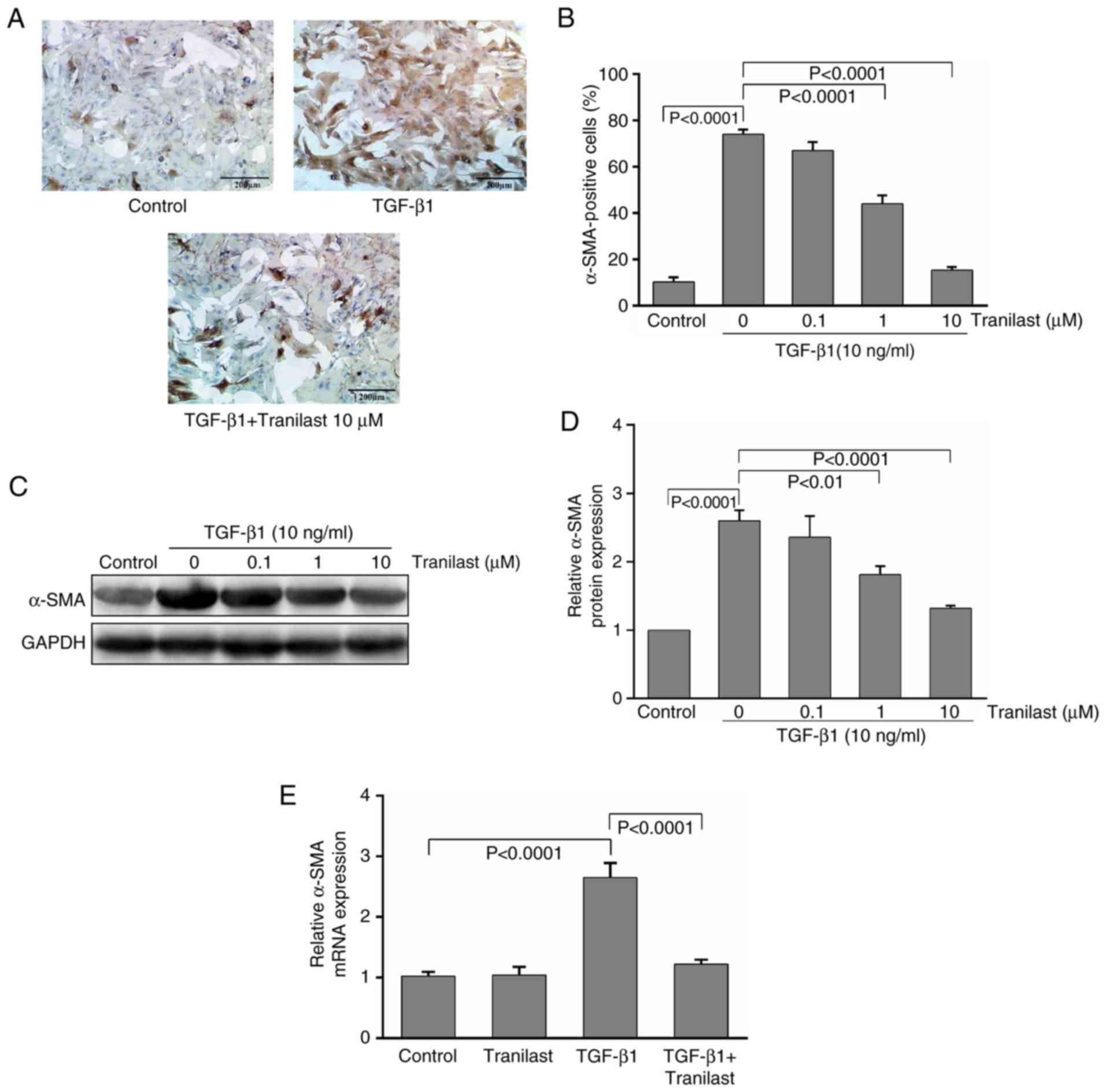
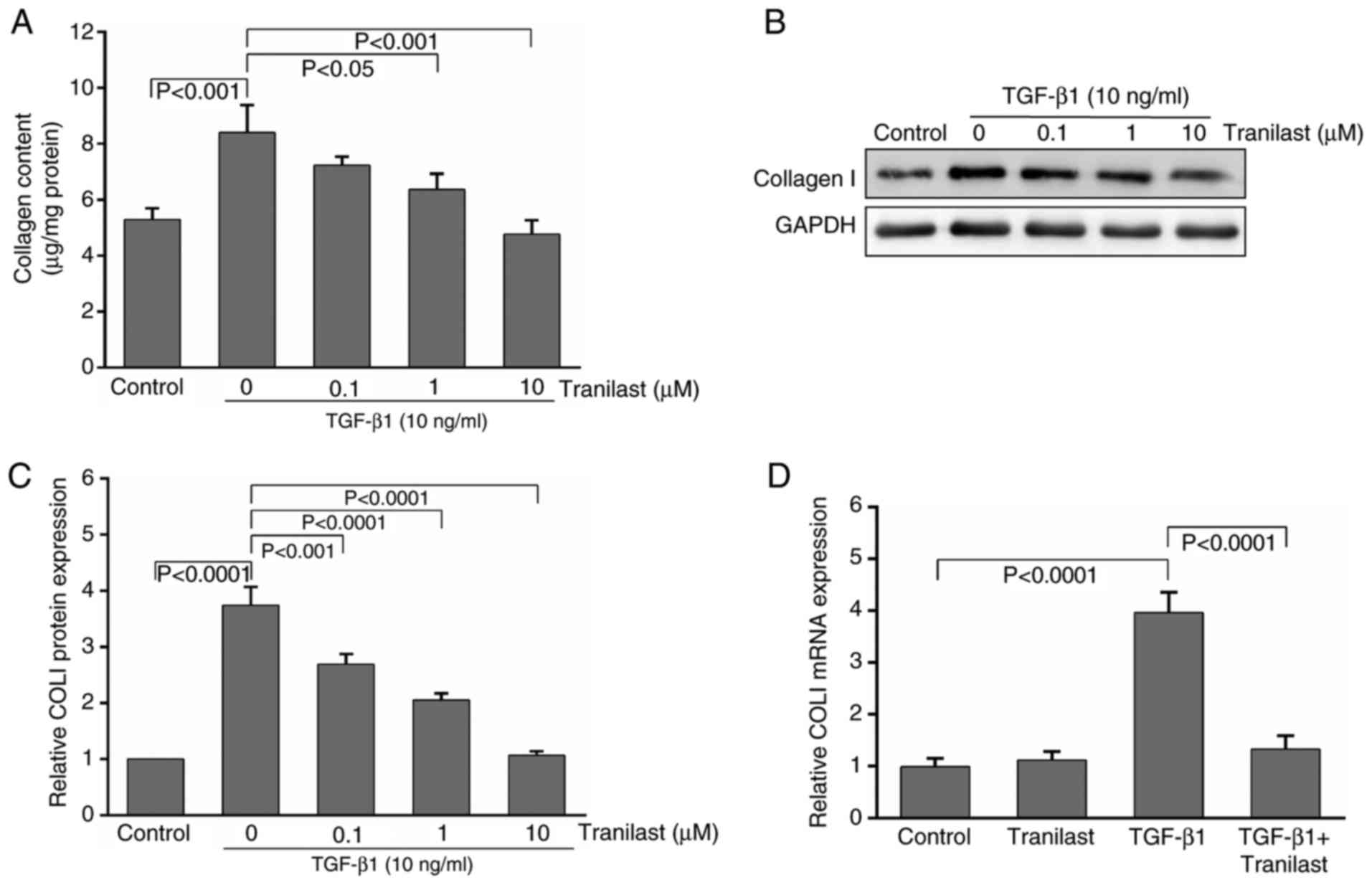
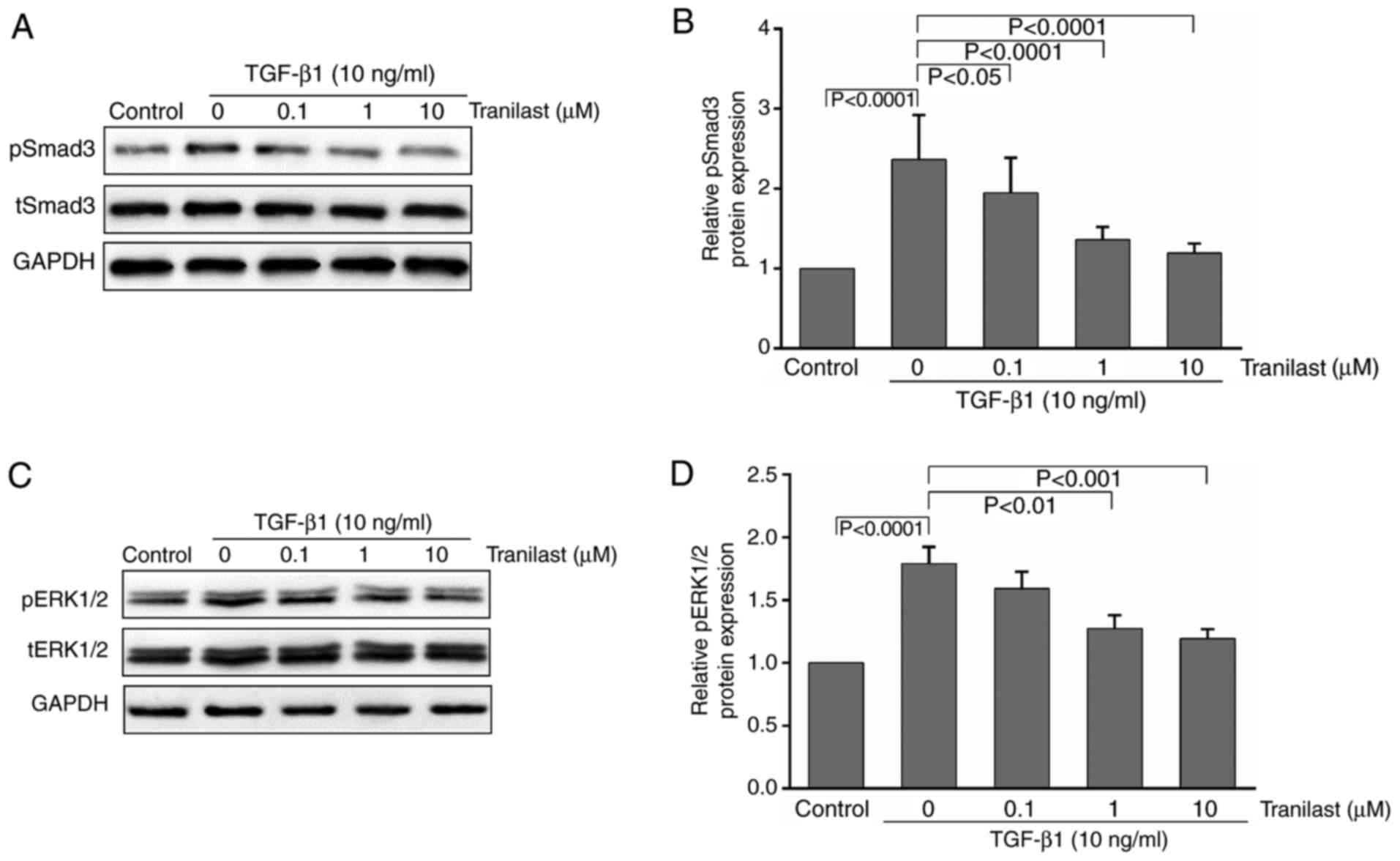
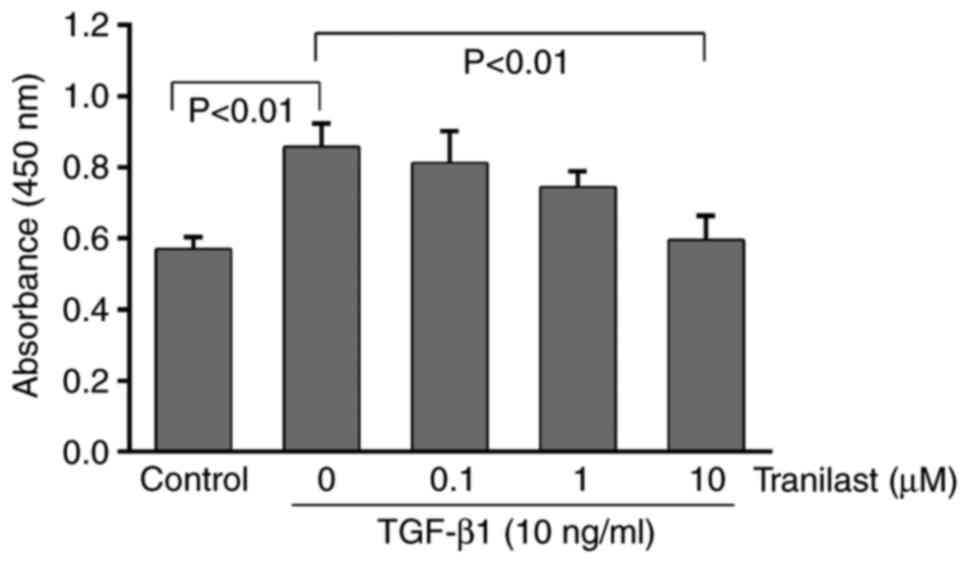
|
1
|
Wynn TA: Cellular and molecular mechanisms
of fibrosis. J Pathol. 214:199–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
El Agha E, Kramann R, Schneider RK, Li X,
Seeger W, Humphreys BD and Bellusci S: Mesenchymal stem cells in
fibrotic disease. Cell Stem Cell. 21:166–177. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hinz B: Formation and function of the
myofibroblast during tissue repair. J Invest Dermatol. 127:526–537.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kalluri R and Neilson EG:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for
fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 112:1776–1784. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
LeBleu VS, Taduri G, O'Connell J, Teng Y,
Cooke VG, Woda C, Sugimoto H and Kalluri R: Origin and function of
myofibroblasts in kidney fibrosis. Nat Med. 19:1047–1053. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kramann R, Schneider RK, DiRocco DP,
Machado F, Fleig S, Bondzie PA, Henderson JM, Ebert BL and
Humphreys BD: Perivascular Gli1+ progenitors are key contributors
to injury-induced organ fibrosis. Cell Stem Cell. 16:51–66. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bonfield TL and Caplan AI: Adult
mesenchymal stem cells: An innovative therapeutic for lung
diseases. Discov Med. 9:337–345. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baertschiger RM, Serre-Beinier V, Morel P,
Bosco D, Peyrou M, Clément S, Sgroi A, Kaelin A, Buhler LH and
Gonelle-Gispert C: Correction: Fibrogenic potential of human
multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in injured liver. PLoS One.
4:e66572009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Russo FP, Alison MR, Bigger BW, Amofah E,
Florou A, Amin F, Bou-Gharios G, Jeffery R, Iredale JP and Forbes
SJ: The bone marrow functionally contributes to liver fibrosis.
Gastroenterology. 130:1807–1821. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tang N, Zhao Y, Feng R, Liu Y, Wang S, Wei
W, Ding Q, An MS, Wen J and Li L: Lysophosphatidic acid accelerates
lung fibrosis by inducing differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
into myofibroblasts. J Cell Mol Med. 18:156–169. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Carlson S, Trial J, Soeller C and Entman
ML: Cardiac mesenchymal stem cells contribute to scar formation
after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 91:99–107. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang S, Cui H, Xie N, Icyuz M, Banerjee S,
Antony VB, Abraham E, Thannickal VJ and Liu G: miR-145 regulates
myofibroblast differentiation and lung fibrosis. FASEB J.
27:2382–2391. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bianco P, Cao X, Frenette PS, Mao JJ,
Robey PG, Simmons PJ and Wang CY: The meaning, the sense and the
significance: Translating the science of mesenchymal stem cells
into medicine. Nat Med. 19:35–42. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu J, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res.
19:156–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang W, Koka V and Lan HY: Transforming
growth factor-beta and Smad signalling in kidney diseases.
Nephrology (Carlton). 10:48–56. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Peng H, Carretero OA, Peterson EL and
Rhaleb NE: Ac-SDKP inhibits transforming growth
factor-beta1-induced differentiation of human cardiac fibroblasts
into myofibroblasts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
298:H1357–H1364. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun Q, Wu Y, Zhao F and Wang J: Maresin 1
inhibits transforming growth factor-β1-induced proliferation,
migration and differentiation in human lung fibroblasts. Mol Med
Rep. 16:1523–1529. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Darakhshan S and Pour AB: Tranilast: A
review of its therapeutic applications. Pharmacol Res. 91:15–28.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamada H, Tajima S, Nishikawa T, Murad S
and Pinnell SR: Tranilast, a selective inhibitor of collagen
synthesis in human skin fibroblasts. J Biochem. 116:892–897. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Isaji M, Nakajoh M and Naito J: Selective
inhibition of collagen accumulation by
N-(3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl)anthranilic acid (N-5′) in granulation
tissue. Biochem Pharmacol. 36:469–474. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim TI, Lee H, Hong HK, Kim KS, Choi SI,
Maeng YS and Kim EK: Inhibitory effect of tranilast on transforming
growth factor-beta-induced protein in granular corneal dystrophy
type 2 corneal fibroblasts. Cornea. 34:950–958. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nakatani Y, Nishida K, Sakabe M, Kataoka
N, Sakamoto T, Yamaguchi Y, Iwamoto J, Mizumaki K, Fujiki A and
Inoue H: Tranilast prevents atrial remodeling and development of
atrial fibrillation in a canine model of atrial tachycardia and
left ventricular dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 61:582–588. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
See F, Watanabe M, Kompa AR, Bing HW,
Boyle AJ, Kelly DJ, Gilbert RE and Krum H: Early and delayed
tranilast treatment reduces pathological fibrosis following
myocardial infarction. Heart Lung Circ. 22:122–132. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Popova AP, Bozyk PD, Goldsmith AM, Linn
MJ, Lei J, Bentley JK and Hershenson MB: Autocrine production of
TGF-beta1 promotes myofibroblastic differentiation of neonatal lung
mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
298:L735–L743. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kakudo N, Kushida S, Suzuki K, Ogura T,
Notodihardjo PV, Hara T and Kusumoto K: Effects of transforming
growth factor-beta1 on cell motility, collagen gel contraction,
myofibroblastic differentiation, and extracellular matrix
expression of human adipose-derived stem cell. Human Cell.
25:87–95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song K, Huang M, Shi Q, Du T and Cao Y:
Cultivation and identification of rat bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 10:755–760. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Phan SH: The myofibroblast in pulmonary
fibrosis. Chest. 122 6 Suppl:286S–289S. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
di Bonzo LV, Ferrero I, Cravanzola C,
Mareschi K, Rustichell D, Novo E, Sanavio F, Cannito S, Zamara E,
Bertero M, et al: Human mesenchymal stem cells as a two-edged sword
in hepatic regenerative medicine: Engraftment and hepatocyte
differentiation versus profibrogenic potential. Gut. 57:223–231.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tang N, Zhao Y, Feng R, Liu Y, Wang S, Wei
W, Ding Q, An MS, Wen J and Li L: Lysophosphatidic acid accelerates
lung fibrosis by inducing differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
into myofibroblasts. J Cell Mol Med. 18:156–169. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yasukawa T, Kimura H, Dong J, Tabata Y,
Miyamoto H, Honda Y and Ogura Y: Effect of tranilast on
proliferation, collagen gel contraction, and transforming growth
factor beta secretion of retinal pigment epithelial cells and
fibroblasts. Ophthalmic Res. 34:206–212. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hattori T and Wang PL: Inhibition by
tranilast of nifedipine-induced proliferation of cultured human
gingival fibroblasts. Eur J Pharmacol. 498:79–81. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang S, Meng XM, Ng YY, Ma FY, Zhou S,
Zhang Y, Yang C, Huang XR, Xiao J, Wang YY, et al: TGF-β/Smad3
signalling regulates the transition of bone marrow-derived
macrophages into myofibroblasts during tissue fibrosis. Oncotarget.
7:8809–8822. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bonniaud P, Kolb M, Galt T, Robertson J,
Robbins C, Stampfli M, Lavery C, Margetts PJ, Roberts AB and
Gauldie J: Smad3 null mice develop airspace enlargement and are
resistant to TGF-beta-mediated pulmonary fibrosis. J Immunol.
173:2099–2108. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sato M, Muragaki Y, Saika S, Roberts AB
and Ooshima A: Targeted disruption of TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling
protects against renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis induced by
unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Clin Invest. 112:1486–1494.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gu L, Zhu YJ, Yang X, Guo ZJ, Xu WB and
Tian XL: Effect of TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway on lung
myofibroblast differentiation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:382–391.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|