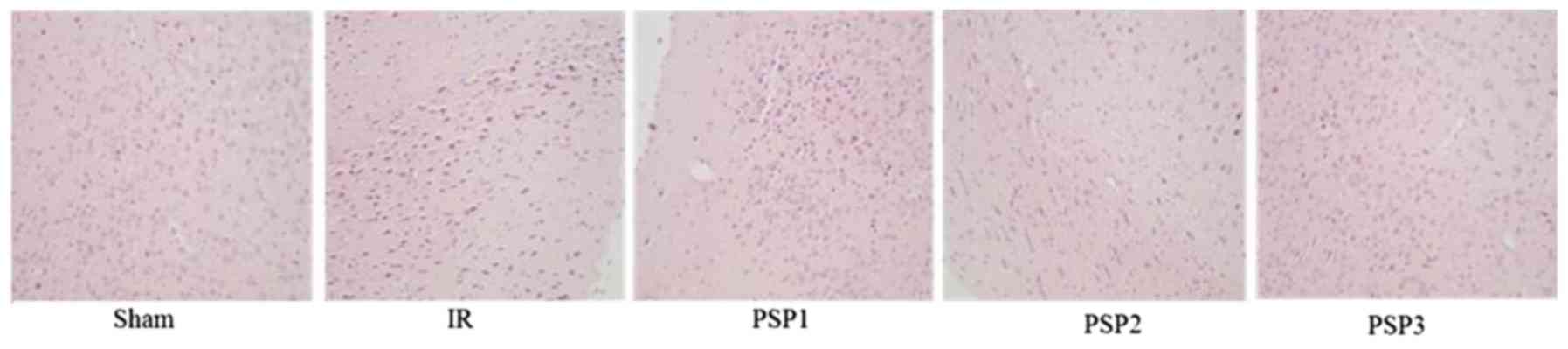
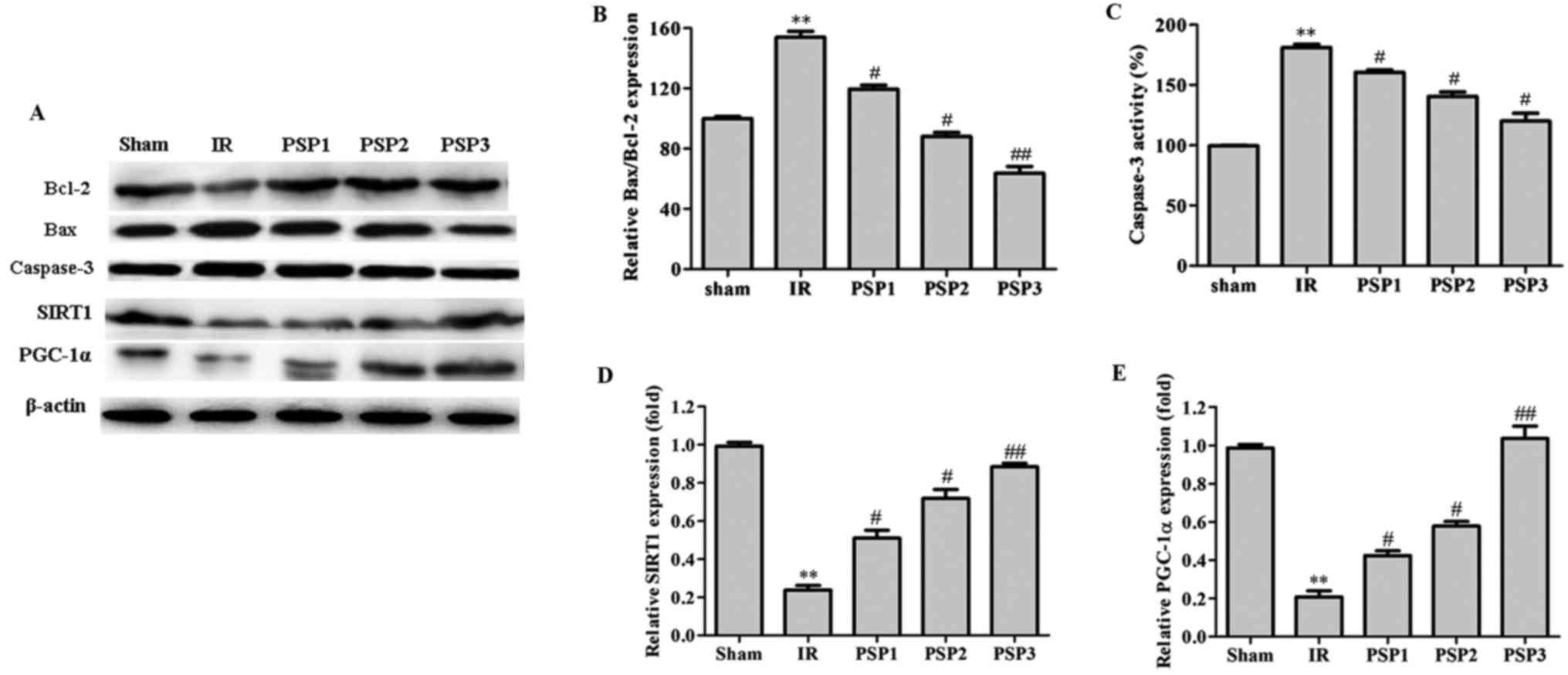
|
1
|
Yamashita T and Abe K: Recent progress in
therapeutic strategies for ischemic stroke. Cell Transplant.
25:893–898. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dong Q, Lin X, Shen L and Feng Y: The
protective effect of herbal polysaccharides on ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Int J Biol Macromol. 92:431–440. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rao PR, Kumar VK, Viswanath RK and
Subbaraju GV: Cardioprotective activity of alcoholic extract of
Tinospora cordifolia in ischemia reperfusion induced myocardial
infarction in rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:2319–2322. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M and
Korthuis RJ: Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int Rev
Cell Mol Biol. 298:229–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zerna C, Assis Z, d'Esterre CD, Menon BK
and Goyal M: Imaging, intervention, and workflow in acute ischemic
stroke: The calgaryapproach. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 37:978–984.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sugawara T and Chan PH: Reactive oxygen
radicals and pathogenesis of neuronal death after cerebral
ischemia. Antioxid Redox Signal. 5:597–607. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Adibhatla Muralikrishna R and Hatcher JF:
Phospholipase A2, reactive oxygen species, and lipid peroxidation
in cerebral ischemia. Free Radic Biol Med. 40:376–387. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu M, Wang HF, Zhang YY and Zhuang HW:
Protection of rats spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury by
inhibition of MiR497 on inflammation and apoptosis: Possible role
in pediatrics. Biomed Pharmacother. 81:337–344. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu T, Yao Q, Hu X, Chen C, Yao H and Chao
J: The role of MCPIP1 in ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced HUVEC
migrationand apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:577–591. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arda-Pirincci P and Bolkent S: The role of
epidermal growth factor in prevention of oxidative injury and
apoptosis induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Acta
Histochem. 116:167–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shokeir AA, Barakat N, Hussein AM,
Awadalla A, Harraz AM, Khater S, Hemmaid K and Kamal AI: Activation
of Nrf2 by ischemic preconditioning and sulforaphane in
renalischemia/reperfusion injury: A comparative experimental study.
Physiol Res. 64:313–323. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ju J, Wu J and Hou R: Role of the p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
inestrogen-mediated protection following flap ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Cell Biochem Funct. 34:522–530. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kovalska M, Kovalska L, Pavlikova M,
Janickova M, Mikuskova K, Adamkov M, Kaplan P, Tatarkova Z and
Lehotsky J: Intracellular signaling MAPK pathway after cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurochem Res. 37:1568–1577. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Imahashi K, Schneider MD, Steenbergen C
and Murphy E: Transgenic expression of Bcl-2 modulates energy
metabolism, preventscytosolic acidification during ischemia, and
reduces ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circ Res. 95:734–741. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei DF, Chen T, Yan M, Zhao W, Li F, Cheng
W and Yuan L: Synthesis, characterization, antioxditant activity
and neuroprotective effects of selenium polysaccharide from Radix
hedysari. Carbohydr Polym. 125:161–168. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sanagi MM, Loh SH, Ibrahim Wan WN,
Pourmand N, Salisu A, Ibrahim Wan WA and Ali I: Agarose- and
alginate based biopolymers for sample preparation: Excellentgreen
extraction tools for this century. J Sep Sci. 39:1152–1159. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gong J, Sun F, Li Y, Zhou X, Duan Z, Duan
F, Zhao L, Chen H, Qi S and Shen J: Momordica charantia
polysaccharides could protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
injury through inhibiting oxidative stress mediated c-Jun
N-terminal kinase 3 signaling pathway. Neuropharmacology.
91:123–134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou ZY, Tang YP, Xiang J, Wua P, Jin HM,
Wang Z, Mori M and Cai DF: Neuroprotective effects of water-soluble
ganoderma lucidum polysaccharideson cerebral ischemic injury in
rats. J Ethno pharmacol. 131:154–164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lu ZQ, Deng YJ and Lu JX: Effect of aloe
polysaccharide on caspase-3 expression following cerebral ischemia
and reperfusion injury in rats. Mol Med Rep. 6:371–374. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang S, He B, Ge J, Zhai C, Liu X and Liu
P: Characterization of chemical composition of agaricus
brasiliensis polysaccharides and its effect on myocardial SOD
activity, MDA and caspase-3 level in ischemia-reperfusion rats. Int
J Biol Macromol. 46:363–366. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Reis C, Wang Y, Akyol O, Ho WM, Ii RA,
Stier G, Martin R and Zhang JH: What's new in traumatic brain
injury: Update on tracking, monitoring and treatment. Int J Mol
Sci. 16:11903–11965. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shi P, Zhang L, Wang J, Lu D, Li Y, Ren J,
Shen M, Zhang L and Huang J: Porcine FcεRI mediates porcine
reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus multiplication and
regulates the inflammatory reaction. Virol Sin. 33:249–260. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bösel J, Ruscher K, Ploner CJ and Valdueza
JM: Delayed neurological deterioration in a stroke patient with
postoperative acute anemia. Eur Neurol. 53:36–38. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Haigis MC and Sinclair DA: Mammalian
sirtuins: Biological insights and disease relevance. Annu Rev
Pathol. 5:253–295. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zille M, Farr TD, Przesdzing I, Müller J,
Sommer C, Dirnagl U and Wunder A: Visualizing cell death in
experimental focal cerebral ischemia: Promises, problems, and
perspectives. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 32:213–231. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hyman BT and Yuan J: Apoptotic and non
apoptotic roles of caspases in neuronal physiology and
pathophysiology. Nat Rev Neurosci. 13:395–406. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Walsh JG, Cullen SP, Sheridan C, Lüthi AU,
Gerner C and Martin SJ: Executioner caspase-3 and caspase-7 are
functionally distinct proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:12815–12819. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Manabat C, Han BH, Wendland M, Derugin N,
Fox CK, Choi J, Holtzman DM, Ferriero DM and Vexler ZS: Reperfusion
differentially induces caspase-3 activation in ischemic core and
penumbra after stroke in immature brain. Stroke. 34:207–213. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ferrer I and Planas AM: Signaling of cell
death and cell survival following focal cerebral ischemi: Lifeand
death struggle in the penumbra. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
62:329–339. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Potente M and Dimmeler S: Emerging roles
of SIRT1 in vascular endothelial homeostasis. Cell Cycle.
7:2117–2122. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Shang YC and Wang S:
Translating cell survival and cell longevity into treatment
strategies with SIRT1. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 52:1173–1185.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rodgers JT, Lerin C, Haas W, Gygi SP,
Spiegelman BM and Puigserver P: Nutrient control of glucose
homeostasis through a complex of PGC-1alpha and SIRT1. Nature.
434:113–118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xia N, Förstermann U and Li HG:
Resveratrol and endothelial nitric oxide. Molecules.
19:16102–16121. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Feng J, Yang Y, Zhou Y, Wang B, Xiong H,
Fan C, Jiang S, Liu J, Ma Z, Hu W, et al: Bakuchiol attenuates
myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by maintaining mitochondrial
function: The role of silent information regulator 1. Apoptosis.
21:532–545. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tsai KL, Huang PH, Kao CL, Leu HB, Cheng
YH, Liao YW, Yang YP, Chien Y, Wang CY, Hsiao CY, et al: Aspirin
attenuates vinorelbine-induced endothelial inflammation via
modulating SIRT1/AMPK axis. Biochem Pharmacol. 88:189–200. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tamaki N, Cristina Orihuela-Campos R,
Inagaki Y, Fukui M, Nagata T and Ito HO: Resveratrol improves
oxidative stress and prevents the progression of periodontitis via
the activation of the Sirt1/AMPK and the Nrf2/antioxidant defense
pathways in a rat periodontitis model. Free Radic Biol Med.
75:222–229. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu S, Xu J, Fang C, Shi C, Zhang X, Yu B
and Yin Y: Over-expression of heat shock protein 70 protects mice
against lung ischemia/reperfusion injury through SIRT1/AMPK/eNOS
pathway. Am J Transl Res. 8:4394–4404. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|