-like MYC and PRC imbalance in high-risk
neuroblastoma. BMC Syst Biol. 11 Suppl 5:922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu P, Su J, Song X and Wang S: Activation
of nuclear β-catenin/c-Myc axis promotes oxidative stress injury in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 493:1573–1580. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yoon MK, Mitrea DM, Ou L and Kriwacki RW:
Cell cycle regulation by the intrinsically disordered proteins p21
and p27. Biochem Soc Trans. 40:981–988. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yanagi T, Nagai K, Shimizu H and Matsuzawa
SI: Melanoma antigen A12 regulates cell cycle via tumor suppressor
p21 expression. Oncotarget. 8:68448–68459. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhou C, Huang J, Li Q, Zhan C, Xu X, Zhang
X, Ai D, Zhu Y, Wen Z and Wang DW: CYP2J2-derived EETs attenuated
ethanol-induced myocardial dysfunction through inducing autophagy
and reducing apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 117:168–179. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen TS, Kuo CH, Battsengel S, Pan LF, Day
CH, Shen CY, Chung LC, Padma VV, Yao CK, Lin YM and Huang CY:
Adipose-derived stem cells decrease cardiomyocyte damage induced by
porphyromonas gingivalis endotoxin through suppressing hypertrophy,
apoptosis, fibrosis and MAPK markers. Environ Toxicol. 33:508–513.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wei X, Yang Y, Jiang YJ, Lei JM, Guo JW
and Xiao H: Relaxin ameliorates high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy and apoptosis via the Notch1 pathway. Exp Ther Med.
15:691–698. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yao C, Cao X, Fu Z, Tian J, Dong W, Xu J,
An K, Zhai L and Yu J: Boschniakia rossica polysaccharide
triggers laryngeal carcinoma cell apoptosis by regulating
expression of Bcl-2, caspase-3 and P53. Med Sci Monit.
23:2059–2064. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lv L and Liu B: Antitumor effects of
bakuchiol on human gastric carcinoma cell lines are mediated
through PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways. Mol Med Rep.
16:8977–8982. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cui X, Jing X, Wu X, Bi X, Liu J, Long Z,
Zhang X, Zhang D, Jia H, Su D and Huo K: Abnormal expression levels
of BMP15/Smad1 are associated with granulosa cell apoptosis in
patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Mol Med Rep. 16:8231–8236.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lustri AM, Di Matteo S, Fraveto A,
Costantini D, Cantafora A, Napoletano C, Bragazzi MC, Giuliante F,
De Rose AM, Berloco PB, et al: TGF-β signaling is an effective
target to impair survival and induce apoptosis of human
cholangiocarcinoma cells: A study on human primary cell cultures.
PLoS One. 12:e01839322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Qiu M, Chen Y, Chen L, Zeng J and Liu J:
Transforming growth factor β1 and Fas ligand synergistically
enhance immune tolerance in dendritic cells in liver
transplantation. J Surg Res. 218:180–193. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen K, Cheng L, Qian W, Jiang Z, Sun L,
Zhao Y, Zhou Y, Zhao L, Wang P, Duan W, et al: Itraconazole
inhibits invasion and migration of pancreatic cancer cells by
suppressing TGF-beta/SMAD2/3 signaling. Oncol Rep. 39:1573–1582.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Imoto S, Sugiyama K, Muromoto R, Sato N,
Yamamoto T and Matsuda T: Regulation of transforming growth
factor-beta signaling by protein inhibitor of activated STAT, PIASy
through Smad3. J Biol Chem. 278:34253–34258. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Imoto S, Ohbayashi N, Ikeda O, Kamitani S,
Muromoto R, Sekine Y and Matsuda T: Sumoylation of Smad3 stimulates
its nuclear export during PIASy-mediated suppression of TGF-β
signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 370:359–365. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Long J, Wang G, He D and Liu F: Repression
of Smad4 transcriptional activity by SUMO modification. Biochem J.
379:23–29. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Tang WB, Ling GH, Sun L, Zhang K, Zhu X,
Zhou X and Liu FY: Smad anchor for receptor activation regulates
high glucose-induced EMT via modulation of Smad2 and Smad3
activities in renal tubular epithelial cells. Nephron. 130:213–220.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|